Lab practical/oral exam
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
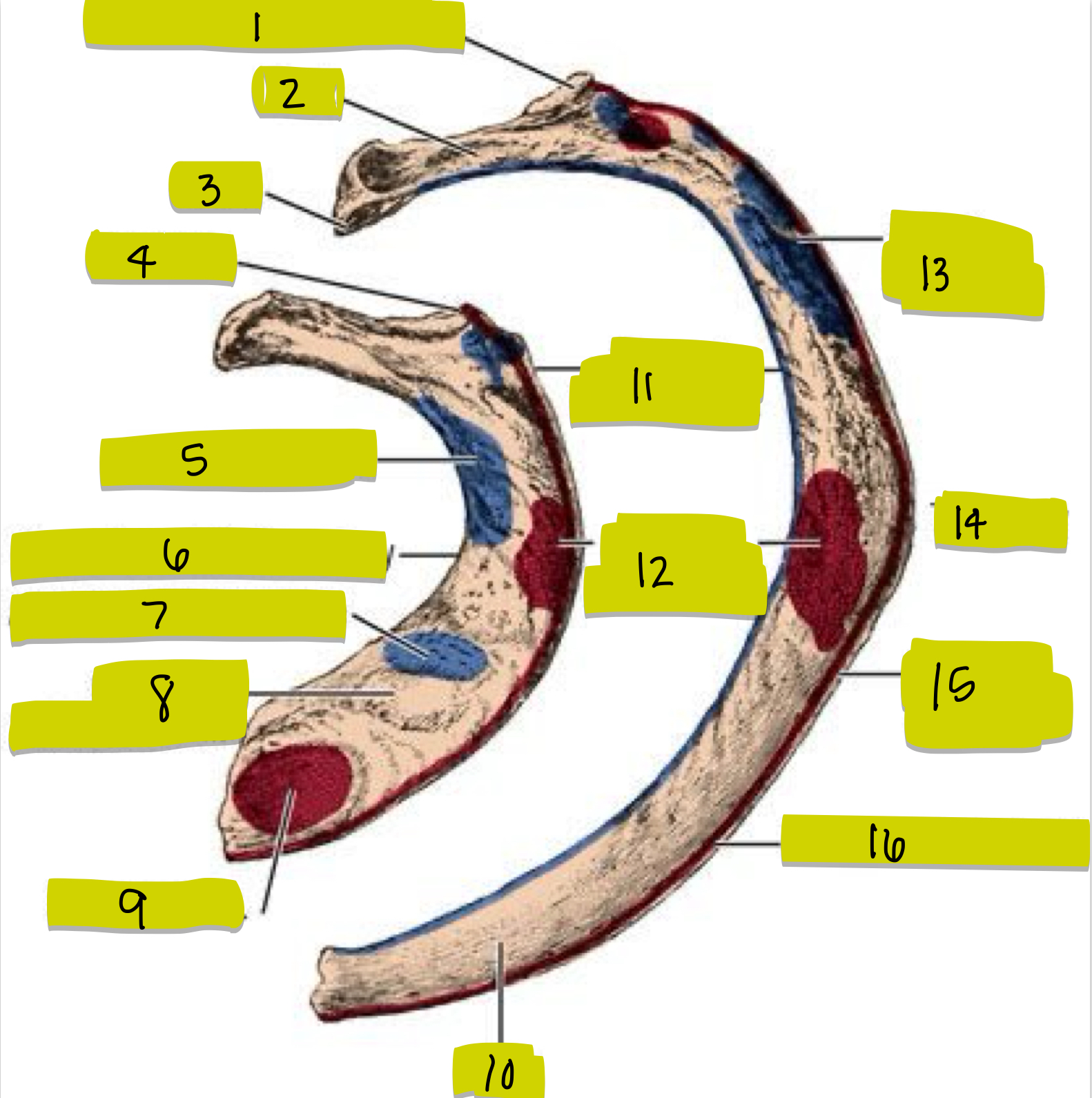
What is 1
Tubercle
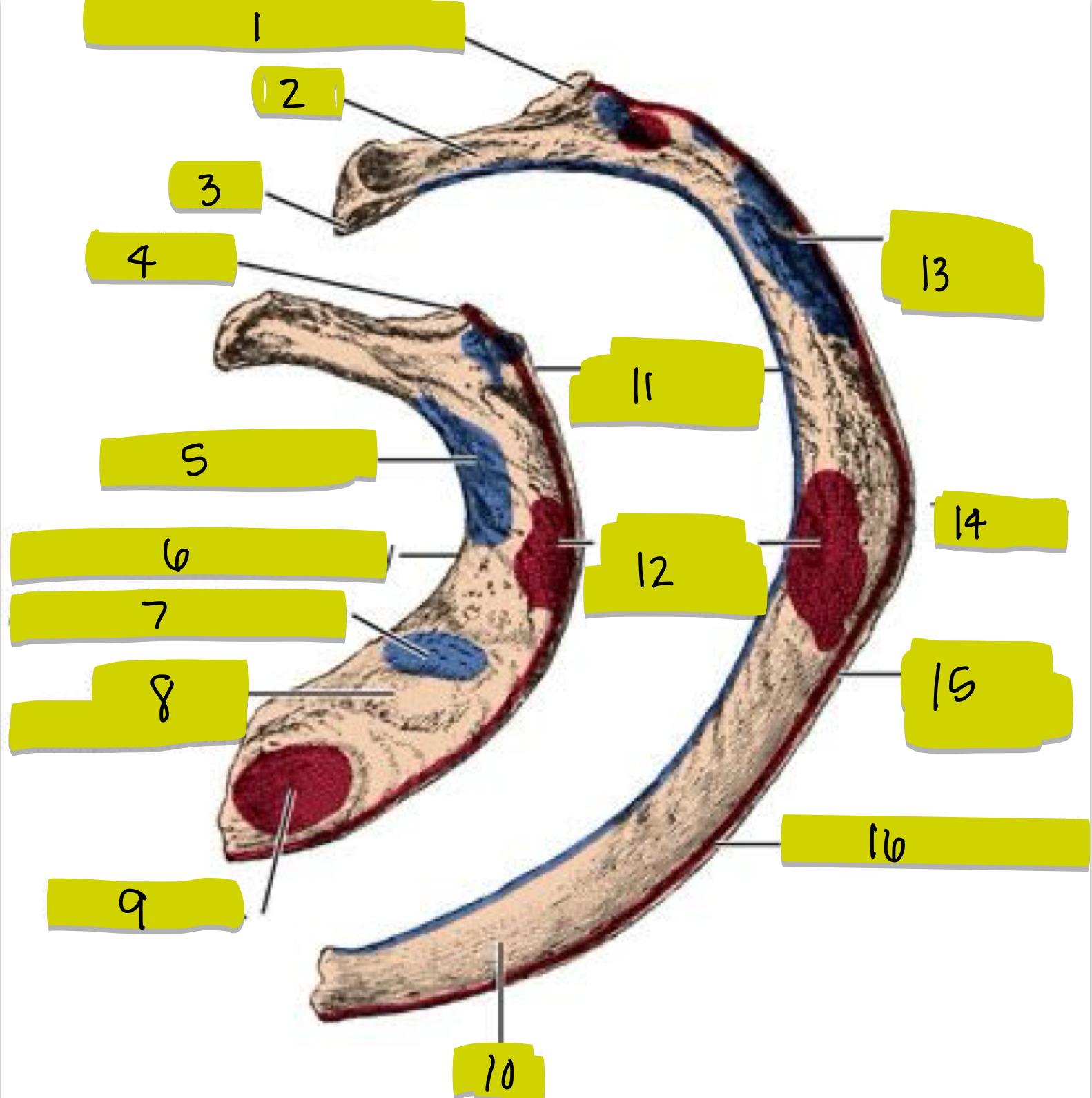
What is 2
Neck

