Business Paper 1
1/285
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
286 Terms
What is an Entrepreneur?
A person who starts a business and takes risks
What is the Role of the Entrepreneur?
To take risks, start the business, organise resources and employ people, negotiate deals, survive the first year
What are the 3 reasons why new business ideas come about?
Changes in consumer wants, products/services becoming obsolete, advances in technology (like apps and internet)
How do new product ideas come about? (2 things)
Creating a completely original product, adapting an already existing product
What are the 3 rewards to a business taking risks?
Profit, business success, independence
What are the 3 consequences to a business taking risks?
Financial loss, lack of security, business failure
How can we minimise risks in business?
Carrying out market research, having a business plan, ensuring sufficient cash available
What is the role of Business enterprise?
To produce goods or services, meet customer needs, add value
What are goods?
Tangible products (e.g., food, phones, clothes etc.)
What are services?
Intangible products (e.g., hairdressers, accounting, internet access etc.)
What are the 4 Customer Needs?
Price (a good price), quality (if it’s good or not), choice (a wide range of items), convenience (if it makes life easy for customers)
What are the advantages to meeting customer needs?
Helps ensure success, can lead to repeat purchases and customer loyalty, customers likely to recommend business to people
Why is knowing customer needs important for a business?
Customers don’t want a product that doesn’t meet their needs, likely to not sell, business is likely to fail
What is Added Value?
The increased worth that a business creates for a product
What are the 5 ways of Adding Value to a product/service?
Convenience, branding, quality, design (aesthetics), unique selling point (USP)
How does Convenience add value to a product/service?
It saves customers time by making it easier to use, so customers are willing to pay more
How does Branding add value to a product/service?
Brand awareness can encourage customers to pay more if they trust the brand of the product
What is Market Research (MR)?
The action or activity of gathering information about customers’ needs and preferences
How does Quality add value to a product/service?
Customers usually pay for higher quality products
How does Design (Aesthetics) add value to a product/service?
The features that a product has or the way that it is presented can add value
How does Unique Selling Point (USP) add value to a product/service?
USP is something that makes a good/service stand out from the competition, so it attracts more customers
Why does a business conduct Market Research (MR)?
They can easily find customer needs, identify competition, identify gaps in the market and market segments, mitigate risk and increase success
What are the 2 types of Market Research (MR)?
Primary research, secondary research
What is Primary Research?
Gathering first-hand information (aka field research)
What are the methods of Primary Research?
Surveys, questionnaires, focus groups, observations
What are Surveys?
A way of finding out people’s opinions and learning customer experiences with a good or service
What are Questionnaires?
A set of questions to find out customers’ opinions; often multiple choice and online
What are the 2 types of questions on a Questionnaire?
Open questions (detailed worded answers), closed questions (yes or no, on a scale of 1-10 etc.)
What is a Focus Group?
A group interview where the business can gather opinions on a product or service and give feedback
What are Observations?
Gathering information by watching customer reactions and actions towards products or services
What are the advantages of Primary Research?
Specific to the business, provides detailed qualitative and quantitative information, relevant and up-to-date
What are the disadvantages of Primary Research?
Time-consuming, costly, sometimes difficult to collect
What is Secondary Research?
Gathering information that already exists (aka desk research)
What are the methods of Secondary Research?
Internet research, market reports, government reports
What is Internet Research?
Gathering data from the internet, such as from competitors’ websites or social media
What are Market Reports?
Information about the overall market situation of a product or group of products
What are Government Reports?
Reports that consist of general information useful to a business (e.g., "People between ages 16-25 would consider working for £6.50/hour")
What are the Advantages of Secondary Research?
Quick and easy to gather, can provide industry-specific info, often easier to analyse, cheaper
What are the Disadvantages of Secondary Research?
Competitors have access to the same info, not specific to the business, could be out of date, can be inaccurate and biased
What are the problems with conducting market research upon starting a business?
It’s time-consuming, can be expensive, lack of money
What is Market Data?
Information that will help a business make marketing decisions
What are the 2 types of Market Data?
Qualitative, quantitative
What is Qualitative Data?
Data based on people’s opinions (e.g., in interviews and focus groups)
What are the advantages of Qualitative Data?
Gives the business detailed verbal data, people are given their personal thoughts and opinions, allows the business to use open-ended questions
What are the Disadvantages of Qualitative Data?
Can be time-consuming and costly to collect, cannot put data into a graph/chart easily (which easily shows data)
What is Quantitative Data?
