Extracellular receptor signalling pathways 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Outline the process of cell signal transduction
Stage 1: an extracellular signal molecule activates a membrane receptor
Stage 2 : signa transduced via a specific pathway
Stage 3 : activates a response
First messenger
Extracellular signal
Second messenger system
Intracellular molecules
Transducers
Proteins that convert the message of extracellular signals into intracellular messenger molecules that trigger a response
Give examples of response to cell signal transduction.
See highlighted
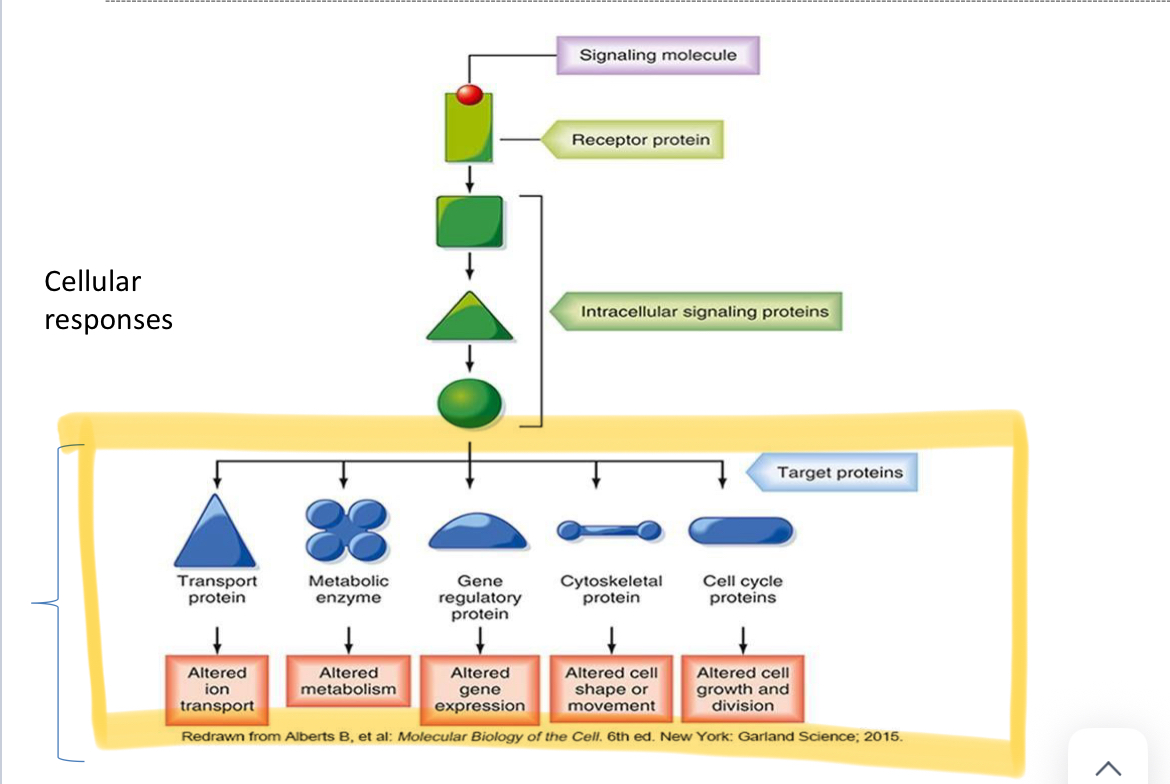
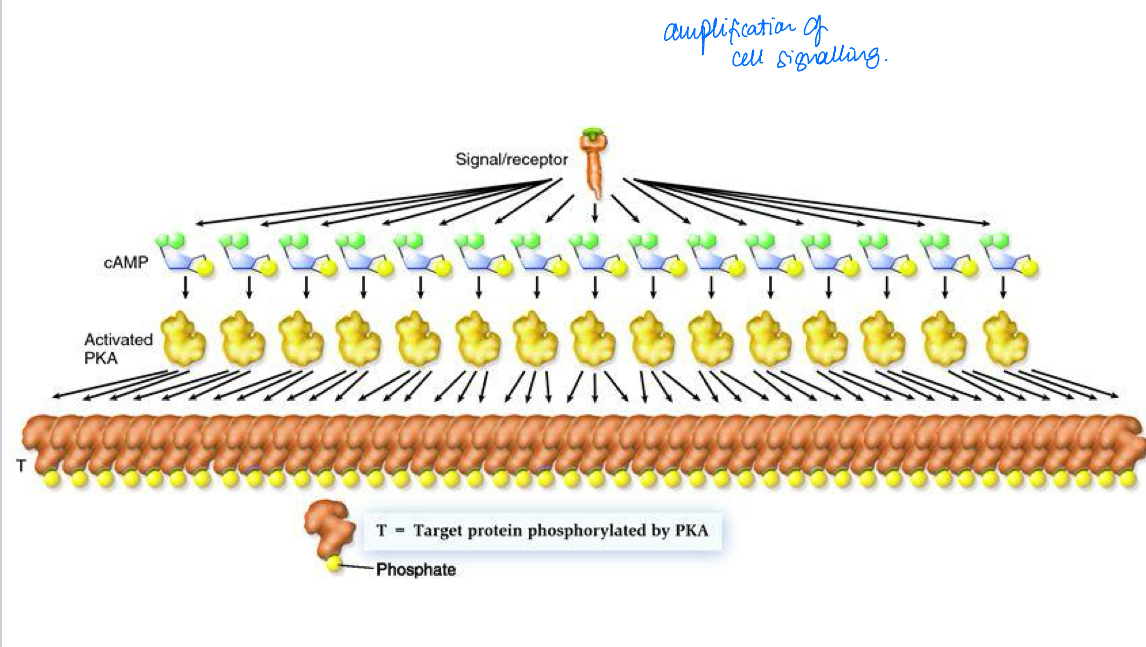
What is the benefit of having an amplified response ?
One small signal can produce a large effect
