Topic 3 - Acids
1/65
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
3.1 What is an acid?
A substance that produces H+ ions
3.1 What are the 3 common laboratory acids?
HCl (aq) hydrochloric acid H+ + Cl-
HNO3 (aq) nitric acid H+ + NO3-
HSO4 (aq) sulphuric acid H+ + SO4-
3.1 What is a base?
A substance that reacts with an acid to produce salt + water
ACID + BASE → SALT + WATER
3.1 What type of reaction is one between an acid and a base?
A neutralisation reaction
3.1 What are the 2 things a base can be?
a solid: Because it is insoluble in water
eg metal oxides (s) such as ZnO, CuO, MgO
Aqueous: Because it is soluble in water
Eg metal hydroxides (aq) such as NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)
3.1 What is an alkaline?
A soluble base which contain OH- ions
What is a salt?
A compound that forms when acids react with various substances
Salts are ionic compounds (composed of negative and positive ions)
where do the 2 parts of the salt name come from?
the first part is from the base and the second from the acid.
Eg NaCl: Na comes from sodium and Cl comes from hydrochloric acid
What is the concentration of hydrogen ions measured by?
pH
What type of scale is the pH scale, and explain why
the pH scale is an inverse scale: As the concentration of hydrogen ions increases the pH decreases
If is also logarithmic: Each whole number pH differs by a factor of 10
How much is the decrease in concentration of hydrogen ions if the pH goes from pH 1 to pH 2? What is the ratio?
increases by 10
10:1
How much is the increase in concentration of hydrogen ions if the pH goes from pH 4 to pH 6? What is the ratio?
increases by 100
100:1
How much is the increase in concentration of hydrogen ions if the pH goes from pH 1 to pH 5? What is the ratio?
10000
10000:1
How much is the decrease in concentration of hydrogen ions if the pH goes from pH 4 to pH 1? What is the ratio?
decrease by 1000
1:1000
Finish the sentence:
The higher the pH the ..
lower the concentration of H+ ions
Finish the sentence:
The greater the concentration of OH- ions …
the high the pH
what is a strong acid? (2 marks)
an acid which fully dissociated into its ions,
producing a solution with a high concentration oh H+ ions
what is a weak acid?
an acid that is not fully dissociated into its ions,
producing a solution with a low concentration of H+ ions
give some examples of strong acids
H2SO4 (aq), sulphuric acid
HCl (aq), hydrochloric acid
HNO3 (aq), nitric acid
give an example of a weak acid
ethanoic acid, CH3COOH
hydrofluoric acid, HF
What does it mean for acid not to fully dissociate into its ions
It means that most of the molecules you dissolve in water do not split up into their ions
What does it mean for an acid to fully dissociate into its ions
It means that every single molecule of the acid you dissolve in water will split up into hydrogen ions
What is concentration in terms of acids?
the measure of the number of moles or mass of the acid, the solute that have been dissolved in a certain volume of water
What is the formula for concentration?
concentration=mass (in grams)/ volumes (in dm³)
C = m/ v
concentration = moles (n)/ volume (dm³)
C = n/ dm³
what are the units for concentration?
g/dm³ or mol//dm³
what does it mean for a strong acid and a weak acid to have the same concentration?
it means that the same number of moles is dissolved in the same volume of water
Eg
However they don't have the same pH, as the strong acid is fully dissociated into its ions but the weal acid is not fully dissociated into its ions

Do strong acids have higher or lower pH’s than weak acids of the same concentration
strong acids have lower pH’s than weak acids of the same concentration
what is concentration the measure of?
concentration is the measure of the amount of particles dissolved in water,
what are the products of the following reactions?
Acid + metal
Acid + metal oxide
Acid + metal carbonate
Acid + metal hydroxide
Acid+ base
Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
Acid + metal oxide → salt + water
Acid + metal carbonate → salt+ water + carbon dioxide
Acid + metal hydroxide → salt + water
Acid+ base → salt + water
What are indicators?
substances that when added to a substance can give us information on the acidity or basicity of that substance depending on the colour of the indicator.
what are 5 the common indicators?
