Lab practical 1 review
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
anterior:
towards the front of the body or structure.
posterior:
towards the back of the body or structure.
superior:
towards the upper part of the body or structure.
inferior:
towards the lower part of the body or structure.
inferior
towards the lower part of the body or structure.
proximal
towards the point of attachment or origin.
distal
away from the point of attachment or origin.
medial
towards the midline of the body or structure.
lateral
toward the side of the body, away from the midline.
superficial
toward the surface of the body or structure.
deep
away from the surface of the body or structure.
dorsal body cavity
the space within the body that houses the cranial cavity and vertebral cavity, containing the brain and spinal cord.
ventral body cavity
the space within the body that houses the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities, containing organs such as the heart, lungs, and digestive organs.
thoracic body cavity
The part of the ventral body cavity located superior to the diaphragm, containing the lungs and heart.
pericardial body cavity
The cavity within the thoracic cavity that surrounds the heart, providing protection and lubrication.
mediastinum cavity
The region in the thoracic cavity between the lungs that contains the heart, aorta, esophagus, trachea, and thymus.
abdominopelvic cavity
The region of the ventral body cavity located inferior to the diaphragm, encompassing both the abdominal and pelvic cavities, and containing digestive organs, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
abdominal cavity
The superior portion of the abdominopelvic cavity, which houses digestive organs such as the stomach, liver, and intestines.
pelvic cavity
The inferior portion of the abdominopelvic cavity that contains the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs.
serous membranes
thin layers of tissue that line body cavities and cover organs, secreting serous fluid to reduce friction.
parietal layer
The outer layer of a serous membrane that lines the body cavity, providing protection and support to the organs within.
visceral layer
The inner layer of a serous membrane that directly covers the organs within the body cavity, providing cushioning and reducing friction.
sagittal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left sections.
midsagittal plane
A specific type of sagittal plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves.
parasagittal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into unequal right and left sections, parallel to the midsagittal plane.
frontal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior sections.
transverse plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior sections.
chemical level
this is the smallest level; chemical ranges from tiny atoms to complex molecules
cellular level
the second level of organization in the body, where cells are formed from molecules and perform various functions essential for life.
tissue level
the third level of organization in the body, where groups of similar cells work together to perform specific functions.
organ level
the fourth level of organization in the body, where different types of tissues come together to form organs that have specific functions.
organ system level
the fifth level of organization in the body, which consists of groups of organs that work together to carry out complex functions necessary for survival.
integumentary system
the organ system that includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands, playing a crucial role in protecting the body and regulating temperature.
two organs in integumentary system
hair and skin
skeletal system
the organ system that consists of bones, cartilage, and joints, providing structure, support, and protection to the body while enabling movement.
two organs in the skeletal system
bones and joints
muscular system
the organ system responsible for facilitating movement of the body through contraction and relaxation of muscles.
organ in muscular system
skeletal muscles
endocrine system
the organ system that produces hormones to regulate metabolism, growth, reproduction, and other bodily functions.
two organs in the endocrine system:
thyroid and adrenal glands
cardiovascular system
the organ system responsible for the circulation of blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hormones throughout the body.
two organs in the cardiovascular system
heart and blood vessels
lymphatic system
the organ system involved in the transport of lymph, a fluid that contains infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body.
two organs in the lymphatic system
spleen and lymph nodes
respiratory system
the organ system responsible for the exchange of gases, allowing for oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion.
two organs in the respiratory system
lungs and trachea
Digestive system
the organ system responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste.
two organs in the digestive system
stomach and intestines
urinary system
the organ system responsible for filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating fluid balance.
two organs in the urinary system
kidneys and bladder
reproductive system
the organ system responsible for producing offspring and regulating sexual traits.
two organs in the reproductive system
testes and ovaries
tissue
group of cells that are similar in structure and function
histology
the study of tissues
organ
contains at least 2 of the primary tissue types
epithelial tissue
covers internal and external surfaces of the body
connective tissue
primarily protect, support, transport, and bind together other tissues of the body
muscle tissue
contract to produce most types of body movements and is responsible for movement or generate heat
nervous tissue
composed of neurons and glial cells, responsible for transmitting signals and processing information throughout the body.
