Lectures 5 & 6: Human Evolution
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Nativism
Knowledge of the world is mostly innate, and determines certain abilities
this view is associated with the idea that nature (genes) determines behavior
Empircism
At birth, mind is a tabula rasa (empty state), nothing in terms of behavior and knowledge is inherited; al is learned
this view is associated with the idea that nurture (environment) determines behavior
Interactionism
Certain basic abilities and knowledge are innate, but can be influenced by experienced, which in turn can change what innate behaviors are expressed, which influences what will be experienced, and so on. This view is supported strongly by the available evidence
Genotype
The compete set of an organisms’ genes
Phenotype
The overt characteristics of an organism (the properties we can observe resulting from what genes are expressed)
phenotype is product of genotype and environmental factors, and experience
Example: skin color in humans. Our genes determine how much melanin we produce, but exposure to UV-B radiation can increase melanin production, which darkens the skin because melanin is black
Monozygotic twins growing up together
Provide data for equal “nature”, similar to”nurture”
Monozygotic twins growing up apart
Provide data for equal “nature”, different “nurture”
Dizygotic twins growing up together
Provides data for similar “nature”, similar “nurture”
Dizygotic twins living apart
Provides data for similar “nature”, different “nurture”
Siblings growing up together
Provides data for similar “nature”, similar “nurture”
Individuals not related to each other living apart