What is 3
Head
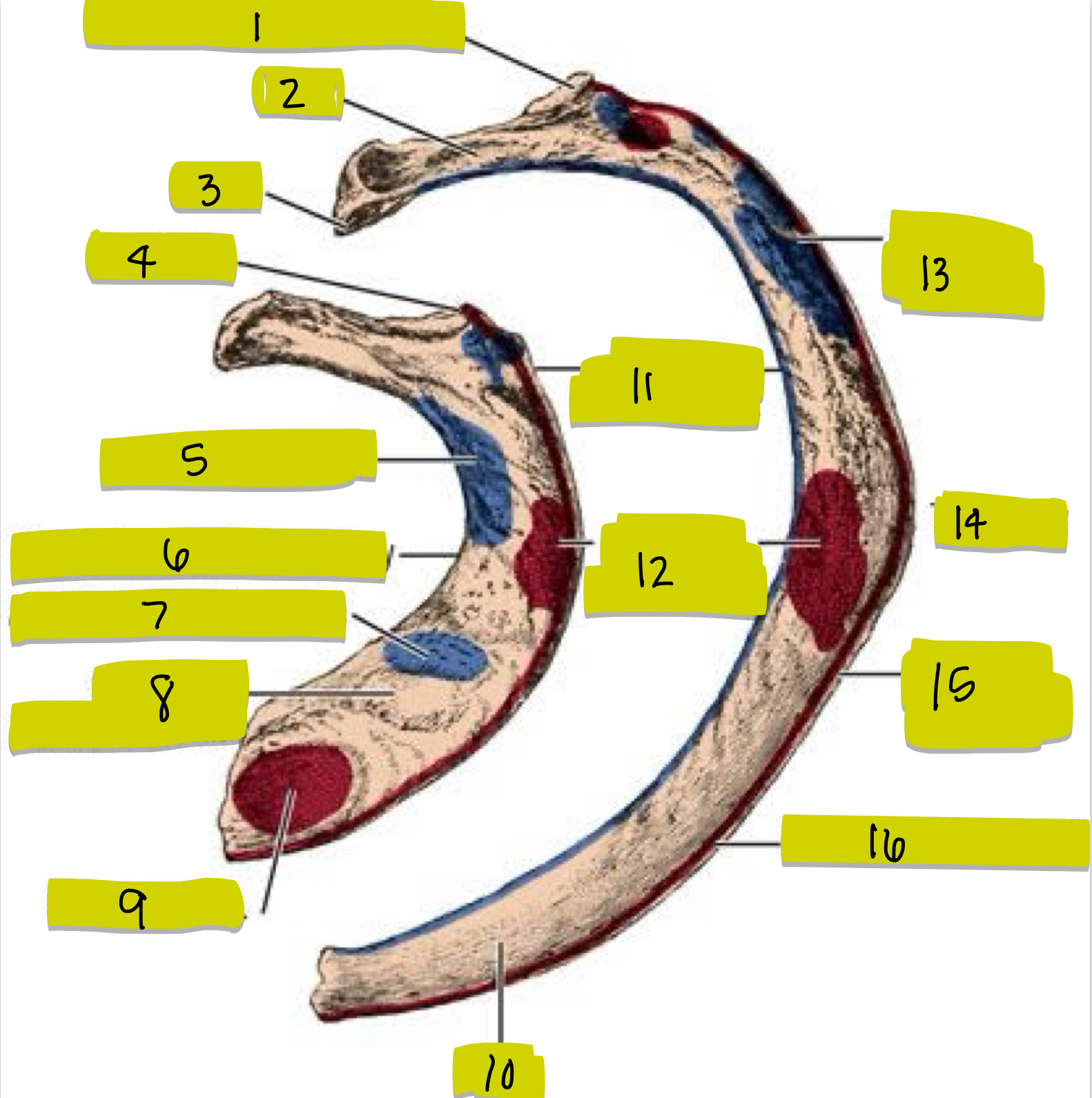
What is 4
Tubercle of 1st rib
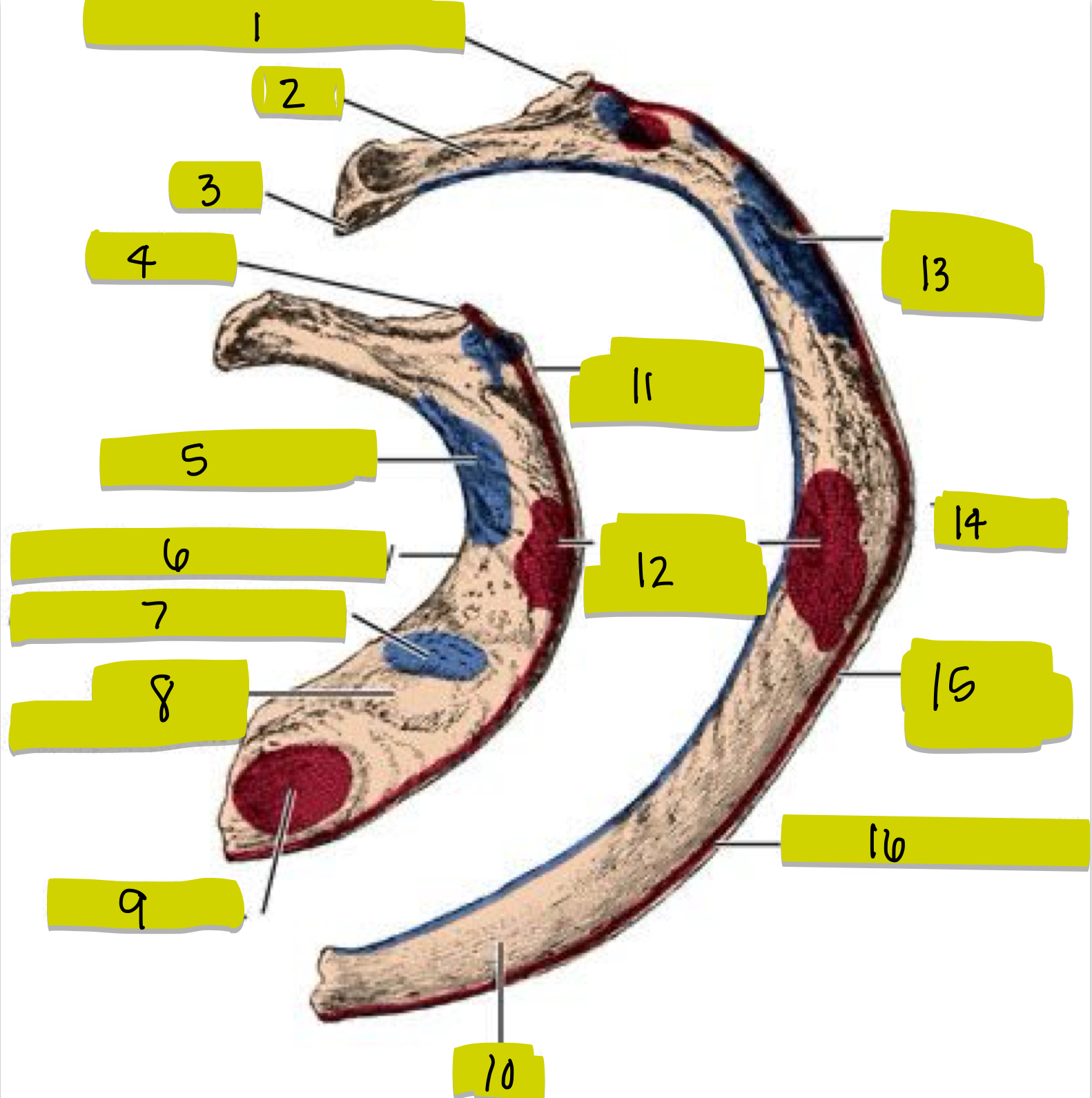
What is 5
middle scalene insertion
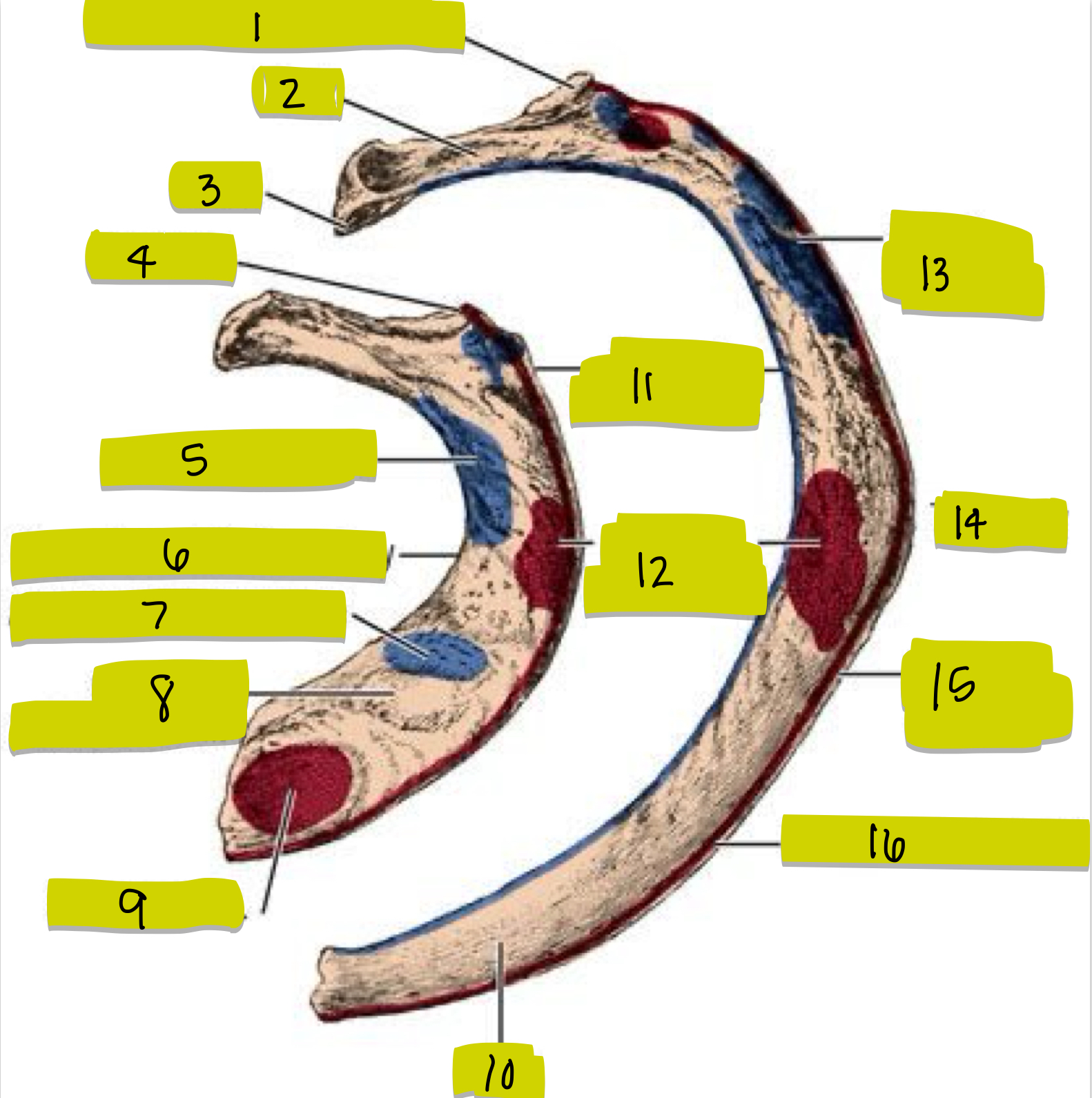
