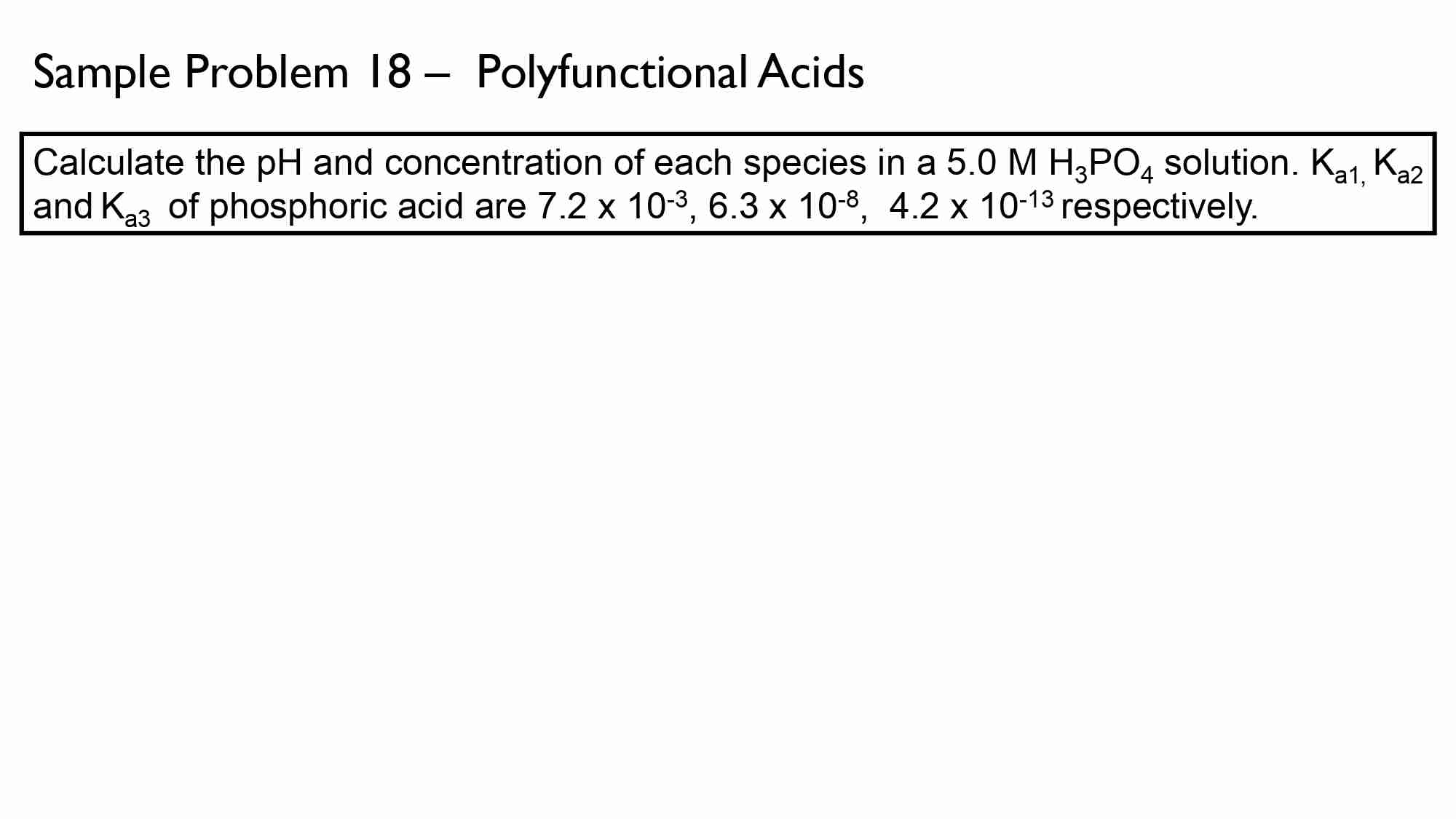
Module 6 — Neutralization Titration, Titration Curves for Polyfunctional Acids [Problem Solving]
