EXAM 3 PATHO
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
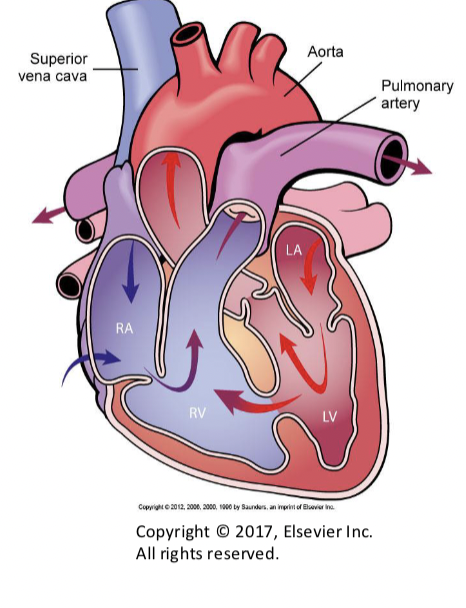
Interatrial septal defect
abormal opening in the interatrial septum
left to right shunt
increased pulmonary blood flow
Ventricular septal defect
most common congenital heart defect in clinical practice
left to right shunt
right ventricle exceeds the pressure in the left ventricle
REVERSES BLOOD FLOW*****
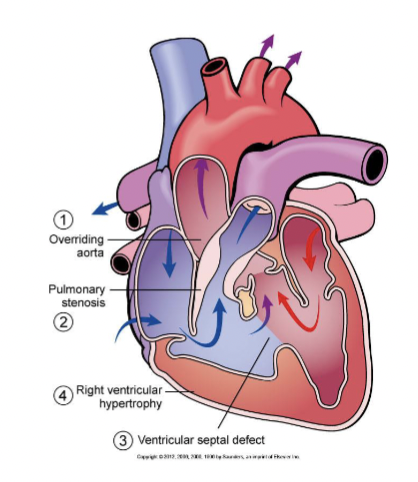
Tetralogy of Fallot
dextroposition of the aorta
stenosis of pulmonary artery
ventricular septal defect involving the uppermost membranous part of the septum
hypertrophy of the right ventricle, which is adaptive in nature and develops as a result of an increased workload of the right ventricle
Transposition of great vessels
congenitial heart defect
aorta arises from right ventricle
pulmonary artery arises from left ventricle
mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
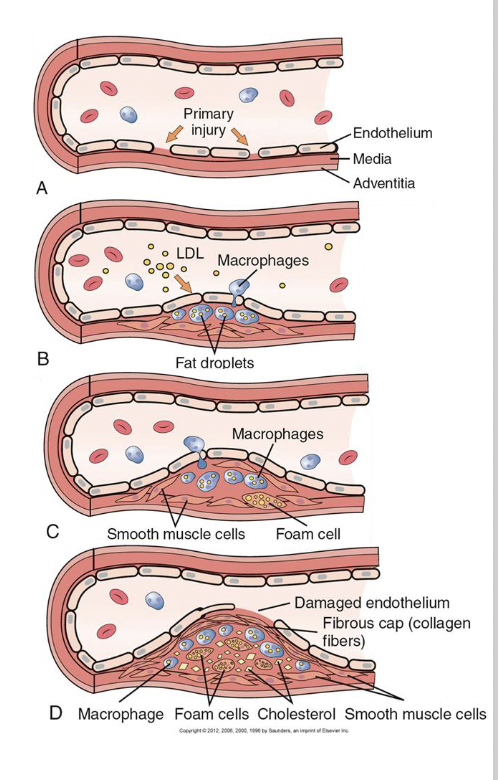
Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis
endothelial cell injury (metabolic derangements, physical force is accompanied by the deposition of blood platelets and serum lipoproteins)
growth factors released from platelets stimulate the proliferation of smooth muscle cells in wall of the artery
internal metabolism (cholesterol and other lipids in their cytoplasm)
smooth muscle cells transform into foam cells
attract macrophages (take up cell remnants) (foam cells) (secrete cytokines TNF, TGF-B—>MORE DAMAGE)
collagen deposition with atheromas leads to hardening of the arteries (sclerosis)
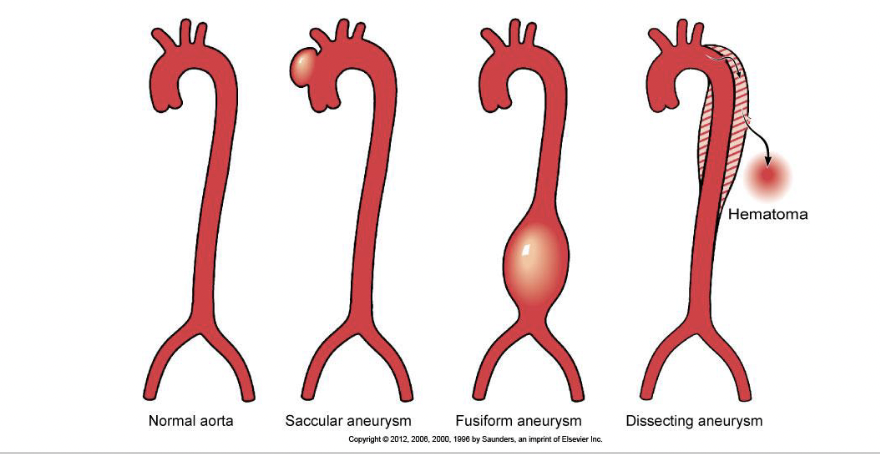
Atherosclerotic aneurysms
can occur in any part of aorta but are most often located in the abdominal aorta and may occur in several forms
dilations of the aortic lumen associated with changes in the wall, most often complicating advanced atherosclerosis
clinically silent
A patient has suffered a myocardial infarction of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. Which artery was occluded?
