MARKET RESEARCH
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
Market research is ?
the systematic and objective :
identification
collection
analysis
dissemination
& use of information
For the purpose of improving decision making related to the
identification and
solution of problems and opportunities in marketing
Market research process ?
Problem definition
Research approach developed
Research design developed
Firework/data collection
Data integrity & analysis
Communicating research findings
Social research ?
→ It's the study of how individuals interact within societies, focusing on understanding social behaviours, norms, and structures that influence market dynamics.
Why do research ?
Must make best use of the ressources because they’re limited
Need to make well-informed decisions
Provides evidence for that decision making
Gather data, analyse it then transform it into info and insights
With insights, you can make informed decision
The use of market research ?
• identify markets and customers
• understand customer needs
• monitor customer satisfaction
• test advertising/marketing effectiveness
• develop a product or service
The value of research ?
→ Its ability to provide high quality data, info and insight.
If ressources are limited, should you spend on research ?
→ 2 questions to ask ourselves : is it Nice to do or Need to do it ?
It depends also :
What is the business problem or issue ?
Why are you thinking about doing research ?
How important is it ?
Some limitations of market research ?
→ We may not being clear about what it is for poor problem definition, lack of understanding of the problem,…
→ We may not doing the right sort of research
→ Or using poor quality data
Why is market research essential ?
It’s for identifying problems and opportunities, assisting decision-making, minimising risks, improving profitability, and ensuring competitive advantage
Research ?
It’s the systematic gathering of data to gain knowledge or understanding to address a specific need
Contexts and use of Market Research ?
Products, services, advertising, policy, communications, attitudes etc.
To address client’s business problem, to help the client make good decisions
Important uses for market research ?
Understanding markets → Size & strength
Understanding customers → Customer needs
Developing the offer → Attitudes to the price & products
Improving communications → Awareness of the brand
Primary data ?
→ is specifically collected by the researcher for the specific problem/opportunity and involves all steps of the marketing research process.
Secondary data ?
Data who has been previously collected for some other problem.
The information research process ?
→ collects, analyses, interprets, and transforms data into decision-making information.
Scientific method ?
It involves formulating hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing data.
The research process ?
It’s transforming data into knowledge
Primary goal of the research process ?
It’s to provide decision makers with knowledge to resolve problems or pursue opportunities.
Data becomes knowledge when … ?
→ someone interprets the data and attaches meaning.
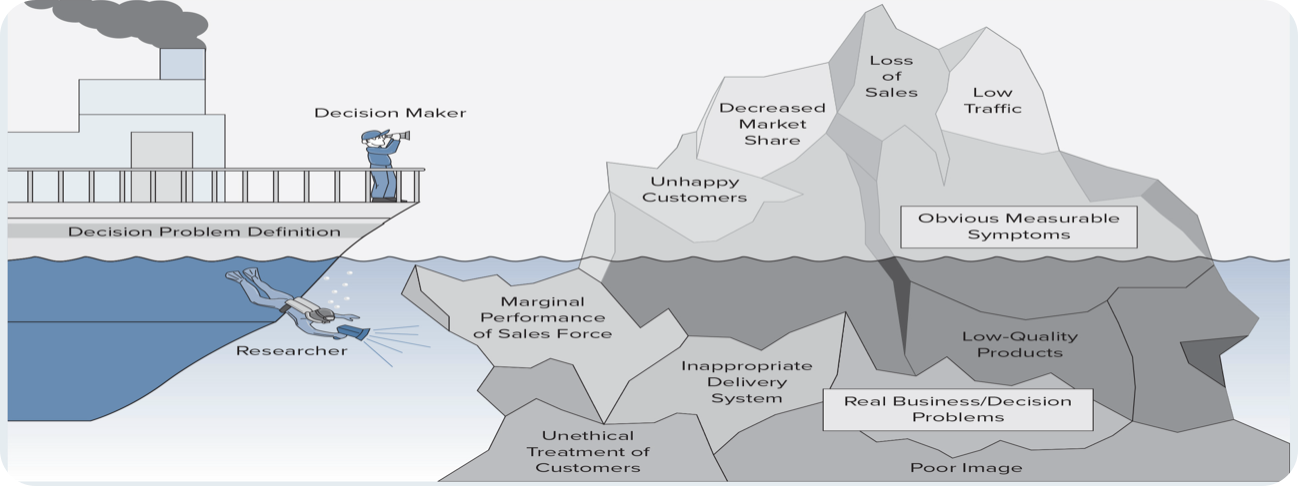
Iceberg principle ?
decision makers know 10% of the true problem.