Red litmus
Blue litmus
Phenolphthalein
Methyl orange
Universal indicator
what colour does blue litmus turn in acidic and alkaline solutions?
Red in acidic
Blue in alkaline
what colour does red litmus turn in acidic solutions?
Red in acidic
Blue in alkakine
what colour does phenolphthalein turn in acidic and alkaline conditions?
Colourless in acidic
Pink in alkaline
what colour does methyl orange turn in acidic and alkaline conditions?
Red in acidic and yellow in alkaline
what is the universal indicator? Why is it useful?
It is a mixture of chemicals.
It is useful as it has a range if colours depending on whether the acidic has a high of low concentration of hydrogen ions or whether the base has a high or low concentration of hydroxide ions.
These colours then match the pH scale and a pH number us given to the solution. This tells us whether it is a strong or weak acid or alkaline
What are the solubility rules for soluble salt?
Common sodium, potassium and ammonium compounds are soluble
All nitrates are soluble
Common chlorides are soluble, except those of silver and lead(ll)
Common sulphates are soluble, except those of barium, calcium and lead(ll)
What are the solubility rules for insoluble salts?
common carbonates are insoluble, except those of sodium, potassium and ammonium
Common hydroxides are insoluble, except those of sodium, potassium and calcium
How do you obtain a solid from a salt?
1) First you need to identify whether it is soluble or insoluble
2) for soluble salts carry out:
Titration (indicator)
Excess insoluble base + Acid
These are both neutralisation reactions
3) for insoluble salts
Precipitation
This is a precipitation reaction
What is the method for preparing insoluble salts?
1) add together the 2 soluble salts and stir
2) filter the solution
3) wash the residue (insoluble salt) with distilled water
4) dry insoluble salt
draw the apparatus needed to filter the insoluble salt from the solution, with labels
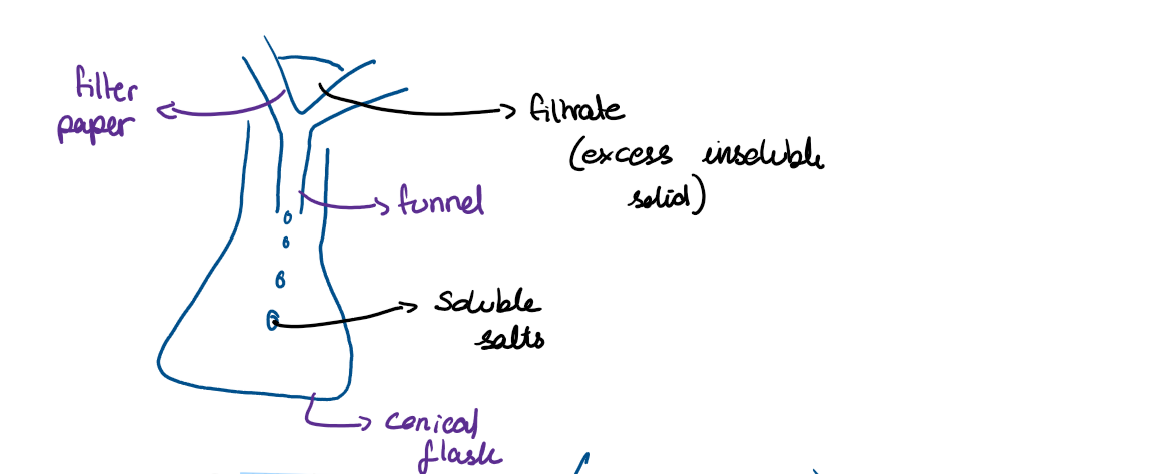
Why do you need to wash the insoluble salt with distilled water?
To get rid of the soluble ions
how do you dry the filtrate
between 2 pieces of filter paper or in a warm oven
Writing equations for the reactions to make an insoluble salt; what will the reactants and products be?