What is 6
Groove for subclavian artery
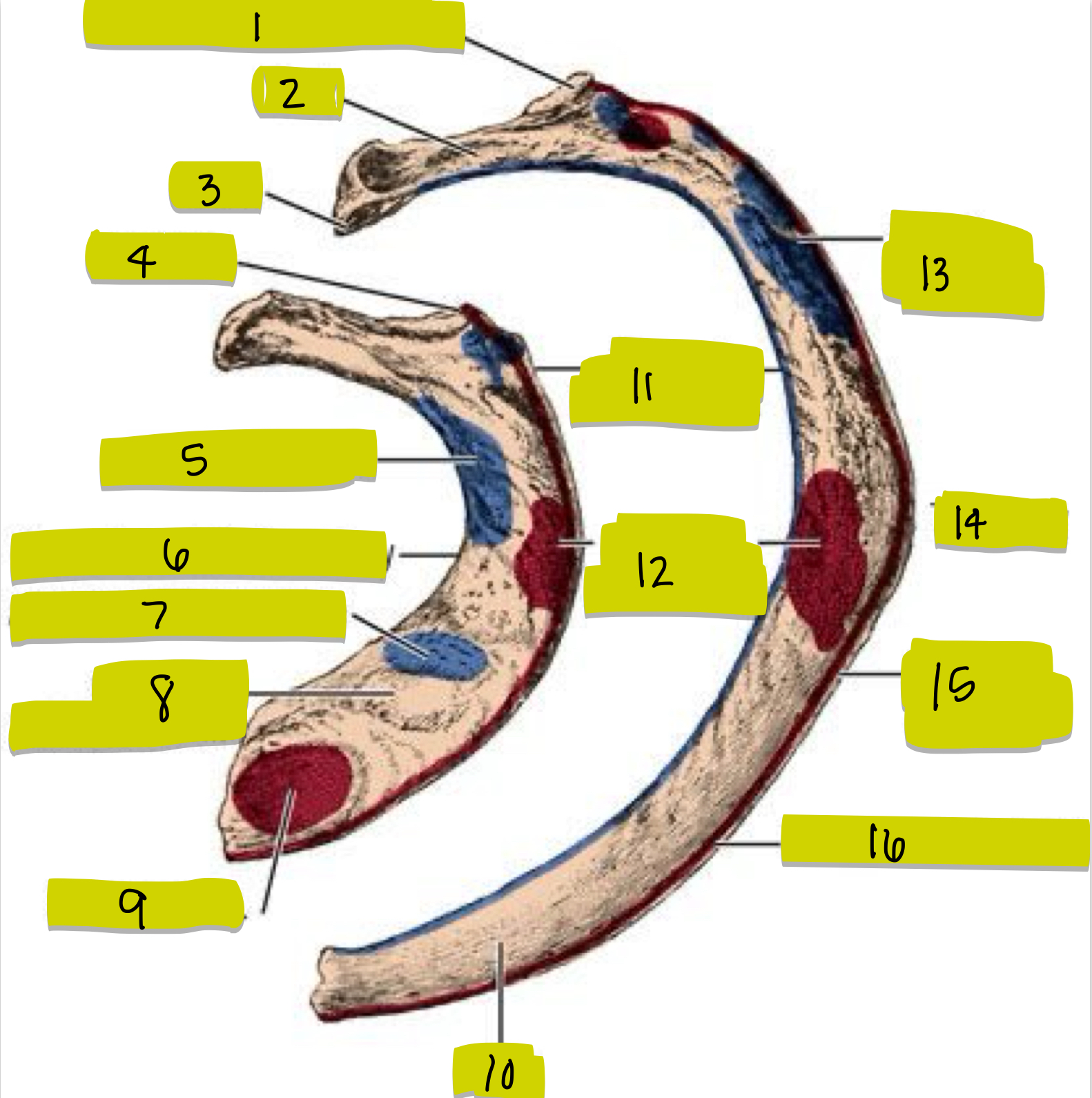
What is 7
Anterior scalene tubercle
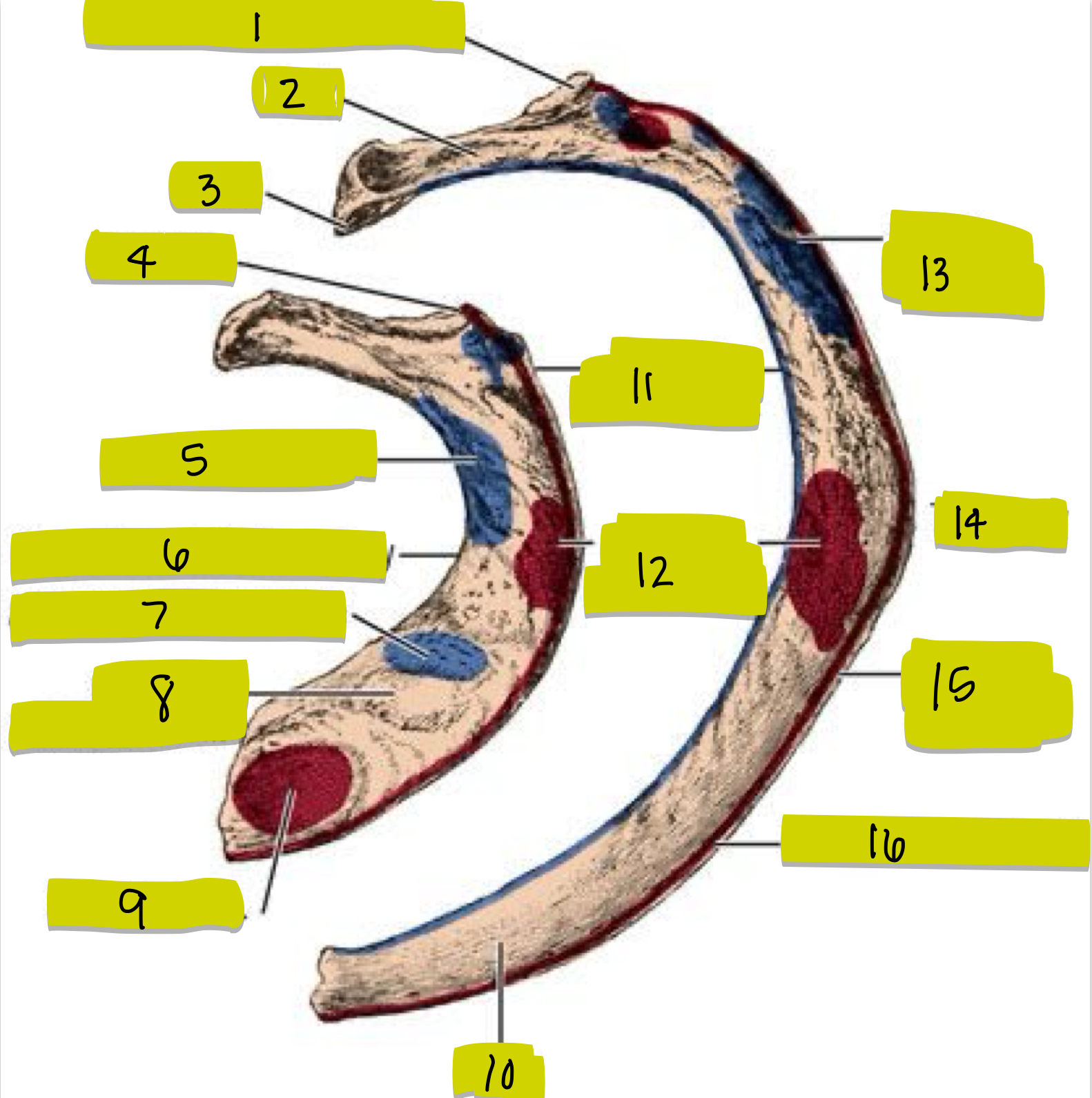
What is 8
Groove for subclavian vein
