Introduction to Geology: Earth's Processes, History, and Plate Tectonics
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What do geologists study?
Geologists study the materials that comprise Earth, its history, and the processes at work on Earth.
Who are considered the Fathers of Geology?
James Hutton (1726-1797) and Charles Lyell (1797-1875).
What is the Principle of Uniformitarianism?
The principle that processes observed on Earth today have worked in much the same way throughout the geologic past.
What characterizes the Earth as an energetically open system?
It absorbs energy from the Sun.
What characterizes the Earth as a chemically closed system?
It involves the exchange between all atoms on the planet.
What are the key components of a good hypothesis?
Testability, verifiability, and predictive power.
What does the Theory of Plate Tectonics unify?
It combines observations from continental drift, sea-floor spreading, fossil distributions, seismology, and volcanology.
What challenges are unique to geology compared to other sciences?
Challenges include appropriate observations, problems with scale, originality, missing data, technology, time, and parsimony.
What is cosmology?
The study of the structure and evolution of the Universe.
Who proposed the geocentric model of the Universe?
Ptolemy in Alexandria, Egypt (100-170 C.E.).
What model did Nicolaus Copernicus propose?
The heliocentric model of the Universe.
What did Galileo's telescopic observations contradict?
The geocentric hypothesis.
What significant distance did 17th-century astronomers calculate?
The distance between the Sun and Earth is approximately 149,600,000 km (about 93,000,000 miles).
What is a light year?
The distance that light travels in one Earth year, approximately 9.5 trillion km.
What evidence did Edwin Hubble provide about the Universe?
He observed that light from distant galaxies exhibits a red shift, indicating the Universe is expanding.
What is the Big Bang theory?
The widely accepted theory that the Universe began from a hot and dense singularity that expanded rapidly.
What are coronal mass ejections (CME)?
Solar material spread throughout the Universe, different from solar flares.
What is a nebula?
Interstellar clouds of dust and gases that are expressions of stellar birth and death.
What does the Nebular Hypothesis explain?
It states that the solar system condensed from a rotating nebula.
What are chondrites?
Stony meteorites that provide information about the origin and age of the solar system.
What is the Heliosphere?
The region of space where solar wind significantly influences, encompassing the entire solar system.
What is the Kuiper Belt?
A disc-shaped region of icy bodies, including dwarf planets and comets, beyond the orbit of Neptune.
What happens to planets as they move farther from the Sun?
They become larger and more gaseous.
What is the relationship between a planet's distance from the Sun and its density?
Planets are smaller and denser when they are closer to the Sun.
What creates Earth's magnetic field?
The molten metal in the Earth's core spinning creates the magnetic field.
What is the magnetosphere?
The region of space where Earth's magnetic field dominates over interstellar magnetic fields.
What are the Van Allen Belts?
Belts of trapped particles that protect life on Earth from dangerous radiation.
What is atmospheric pressure also known as?
Barometric pressure.