2 reactants: Will be solutions of the 2 aqueous salts
2 products: Will be 2 salts made from swapping around the 2 cations or 2 anions
Of the 2 salts made in the precipitation reaction to obtain a solid from a salt, how many will be soluble?
one will be soluble and the other will be insoluble
write the symbol and ionic equation for the reaction of lead (ll) nitrate with potassium iodide, including state symbols
Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) → PbI2(s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
Pb2- + 2I- → PbI2
what is the method for the precipitation reaction between lead nitrite and potassium iodide
1) measure out 25cm³ of lead nitrate and 25cm³ of potassium iodide in separate measuring cylinder
2) mix the two solution in a 100cm³
3) filter the mixture in the beaker and wash the residue with cold distilled water
4) Leave the lead iodide formed to dry in a warm oven
Why id deionised (distilled) water used instead of tap water to wash the lead iodide
Because distilled water doesn't contain any dissolved ions
Why is the solid lead iodide not dried by direct heating with a Bunsen burner flame?
because this may break it down or react with the oxygen in the air
why is the insoluble solid dried in a cool oven instead of a hot one?
because the dead may break it down or redact with the oxygen in the air
What is the method for obtaining a solid from a soluble salt through reacting with excess insoluble base.
Preparation of copper (ll) sulphate using copper (ll) oxide and sulphuric acid
measure 50cm³ of dilute sulphuric acid into the 250cm³ beaker using a measuring cylinder
Add a small spatula of copper (ll) oxide
Place on a tripod and gauze and warm gently (airhole open) while stirring with a glass rod
When the solid has disappeared add a bit more of the copper (ll) oxide
Continue until there is excess solid left over
Turn off the Busen burner. Leave to cool
Filter the solution into a conical flask
Transfer the contents of the conical flask into an evaporating dish
Heat to reduce the volume to half or until crystals jst star to for. DO NOT EVAPORATE TO DRYNESS
remove from heat and allow to cool
Leave the solution over night or allow to crystallise
When returning to the crystals the following day filter off an remaining solution and dab crystals dry by pressing between two sheets of filter paper
How do you check if crystals have formed ?
You will see a ring of crystals form around the edge of the evaporation dish or
A thin layer of crystal will form when a glass rid is dipped in the solution, removed and allowed to cool.