posterior descending artery
A patient presents with edema in the lower extremities, ascites, and dyspnea with activity. What do you suspect the patient is suffering from?
heart failure (CHF- congestive heart failure)
Marker of myocardial infarction
troponin (best marker)
occlusion of coronary artery
complications:
ventricular rupture
ventricular aneurysm
endocardial mural thrombus
Alanine aminotransferase
marker of liver injury/ enzyme found in the liver
heart conditions (myocardial infarction, troponins)
high levels—> acute liver injury, viral hepatitis, ischemic live injury
Aspartate aminotransferase
enzyme found in liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidney, brain and red blood cells
biomarker of tissue damage
Troponin I (troponin T)
cardiac specific proteins that regulate muscle contraction in the heart
diagonsing myocardial infarction
elevated troponin: heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, myocarditis
CK
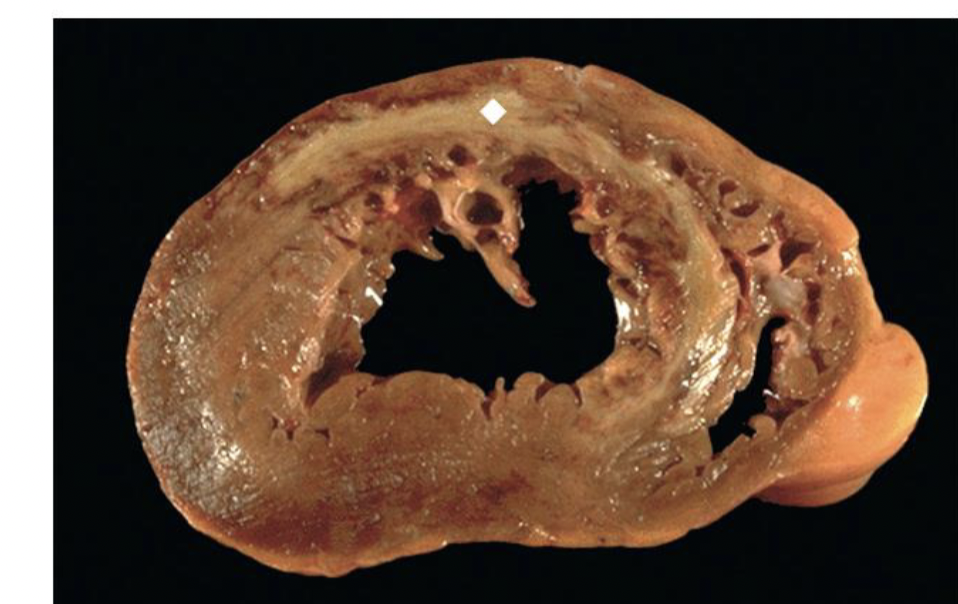
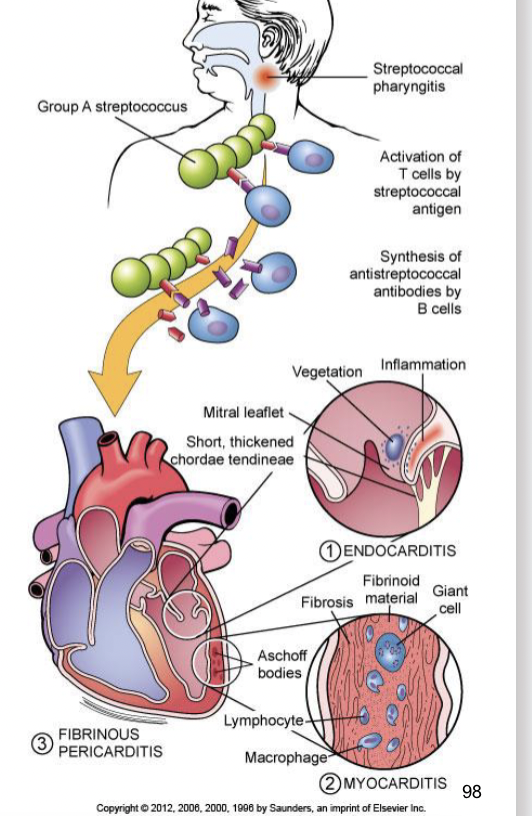
Rheumatic fever
occurs 2 weeks after an episode of strep throat
affects joints, the skin, and the brain
cell mediated immune reaction develops and the suppressor t lymphocytes and macrophages many also damage various tissues
Cause of infectious myocarditis
heart failure
cardiogenic shock
arrthymias
viral and bacterial infections
Angina pectoris
chest pain due to myocardial ischemia
clinical presentation of coronary heart disease
Which of the following organs helps regulate arterial blood pressure?
