2. General Etiology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is the specific cause of leukemia?
Still not known
Higher incidence of Leukemia in:
Radiation
Alkylating agents
Down Syndrome
Genetic predisposition
Chemicals
RAD is a Good Cure
People with down syndrome have a __X increased risk of leukemia
10-30
What genetic predisposition may cause leukemia
Families where people are born with chromosomal damage, which causes genes that increase chances of leukemia
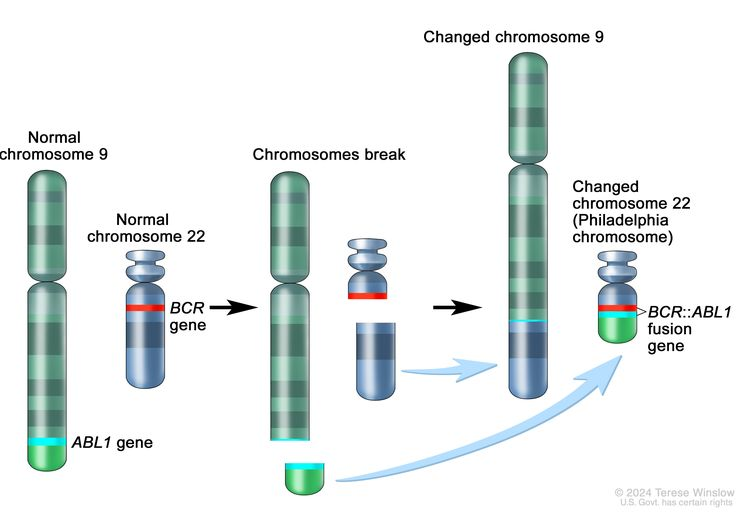
The most common chemical exposure linked to leukemia is___, but other chemicals that may cause leukemia are:
Cigarette smoking
Benzene (from PVC pipes)
Organic chemicals
Give an example of ionizing radiation causing leukemia
atomic bomb survivors & people who get high levels of radiation
Difference between acute leukemia and chronic leukemia
Acute leukemia- arises from stem cells that go bad right away
Chronic leukemia- happens when the stem cell defect is not so prominent, and the disease progresses into chronic leukemia
FYI: If there is a malignant transformation of the immature lymphoid, myeloid cells, and it presents as a cancer right away → acute leukemia
If that defect does not turn into a cancer right away, then the immature cells can develop into mature cells and if they turn cancerous, it’s a chronic leukemia
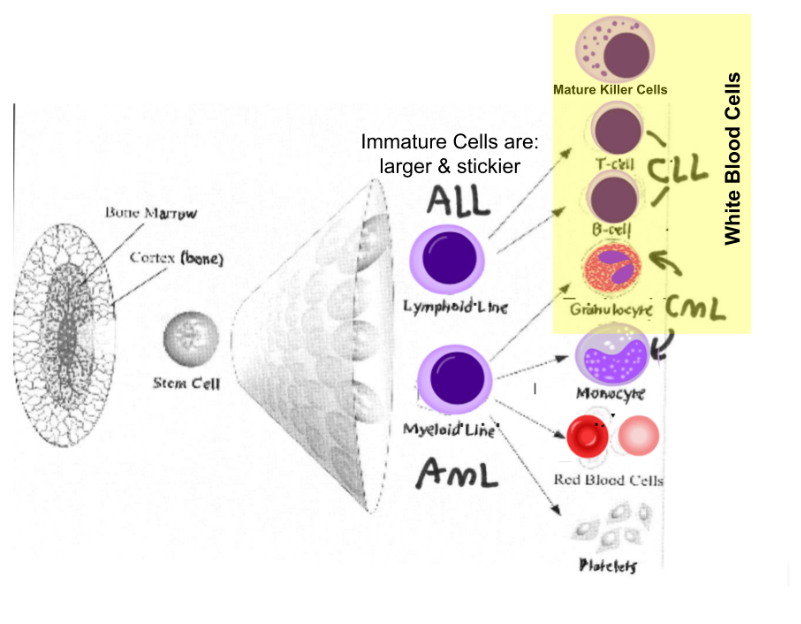
(acute/chronic) leukemias tend to occur in younger patients
acute
(acute/Chronic) leukemia cells cause more symptoms? Why?
Acute, cuz they are larger and stickier cells
FYI: so you can detect it earlier cuz there are more symptoms