Examples of molecules that act as extracellular signalling molecules
Amines, peptides and proteins, steroids, other small molecules e.g amino acids, ions and gases
What are the 4 main classes of receptors ?
Ligand gated ion channels
G-protein coupled receptors
Enzyme-linked receptors
Nuclear receptors
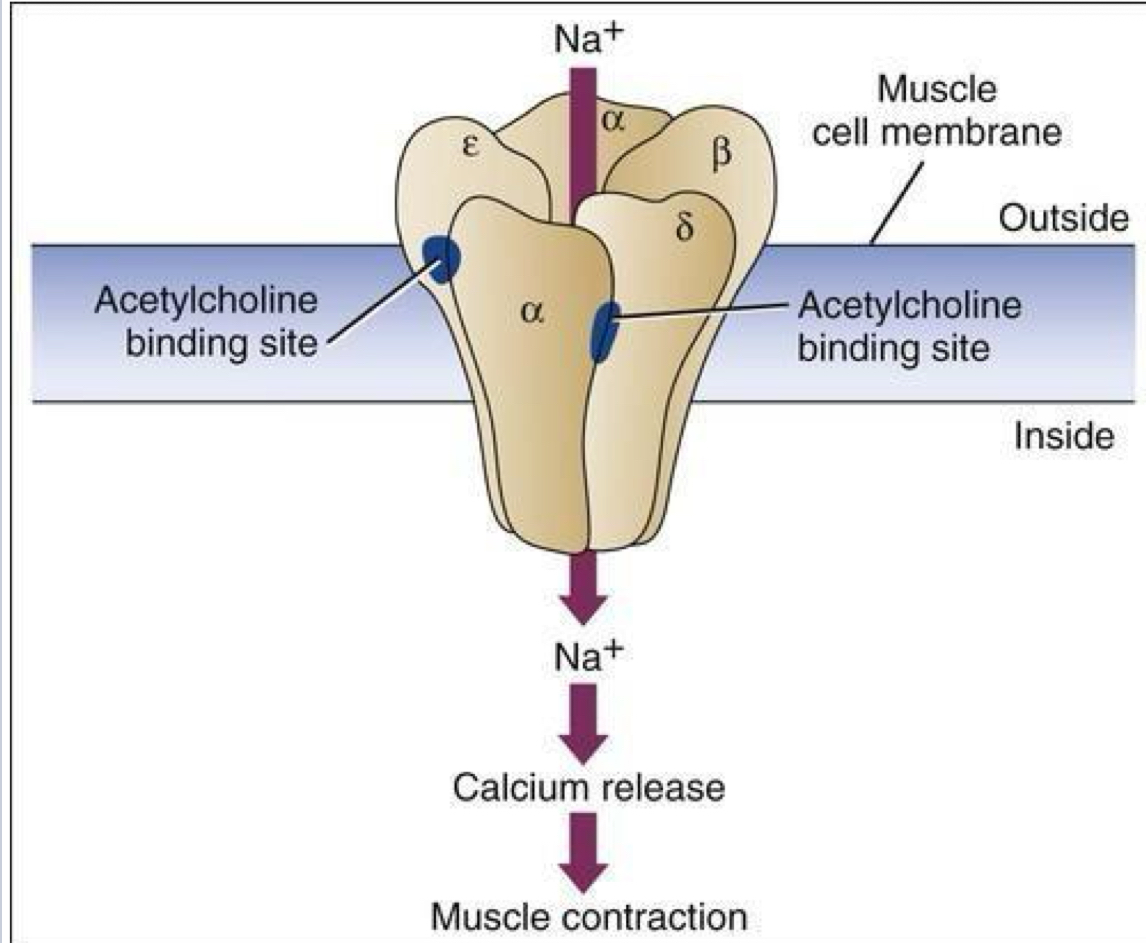
What is a Ligand-gated ion channel ?
An ion channel that is mediated by a signal molecule. Upon activation allows ions to flow through it
Explain how a ionotropic receptor is a ligand gated ion channel ( Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor )
Ligand gated ion channel that is mediated by acetylcholine (and nicotine)
Binding of Acetylcholine Na+ channel
Inward Na+ current causes polarisation - which in turn causes a response
How is GABA receptor an ionotropic receptor ?
GABA - signal molecule - neurotransmitter
GABA binds to ion channel - causes influx of Cl- ions - inhibitory receptors - causes relaxation
What are metabotropic Aka muscarinic receptors ?
Receptors that produce molecules that act as precursors for the signal molecule for the ion channel receptor
Provide indirect link with ion channels through signal transduction pathways
Differences between Ionotropic and metabotropic receptors.
Ionotropic - direct response by ion channel pore
Metabotropic - indirect - slower - mediated by G proteins - transducers
What are G protein coupled receptors ?
Receptors that transduce a signal by forming a receptor-g protein complex which in turn activates an enzyme to produce a response.