kidney
heart
blood vessel
Common infection of the respiratory tract
UPPER: Common Cold, Sinusitis, Pharyngitis
LOWER: Bronchitis, Pneumonia, Influenza, Tuberculosis, RSV
Hypostatic pneumonia
lung inflammation—> prolonged immobility
symptoms: cough, fever, chills, chest pain, fatigue
risk factors: COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
Lobar pneumonia
caused by the streptococcus pneumoniae and haemophilus influenzae
consolidation of the lung tissue
symptoms: high fever, cough dyspnea
Lobular pneumonia
affects bronchi and lung tissue
scattered areas of infection
RSV, COPD, SP, HI
symptoms: cough, fever, chest pain
Aspiration pneumonia
lung infection that occurs when food, liquid or saliva is inhaled into the lungs causing infection and inflammation
COPD
Interstitial pneumonia
inflammation of interstitial tissue in the lungs (air sacs alveoli)
caused by: flu, RSV, mycoplasma pneumoniae
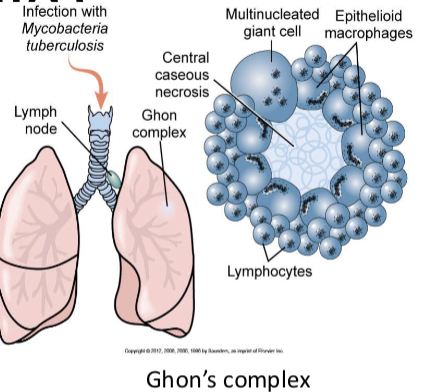
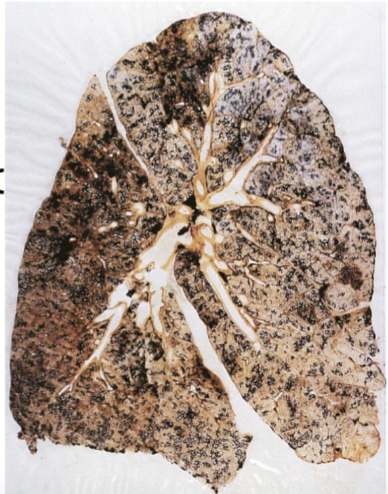
Tuberculosis everything (lab diagnostics, symptoms, classifications….)
primary infection: Ghons complex (parenchyma with granulomas and lymph node enlargement)
secondary TB: reactivation or second infection (cavernous TB)
symptoms: nonrpoductive cough, night sweats, weight loss
classifications: Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary
lab diagonostics: chest x ray, skin test, sputum culture
Causes of emphysema
cigarette smoking
alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
air pollution
chronic respiratory infections
genetic factors
Sarcoidosis
inflammatory disease that affects the lungs
formation of granulomas
organs affected: lungs, lymph nodes, skin, eyes
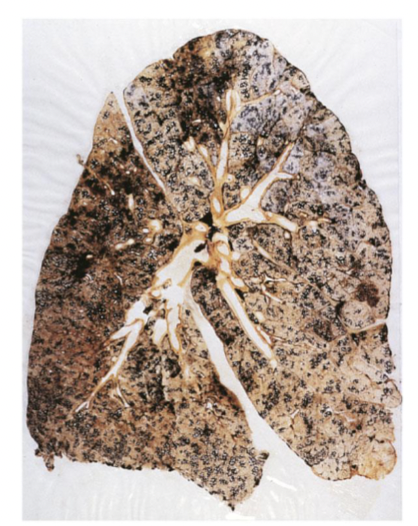
Coal-workers’ lung
black lung disease
increase carbon particles of impurities
dust accumulates and incites fibrotics
Asbestosis
Associated with:
pulmonary fibrosis
pleural fibrosis and pleural plaques
lung cancer
malignant mesothelioma
Pathology:
-asbestos bodies
Clincial:
restrictive lung disease
risk of cancer
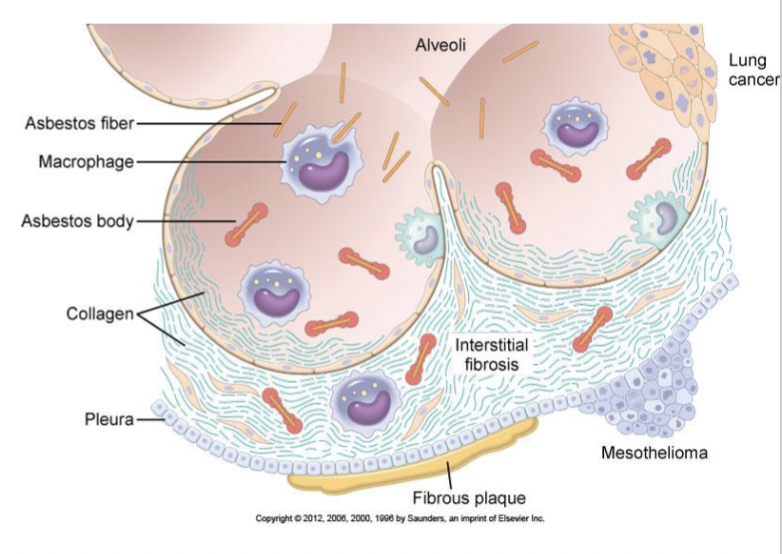
Pneumoconiosis
inhalation of mineral dusts, fumes, and various organic and inorganic particulate matter
duration of exposure
size of particle/ larger filtered out
concentration and makeup
inflammatory response—> fibrosis
Malignant mesothelioma
rare and aggressive cancer primarily affects the mesothelium
most common type is pleural mesothelioma
Symptoms of lung cancer
symptoms depend on the location of the tumor and its size
persistent cough, hemoptysis, shortness of breath, chest pain, wheezing, fatigue, fever, loss of appetite
Edema in different organs (terminology)
excess of fluid in the interstitial space and or the body cavities
localized edema may involve any tissue or organ
Pulmonary edema is a typical complication of
