System Cooling 3.4
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Why is cooling important for all computer components?
Because every powered component generates heat and can fail or get damaged if overheated.
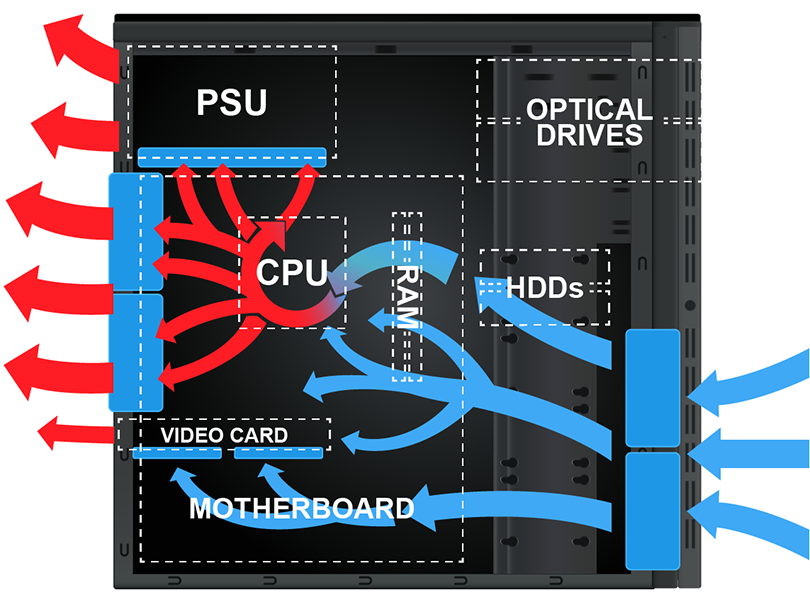
How does case airflow work in a modern system?
Cool air flows front-to-back over components; hot air is exhausted out the back or top.
Why is front-to-back airflow critical?
It prevents hot air from stagnating and ensures consistent cooling across all components.
What creates negative pressure in a computer case?
Exhaust fans pulling more air out than intake fans push in.
Why is removing the side panel a bad idea for cooling?
It disrupts airflow and can trap hot air inside the case.
What parts of a case should be sealed to maintain airflow?
Side panel, I/O shield, and unused expansion slots.
Where are intake fans usually located?
At the front (and sometimes side) of the case.
Where are exhaust fans usually located?
At the rear or top of the case.
How do side panel fans usually function?
They pull cool air in, typically to help cool the CPU.
How does the power supply aid cooling in top-mounted configurations?
Its fan exhausts hot air from inside the case.
What happens with bottom-mounted power supplies?
They cool only themselves and don’t assist with case airflow.
What is the CPU heatsink made of and why?
Copper or aluminum to conduct heat away from the CPU.
What’s the difference between active and passive heatsinks?
Active has a fan; passive doesn’t.
Where are passive heatsinks typically used?
On RAM, chipset, and low-end GPUs.
Where are active heatsinks typically used?
On CPUs and high-end graphics cards.
Why is upright heatsink design preferred?
It aligns better with front-to-back case airflow.
What maintenance helps airflow and cooling?
Regular cleaning of dust from fans, components, and filters.
How do dust filters help with cooling?
They block dust from entering but need regular cleaning.
What ambient temperature is ideal for desktops?
Between 60°F and 75°F.
What happens if ambient temperature is too high?
Component cooling becomes less effective.
How can internal airflow be obstructed?
Sloppy cable management, tightly packed drives, excess expansion cards.
Why should hard drives be spaced out?
To allow better airflow between them and avoid heat pockets.
How can you monitor system temperatures?
Using built-in sensors via BIOS or system software.
Why install an internal temperature sensor?
To measure overall case temperature, not just component temps.
When is liquid cooling typically used?
In high-performance gaming or server systems with heavy thermal loads.
How does liquid cooling work?
It uses fluid, hoses, and a radiator to transfer and dissipate heat.
What do fan filters do in a PC case?
Minimizes dust and debris entering the case.
What type of power supply helps with case cooling?