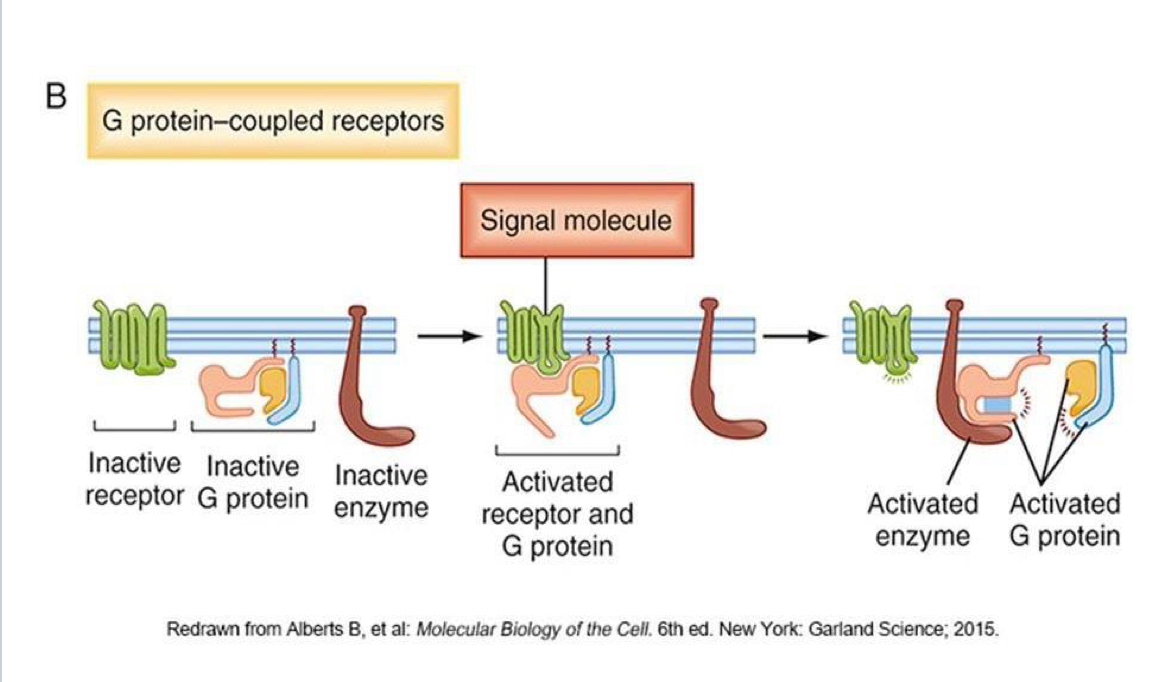
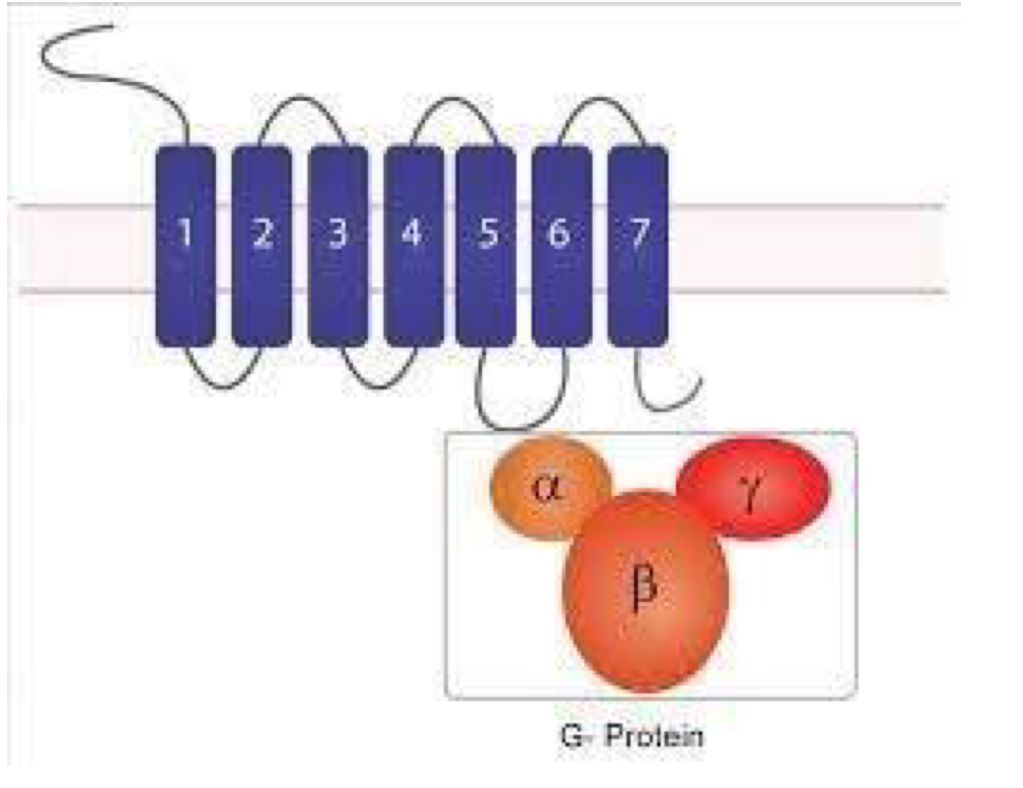
Structure of G proteins
7 transmembrane domains
3 polypeptide chains - alpha, beta and gamma
16 alpha subunits, 5 beta, 11 gamma
All beta and gamma subunits bind tightly to each other to form one beta-gamma unit
