BCS 111 Midterm Review
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Frontal lobe functions
language production, motor control, cognitive control/self-processing
Temporal
auditory processing, language comprehension, object/face recognition
Parietal
attention, primary somatosensory cortex
Occipital
visual processing
Limbic system and their functions
-
Thalamus
relays info to cortex
Hypothalamus
regulation of thirst, hunger, desire, and temperature
Hippocampus
memory
Amygdala
emotion
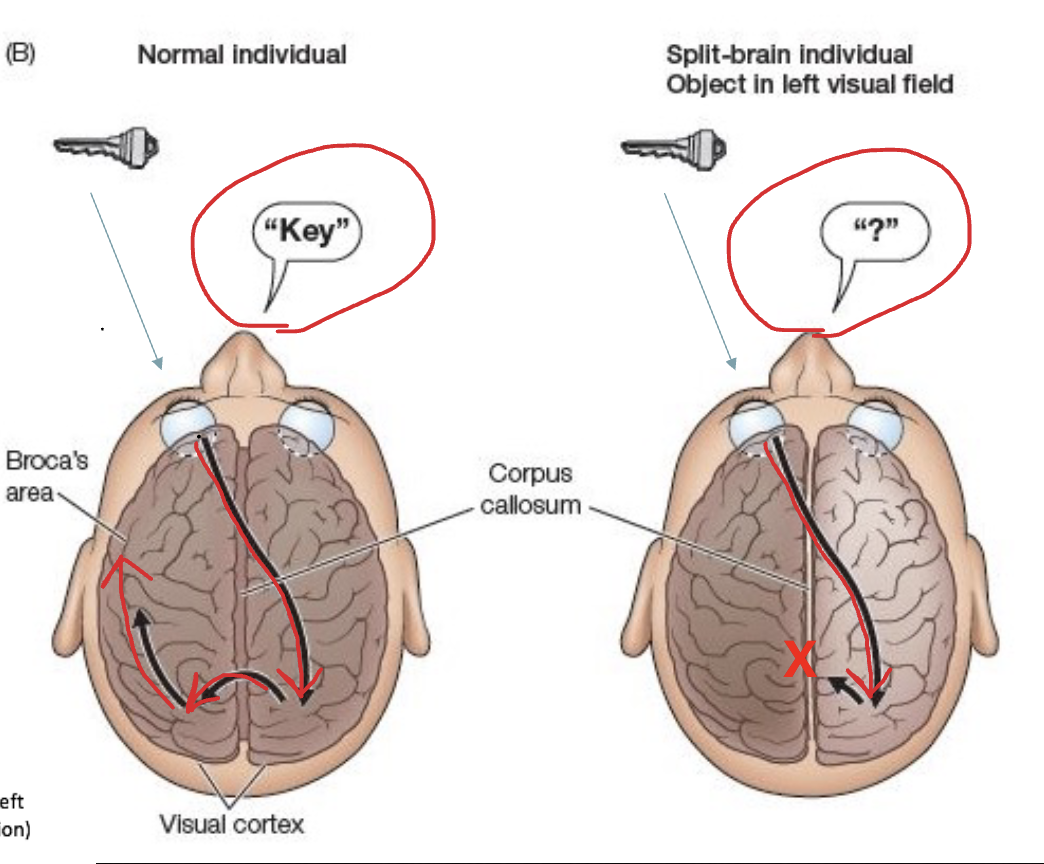
Lateralization

example
Evolution of brain functions: Implications of Petersson et al’s (2012) fMRI study
