MCAT Bio/Biochem Exam
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What direction is DNA/RNA read and synthesized?
Read in the 3’-5’ direction and synthesized in the 5’-3’ direction
heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA)
The immediate product of transcription in eukaryotes before it is matured into mRNA
3’ poly-A tail
a string of approximately 250 adenine (A) nucleotides added to the 3' end of an hnRNA transcript to protect the eventual mRNA transcript against rapid degradation in the cytosol
Splicing
the process in which noncoding sequences (introns) are removed and coding sequences (exons) are ligated together
Restriction enzyme I
a type of restriction enzyme where the cleavage site is far from the recognition site, often >1000 bp away
Requires ATP and S-Adenosylmethionine
Restriction enzyme II
a type of restriction enzyme in which the cleavage site is within or very close to the recognition site
Does not require ATP
Restriction Enzyme III
a type of restriction enzyme in which the cleavage site is a short distance away from the recognition site (20-30 bp)
Requires ATP but does not hydrolyze it and magnesium
Restriction enzyme IV
a type of restriction enzyme in which the cleavage site targets modified DNA.
Primarily requires magnesium
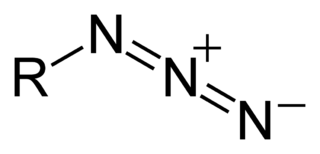
azide
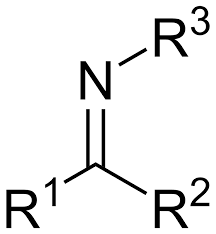
imine
nitrile
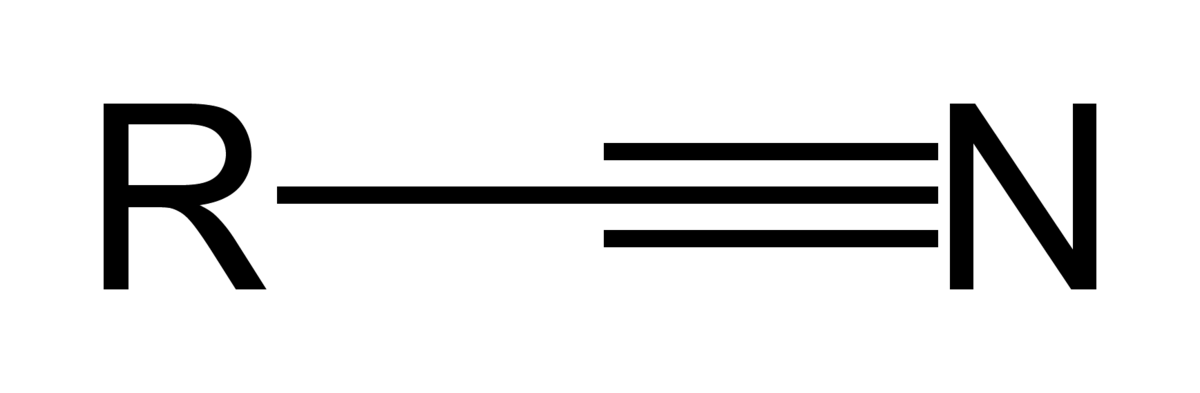
enhancers
DNA sequences that can be located further from the gene of interest, and work by binding transcription factors that twist DNA into a hairpin loop, bringing distant regions into close proximity for transcription to begin
Silencers
they are regions of DNA to which transcription factors known as repressors bind
effects of methylation on C and A residues
Methylation of C and A residues can reduce transcription by blocking the binding of transcription factors and creating a more compact, inaccessible chromatic structure
How does acetylation promote transcription?
attaching acetyl groups to lysine residues on histones, making them less positively-charged and causing a looser wrapping pattern that allows transcription factors to access the genome more easily
Role of MicroRNA in transcription and translation?
miRNAs can either repress transcription in some instances or activate transcription in others. To repress, miRNAs bind to the 3’ end of target mRNA, leading to its destruction or blocking ribosomes from translating.