Baseline control group. Provides data for genetically unrelated, separately living individuals that should correlate in IQ scores randomly
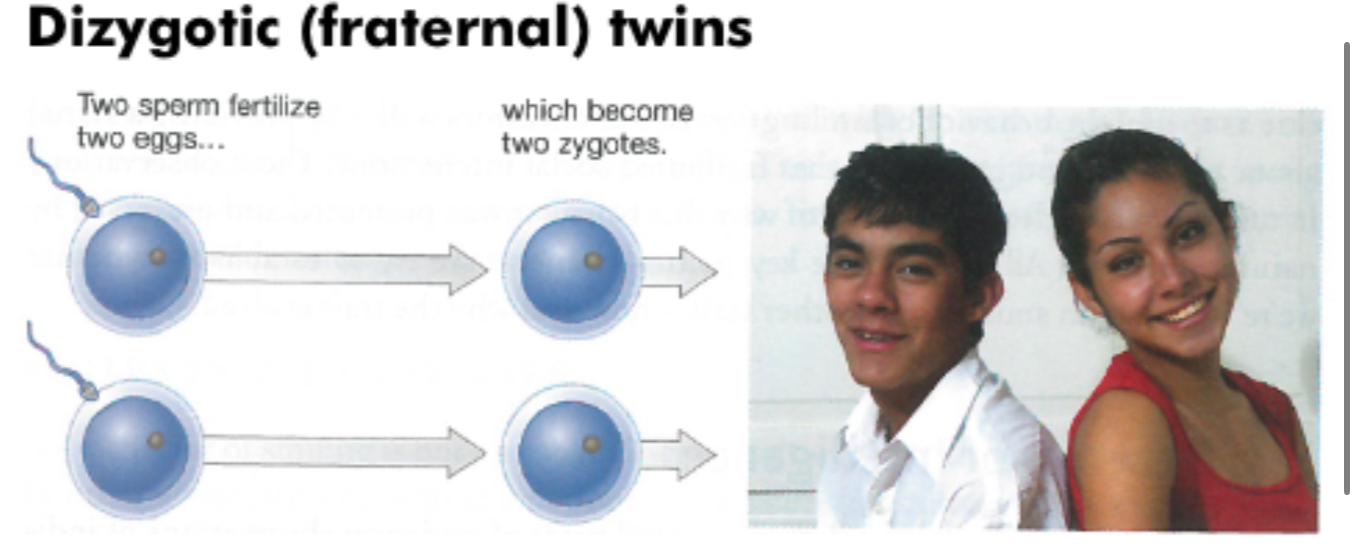
Dizygotic (fraternal) twins
Two sperms fertilize two eggs
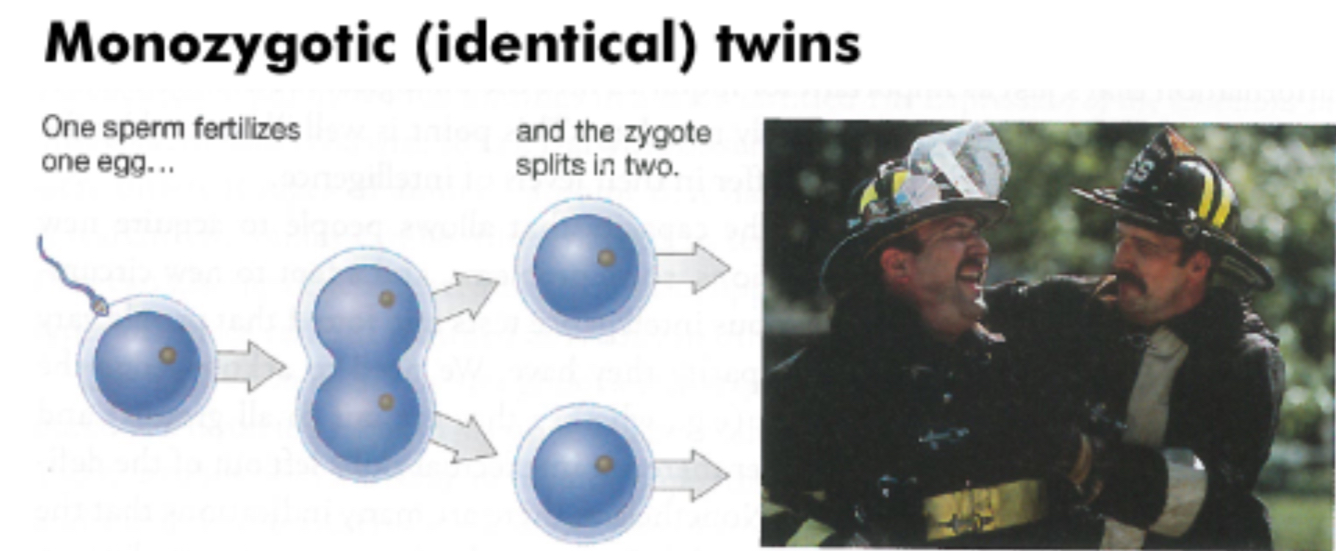
Monozygotic 9identical) twins
One sperm fertilizes one egg and the zygote splits in two
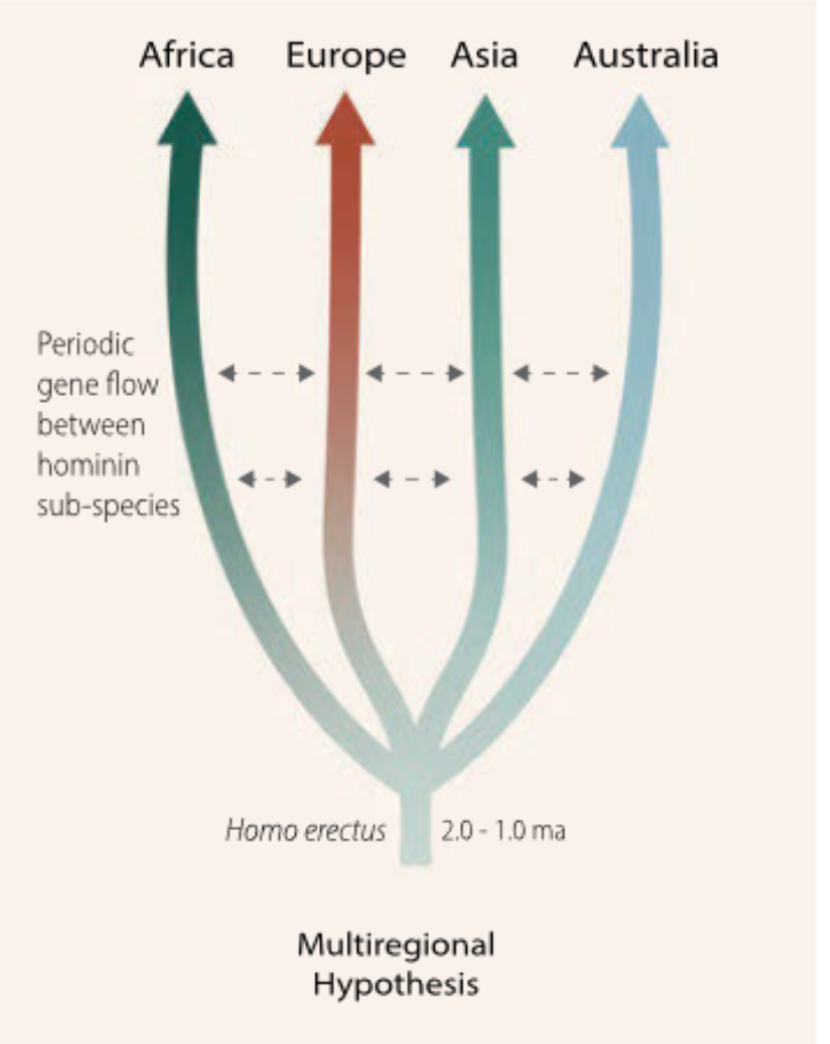
The multiregional hypothesis
Proposes regional continuity with gene flow maintaining one species
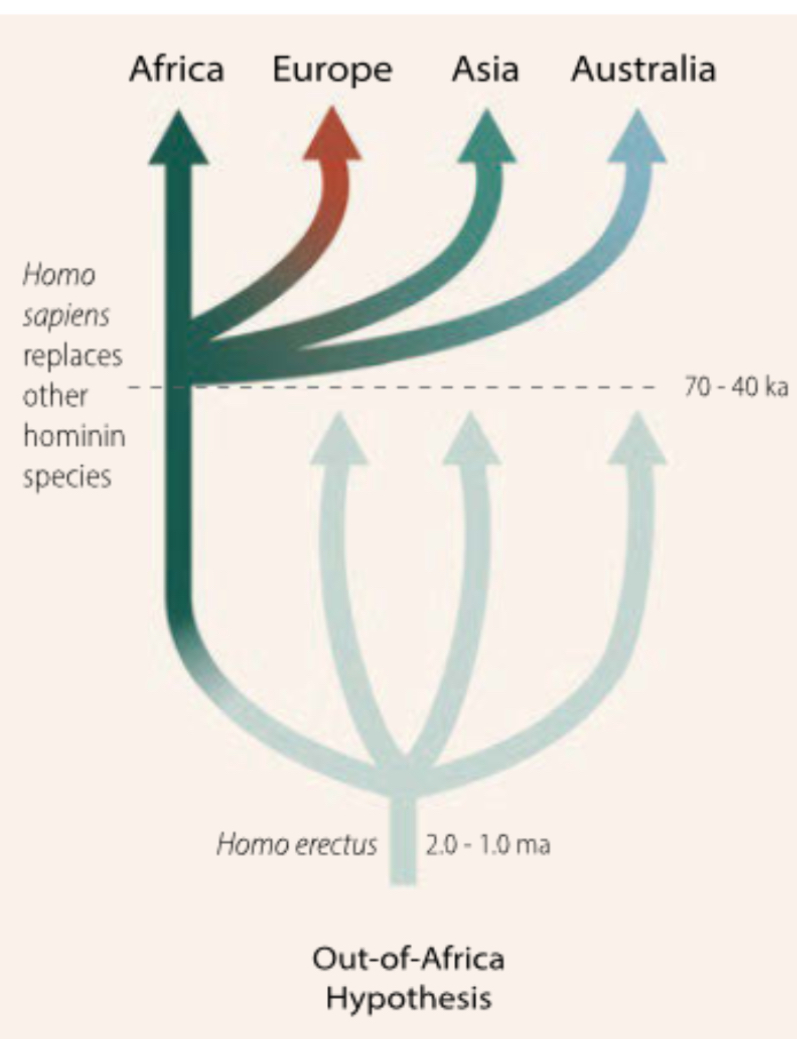
Out of ΑFrida hypothesis
Argues modern humans originated recently in Africa, replacing archaic populations elsewhere
Domain
Broadest division of life; based on cell type and molecular structure
ex: eukaryotic (cells with nuclei)
Kingdom
Groups organisms with basic body organization and nutrition
ex: animalia (multicellular, heterotrophic)
Phylum
Groups organisms with major structural features or body plans
ex: chordata (notochord, meaning “back cord”, or dorsal nerve cord)
Class
Subdivision of phylum; shares more detailed traits
mammalia (hair, mammary glands)
Order
Animals sharing major adaptive traits: mammals with grasping hands/feet, forward-facing eyes, large brains relative to body size) is primate
Family
(Animals generally originating from common ancestor with more detailed morphological similarities) is hominid are (“great apes”, consisting of chimpanzee, gorillas, orang-tuna’s, bonobo)
Genus
(Subdivision of a family — closely related species that evolved from recent common ancestor) is Homo
Species
Animals that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring is sapiens
Cognitive revolution
Started about 70k years ago
Mind’s Big Bang (50,000 years ago). Rapid shift to symbolic behavior, art, ornaments, complex tools, long-distance exchange, possibly trade