The researcher conducts … ?
a review of the literature. Important step because it influences the remaining steps.
Situation analysis ?
→ uncovers the problem’s complexity.
Identify measurable symptoms.
Clarify the problem separate out causes and symptoms.
Research objectives ?
→ provide guidelines for determining other steps.
If the objectives are achieved, the decision maker will have the information needed to answer the research questions.
Exploratory research qualitative ?
→ It’s investigatory, has 1 of 2 objectives, response driven & generates soft data.
Use focus groups & in-depth interviews
Generating insights that help define the problem situation.
Understanding consumer motivations, attitudes, and behaviours.
Descriptive research - Quantitative ?
→ Highly structured, formal, mathematically-based & generates hard data.
Predictive research ?
Goal → is to determine the cause/effect relationship
compares 2 or more variables.
Looks at specific relationships & looks at their effects.
Used to understand how 1 variable impacts a dependent variable
Researchers need to identify ?
the relevant target population.
census ?
complete survey of a population, collecting data from every person living in Ireland to understand demographic and social characteristics.
For large populations, use a … ?
representative sample and generalize.
A sampling plan ?
is 1 of 2 general types.
Probability sampling ?
each member of the target population has a known chance of being selected, allows assessment of sampling error.
Nonprobability ?
cannot measure sampling error, limits findings, and does not provide each member of the population a known chance of selection.
Researchers must ?
Select the correct type of questions.
Consider the sequence and format.
Pretest the questionnaire.
Pretest respondents are asked about which issues ?
Clarity of instructions and questions.
Sequence of the topics and questions.
Anything potentially difficult or confusing.
2 approaches to gathering data are?
Using interviewers or self-completion questionnaires.
Observing individuals or market phenomena.
major advantage of questioning over observation ?
Questioning answers not just how a person is behaving, but why → It explores motivations and feelings.
Interpretation ?
It integrates the aspects of the findings into conclusions used to answer the research questions.
Sections included in any research report ?
Executive summary.
Introduction.
Problem definition and objectives.
Methodology.
Results and findings.
Limitations of the study.
research proposal ?
Communicates the research framework to the decision maker. It’s not the same as a final research report.
purpose of a written market research brief ?
Helps the initiator to be more sure of how decision-making will be supported
Agreement among all parties who may benefit from research
Helps to plan and administer research
Helps to reduce disputes
Forms the basis for negotiation.
Research questions (RQs) ?
are refined statements of the specific components of the problem.
Hypothesis (H) ?
is an unproven statement about a factor that is of interest to the researcher. Often, a hypothesis is a possible answer to the research question.
Problem defintion ?
translates the management decision into research information needs
Desk research ?
It’s the systematic collection & analysis of secondary sources of data
Field Research ?
It generates primary data. Data is collected first-hand by the investigator for the specific problem at hand.
Criteria for Judging Secondary Data ?
Objectivity is used to evaluate Desk Research :
How was it collected?
Why was it collected?
When was it collected?
Why was it published?
How dependable is the data source?
Secondary data can be … ?
→ internal (ready to use, requires further processing) or external (Published materials, Computerised databased, …)
Criteria for evaluating secondary data ?
Currency
Objective
Nature
Dependability
Specifications & research design
Error & accuracy
Data collection begins with … ?
→ secondary data.
Secondary data tends to be … ?
inexpensive, easy to access, but may not be accurate or timely.
External data is data … ?
→ already in existence outside the firm. → can be sourced from various organisations, government reports, market research firms, and public databases.
the most important aspect of desk research ?
→ It’s to be thorough, exhaustive and diligent.
secondary data always be considered before … ?
engaging in any primary research.
Research design ?
→ blueprint for conducting research, detailing the methods and procedures for data collection and analysis.
Qualitative market research ?
An unstructured, exploratory design based on small sample, intended to provide depth, insight and understanding. → perceptions, attitudes & motivations
Quantity ?
relating to or measured by quantity → statistical results
IDI ?
In-depth interviews conducted with individuals to gather detailed qualitative insights on their thoughts and experiences.
Focus groups ?
→ small group of people discusses a product, service, guided by a moderator to gather diverse opinions and insights.
For the people we interview, we have to … ?
→ get the conversation / Comfortable → Honest thoughts/feelings/emotions
In depths interviews length ?
→ 30-60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the topic.
How to structure an in-depth interview ?
→ Create a discussion guide where topics are in bullet points with questions
A questionnaire can be on ?