To activate, miRNAs interact with gene promoters and recruit complexes that make the ribosomes more permissive
A, D, E, and K
what are the lipid-soluble vitamins
B and C
what are the water soluable vitamins
glycine (Gly, G)
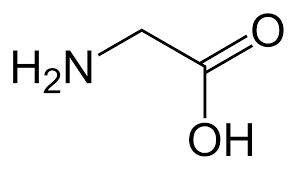
alanine (Ala, A)
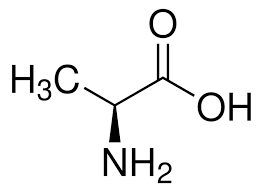
valine (Val, V)
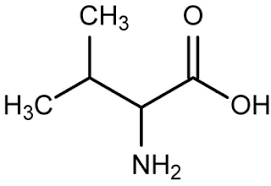
methionine (Met, M)
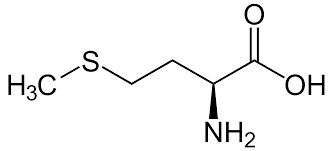
leucine (Leu, L)
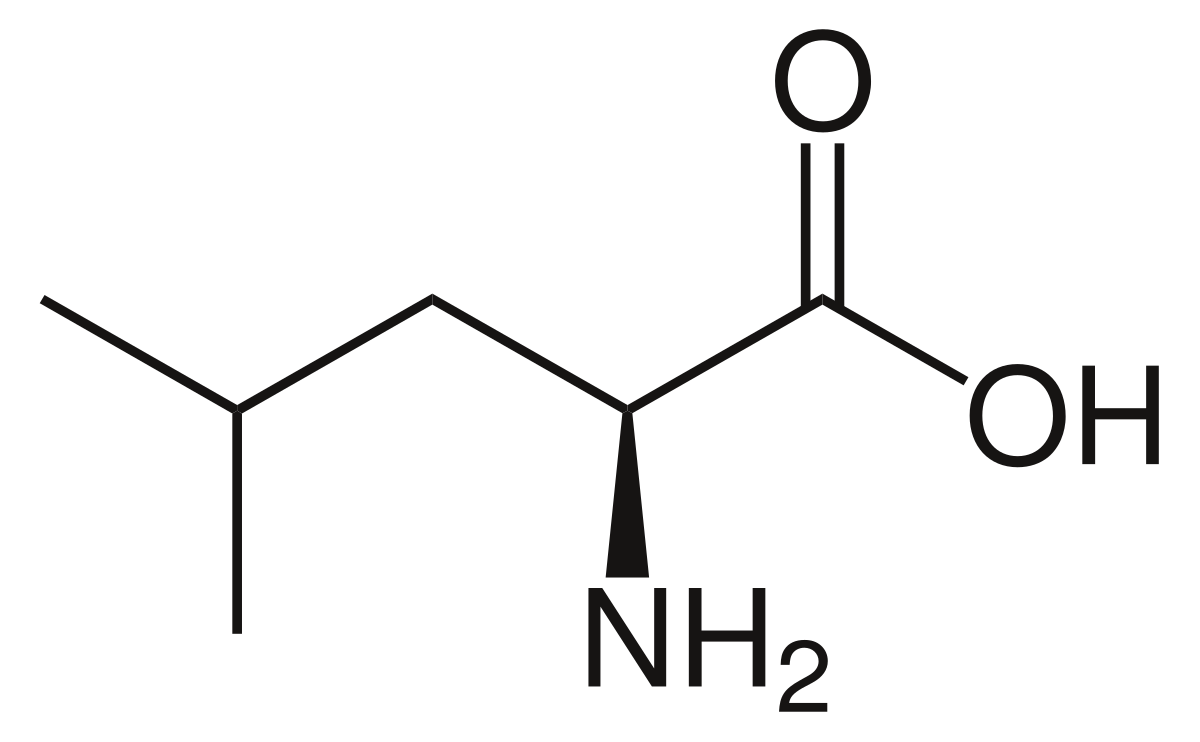
isoleucine (Ile, I)
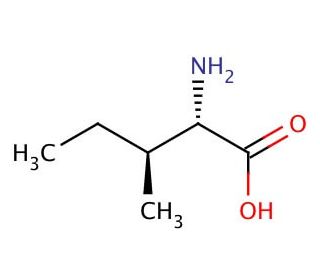
proline (Pro, P)

phenylalanine (Phe, F)

tryptophan (Trp, W)
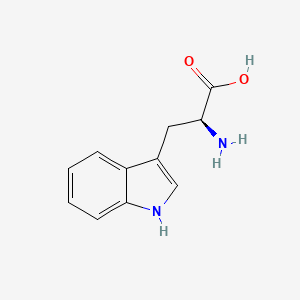
serine (Ser, S)

threonine (Thr, T)
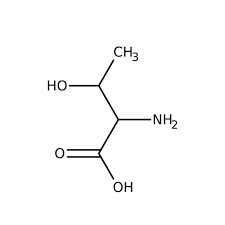
asparagine (Asn, N)
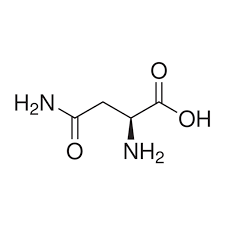
glutamine (Gln, Q)
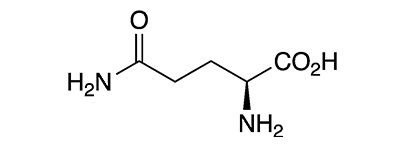
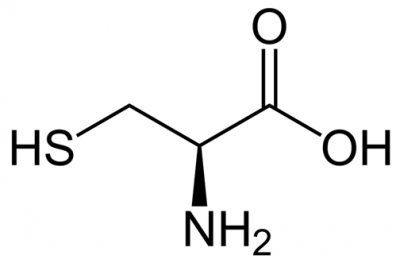
cysteine (Cys, C)
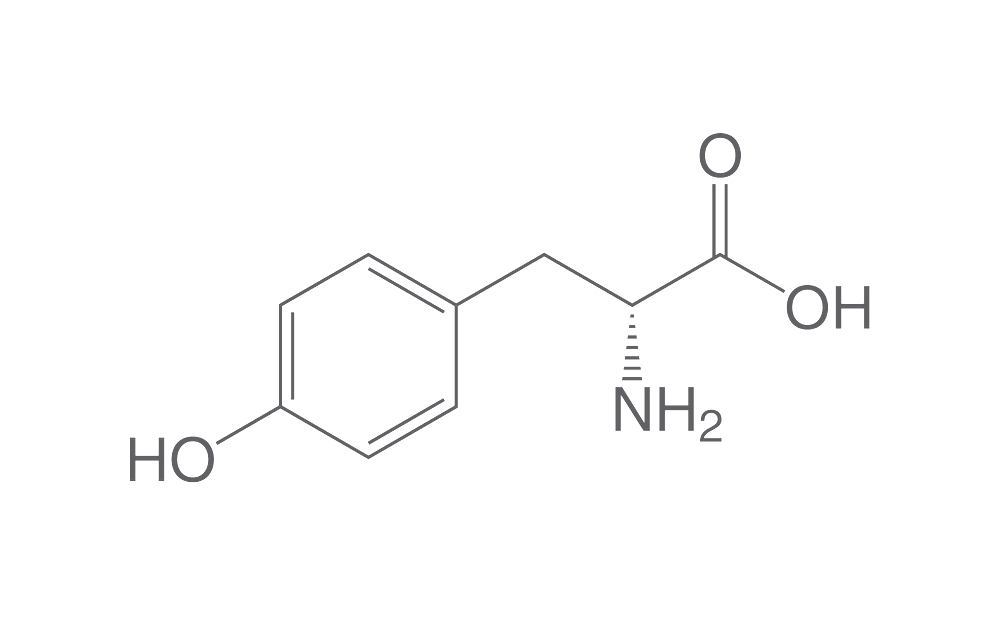
tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
aspartic acid (Asp, D)

glutamic acid (Glu, E)

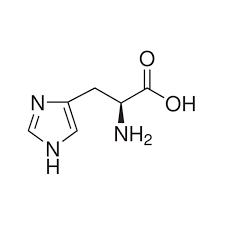
histidine (His, H)
lysine (lys, k)
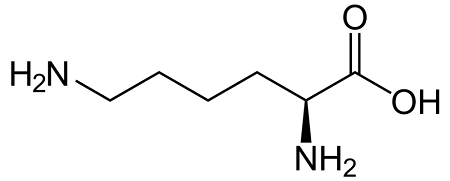
arginine (arg, R)

positive sense RNA
a term for viruses synonymous to sense strand for DNA referring to the host mRNA that can be directly translated into proteins
negative sense RNA
a term for viruses synonymous to the antisense strand for DNA, referring to viral genome, or the complementary strand to the functional mRNA
RNA replicase
refers to an enzyme used by RNA viruses to copy their RNA genomes (negative-sense strands) to create the complementary RNA (positive sense strand)
in vitro
in a test tube or petri dish
in vivo
in the living body
viral envelope
a lipid bilayer derived from the host cell membrane, which is embedded with glycoproteins