characteristics of epithelial tissue
Polarity: cells have apical and basal surfaces
Specialized Contact: cells grow in sheets and may be bound together by specialized junctions
Basement Membrane: connective tissue layer that adheres the epithelial cells to the layer underneath
Avascular: have no direct blood supply
Highest Mitotic Rate: regenerates easily
Characteristics of Connective Tissue
Matrix: contains non-cellular, nonliving material between the cells
Contains many types of specialized cells
Highly Vascularized: with the exception of cartilage (avascular) and tendons and ligaments (poorly vascularized)
Matrix
a. matrix may be liquid, gel, semisolid, or solid
b. matrix contains fibers (collagen, elastic, and reticular) and ground substance (interstitial fluid, proteins, and proteoglycans).
characteristics of muscle tissue
muscle cells are elongated
muscle cells may be myogenic or neurogenic
may be voluntarily or involuntarily controlled
myogenic
contract without nervous system control
neurogenic
requires nervous system control
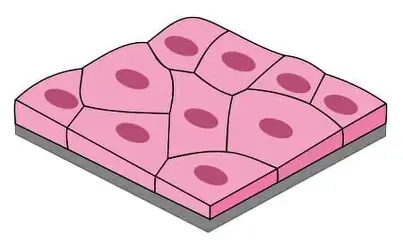
type of epithelial cell that is thin and flat, allowing for rapid diffusion and filtration.
squamous
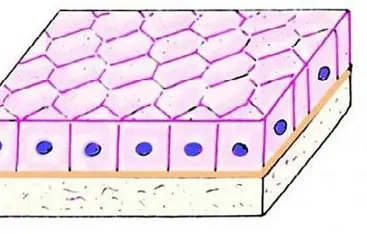
cells that are as tall as they are wide, often involved in secretion and absorption.
cuboidal
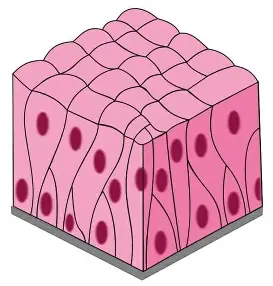
columnar
cells that are taller than they are wide, typically found in areas involved in absorption and secretion.
simple
squamous epithelium consisting of a single layer of flat cells, facilitating processes such as diffusion and filtration.
stratified
epithelium made up of multiple layers of cells, offering protection against abrasion and typically found in areas subject to wear.
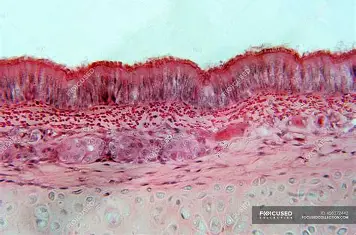
pseudostratified
columnar epithelium that appears stratified due to varying cell heights but is actually a single layer. It is often found in the respiratory tract. (may have cilia)
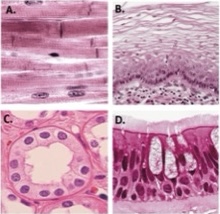
A
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue
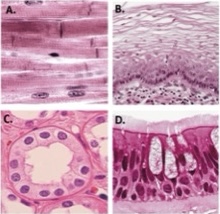
B
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
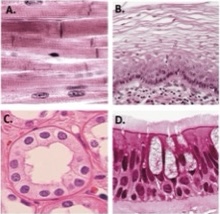
C
simple cuboidal epithelium
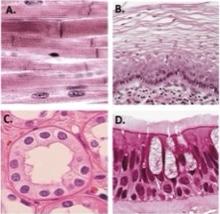
D
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
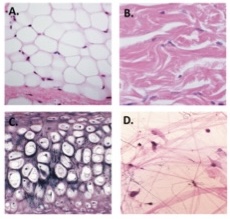
A
Adipose tissue (from hypodermis)
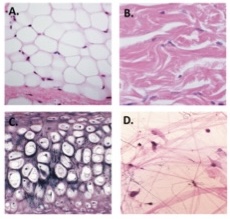
B
Dense irregular connective tissue (from reticular dermis of skin)
Loose connective |
It consists of fibroblasts and all three types of protein fibers embedded in gel-like substance ground substance. Provides supports and protection in the walls of hallow organs |
Reticular connective |
A fine network of reticular fibers that forms the structure of many organs and supports small structures such as blood vessels and leukocytes is found in most lymphoid |
Elastic cartilage |
Is largely limited to the epiglottis preventing food from entering the trachea |
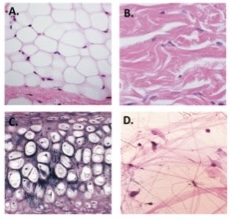
C
Elastic cartilage (from epiglottis)
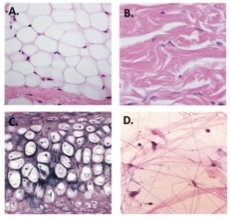
D
Loose connective tissue (from papillary dermis of skin)