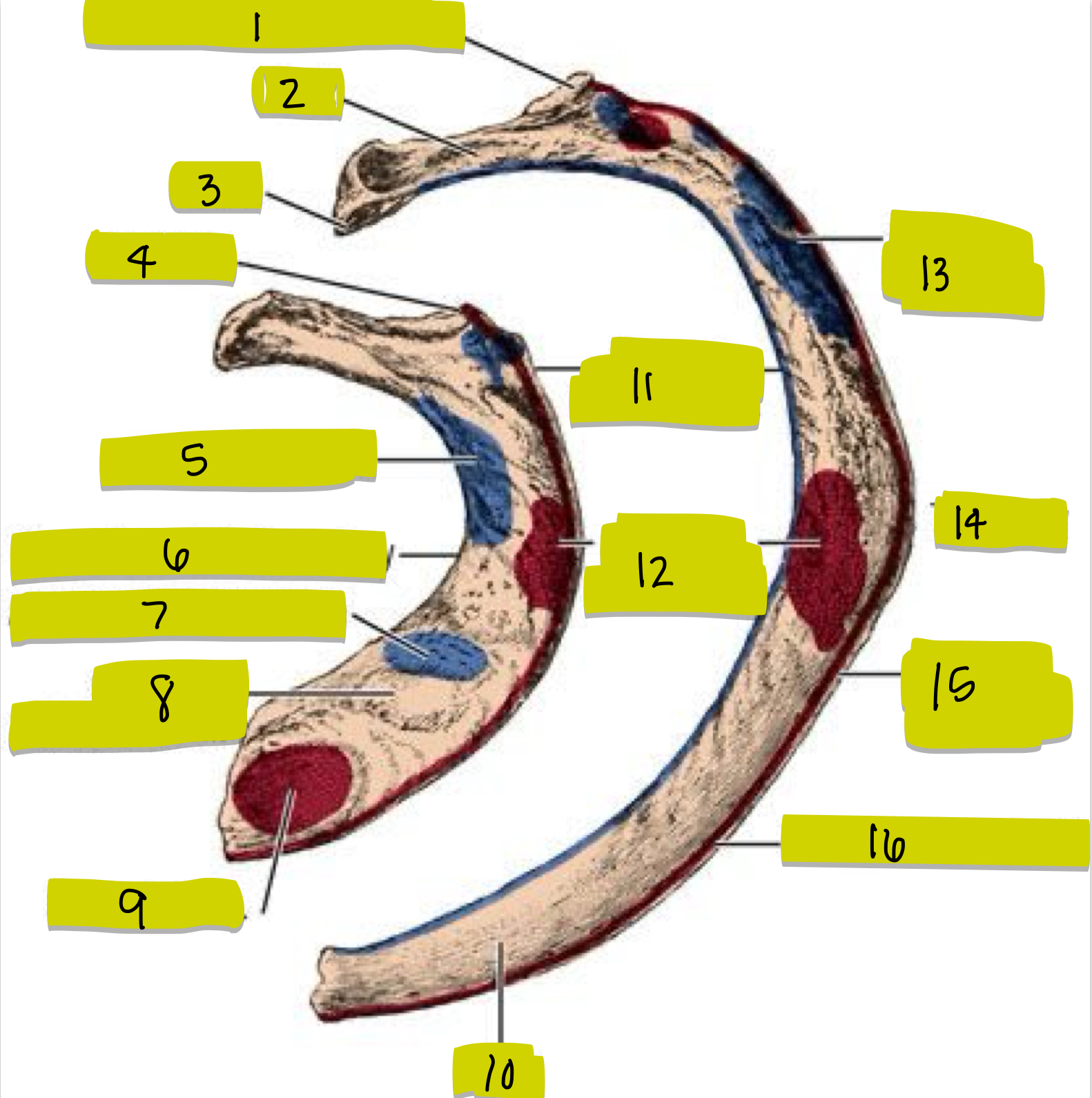
What is 9
Subclavian origin

What is 10
Shaft of Rib
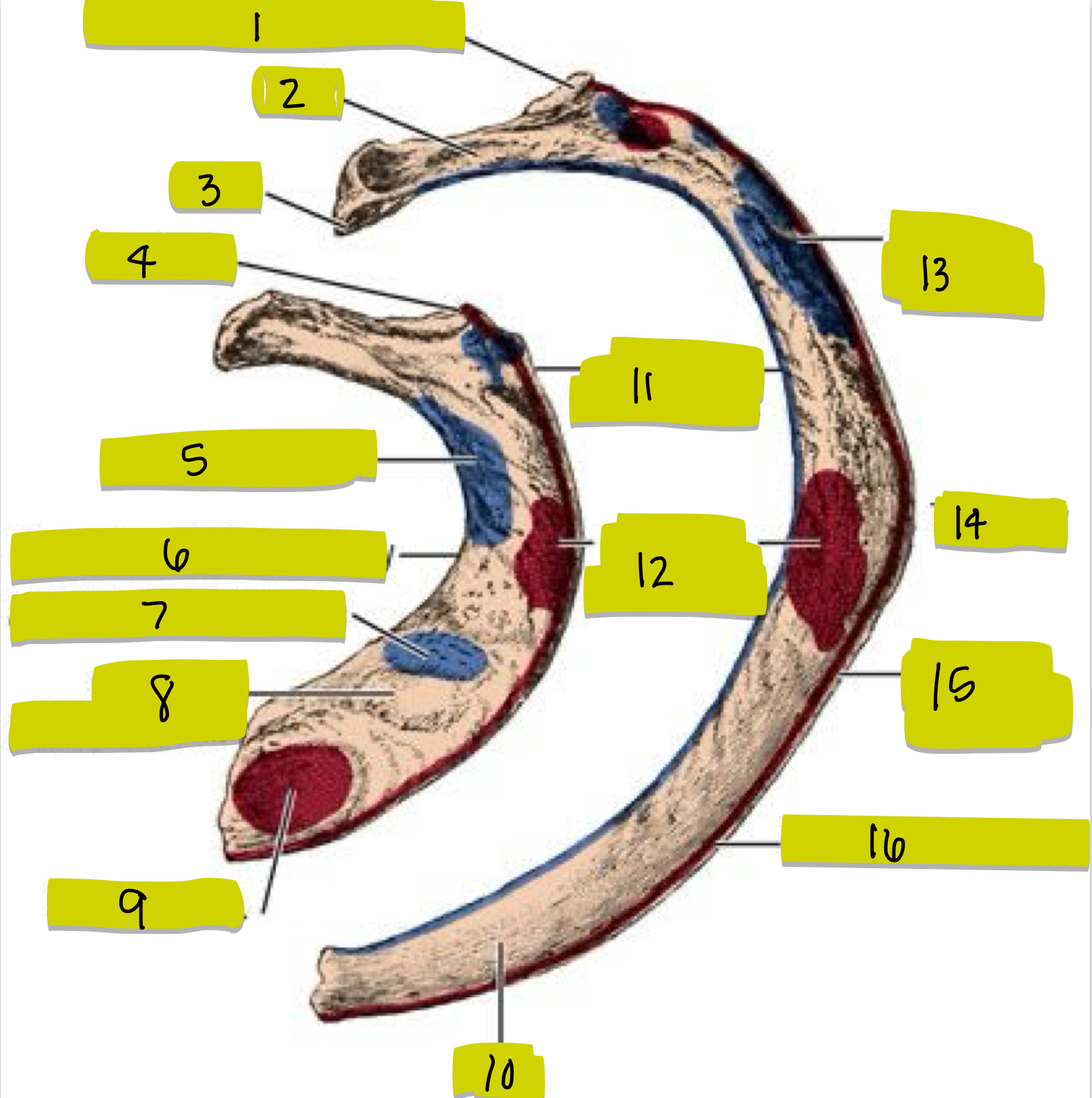
What is 11
External intercostal attachment
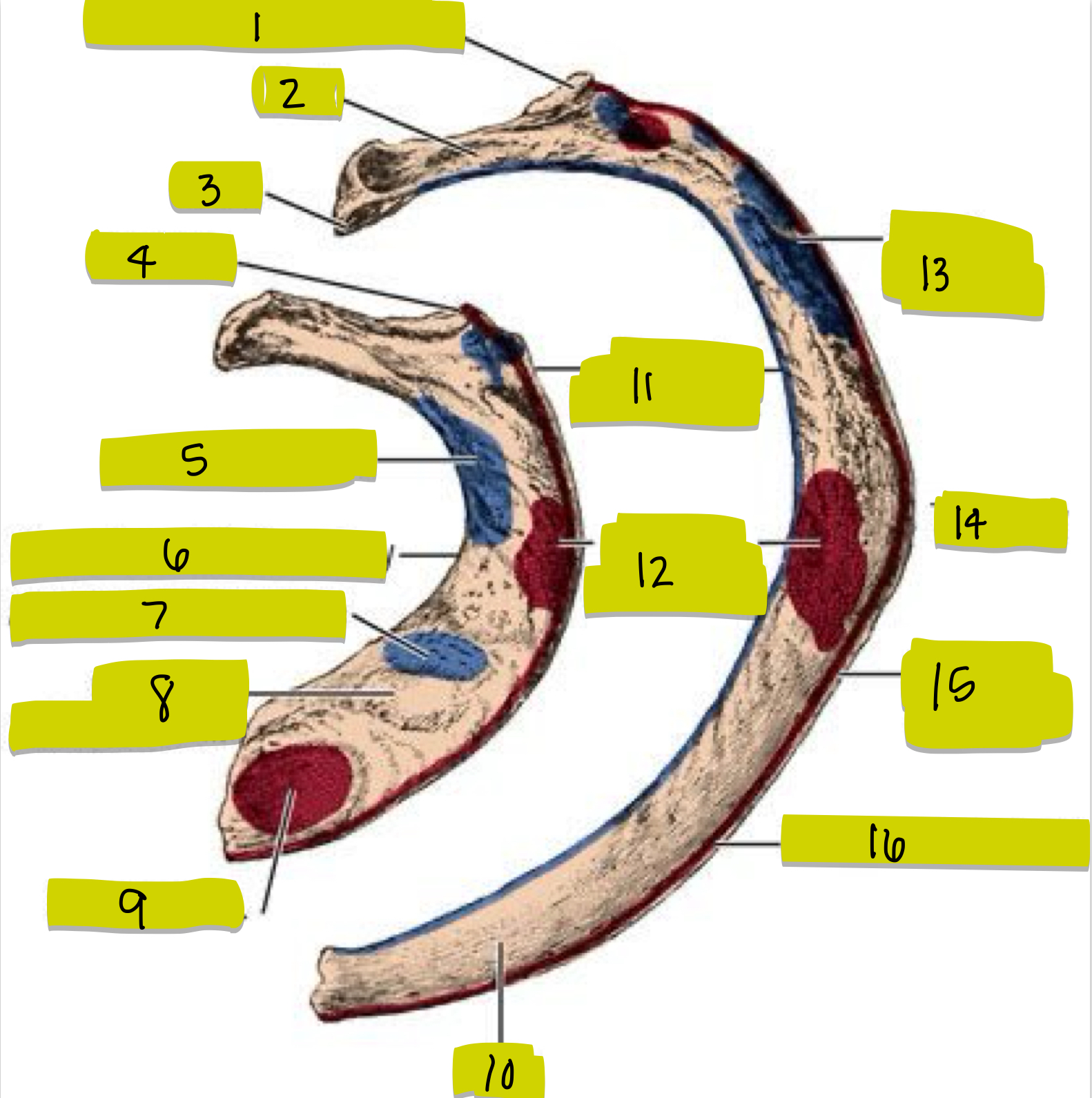