Online Survey
F2F
Phone Call
Mail Survey
Descriptive Research Methods ?
they describe a phenomenon, through surveys to gather quantitative or qualitative data.
Benefits of surveys ?
Quick results to analyse
Quantitative data → large sample sizes,
Administered easily across various platforms
Help in understanding consumer preferences and behaviors efficiently.
Projective techniques ?
→ qualitative research method used to encourages participants to project their thoughts and emotions onto the stimuli, revealing underlying motivations.
Association techniques ?
→ It’s when participants are presented with a stimulus and are asked to respond with the first thing that comes to mind.
Word association ?
Method which participants are presented with a list of words, one at a time.They’re asked to give the first word that comes to mind.
Completion techniques ?
→ participants are asked to complete an incomplete stimulus situation. Helping to uncover their perceptions, thoughts, and attitudes toward the subject.
Construction techniques ?
→ Requires participants to construct a response in the form of a story. → related to completion techniques
Cartoon tests ?
projective techniques involving cartoon images, where participants interpret scenarios, revealing their feelings and attitudes.
Expressive techniques ?
participants express their feelings through artistic means, such as role playing, third-person technique & personification. Participants imagine that the brand is a person & describe the characteristics of that person.
Trace analysis ?
It’s when participants' responses are analysed for patterns and themes, often used to understand consumer behaviour and preferences.
Quantitative market research ?
Research techniques that seek to quantify data, apply some measurement and statistical analysis
Primary research methods ?
Survey Research
In depth interview, Focus group
Observation
Projective techniques
4 methods of projective techniques ?
Association
Completion
Construction
Expressive
Advantages of projective techniques ?
They elicit responses that participants would be unwilling/unable to give if they knew the purpose of the study
Helpful when the issues are personal or sensitive
Helpful when underlying motivations, beliefs & attitudes are operating at a subconscious level
Disadvantages of projective techniques ?
Suffer from nay of the disadvantages of unstructured direct techniques, but to a greater extent.
Require highly-trainers interviewers
Skilled interpreters are also required to analyse the responses
They tend to be expensive
Quantitative observation techniques ?
→ Involves recording the behavioural patterns of people, objects & events in a systematic manner to obtain information about the phenomenon of interest
Structured observation ?
→ researcher specifies in detail what is to be observed and how the measurements are to be recorded
Unstructured observation ?
→ Observer monitors all aspects of the phenomenon that seem relevant to the problem at hand
Natural observation ?
involves observing behaviour as it takes places in the environment.
Contrived observation ?
participants’ behaviour is observed in an artificial environment, such as a test kitchen.
CATI ?
Computer-Assisted Telephone Interviewing → method where interviewers use a computer to collect responses via phone.
Survey ?
method of obtaining info based upon the use of structured questionnaires administered to a sample of a target audience
Structured direct survey ?
method that utilizes a pre-determined set of questions, ensuring consistency in responses across all participants
advantages of survey ?
provide quantitative data, cost-effective, large sample sizes, can be conducted quickly, diverse insights, data quality
disadvantages of survey ?
Low response rate
Technical issue
may be misinterpreted
Reasons for the decrease in survey responses rate ?
lack of interest,
perceived time commitment,
trust issues with data privacy
length of questions
Number of requests
First step of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Specify the info needed → define the objectives and target audience for the survey.
Research questions (RQs) ?
refined statements of the specific components of the problem
Hypothesis ?
unproven statement about a factor that is of interest to the researcher → can often be a possible answer to the research question
Step 2 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Specify the type of interviewing method
Step 3 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Determine the question format, is the question necessary
The questions have to be … ?
→ clear, not too long, and not be a double barrelled questions
Step 4 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Overcoming inability & unwillingness to answer
Is the participant informed ? Can the participant remember?
→ minimise the effort required of the participants, and ensure questions are relevant and straightforward.
→ Use statements, or examples to aid understanding.
Branching ?
question format that allows respondents to answer follow-up questions based on their previous answers, ensuring relevance and clarity. (Yes/No)
Step 5 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Use open-ended questions to gather in-depth insights and qualitative data.
→ Multiple choice questions
→ Dichotomous questions → Include a mix of question types to capture both qualitative and quantitative data.
Step 6 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Choosing question wording
→ Use ordinary words, not ambiguous words, leading questions, implicit alternatives, and technical jargon to ensure clarity and understanding. Aim for neutrality to avoid bias in responses.
Step 7 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Arrange questions in proper order, the opening questions’d be interesting, simple & non-threatening
Step 8 of the design of a questionnaire ?
→ Design form & layout, divide the questionnaire into several parts, questions should be numbered