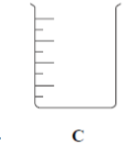
Apparatus for titration:
What is this apparatus?
Pipette
Apparatus for titration:
What is this apparatus?
Beaker

Apparatus for titration:
What is this apparatus?
burette
Apparatus for titration:
What is this apparatus?
Funnel
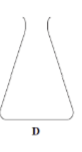
Apparatus for titration:
What is this apparatus?
Conical flask
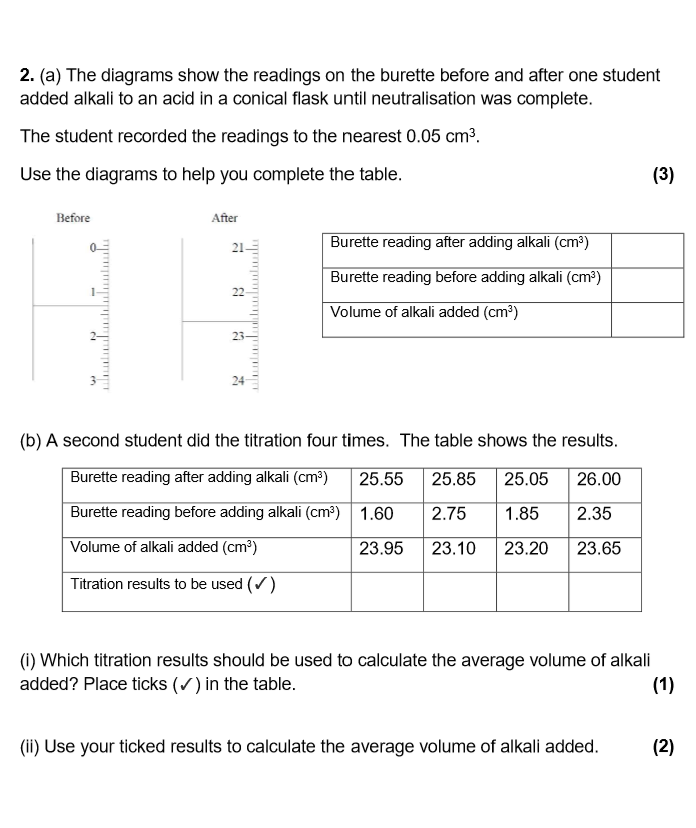
compete these questions
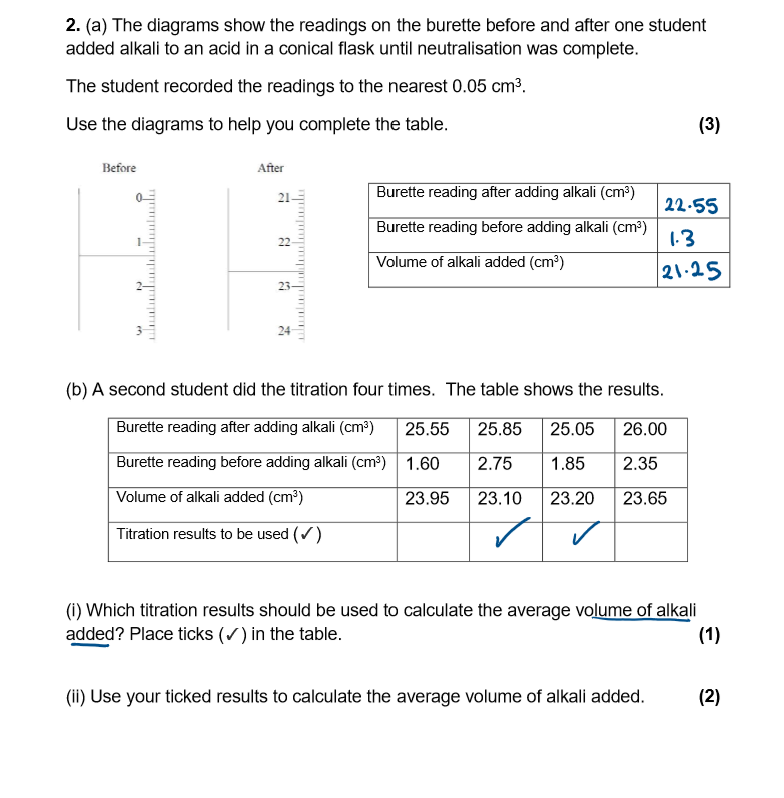
what is titration?
Titration is a method used to accurately add volumes of liquids together
What is the method to carry out titration?
Fill burette with one solution (acid). Record initial volume on burette
Pipette 25cm³ of the other solution (alkaline) into a conical flask. Add the indicator to the conical flask, and put on white tile
Add solution from burette slowly into conical flask, swirling in between additions
Stop when the end point is reached (indicator changes colour; end point- when neutralisation has been achieved)
Record final volume on the burette, and then find the total amount of acid added by subtract initial volume from end volume
Repeat until you get concordant results (volumes are within 0.2cm³ of each other).
Use concordant results to calculate the mean volume of acid required to neutralise alkaline
what is a titre?
titres are within 0.2 cm³ of each other
What is the method to find the volume of sodium hydroxide needed to neutralise hydrochloric acid using titration?
titrate 25cm³ aliquots of the hydrochloric acid solution against a solution of sodium hydroxide using phenolphthalein as an indicator
Burette: NaOH
Conical flask: 25cm³
Indicator: 4,drops of phenolphthalein
Colour change at endpoint: Colourless → pink
Record all volumes to 2 dp
How do you get a pure and dry sample of the salt (After a titration or reacting an acid with excess insoluble base)
1) heat the solution in an evaporation basin to evaporate off about half of the water
2) leave to cool for crystallisation to occur
3) Dry the crystals between 2 pieces of filter paper or in a warm oven
How can you test to see when you should stop heating the solution during a evaporating of salts experiment?
if you that crystals form after dipping a glass rod into the solution and withdrawing it
Why does the evaporating basin need to be left to cool for crystallisation to occur?
because solubility decreases as the temp decreases
what is the ionic equation for neutralisation?
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O (l)