Numerical data from closed questions (e.g., "on a scale of 1-10")
What are the advantages of Quantitative Data?
Easy and quick to analyse, can easily be put into graphs/charts
What are the disadvantages of Quantitative Data?
Doesn’t give detailed data (lack of persons’ opinions), doesn’t fully allow the business to see what the customer thinks
How does Social Media help with Market Research (MR)?
It allows a business to conduct MR on a larger scale cheaply, easy access to local, national, or international markets
What are the advantages of using Social Media for Market Research?
Cheaper than other forms, often free, can save time putting info together (e.g., some online surveys may automatically put the data into a graph), can allow a business to easily spot trends and monitor their competition
Why is it important that Market Research Data is reliable (has a high level of validity)?
So the business doesn’t have false, unreliable data, which makes it costly for the business
What are the advantages of Reliable Market Research Data?
The business can make properly informed decisions, reduced risk, less money is wasted, gives a higher chance of business success
What are the disadvantages of Reliable Market Research Data?
The business can make unwise decisions, it could ultimately cost the business money, the business can make a product that doesn’t properly sell, the business could fail
What is Market Segmentation?
Dividing the target market into smaller categories with particular needs or interests
Why do businesses do Market Segmentation?
To make it easier to conduct market research and aim certain products at certain people
What are the 6 Market Segments in Market Segmentation?
Location, demographics, behaviour, lifestyle, income, age
What is Location in Market Segmentation?
Segmenting the market by location (e.g., people who live near the Lake District would be more likely to buy hiking boots rather than people who live in the city)
What is Demographics in Market Segmentation?
This considers the characteristics of people, their age, religion, race, sex, etc. (e.g., a business may try to target females for their next product, or make their product halal, etc.)
What is Behaviour in Market Segmentation?
This considers how people behave in relation to purchases at different times of the year/situations (e.g., Easter eggs only sell during Easter time, but gift and card businesses thrive all year)
What is Lifestyle in Market Segmentation?
This considers what sort of lives people live, their hobbies, interests, etc. (e.g., a camera retailer would target people who are interested in photography)
What is Income in Market Segmentation?
This considers how much people make and their disposable income (e.g., a sports car business will target people with high incomes with high-quality luxury, but a budget brand of baked beans would target people with low levels of income)
What is Age in Market Segmentation?
This is targeting certain age groups, children, teens, elderly, etc. (e.g., children would be attracted to bright-colored plastic toys, whereas teens may be interested in cool clothes and the latest trends)
What are the advantages of Market Segmentation?
Meets specific customer needs, differentiates products, develops a unique brand image, builds closer customer relationships
What are the disadvantages of Market Segmentation?
Targeting a range of different customers with different products can be costly, focusing on one group of customers can cause a business to miss another opportunity, customer characteristics change over time, such as lifestyle, income, and demographics
What is Market Mapping?
A way to help businesses position their products by identifying gaps in the market
What is a Market Map?
A diagram that can be used to position and compare products in a market based on two variables, e.g., price and quality
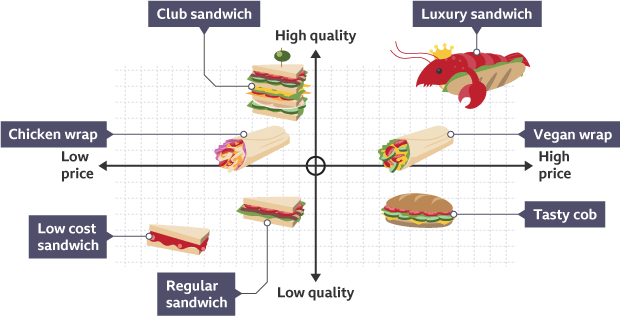
What are the advantages to Market Mapping?
Helps spot gaps in the market, helps businesses identify their closest rivals, helps businesses make decisions about marketing and positioning their brand
What are the disadvantages of Market Mapping?
Based on opinions and perceptions rather than accurate data, compares businesses based on only two variables, which is simplistic, can be difficult to identify the most appropriate variables
Why is it important to understand the strengths and weaknesses of a business?
So the business knows how to compete against them to become the one on top
What are the 2 types of Competition?
Direct, indirect
What is Direct Competition?
Competitors selling the same type of product or service
What is Indirect Competition?
Competitors that sell different products and services but are still in competition with each other
Why must a business know their competition?