Cave art and music, indicating the capacity for symbolic cognitive processing, imagery
They used beads and other body ornaments, which suggests awareness of social identity, and the need for cultural expression
They improved weapons and tools, which made hunting safer and more efficient, and it knowledge was preserved and transmitted between generations
Likely these humans had their of mind and were highly cooperative, implying significant complexity
Language enabled new forms of memory, teaching, gossip, and coordination
Possible consequences of increase in brain development affecting our mind/behavior are:
We spend more time looking for food to provide energy for brain
Muscle atrophy to help feed energy needs of brain
Human premature bright due to bigger brain of newborn and smaller pelvis of mother (upright walk)
Babies are very plastic and not “set” in their way: highly adaptive
Human children are helpless for a long time
Requires raising child by help of group; evidence for “kindergartens” as early as homo neanderthalensis
Cooking (handling fire, started around 300K years ago), which increases nutritional density of food and dramatically improves digestion speed
Humans have a language that is unparalleled compared to the languages of other animals
Ability to communicate knowledge about world planning complex actions (avoiding predators)
Ability to communicate about social structure: larger groups of humans can live together (up to 150, after that information cannot be shared effectively about everyone)
Ability to communicate about things that do not exists (such as myths, laws, rules, concepts)
Friendliness, cooperation of strangers (myths, concepts)