cholesterol at high temperatures
stabilizes the phospholipid bilayers and reduces fluidity
cholesterol at low temperatures
prevents the fatty acid chains from getting too close to one another and freezing into a solid state
G1 phase
phase of the cell cycle in which the cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes the molecule building blocks it will need in later steps
S phase
The phase of the cell cycle in which the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus
G2 phase
the phase of the cell cycle in which the cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles, and begins to reorganize its contents in preparation for mitosis
interphase
the collective name for G1, S, and G2
M phase
The phase of the cell cycle in which the cell divides its copied DNA and cytoplasm to make two new cells
G0 phase
The phase of the cell cycle in which the cell is resting and not actively preparing to divide
30s subunit
the smaller component of the prokaryotic ribosome responsible for binding to messenger RNA and decoding the genetic message
50s subunit
the larger component of the prokaryotic ribosome that catalyzes peptide bond formation
60s subunit
the larger subunit of the eukaryotic ribosome
40s subunit
the smaller subunit of the eukaryotic ribosome
peptidoglycan
an important component of many bacterial cell walls and is not found in animal cells
gram-positive bacteria
a type of bacteria that contains a thick peptidoglycan cell wall outside its cell membrane. Crystal violet stain adheres to the cross-links within the peptidoglycan structure, causing the bacterium to appear purple when visualized
gram negative bacteria
a type of bacteria that contains both an outer and an inner plasma membrane and a thin peptidoglycan wall causing it to appear stained pink when visualized
does anabolism or catabolism produce energy?
