Parasitology Exam 2: Platyhelminthes
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Are Platyhelminthes segmented?
NO! tapeworms are Strobilated
Platyhelminth coelum
acoelomates
Parenchyma
the “packing peanuts” for acoelomates that holds organs in place
Osmoregulation organ in Platyhelminthes
protonephridia
Platyhelminth digestive system
incomplete gut (lost gut in tapeworms)
Platyhelminth muscular system
circular & longitudinal muscles
Digenea
endoparasitic flukes of vertebrates in the adult stage of their life cycle
Platyhelminth Classes
Turbellaria, Trematorda, Monogenea, Cestoidea
Syndesmis
parasitic Turbellarian of sea urchins and sand dollars
Turbellaria
class of Platyhelminthes that are mostly free-living
Trematoda
class of Platyhelminthes: the parasitic flukes
flukes class
Trematoda
Tegument
mass of protoplasm without division of cells on the outside of the trematoda and cestoideas.
used for inhibiting digestive enzymes, nutrition uptake and anchoring with actin spines
actin spines
on the tegument, used for anchoring self to hold
Aspidobothrea
Trematoda that are endoparasites of molluscs
Opisthaptor
body part used for attachment to host
Protonephridia
“flame cell” used for excretion of NH3
Fluke digestive system
incomplete (one opening- oral sucker)
Operculum
lid on fluke egg
Acetabulum
a sucker on a fluke use for attachment (central of body)
Fluke reproduction
all monecious, EXCEPT Schistosoma-dioecious
cirrus
male copulatory organ on flukes
Fluke Life Cycle (body forms)
Egg —> Miracidium —> Sporocyst —> Redia/daughter sporocyst —> cercaria —> encysts on/in host (Schistosoma skips this) —> metacercariae/adult
What life stage is used for fluke diagnoses?
egg
Miracidium
fluke: “hairy peanut” non-feeding, swimming body form that emerges from the egg and is finding its first host
Sporocyst/Redia
fluke: life stages in 1st host (snail) -non-feeding, begins proliferation (asexual), makes germ balls that give rise to cercaria
Cercaria
fluke: life stage leaves the snail host and is looking for the next host, non-feeding stage, swimming stage, has a tail (split tail= Schistosoma)
Encysted metacercaria
fluke: infective stage, encysted in or on 2nd host (except Schistosoma-skips this step), can survive stomach acid: excysts in small intestine
Metacercariae
fluke: adult form: in the vertebrate host (definitive), sexually mature
Fluke growth & metamorphosis stages
egg, miracidium, sporocyst
Fluke proliferation stages
daughter sporocyst, redia, cercaria
infective stage of most flukes
encysted metacercaria (except Schistosoma)
Alaria americana
Fluke of canids (dogs, fox, etc)
Alaria americana hosts
Snail (intermediate 1)—> tadpole (intermediate 2)—> snake (paratenic) —> canid (definitive)
How can humans get infected with Alaria americana?
eating frog legs- becomes ectopic in lungs, stomach, brain- fatal
miracidium always penetrates a _____ host
snail (1st intermediate host)
heart lung migration purpose
mimics an additional host
Alaria americana transmission
Trophic- fox eats infected snake (or frog)
Bilharzia disease is caused by…
Schistosoma spp.
Blood flukes
Schistosoma spp.
How are Schistosomes different from other flukes?
diecious, skips encystment stage, in blood
Schistosoma japonicum where in the body does the female release eggs?
mesenteric veins of the small intestines (released via feces)
Schistosoma mansoni where in the body does the female release eggs?
mesenteric veins of the large intestines (released via feces)
Schistosoma haematobium where in the body does the female release eggs?
venus plexus near urinary bladder and ureters (released via urine)
Schistosoma world locations
Egypt, China, AfJorica, S. America, Caribbean
Joshua’s curse on Jericho parasite
Schistosomes
What parasite is common in the Nile River (Egypt)?
