(7) Peripheral Nervous System
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What are the 4 main anatomic parts of the PNS?
cranial nerves, spinal nerves, ganglia, sensory nerve endings
How many pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain?
12
How many pairs of spinal nerves arise from the brain?
31
collections of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
ganglia
What are the 2 main functional parts of the PNS?
autonomic, somatic
involuntary portion of the peripheral nervous system that controls cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
**sometimes includes visceral afferents that carry sensory info from these structures
autonomic
What are the 2 parts of the autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic, parasympathetic
more voluntary portion of the peripheral nervous system that controls all of the other structures of the body
**generally includes somatic afferents that carry sensory info from these structures
somatic
What 3 parts of the body that the autonomic nervous system controls?
cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
What are 5 parts of the body that the somatic nervous system controls?
skeletal muscles, bones, joints, skin, sensory organs
collection of nerve fibers (axons + supporting cells) that are bundled together in connective tissue and communicate between the CNS and some other body part
nerve
True or false: Nerves are found in both the CNS and PNS.
false
(PNS only)
Nerve fibers are classified into several groups based on what two criteria?
diameter, myelin
What is the difference between the lettering and numbering systems of classifying nerve fibers?
lettering is anatomical, numbering is functional and only for sensory fibers
Group A neurons: Do they have myelin?
yes
Group A neurons: What is their diameter range? (micrometers)
1-20 (largest)
Group A neurons: What is their speed of conduction range? (m/sec)
5-120 (fastest)
Group A neurons: What is their function?
includes somatic efferents & afferent fibers for proprioception, vibration, touch, pain, and temperature
Group B neurons: What is their diameter range? (micrometers)
1-3 (medium)
Group B neurons: Do they have myelin?
yes, some myelin
Group B neurons: What is their speed of conduction range? (m/sec)
3-15 (medium speed)
Group B neurons: What is their function?
visceral afferents & preganglionic visceral efferents
Group C neurons: Do they have myelin?
no
Group C neurons: What is their diameter range? (micrometers)
0.5-1.5 (smallest)
Group C neurons: What is their speed of conduction range? (m/sec)
0.6-2.0 (slowest)
Group C neurons: What is their function?
postganglionic visceral efferents & afferent fibers for pain and temperature
What kind of receptors are included in Group Ia neurons?
annulospiral endings of muscle spindles/muscle spindle nerve endings
What is the letter equivalent of Group Ia neurons?
Aa
What kind of receptors are included in Group Ib neurons?
Golgi tendon organs
What is the letter equivalent of Group Ib neurons?
Aa
What kind of receptors are included in Group II neurons?
flower spray endings of muscle spindles, touch and pressure receptors
What is the letter equivalent of Group II neurons?
AB and Ay
What kind of receptors are included in Group III neurons?
pain and temperature receptors
What is the letter equivalent of Group III neurons?
Ad
What kind of receptors are included in Group IV neurons?
pain and temperature receptors
What is the letter equivalent of Group IV neurons?
C
Which is larger: alpha motor neurons or gamma motor neurons?
alpha (Ia and Ib)
Rank in order from largest to smallest:
A delta neurons
Gamma motor neurons
Group C neurons
Alpha motor neurons
alpha motor, gamma motor, A delta, group C
Rank in order from largest to smallest: groups II, IV, Ia/Ib, III
Ia/Ib, II, III, IV
receptors that process information from outside the body: photoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, & nociceptors
exteroceptors
receptors that process information that originates from the viscera (organs): mechanoreceptors & nociceptors
interoceptors
receptors that process information from muscles, tendons, and joints, mostly about body position & movement
proprioceptors
cutaneous receptors that are "bare" nerve fibers that lack CT or Schwann cells; may be mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, or nociceptors
found in the skin (epidermis and dermis), subcutaneous tissue, and hair follicles
free nerve endings
What do free nerve endings detect?
touch, pressure, heat, cold, pain
cutaneous receptors that are mechanoreceptors that are more numerous in skin where touch reception is acute
**combination of an axon and several specialized cells
Merkel disks
What do Merkel disks detect?
light touch
cutaneous receptors that are large and encapsulated mechanoreceptors (touch and vibration), appearing as concentric lamellae that surround a nerve fiber
**found in the dermis, subcutaneous tissues, in many connective tissues (especially in viscera), and joints
Pacinian corpuscles
What do Pacinian corpuscles detect?