Learning of sequences: similar to learning a language
Processing of artificial grammar is similar to that of real linguistic sequences
(cont)
Implicit learning of sequences without
prior knowledgeOriginal function of Broca’s area: potentially a region for general sequential processing
Memory chart
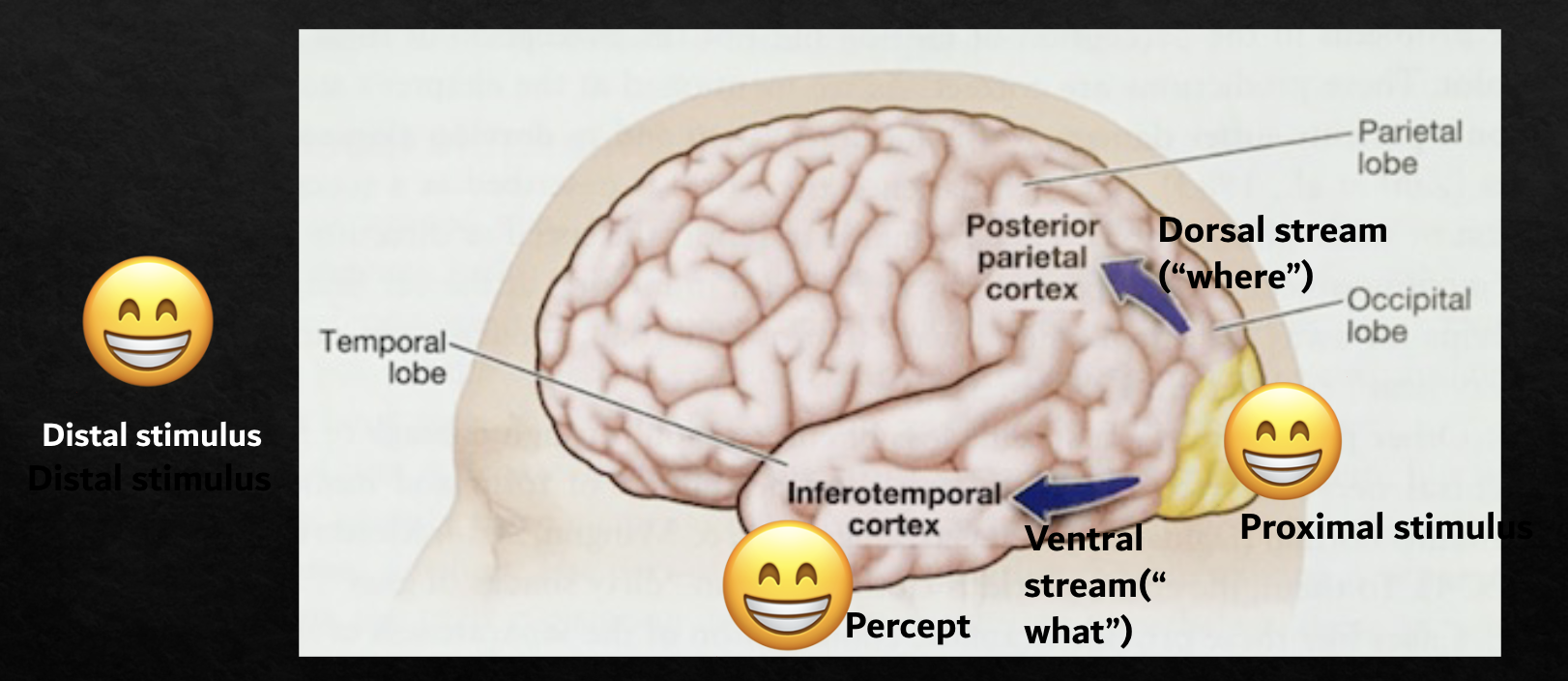
Typical visual perception stages
Distal stimulus → Proximal stimulus (processed in Visual Cortex) → Percept (processed in Temporal cortex)
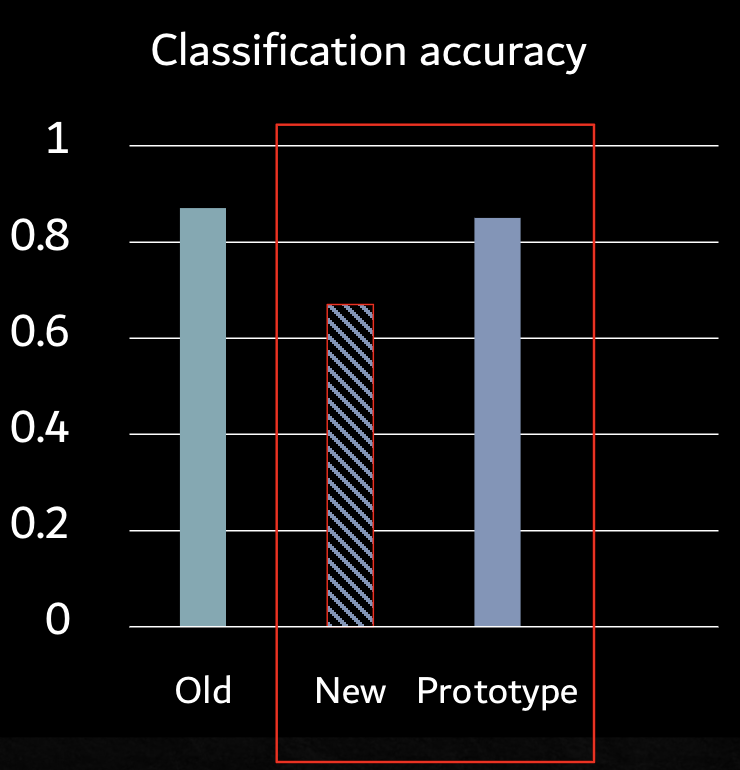
Evidence for prototype: Posner and Keele
Goal of the study: to see if we can form a prototype by getting exposed to a large amount of exemplars