Schistosomes
Schistosoma hosts
snail —> humans
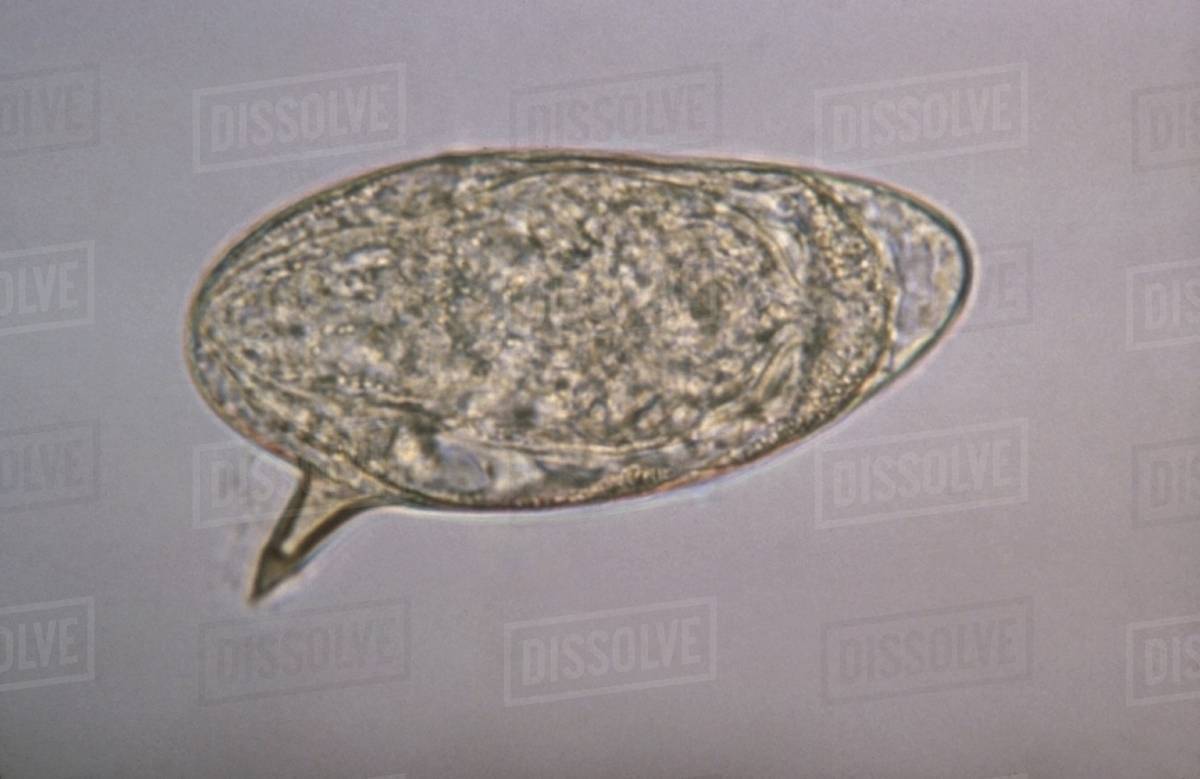
Schistosoma mansoni egg
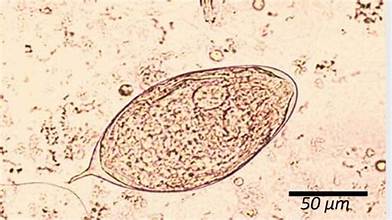
Schistosoma haematobium egg
Life cycle of Schistosomes (starting at egg)
eggs released in human feces or urine
egg hatches into miracidium when in freshwaters
miracidium swims to find snail host
miracidium penetrates snail
develops into cercaria in snail
cercaria released from snail
cercaria swims to find definitive host
cercaria penetrates through the skin of human & loses tail
covers itself in host antigens
migrates to liver to feed & mature
develops into adults
sexual reproduction in mesenteric veins of intestine or bladder
male dies, female migrates to specific host site
female releases eggs with stool or urine
What is unique about the Schistosome cercaria
forked/split tail
Schistosome symptoms
localized dermatitis (where penetrated skin)
fever & congestions during migratory phase (or asymptomatic)
chills, fever, fatigue, headache, malaise (acute phase/egg production)
for S. haematobium: hematuria, pain with urination, loss of bladder function
Ascites- build up of fluid
Where in the world is Schistosoma mansoni?
New & Old World (Brazil, Caribbean, Africa)
Where in the world is Schistosoma haematobium?
Old World (Africa)
Where in the world is Schistosoma japonicum
Old World (China, Japan)
Chronobiology
the release of cercariae at a specific time of day when definitive host is most active
Reservoir host of Schistosoma japonicum
dog/cat
Schistosome treatment
Praziquantel
Swimmer’s Itch
Cercarial dermatitis
schistosomes that are in the wrong host (usually a bird)
very common in the great lakes
Swimmers Itch symptoms
tingling after emerging from water
red spots form
intense itching for several days
How to avoid swimmer’s itch?
towel off when you exit water
swim away from shallow areas
apply sunscreen
If there are schistosomes in the water, does that make it polluted?