What is 12
Serrated anterior attachment
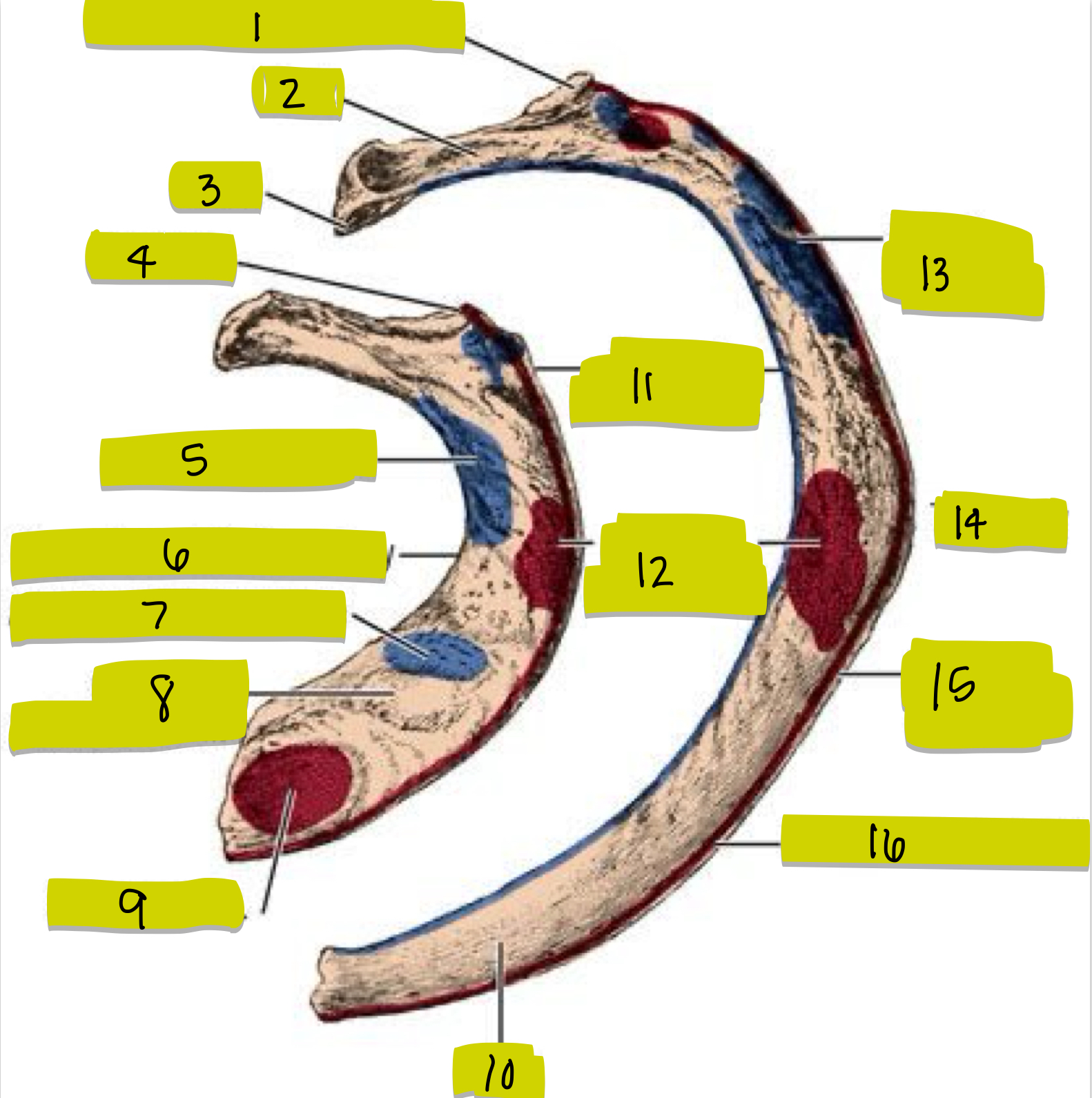
What is 13
Insertion for posterior scalene
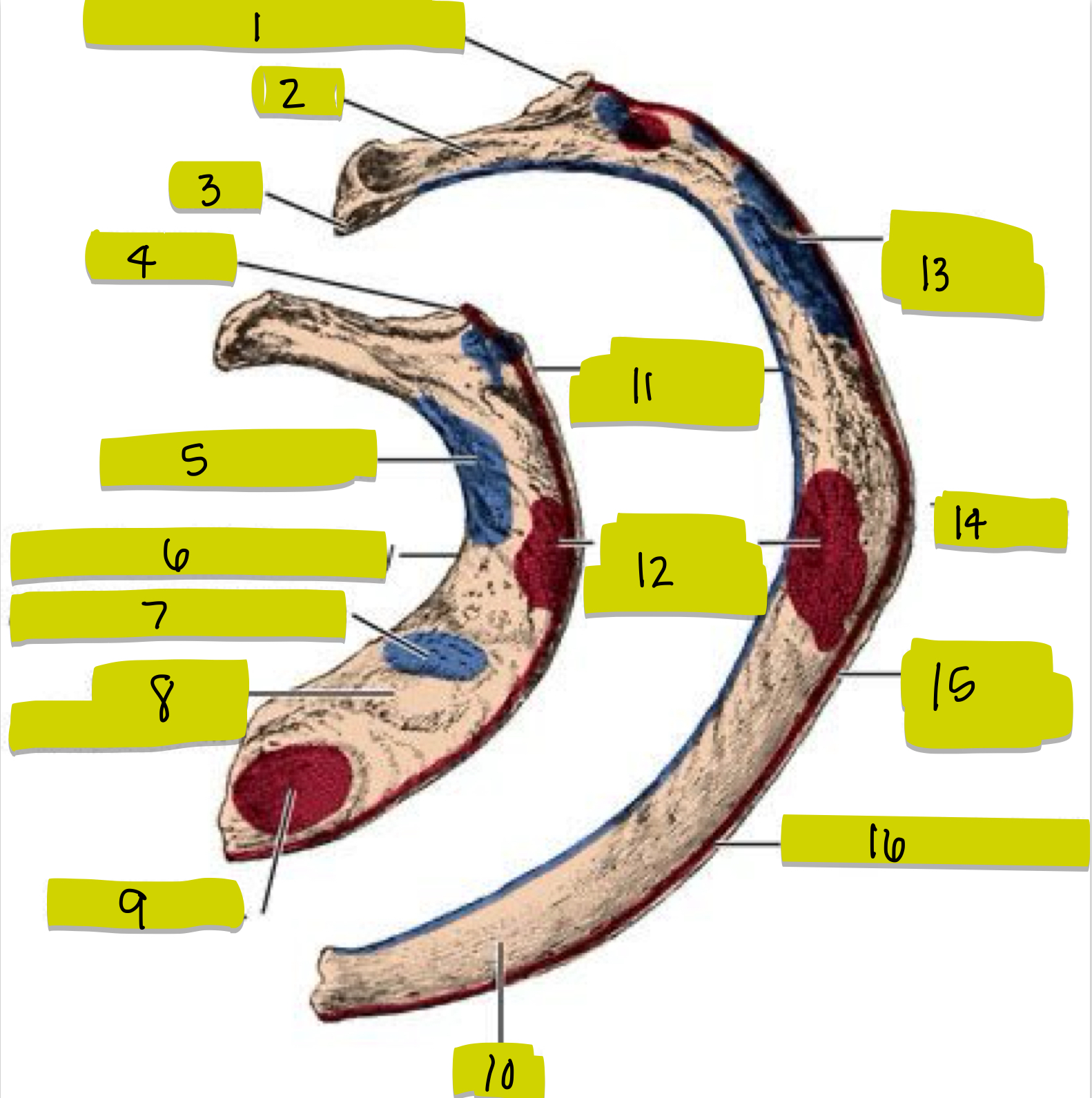
What is 14
Angle of rib