deep pressure and vibration
cutaneous receptors that are encapsulated mechanoreceptors (fine touch) and structured as a tapered cylinder with nerve fiber spirals inside
**located in dermal papillae, especially in the lips and thick skin where they are vastly the most numerous receptor in these regions
Meissner corpuscles
What do Meissner corpuscles detect?
fine touch
cutaneous receptors that are spindle-shaped mechanoreceptors (stretch) consisting of nerve fibers entwined between parallel collagen fibers
**found in thin skin, joints, and the CT capsules of viscera
Ruffini endings
What do Ruffini endings detect?
stretch
cutaneous receptors that are round nervous “bulbs” with a thin capsule of connective tissue; modality not really known, but probably mechanoreceptors and may also be cold receptors
**found in skin, mucous membranes, and the conjunctiva
end bulbs of Krause
What do end bulbs of Krause detect?
pressure and cold
What is the most numerous type of cutaneous receptor found in almost all regions of the skin?
free nerve endings
What is the most numerous type of cutaneous receptor specifically in the lips and thick skin?
Meissner corpuscles
Which cutaneous receptors are found in the conjunctiva?
end bulbs of Krause
stretch receptor in skeletal muscle that gives information about when a muscle is lengthening (but NOT shortening)
muscle spindle
tension receptor located in tendons that gives information about when a muscle/tendon is being pulled on (i.e., under tension)
Golgi tendon organ
List all 12 cranial nerves in order from rostral to caudal.
olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal
Each spinal nerve is attached to the spinal cord by 2 roots. Which root contains only motor nerve fibers? (2 terms)
ventral/anterior
Each spinal nerve is attached to the spinal cord by 2 roots. Which root contains only sensory nerve fibers? (2 terms)
dorsal/posterior
collection of cell bodies of first order sensory neurons
dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion)
True or false: There are synapses in the dorsal root ganglion.
false
Where do the two spinal nerve roots unite to form the actual spinal nerve?