No! natural lake conditions with lots of diversity
Eosinophilia
high eosinophil count- associated with helminth infection
Echinostoma
fluke parasite of birds, mammals, crustaceans and amphibians
common in frogs- inhibit tadpole growth-legs
“spiney head”
non-host specific
Fasciola hepatica common name
Sheep Liver Fluke
Fasciola hepatica transmission
trophic
Fasciola hepatica hosts
definitive: sheep, cattle, goats
intermediate: snail
encysts ON aquatic plants
Where in the mammal body is Fasciola hepatica?
bile ducts, gallbladder and liver
Fasciola hepatica life cycle (start at egg)
egg passed through sheep feces
miracidium hatches in water
miracidium swims to find and penetrate snail host
develops into sporocyst —> redia —> cercaria
leaves snail and swims to encyst on aquatic plant
plant and cyst ingested by mammal
develops into metacercaria
migrates to bile ducts/liver & sexual reproduction
eggs released in the feces
acute phase Fasciola symptoms
migratory phase of the larvae that can last for weeks
diarrhea
fever
nausea
stomach ache
vomiting
eosinophilia
Fasciola chronic phase symptoms
adults are in the large biliary ducts
liver inflammation
bile fluid obstruction
Fasciola eggs
oval shape with an operculum
Dicrocoelium dentriticum
parasite of sheep, cattle, goats and pigs
causes behavior change in the intermediate host (ant) where they climb to the top of a blade of grass, increasing odds of getting eaten by determinate host
Paragonimus westermani common name
lung fluke
Paragonimus westermani life cycle starting at egg
eggs passed via feces or coughed up with sputum
miracidium develops in eggs when in freshwater
miracidium hatches and swims to penetrate snail
miracidium —> sporocyst —> redia —> cercaria
cercaria shed into water
cercaria swim ot find and penetrate crustacean
encysts as metacercaria in crustacean tissues
crustacean ingested by human
excysts in human gut
migrates to peritoneal cavity
develops into adult & migrates to lungs in pairs
How do humans get Paragonimus westermani?
eating undercooked crabs or crayfish
-used in traditional medicine in Korea, Japan & Africa
-consumed raw or prepared only in vinegar or wine w/o actually cooking it
Zone of Immune Privilege which species?
Paragonimus westermani
secretes enzymes around self that are able to digest host antibodies
Clonorchis sinensis common name
Chinses liver fluke
Clonorchis sinensis life cycle starting at egg
egg released in feces
egg ingested by snail
miracidium —> sporocyst —> redia —> cercaria
cercaria leaves snails
cercaria swims to find and penetrate fish
encyst inside fish muscle into metacercaria
human consumes undercooked fish
excyst metacercaria in duodenum
migrate to bile duct/liver
mature into adults & sexual reproduction
Paragonimus westermani transmission type (to human)
trophic (eating)
Clonorchis sinensis egg
flask shape, narrowing at operculum
Clonorchis sinensis transmission type (to human)
trophic: human eating undercooked fish
Heterophyes heterophyes
intestinal fish fluke
Heterophyes heterophyes hosts
snail —> fish —> fish eating mammals
How many suckers does Heterophyes heterophyes have
3: oral, acetabulum (ventral) & gonodyl (genital)
Ribeiroia ondatrae
causes limb deformities in frogs (easier for bird predators to eat frog)
Ribeiroia ondatrae hosts
snail —> tadpole —> bird
Glochidia
parasitic life stage of a freshwater bivalve that is an obligate parasite of fish gills/fins (used for transportation of larvae)
opisthaptor
sucker or claws/hooks for attachment of monogenean to host
Gyrodactylus
monogenean parasite of fish that is viviparous
Polystoma
monogenan parasite of fish that is ovoviparous
viviparous
gives birth to live young
oviparous
lays eggs (not live birth)
polyembryony
Gyrodactylus
splitting of one sexually produced embryo into many
Cestoidea
tapeworms
all parasitic
tapeworm gut
no digestive tract
Cestoidea reproduction
duplication of reproductive systems as each proglottid has its own set (monecious)
What does “armed scolex” mean?
the scolex has spikes (for attachement)