Rapid innovation of social behavior (laws, traditions)
Increasing size of functional human society’s from kinship tribes to villages, cities, nations
Agricultural (or Neolithic) revolution
STarted about 12k years ago
for 100k years hominids depended on hunting and gathering for survival
Humans followed their food around, camped around protective sites and waterholes
Bit about 12k years ago agriculture emerged, annals were domesticated
Consequences of agricultural lifestyle
concept of ownership
Instead of kinship tribal bands, villages and cities and nations became default social structures
Diet change from wholesome and varied to monocultural. Nutrition-related diseases occurred, such as tooth caries
Settled humans have reduced knowledge about the wider surroundings, such as animals, plants, geography compare to nomadic humans
Sedentary lifestyle due to spending significant more time on working for food compared to hunter and gatherers. Work-related diseases emerged
Evolutionary psychologists argue that our minds remained hunter-gatherer minds and our behavior reflects this. We are not yet adapted to the settled lifestyle
Scientific revolution
Started about 500 years ago. Galileo, Bacon, Descartes and others developed scientific method to understand nature with the aim to control it (an old human dream , perhaps born it of our past animal in the middle of the food chain)
Industrial Revolution
Started about 200 years ago
Anthropocene
Maybe since 12k years, maybe since the 1960s. Proposed new epoch. Outcomes of agricultural and scientific revolution led to a new era in Earth history, characterized by human ability to modify entire biosphere, changing climate, geology, ecosystems