You may lose customers as the competition may be doing something that steals a business’ customers, always looking at the competition allows businesses to remain innovative
How does a business compete? (7 things)
Wider product range (product differentiation), better customer service, stronger brand image, more convenient location, higher quality, better design, lower prices
What is Product Differentiation?
Making a product different from others
Why does a business do Product Differentiation?
To position their products and target different market segments, to gain an advantage over rivals when faced with competition
What are the advantages of a Highly Competitive Market?
Brand-loyal customers will stay, business can offer better value than the competition, keeps businesses innovative, a business can add value to their product
What are the disadvantages of a highly competitive market? (5 things)
Lower prices to compete, accept lower profit margins, cut back on expenditure (spending cash or resources), can lead to unethical practices to ensure prices stay low, such as cutting wages or dumping waste
Why do consumers take advantage of a highly competitive market?
Businesses have to lower prices and improve customer service and quality to compete, so consumers get better products
What is a business aim/objective?
Aims - the general goals a business wants to achieve, objectives - more specific than aims, they contribute to a business’ aims
How are business objectives created?
Using the SMART acronym
What does SMART mean?
Specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, time-bound
What are the 2 types of business objectives?
Financial, non-financial
What are Financial Objectives?
Objectives linked to money
What are the 5 Financial Objectives?
Survival - keeping the business afloat, sales and sales revenue - the amount of goods sold in a period of time, profit - how much was made in a period of time, market share - whether they’ve increased or decreased, financial security - if the business has enough cash to survive
What are Non-financial objectives?
Objectives linked to anything other than money
What are the 5 non-financial objectives?
Social objectives - if the business is ethical and environmentally friendly, personal satisfaction - if the entrepreneur is satisfied with the business, challenge - whether the business takes the entrepreneur out of their comfort zone, control - if the entrepreneur has control over the business/making business decisions, independence - if the entrepreneur can run the business without outside help (e.g., a loan)
What are the 2 types of costs a business has to pay?
Fixed costs, variable costs
What are Fixed Costs?
Costs that don’t vary with the output of the business (e.g., rent, insurance, etc.)
What are Variable Costs?
Costs that vary with the output made (e.g., raw materials)
How do we calculate Variable Costs?
Cost per unit x quantity produced
What are total costs?
Fixed costs + variable costs = total costs
What is revenue/sales revenue/turnover?
Money obtained from goods or services
How do we calculate revenue?
Price x quantity (products sold)
How do we calculate profit?
Total revenue - total costs
What is Break-Even?
The point where total costs are made back and no profit is made
What does Break-even analysis provide?
A simple means of measuring profit and losses at different levels of output
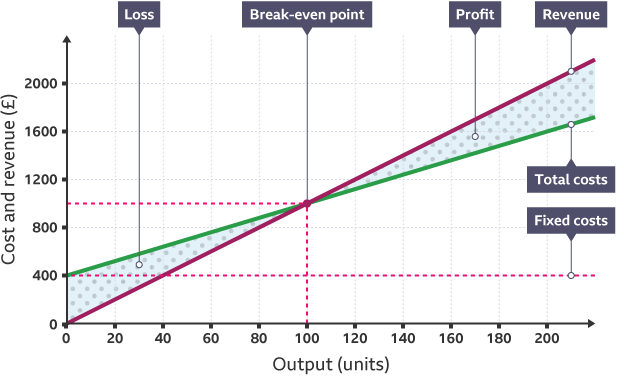
What do we use break-even for in a business?
To calculate the minimum amount of sales to break even, to see how changes in output, selling price, or costs will affect profit, to calculate the level of output to reach profit, to allow various "what if…" scenarios to be tested
How do we work out Break-even?
1st one is break-even in units, 2nd one is break-even in costs/revenue
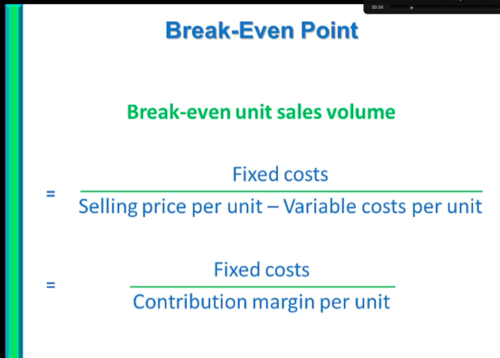
How is the Break-even point increased?
Business charges a lower selling price, business has a higher variable cost per unit, business has increased fixed costs