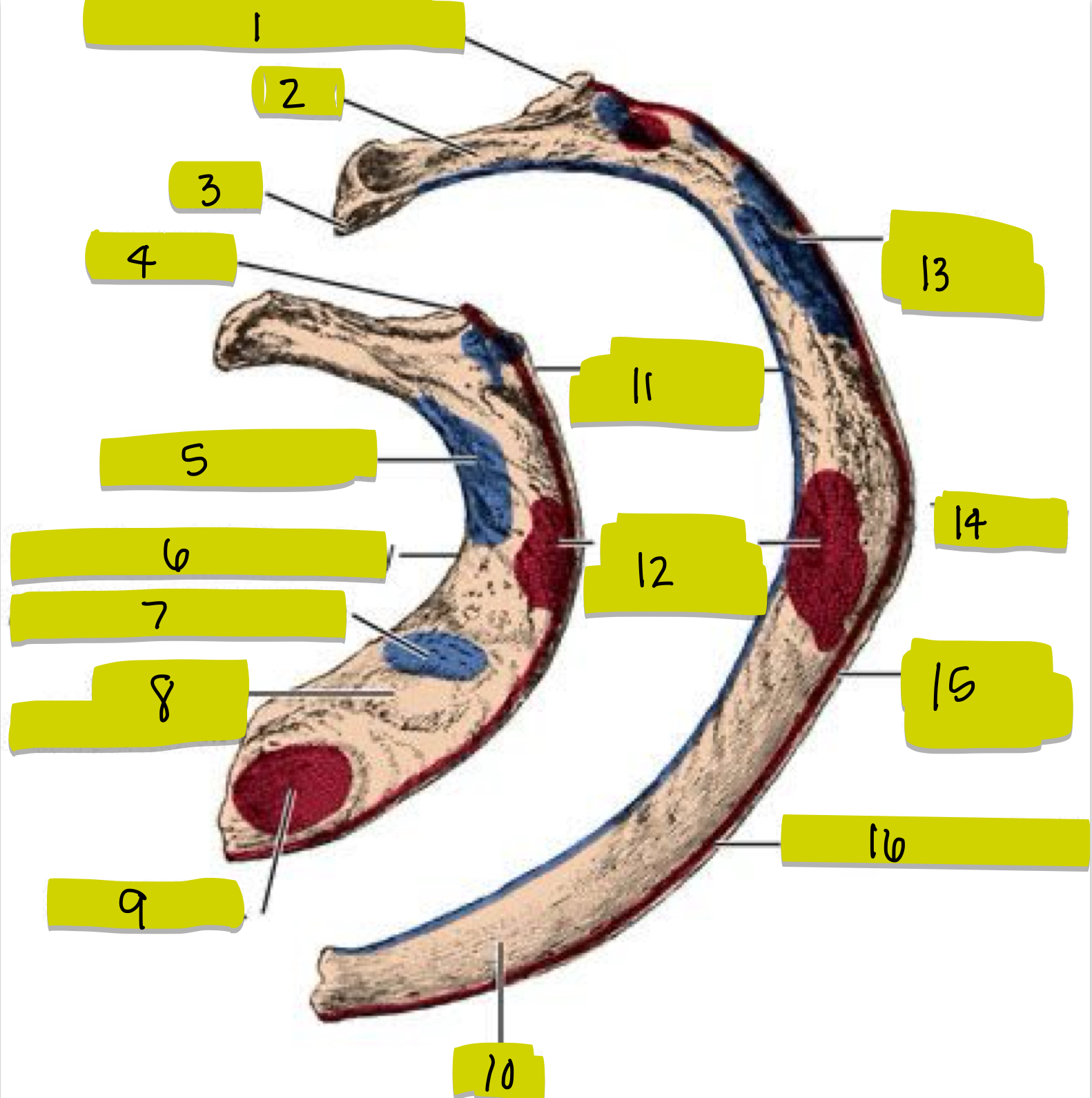
What is 15
Attachment for serrated anterior m

What is 1
Head
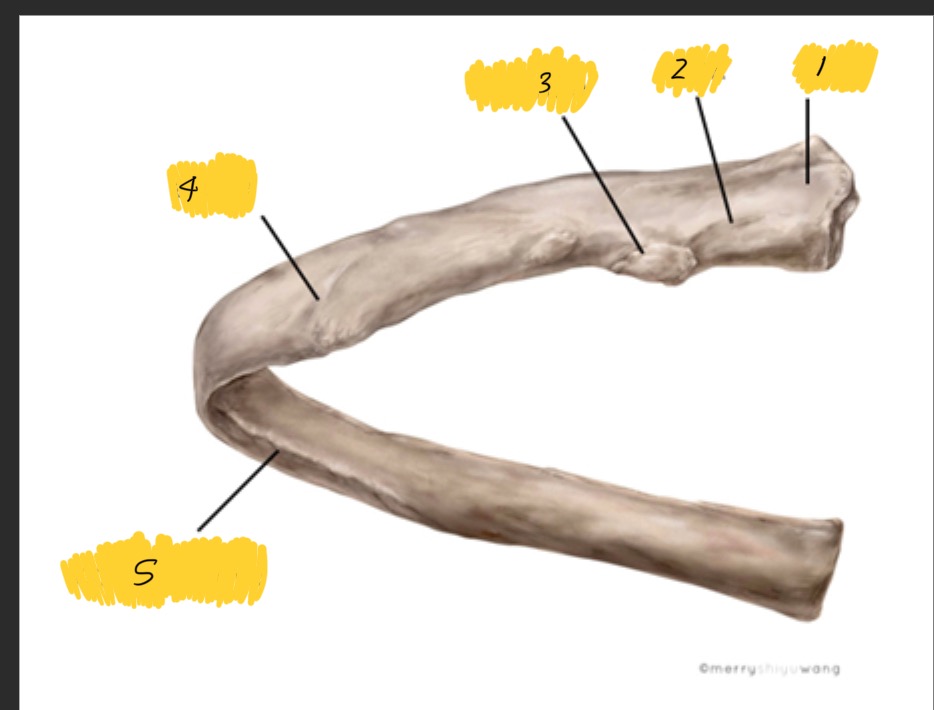
What is 2
Neck
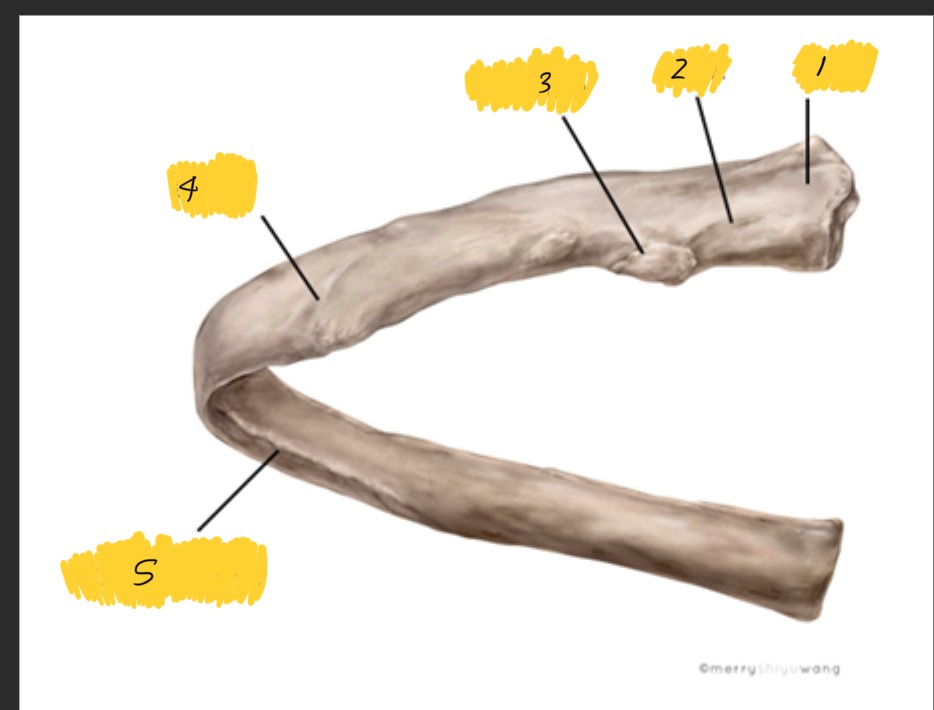