as they exit the intervertebral foramen
Where are preganglionic neuron cell bodies: CNS or PNS?
CNS
Where are postganglionic neuron cell bodies: CNS or PNS?
PNS
Where are central neurons usually found? (Hint: "upstream" of preganglionic neurons)
brain stem or hypothalamus
Why is the sympathetic nervous system sometimes called the thoracolumbar division of the autonomic nervous system?
preganglionic sympathetic neuron cell bodies are located in the lateral horns of the C8 through L3 levels
Specifically, where are the cell bodies of the preganglionic sympathetic neurons for the dilator pupillae muscle (and other eye structures) located?
C8-T2 levels
What letter group of fibers are preganglionic sympathetic neurons?
B
What letter group of fibers are postganglionic sympathetic neurons?
C
In the sympathetic nervous system, once a spinal nerve exits the vertebral canal via the anterior root, the pre-ganglionic sympathetic fiber leaves the spinal nerve via what structureto join the sympathetic trunk/sympathetic chain?
white ramus communicans
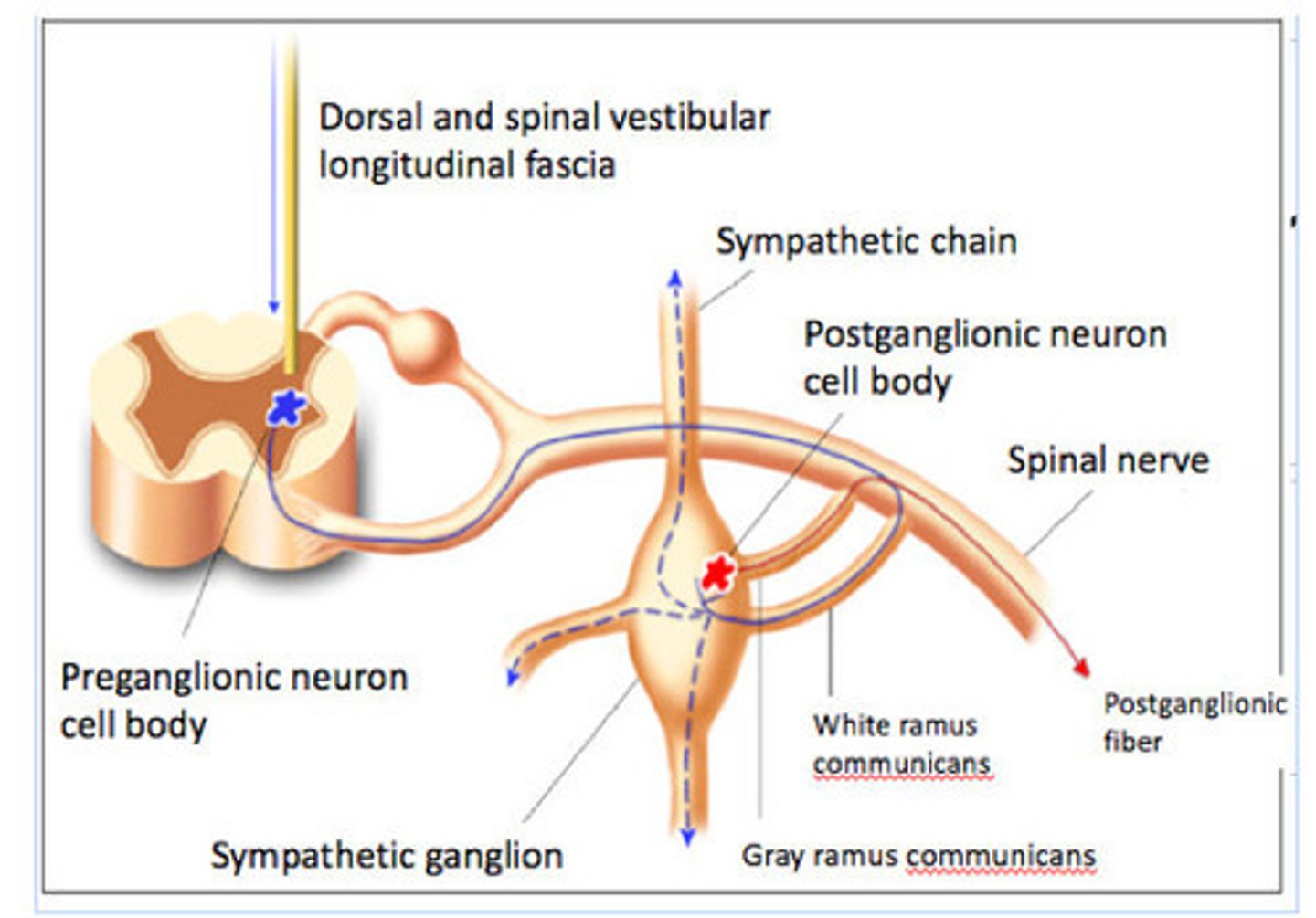
True or false: Every single preganglionic sympathetic fiber gets into the sympathetic chain via a white ramus communicans.
true
In the sympathetic nervous system, once a spinal nerve exits the vertebral canal, the pre-ganglionic sympathetic fiber leaves the spinal nerve via a white ramus communicans to join the what?
sympathetic chain

Where are postganglionic sympathetic neuron cell bodies mostly located?
sympathetic chain ganglia
(although those supplying the abdominopelvic regions are located in autonomic ganglia in or near those structures)
If the preganglionic sympathetic fiber synapses in a paravertebral ganglion in the sympathetic trunk, then the postganglionic sympathetic fibers may reach their eventual effector targets by rejoining the spinal nerve at the level of the ganglion via a what and following the spinal nerve to the effector target?
Basically, nerve fibers of the neurons whose cell bodies are in the sympathetic chain rejoin a spinal nerve via a ____ ____ ____ and are distributed to their eventual targets.
