Oxidation of aldehydes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
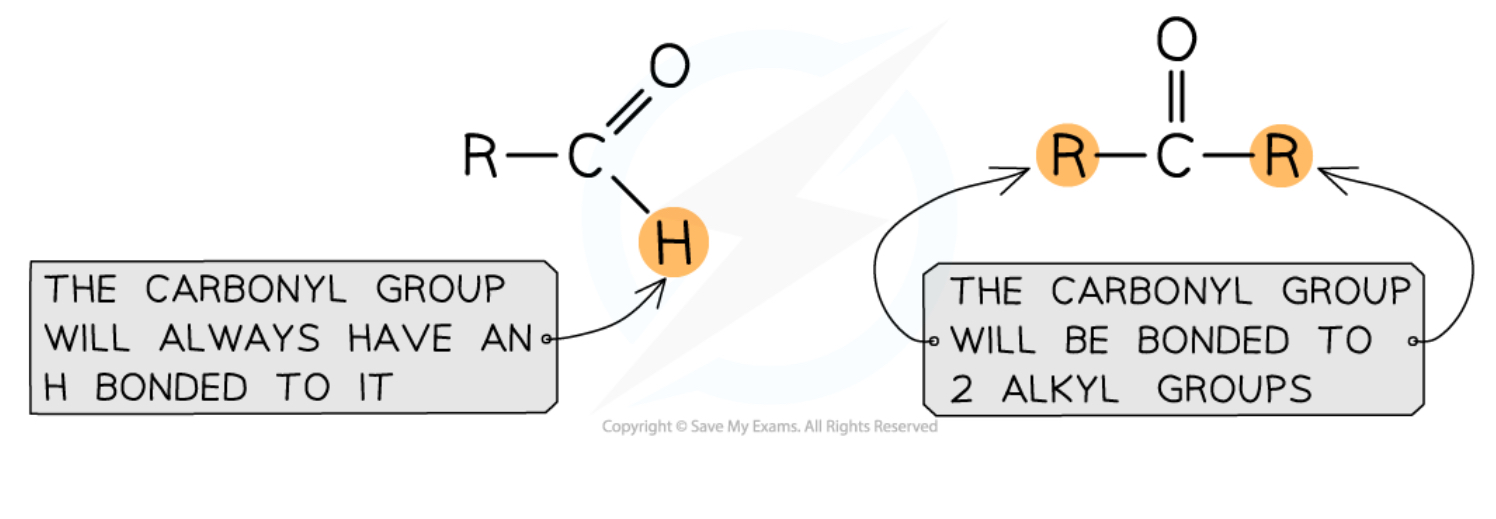
aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl functional group…
C=O
what is the difference between aldehyde and ketone?
aldehydes: C=O at the end of the chain
ketone: C=O somewhere in the chain(not ends)
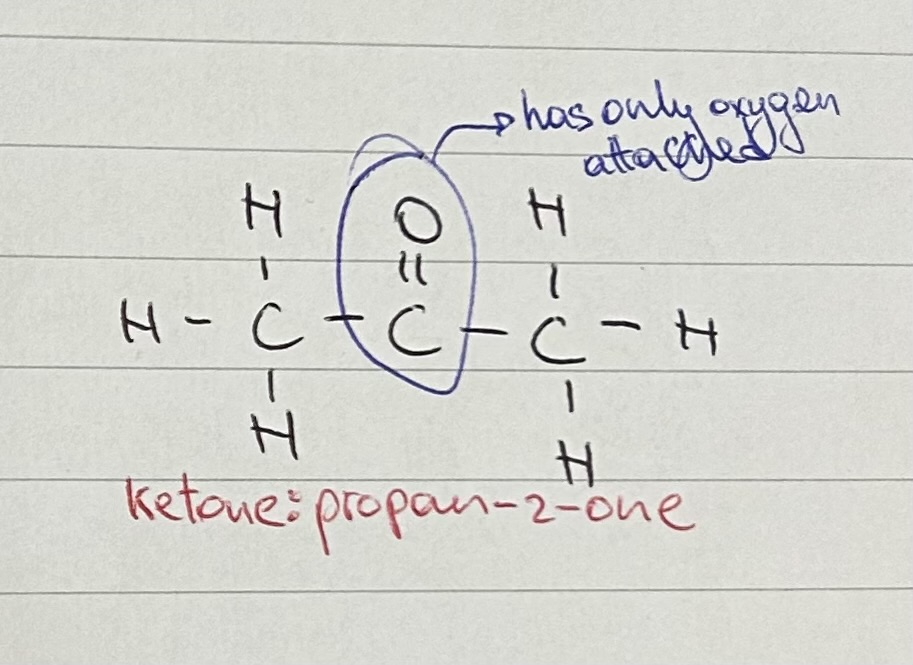
give name and structural formula of simplest aldehyde and ketone
aldehyde: methanal; HCHO
ketone: propan-2-one; CH3COCH3
oxidation of primary alcohol
primary alcohol —> aldehyde —> carboxylic acid
oxidation of secondary alcohol
secondary alcohol —> ketone —> nothing
oxidation of tertiary alcohol
tertiary alcohol —> nothing
to get aldehyde from oxidation, what do you have to do?
as you oxidise primary alcohol, you have to distill off aldehyde produced as if it oxidises even further, you would get carboxylic acid
when would you use reflux in oxidation process
when you want to oxidise primary alcohol straight into carboxylic acid
note: aldehyde would be still produced, however, as it evaporates, it would condense and drop back into the reaction mixture, to be further oxidised into carboxylic acid
what is the oxidation agent of ocr examboard choice?
acidified potassium dichromate
K2Cr2O7/H2SO4
what is the oxidation agent of ocr examboard choice?
sodium borohydride
NaBH4
why ketones will not oxidise further?
-they don’t have readily available hydrogen atoms to lose
-as a result, only with really strong oxidising agent it is possible to oxidise ketones further
-in this case oxidation is most likely to break C-C bond and destroy the ketone