(W4) Ch 8 The body in health and illness
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Hindbrain
medulla oblongata: blood pressure, heart rate, respiration
reticular formation: attention, wakefulness
pons and cerebellum: integrating reflexes and automatic behavior
midbrain
reticular system, sensory and motor correlation centres: integrating reflexes and automatic behavior
forebrain
influences mood and behavior
thalamus: attention, memory, central hub
hypothalamus: hunger, sexual arousal, thirst
limbic system: hippocampus, fornix, mammillary bodeis, thalamus, cingulate cortex, hippocampus, amygdala
cerebrum
basal ganglia: complex motor coordination
cortex: 4 lobes, 2 hemispheres, connected by corpus callosum
frontal lobe: executive functions, motivation, connections to limbic system
temporal lobe: left temproal lobe=language, right= visuospatial skills (in right handed ppl), smell, hearing, integrating sense, memory, linking emotions to memory
occipital lobe: visual perception
parietal lobe: integration of sensory information
symptoms possible after stroke

Autonomic nervous system
monitors and if needed takes control over activity level of key organs and organ systems so that it is all coordinated
hypothalamus receives info from many diff sources :
reticular formation - temperature
optic nerve (light and dark)
hypothalamus itself - ion balance and temperature of the blood
links to cortex and limbic systems - response to psych demands possible
ANS consists of:
sympathetic nervous system (fight/flight): activation and arousal
Parasympathetic Nervous System (rest/recover): relaxation
ANS overview
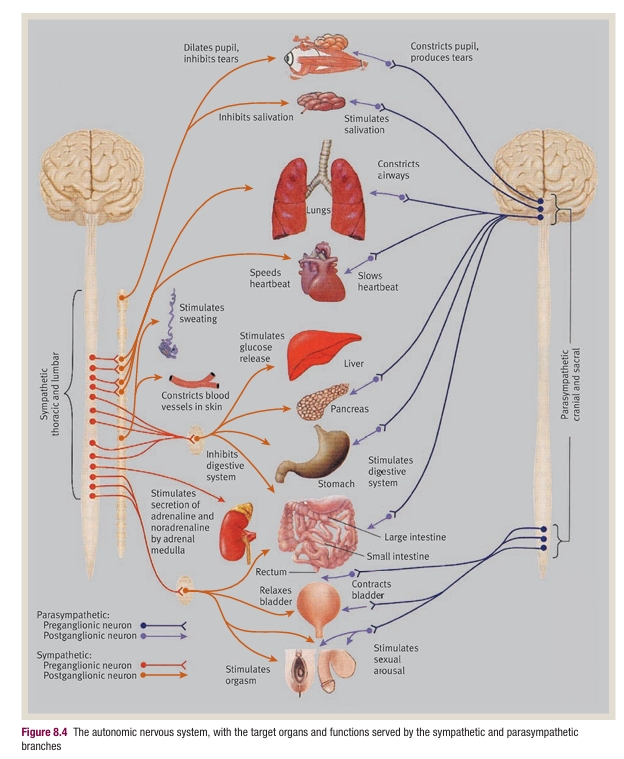
ANS contid
both systems start in the medulla oblongata
pass down the spinal cord to various synapses
there they link to a second series of nerves which are linked to all key body organs
sympathetic sys:
neurotransmitter involved at the synapse betw spinal cord nerves and nerve of target organ is acetylcholine
activity at the synapse betw second nerve and end organ mainly is NT noradrenaline and to lesser extent adrenaline (also called norephinephrine and epinephrine)
parasympathetic sys:
Acetylcholine at both synapses
ENDOCRINE PROCESSES»
activity initiated by sympathetic nervous system is short lived
longer term effects on arousal are done by endocrine glands
adrenal glands
situated above the kidneys, extend SNS activity
two functional areas:
adrenal medulla activated by the SNS causing it to secrete the hormone version of noradrenaline (SNS adrenal medulla xis/ SAM axis)
pituitary gland is stimulated by the hypothalamus and releases hormones into the blood incl ACTH, ACTH controls the release of corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory hormones incl cortisol that are made naturally in the body) in the adrenal cortex. cortisol is a stress hormone that incr availability of energy stores and fat as fuel for long periods of exercise. supresses inflammatory response of damaged tissue (Hypothalamus Pituitary Adrenal axis /HPA axis)
see figure p63
the immune system