What is 3
tubercle
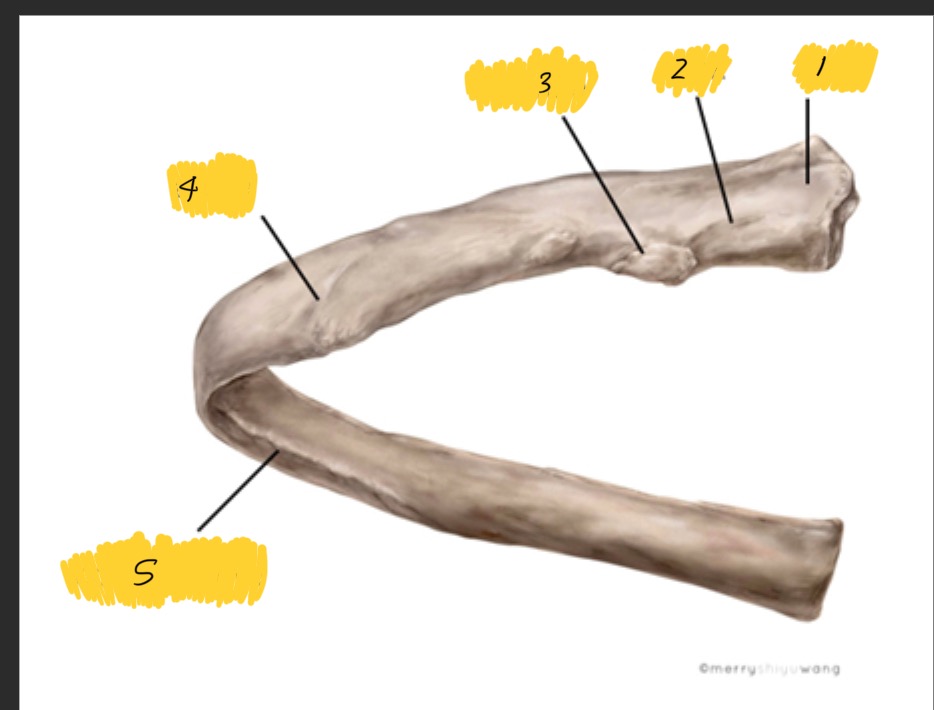
What is 4
Angle
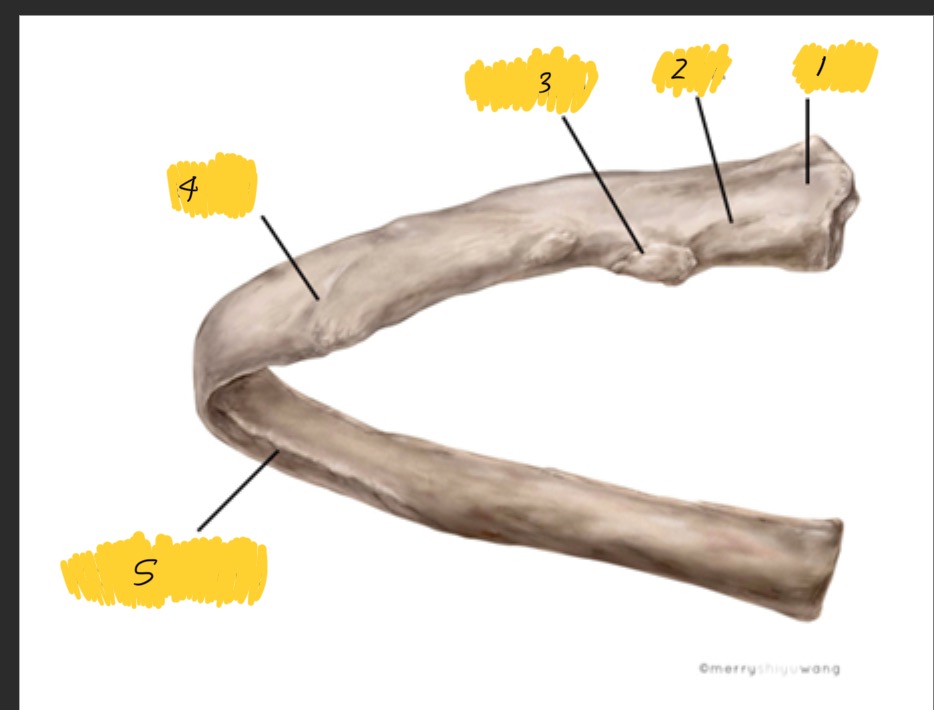
What is 5
Costal groove
What makes up the anterior wall of the thoracic cage?