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
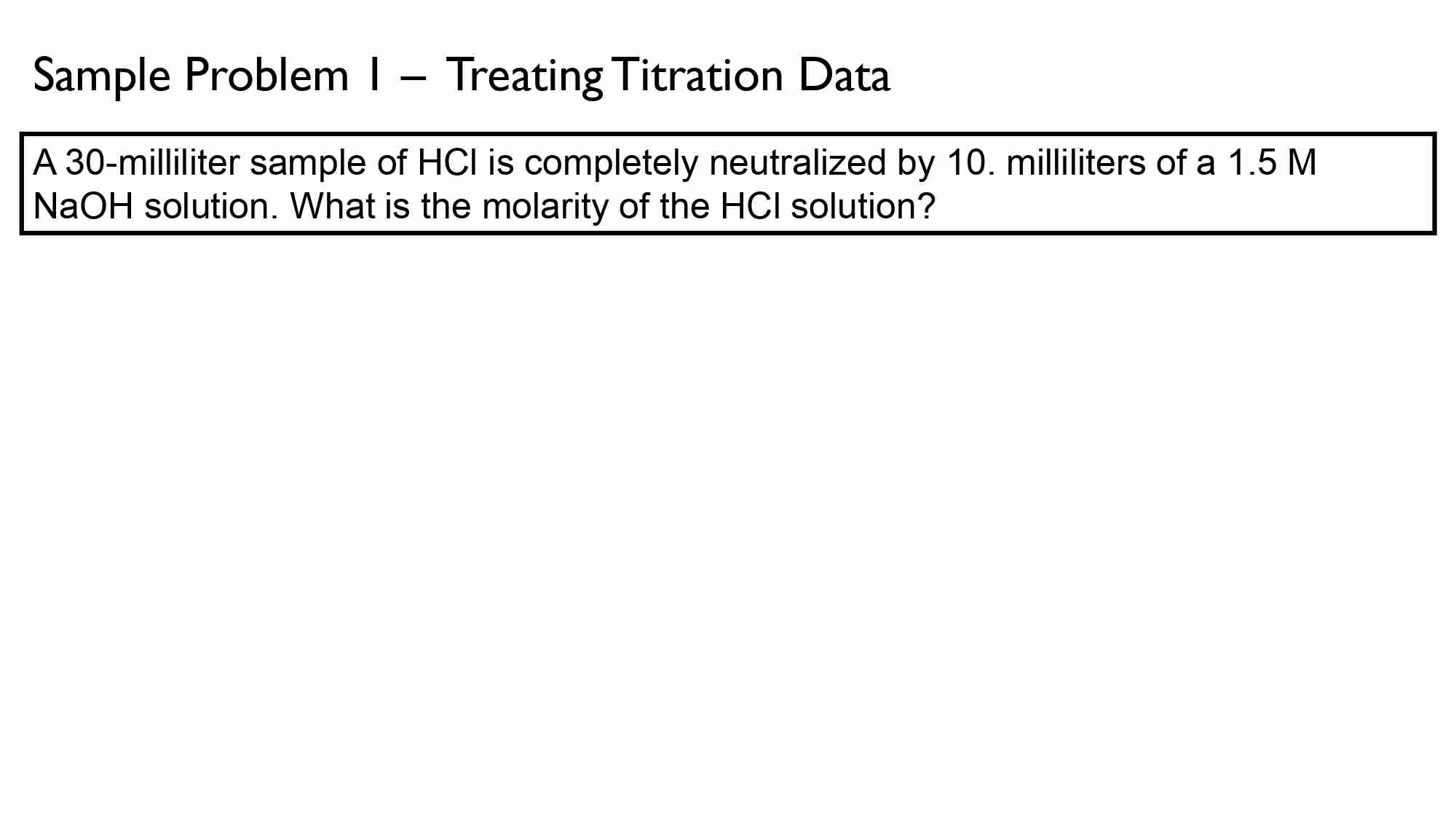
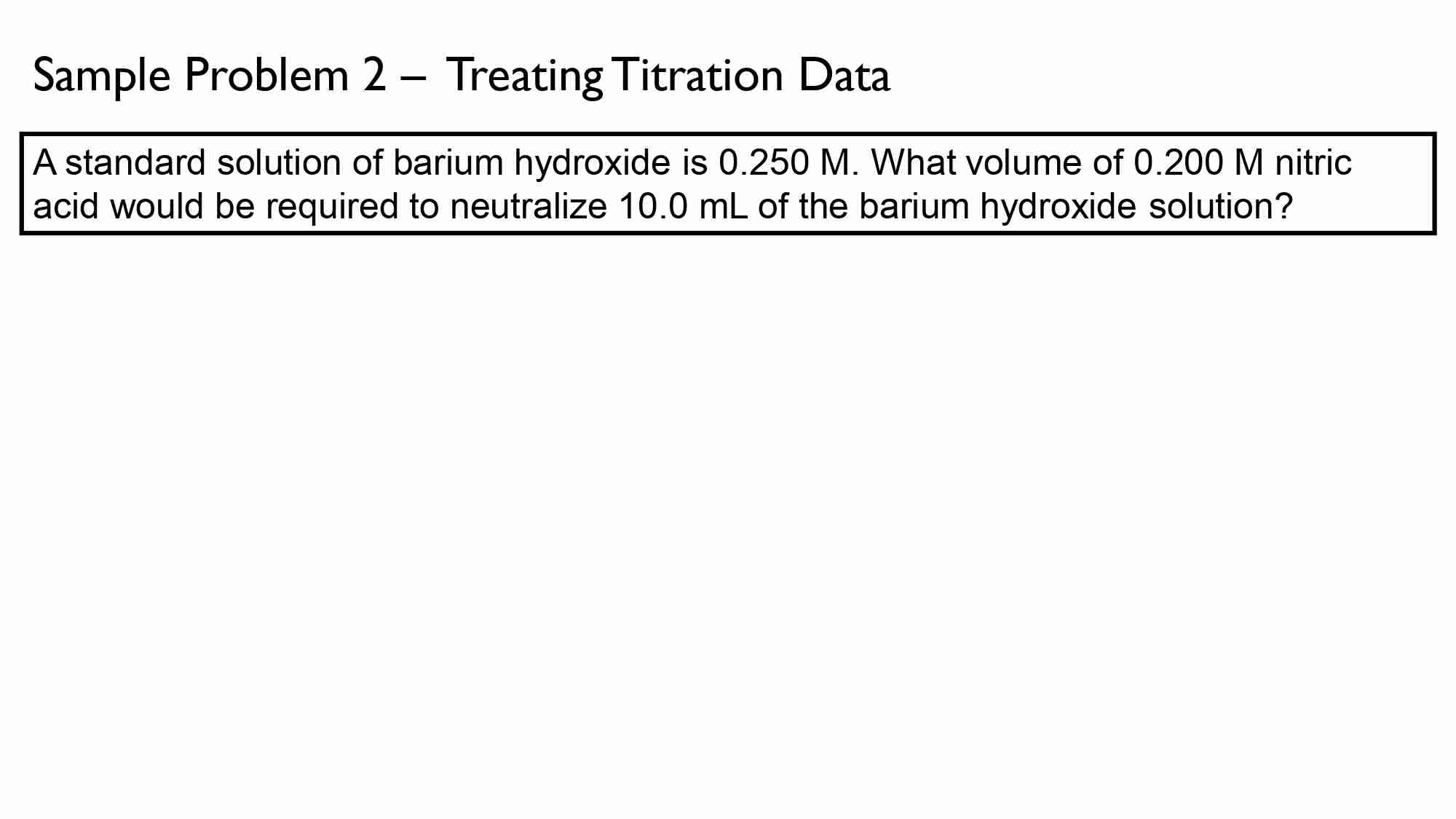


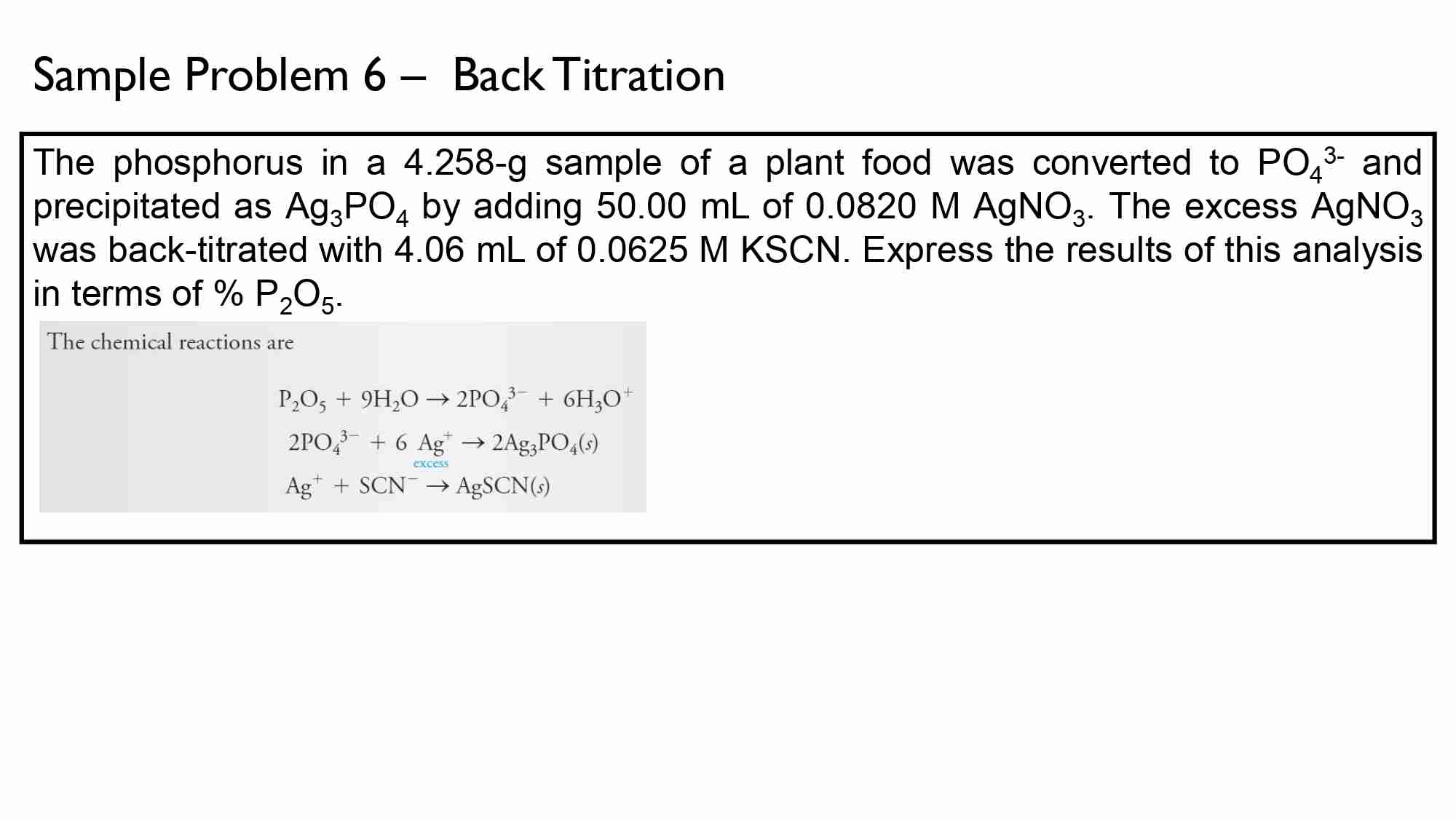






If It takes 50.0 ml of 0.50 M KOH solution to completely neutralize 125 ml of sulfuric acid solution (H₂50), What is the concentration of the H_{1}*S O + solution
Calculate the pH of the solution resulting from the addition of 20.0 ml of 0.100 M NaOH (strong base) to 30.0 ml of 0.100 M HNO, (strong acid).