heart failure
failure of the left ventricle leads to pulmonary congestion
left side CHF: shortness of breath/dyspnea
Active hyperemia
increased blood flow
causes (exercise, inflammation, heat)
vasodilation of arterioles
Hemoptysis
respiratory tract bleeding with expectoration
coughing up of blood
causes of hemoptysis: bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer)
Melena
the production of melena, following internal bleeding or the swallowing of blood
digested blood
black stools
HEMORRHAGE
The proteinaceous meshwork that holds a thrombus together is composed of
fibrin
Clinically significant emboli are most often composed of
blood clots (thromboemboli)
Most venous emboli that are of clinical significance originate in the veins of the
deep veins of the legs
DVT (deep vein thrombosis)
Organs is most affected by venous embolism
lungs (PE-pulmonary embolism)
PE occurs when a venous thrombus
Most arterial emboli that cause cerebral infarcts originate from the
heart
left atrium or left ventricle
cartoid arteries
Shock resulting from massive bleeding is best classified as
hypovolemic shock
blood loss, death, exsanguination
What are most congenital malformations in humans caused by? Most malformations have an unknown cause
genetic, environmental, multifactorial factors
Atherosclerosis is the most important complication encountered in persons affected by familial hypercholesterolemia
true
Anasarca
severe and generalized edema
fluid accumulation in the subcutaneous tissue and body cavities
causes: heart and liver failure, nephrotic syndrome
Ascites
accumulation of edematous fluid in the abdominal cavity (hydroperitoneum)
Hydrothorax
accumulation of serous fluid in the pleural cavity
classified as a transudate
causes: CHF (congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis)
Hematopericardium
presence of blood within the pericardial sac
can lead to life threatening cardiac tamponade
Exudate (in diseases such as cirrhosis of the liver) vs transudate
exudate:
rich in protein and blood cells and is typical of inflammation
inflammatory edema is related to the increased permeability of the blood vessels
transudate
less proteins and fewer cells than exudate
edema is in essence an ultrafiltrate of plasma fluid that may accumulate in tissue because of factors including:
increased hydrostatic pressure inside the blood vessels
decreased oncotic press of the plasma
obstruction on lymphatic vessels impeding interstitial fluid drainage
increased tissue hydration because of sodium retention
What type of embolus is most commonly found in clinical practice?
thromboembolism
pulmonary embolism (PE)
What condition could develop from the heart failure seen in decompensated shock?
-pulmonary edema
-hydrostatic (increased arterial pressure and increased venous backpressure)