catablolism
what happens to reduced cofactors when they are used for anabolic processes?
they become oxidized
ratio of cofactors that drives catabolism?
high NAD+/NADH ratio or low NADH/NAD+ ratio
More of the oxidized form encourages catabolism and the release of energy
AUG codon
start codon - codes for methionine
UGA, UAG, and UAA codons
stop codons
degree of burial
refers to the extent to which a specific amino acid residue or a functional group within a protein is shielded from the surrounding solvent; in other words, it measures it’s degree of hydrophobicity
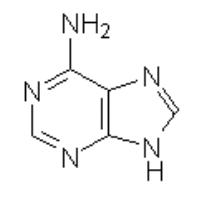
adanine
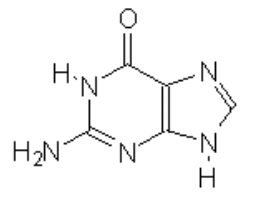
guanine
cytosine
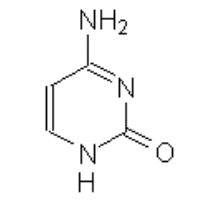
thymine
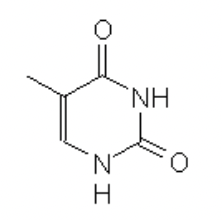
uracil
common labeling agents in an assay?
fluorophores, enzymes, or radioisotopes
is insulin a peptide hormone or a steroid hormone?
peptide
what are the common steroid hormones?
cortisol, aldosterone, testosterone, estradiol, and progesterone
What are the common peptide hormones? (water soluable)
insulin, glucagon, parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, growth hormone, prolactin, oxytocin, antidiuretic hormone, Adrenocorticotropic Hormone, Luteinizing Hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone
PCR
a lab technique that creates millions of copies of a specific DNA segment rapidly. The process consists of repeating three core steps:
denaturation
annealing
Extension
dNTPs
the standard building blocks of natural DNA and are used for replication and PCR
ddNTPs
modified nucleotides that are lacking a hydroxyl group, preventing the addition of the next nucleotide. Used in Sanger Sequencing to determine the DNA sequence
divalent ions
ions that carry an electrical charge of +2 or -2
nondisjunction
when a cell can receive too many or two chromosomes during anaphase
prophase I
Homologous chromosomes (1 chromosome (2 chromatids) from the mother and 1 chromosome (2 chromatids) from the father) pair up to form structures called tetrads. Crossing over occurs, leading to the genetic exhcange of information between non-sister chromatids
chiasmata
points on the non-sister chromatids where crossing over occurs
metaphase I
the paired homologous chromosomes align randomly along the metaphase plate
independent assortment
the orientation of each pair of homologous chromosomes is random
anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move toward opposite poles while sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere and move together as a single unit
telophase I
chromosomes arrive at the poles. The nuclear envelope reforms around the haploid sets
prophase II
The nuclear envelope breaks down and the spidle apparatus reforms
metaphase II
the chromosomes (each still composed of two sister chromatids) aling individually along the metaphase plate
anaphase II
sister chromatids finally separate at the centromere and move as individual chromosomes toward opposite poles
telophase II
chromosomes arrive at the poles and the nuclear envelope reforms
kinase
an enzyme that produces phosphorylation
Henderson Hasselbalch equation
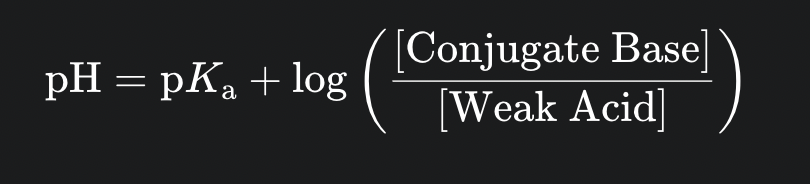
the primary use for this equation is to describe and design buffer solutions with a desired pH