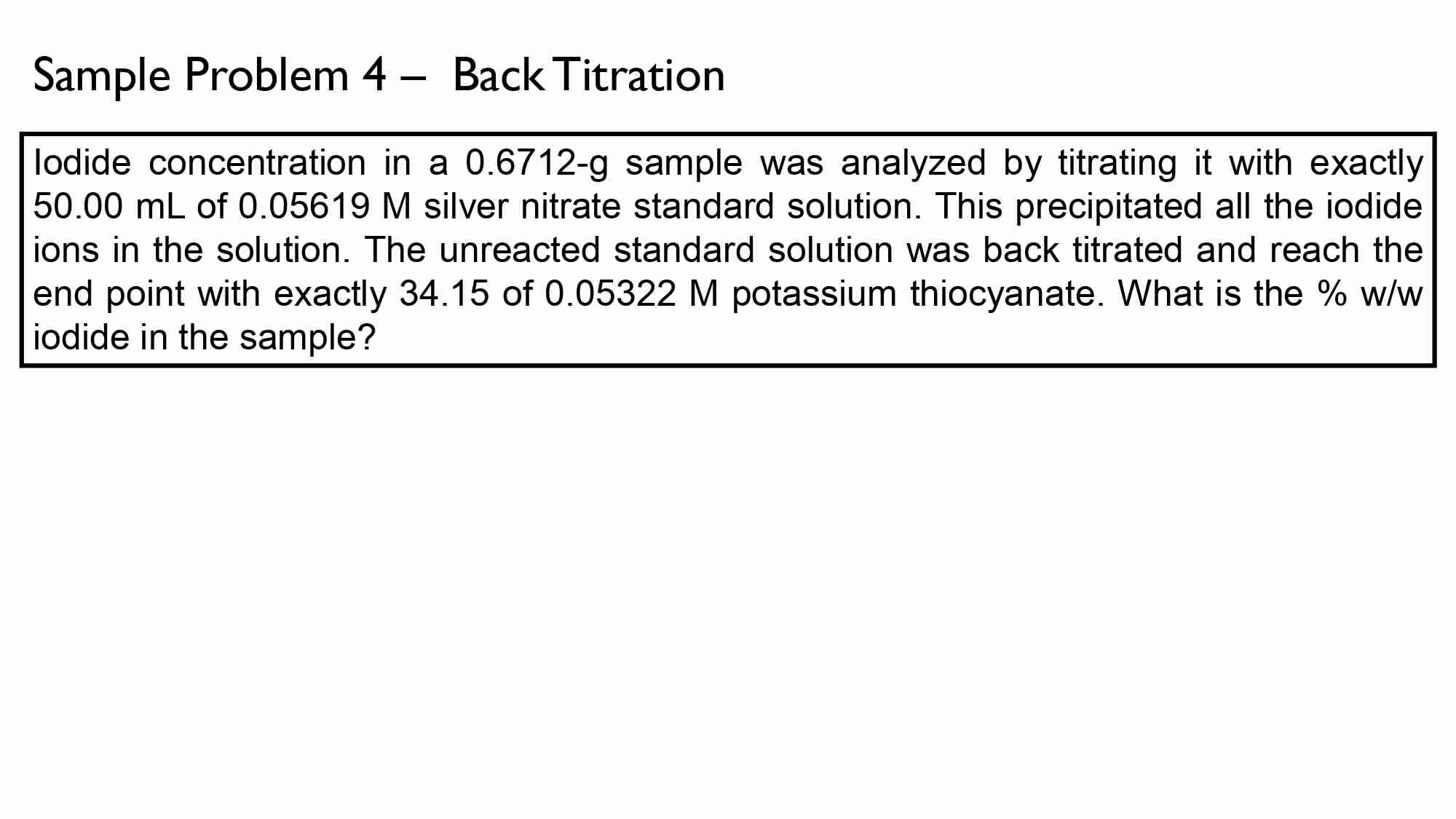
lodide concentration in a 0.6712-g sample was analyzed by titrating it with exactly 50.00 mL of 0.05619 M silver nitrate standard solution. This precipitated all the iodide ions in the solution. The unreacted standard solution was back titrated and reach the end point with exactly 34.15 mL of 0.05322 M potassium thiocyanate. What is the % w/w iodide in the sample?
Measured: Ag+ + I- » AgI
Excess: Ag + SCN- » AgSCN
Determine the pH of a buffer solution prepared by dissolving 0.35 M of NH4Cl in 0.25 M aqueous NH3. Kb for NH3 is 1.77 x 10^-5.
Calculate the pH at equivalence point for the titration of 50.00 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH with 0.100 M NaOH. Ka of CH3COOH is 1.8 × 10^-5.