gray ramus communicans
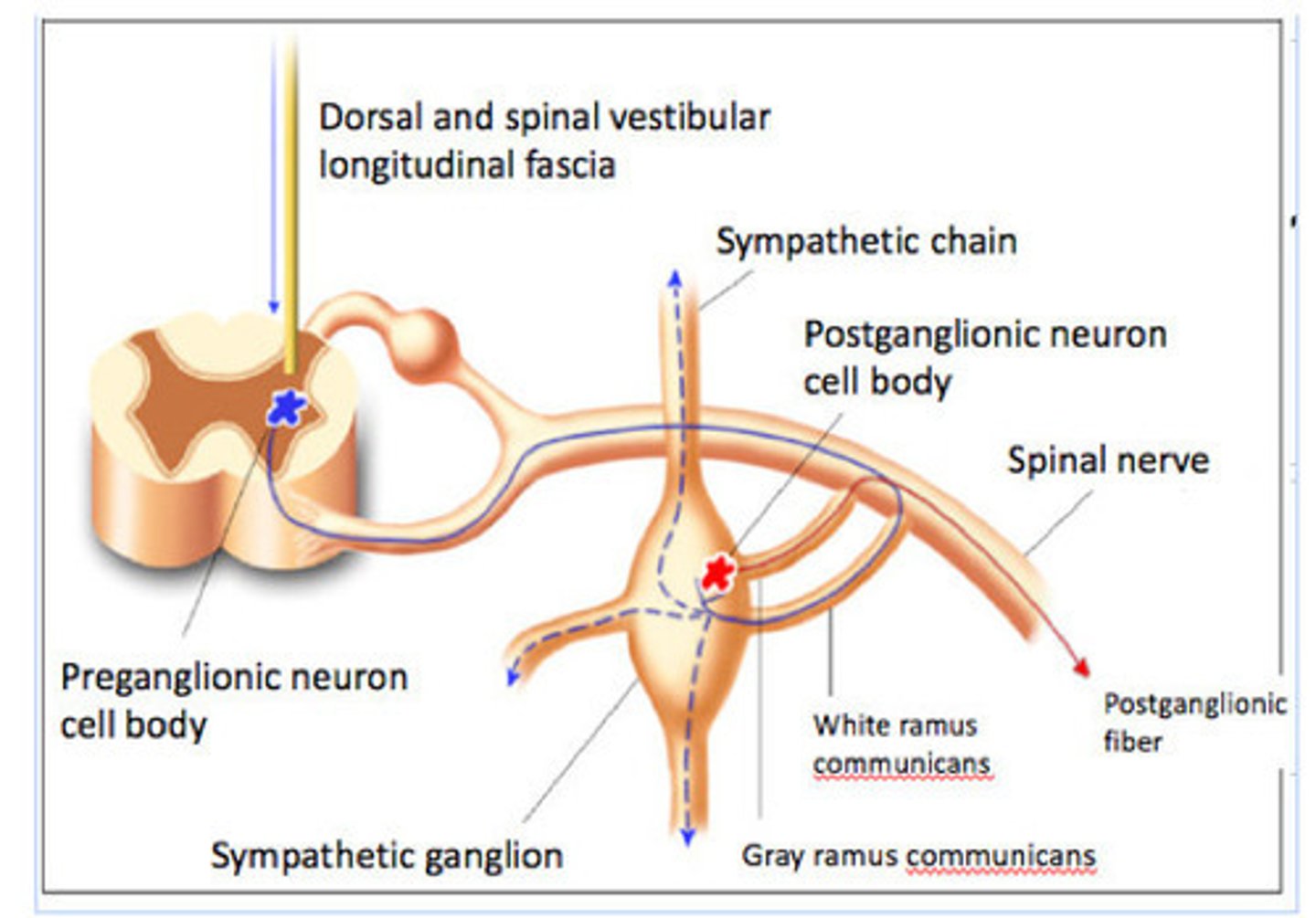
What neurotransmitter is typically found at synapses between postganglionic sympathetic fibers and their targets?
noradrenaline
Why is the parasympathetic nervous system sometimes called the craniosacral division of the autonomic nervous system?
preganglionic parasympathetic neuron cell bodies are located in the brainstem and lateral horns of S2-4
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus travel?
CN III
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in the lacrimal nucleus travel?
CN VII
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in the superior salivatory nucleus travel?
CN VII
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in the inferior salivatory nucleus travel?
CN IX
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in the nucleus ambiguus travel?
CN X
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in the dorsal motor nucleus travel?
CN X
In which nerve(s) do preganglionic parasympathetic neurons originating in gray matter lateral horns travel? (to become splanchnic nerves)
S2-4
Where do fibers from CN III that came from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus synapse?
ciliary ganglion
Where do fibers from CN VII that came from the lacrimal nucleus synapse?
pterygopalatine ganglion
Where do fibers from CN VII that came from the superior salivatory nucleus synapse?
submandibular ganglion
Where do fibers from CN IX that came from the inferior salivatory nucleus synapse?
otic ganglion
Where do fibers from CN X that came from the nucleus ambiguus synapse?
cardiac ganglia
Where do fibers from CN X that came from the dorsal motor nucleus synapse?
various parasympathetic ganglia in/near effector organs
What do fibers from the ciliary ganglion that came from CN III supply?
iris and ciliary body muscle
What do fibers from the pterygopalatine ganglion that came from CN VII supply?
lacrimal and nasal glands
What do fibers from the submandibular ganglion that came from CN VII supply?
submandibular and sublingual glands
What do fibers from the otic ganglion that came from CN IX supply?
parotid gland
What do fibers from the cardiac ganglia that came from CN X supply?
heart and lungs
What do fibers from the ganglia in/near thoraco-abdominal & pelvic viscera that came from CN X & S2-4 supply?
their respective organs