Alpha subunit has a guanine nucleotide binding site that binds GTP or GDP
Explain the G protein cycle
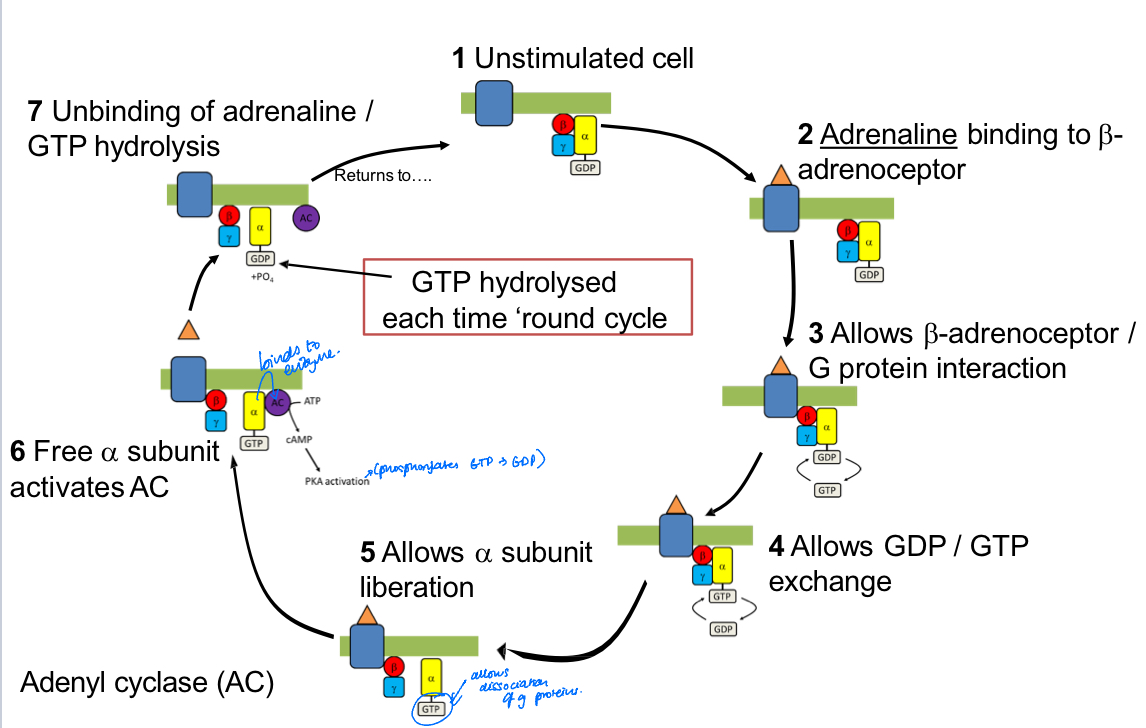
What is the cAMP/PKA pathway ?
Important mechanism that allows hormones /neurotransmitters to evoke response in target cells
Present in virtually every cell
Uses proteins that get phosporylated by PKA to transduce a signal