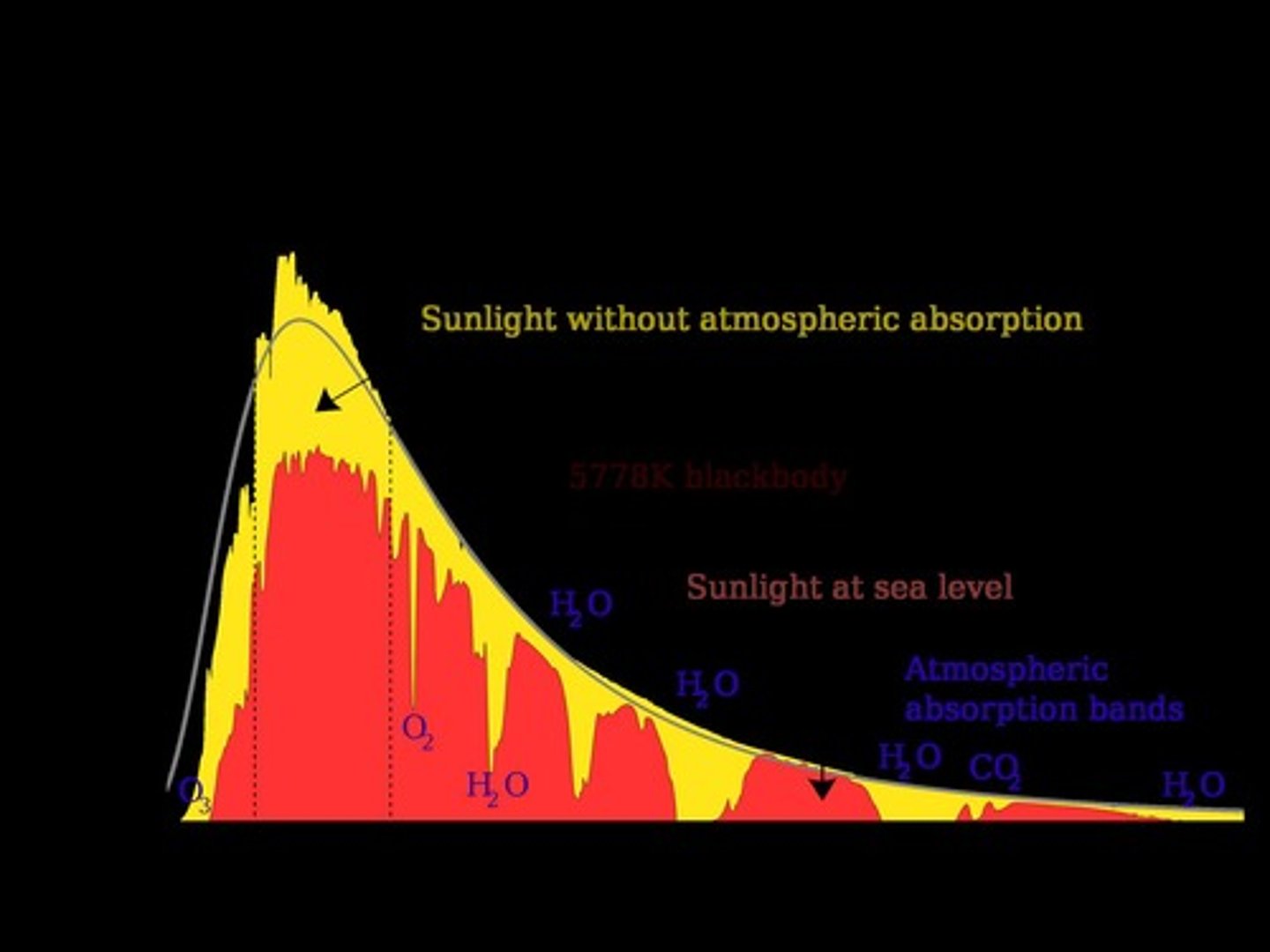
What is the average atmospheric pressure at sea level?
1 atm = 1.01 bars or 14.7 psi.
What is topography?
The physical features of the land surface represented by changes in elevation.
What does the lithosphere consist of?
All of Earth's rock and sediments.
What is the hydrosphere?
Water on Earth, including both surface and groundwater.
What is the cryosphere?
The portion of Earth where water is in solid form, including snow, ice, and glaciers.
What does the biosphere include?
The planet's living organisms and the abiotic parts they interact with.
What was the early Earth like?
It was very different and inhospitable, with constant volcanism and a lack of liquid water.
What gases were present in Earth's first atmosphere?
Mostly hydrogen (H) and helium (He).
What was the second atmosphere composed of?
Gases from differentiation, outgassing, and impacts, including water, nitrogen, CO2, and methane.
What is the average density of Earth?
Approximately 5.5 g/cm³.
What are the two types of Earth's crust?