sternum and costal cartilage
What makes up the lateral wall of the thoracic cage?
ribs and costal cartilages, + intercostal spaces
What makes up the posterior thoracic cage?
thoracic spine, posterior ribs
Which side of the thoracic cage is longest?
posterior
In what direction is the thoracic cage flattened?
anteroposterior
What are the boundaries of the superior thoracic aperature?
posterior: body T1
lateral: 1st rib and 1st costal cartilage
anterior: superior border of manubrium
What are the boundaries of the inferior thoracic aperature?
Posterior: T12, 12th rib, tip of 11th rib
lateral: inferior borders of 10-7 costal cartilages (=costal margin)
anterior: xiphisternal joint
What traverses through the superior thoracic aperature?
esophagus
trachea
vessels and nerves
What traverses through the inferior thoracic aperature?
diaphragm — structures pass through or behind to get to pelvic region
Where is the infrasternal angle located?
between the right and left costal margins
What parts of the rib articulate with something?
head (inferior and superior facets)
tubercle (TVPs)
What is found in the intercostal space?
Vein
Artery
Nerve
all intercostal
what level is the manubrium located at?
T2-3 disc
What articulates with the manubrium?
clavicle
1st rib
what level is the body of the sternum located at?
T5-9
What are transverse ridges on the body of the sternum?
slits of fusion between segments of the body
When does fusion of the body of the sternum occur?
puberty
What level does the xiphoid process sit at?
T10
What articulation does the xiphoid process have?
xiphisternal
7th rib
The xpiphoid process is the site of what structures?
superior surface of liver, diaphragm, and inferior angle of heart
what happens to the xiphisternal joint as you get older?
calcifies
What is unique about the 2nd rib?
Oblique angle
2x length of 1st rib
Tuberosity for serratus anterior
What is unique about the 10th rib?
Only one articulation (for T10 body)
What is unique about the 11th rib
Shorter
Floating not attached
Only one articulation (T11)
No tubercles
What is unique about the 12th rib
Shorter
Only one articulation (T12)
No tubercles
What is unique about the 1st rib?
Flat angle
Grooves for subclavian vein (anterior edge of superior surface) and subclavian artery (posterior edge of superior surface)
Insertion for anterior scalene muscle (scalene tubercle)
Shortest
1 articular facet (goes to T1 body)
Forced inspiration movement of the rib is characterized by?
pump handle movement
Resting inspiration movement of the rib is characterized by?
bucket handle movement
pectoralis minor OIAN
O: ribs 3-5
I: coracoid process
A: draws scapula anteroinferiorly, stabilize
N: medial pectoral nerve
pectoralis major OIAN
O: clavicle, anterior surface of sternum and ribs 1-6, rectus sheath
I: intertubercular groove of humerus
A: adduction, medial rotation flexion and extension of humerus, bring scap anteroinferiorly
N: medial and lateral pectoral nerves
serratus anterior OIAN
O: ribs 1-9
I: anterior aspect of medial border of scapula
A: stabilize scap, hold to thoracic cage, anterolateral movement of scap
N: long thoracic nerve
action and direction of fibers of external intercostals
elevate ribs
anterior and inferior
action and direction of fibers of internall intercostals
depress ribs
posterior and superior
action and direction of fibers of innermost intercostals
depress ribs
same as external = anterior and inferior
branches of internal thoracic artery?
musculophrenic
superior epigastric
What do the perforating branches supply?
blood to breast
What do the pericardiacophrenic artery supply?
pericardium, pleura, diaphragm
What does the pericardiaophrenic artery run with?
phrenic nerve
What does the superior epigastric artery supply?
central part of the anterior abdominal wall above umbilicus
What does the musculophrenic artery supply?
diaphragm and anterior intercostal arteries of lower 5 intercostals
What does the posterior intercostal arteries branch from?
subclavian artery
T/F: posterior intercostal arteries are larger than anterior intercostal arteries
true
What does the posterior intercostal veins drain into?
hemiazygos, accessory hemiazygos, and azygos
what do the anterior intercostal veins drain into?
internal thoracic or musculophranic veins, which goes to the brachiocephalic vein
What is the innervation of the thorax?
ventral rami of T2-11 spinal nerves
what ramus makes up the subcostal nerve?
ventral ramus of T2
what nerves supply the thoracic wall?
upper 6 intercsotal nerces
what nerves supply the anterior abdominal wall?
thoracoabdominal nerves 7-11
What are the branches of the ventral rami of T2-11
communicating rami
collateral branch
lateral cutaneous branch
anterior cutaneous branch
What do the intercostal nerves supply?
skin and parietal pleura
serratus posterior inferior and superior, intercostal, subcostal and transversus thoracis muscles
In what location is the heart?
vertical: ribs 2-6
horizontal: axillary region to lateral margin of sternum
How many lobules make up the breast
15-20
what separates the lobules of the breast?
cooper’s ligament
what occurs when there is a pathology in cooper’s ligament?
dimpling of the breast
what is found in the retromammary space?
loose CT seaprating breast and pectoralis major
What are the blood vessels of the breast? and where do they come from/drain to?
medial mammary branches (branch from internal thoracic artery)
lateral mammary branches (branch of lateral thoracic artery and posterior intercostal arteries)
veins: internal thoracic, lateral thoracic, and posterior intercostal veins
Where does most of the lymph drain in the breasts?
axillary lymph nodes
What are the secondary lymph nodes of the breasts?
parasternal and intercostal lymph nodes
What is the transverse pericardial sinus?
Behind aorta and pulmonary trunk
Right end between aorta and superior vena cava
Left end on left margin of pulmonary trunk
What is the oblique pericardial sinus?
area behind L atrium, has no exit and esophagus lies posterior
what is the innervation of the pericardium
sympathetic chian
parasympathetic: phrenic nerve (fibrous and parietal) and cardiac plexus (visceral)