Oceanic crust and continental crust.
What is the thickness of the continental crust?
25 to 70 km thick, typically granitic in composition.
What is the thickness of oceanic crust?
7 to 10 km thick, thinnest at mid-ocean ridges and thickest at the shelf.
What is the mantle composed of?
Iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg) rich material, making up 84% of Earth's volume.
What is the core primarily made of?
Iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni), with a density up to about 13 g/cm³.
What is the significance of pillow basalts?
They provide evidence for the existence of liquid oceans on early Earth.
When is the first evidence of life on Earth?
Approximately 3.5 to 4.0 billion years ago.
What is the carrying capacity of Earth?
The ability for Earth to sustain its population at a basic, healthy, moderately comfortable style of living.
What was Alfred Wegener's hypothesis about continental drift?
Continents were once a large land mass called Pangea that has since drifted apart.
What are the three types of stress in geology?
Compressive (squeezing), tensional (pulling), and shearing (sliding past).
What is strain in the context of geology?
The deformation resulting from stress, which can be elastic or permanent.
What is strain in geological terms?
The deformation resulting from stress, indicating a change in shape.
What is elastic deformation?
A temporary strain where the shape is recovered after the stress is removed.
What is plastic deformation?
Permanent deformation that occurs once the elastic limit has been exceeded.
What does rupture refer to in geology?
The limit of strength where a material breaks or fractures.
How does temperature affect rock behavior?
Rocks behave more plastically at higher temperatures.
What is the effect of confining pressure on rocks?
Increased confining pressure makes rocks behave more plastically and less brittle.
What is the lithosphere?
The rigid outer layer of Earth, including the crust and elastic upper mantle.
What is the asthenosphere?
A plastic, more ductile layer below the lithosphere, where solid rocks can flow.
What is the relationship between volcanoes and tectonic plates?
Volcanoes are concentrated in belts consistent with tectonic plate boundaries.
What is seafloor spreading?
The process where new crust forms at mid-ocean ridges and moves laterally away.
What is paleomagnetism?
The study of the magnetic properties of rocks to understand Earth's magnetic field history.
What are mid-ocean ridges?
Underwater mountain systems formed as a result of divergent plate boundaries.
What is a subduction zone?
A region where dense oceanic lithosphere slides under lighter continental lithosphere.
What are Benioff zones?
Dipping zones of increased earthquake activity produced within a subducting oceanic plate.
What is the difference between igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks?
Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, sedimentary rocks from compacted sediments, and metamorphic rocks from altered pre-existing rocks.
What is lithification?
The process of turning sediments into rock through compaction and cementation.
Why are most fossils found in sedimentary rocks?
Fossils are often destroyed in the high pressures and temperatures of igneous and metamorphic rock formation.
What are clastic rocks?
Rocks made of clasts held together by cement, formed from fragments of minerals or rocks.
What are crystalline rocks?
Rocks whose crystals grow in place and interlock with each other.
What is metamorphism?
The process of change in rocks due to exposure to intense heat and/or pressure.
What is the rock cycle?
The continuous process where rocks of any type can be transformed into any other type through geological processes.
What is the average rate of movement for tectonic plates?
Typically ranges from 1 to 10 cm per year, with variations among different plates.
What is a rift?
A region where tectonic plates diverge, causing the crust to thin and tear.
What is a transform boundary?
A conservative boundary where tectonic plates slide past one another.
What is the significance of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge?
It is a mid-ocean ridge where tectonic plates diverge, generating new oceanic crust.
What are hotspots in geology?
Stationary areas in the mantle that create volcanic activity as tectonic plates move over them.
What is missing from Earth's second atmosphere?
Oxygen (O2)
The avg density of Earth exceeds that of its surface rocks. Why?
Because Earth differentiated
What fossil provided strong evidence that the continents were once amalgamated?
Fossils of Glossopteris
What factor is NOT related to strain?
weight