One example: seeing a bunch of distorted/blurry faces (exemplars) and see if you can figure out what the “original” face (prototype) looks like
Training: present one pattern at a time (each pattern is derived from one of the 4 original prototypes)
Classification task
Compare one dot pattern to the other 4 patterns that were derived from 4 different prototypes (feedback provided)
Testing
Three types of stimuli: new distortions (not seen before), old distortions, original prototype (not seen before)
Classification task: same as in training
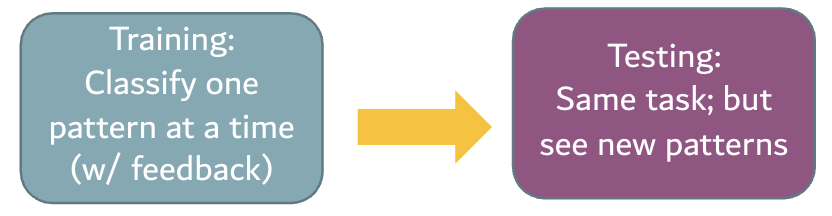
Key points from Posner and Keele’s study
Same task in both training and testing
Feedback given only during training
NO feedback during testing
Conclusion: prototype formed during training
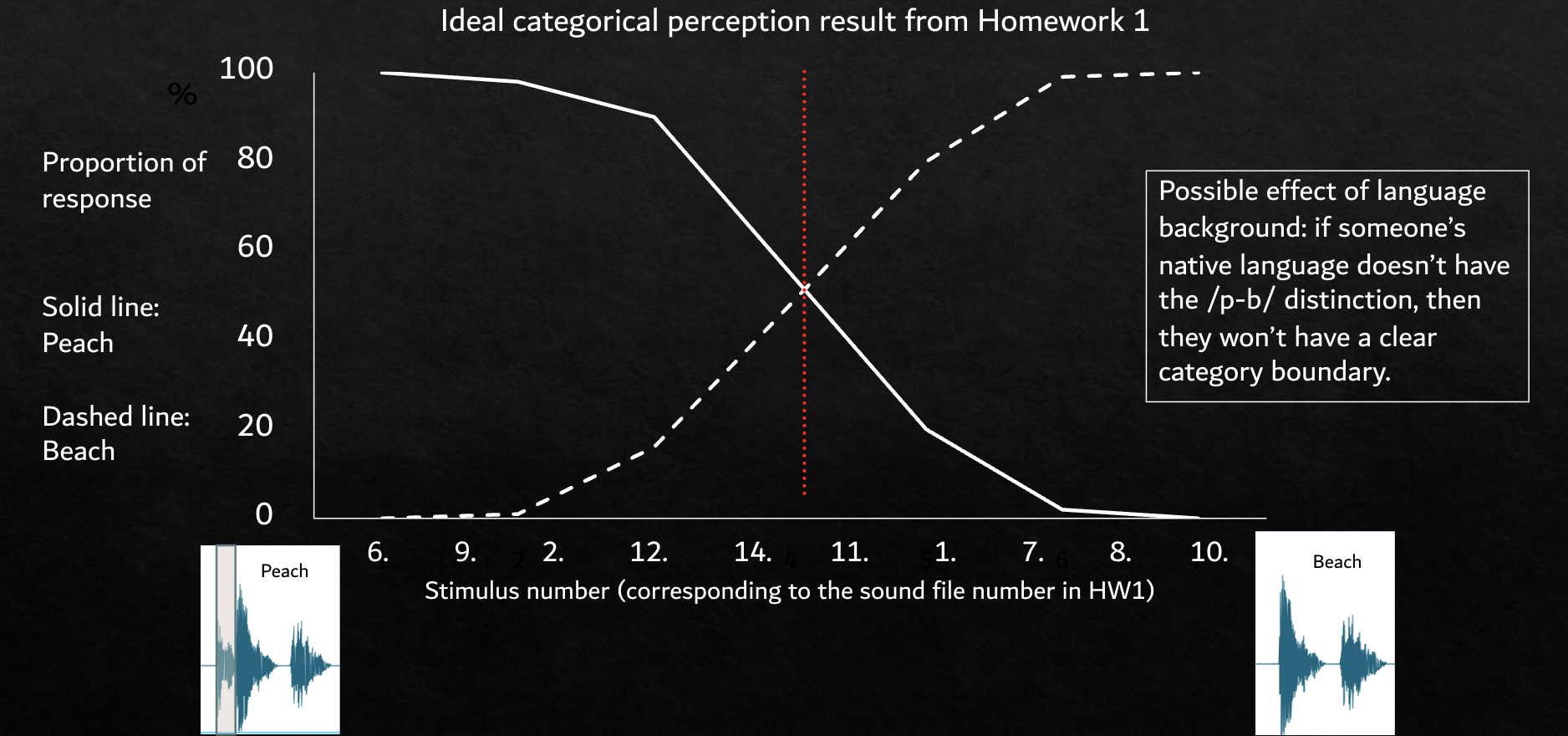
Categorical Perception
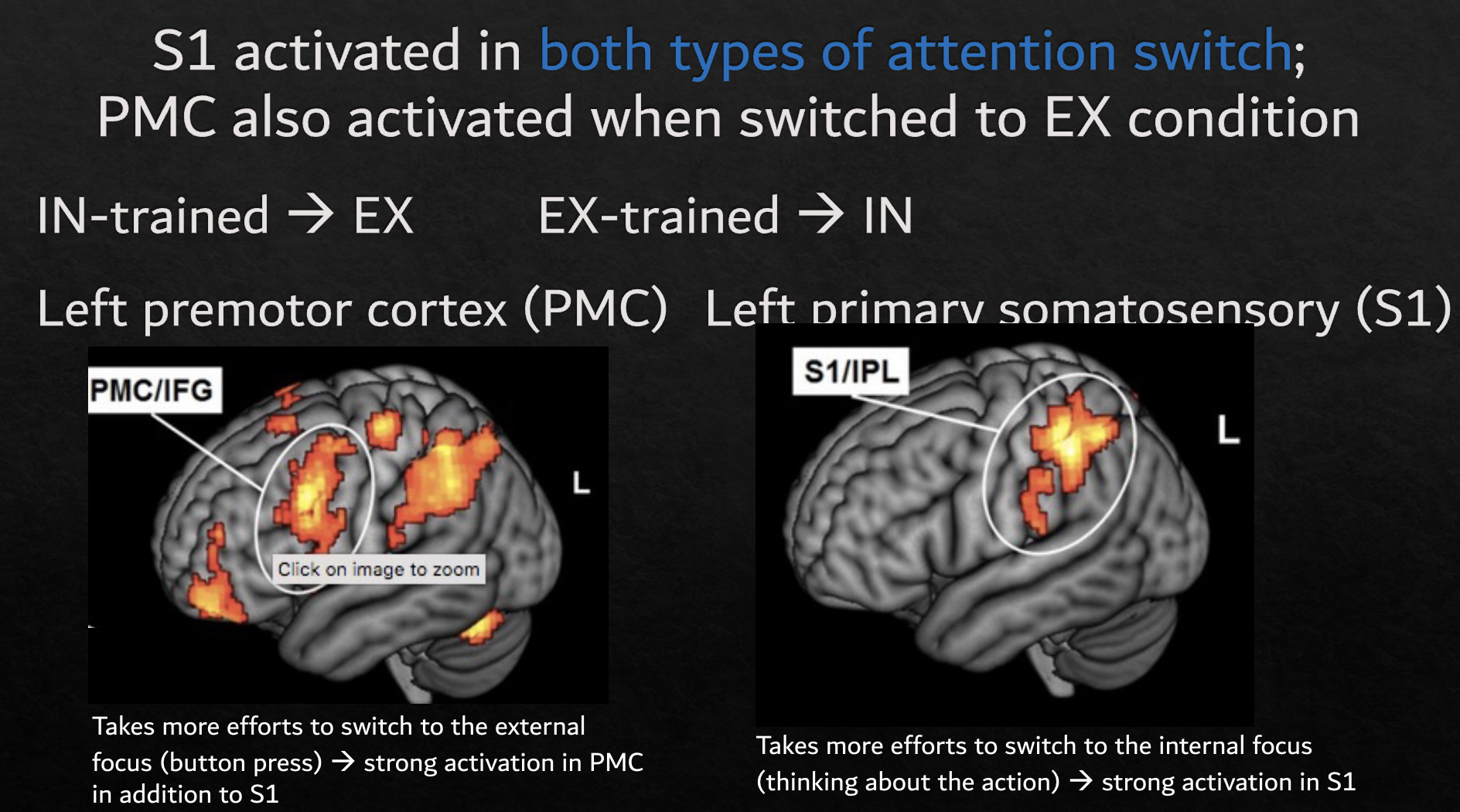
Evidence against the filter theory: When we notice something from the unattended ear in the DLT task
When message in the unattended ear
In English but with an “oddball” (reversed speech)
In English and with our name
Continues the message from the unattended ear (“switch ear”)
They’re also examples of top-down processing
brain activation
How to test “automatic processing”
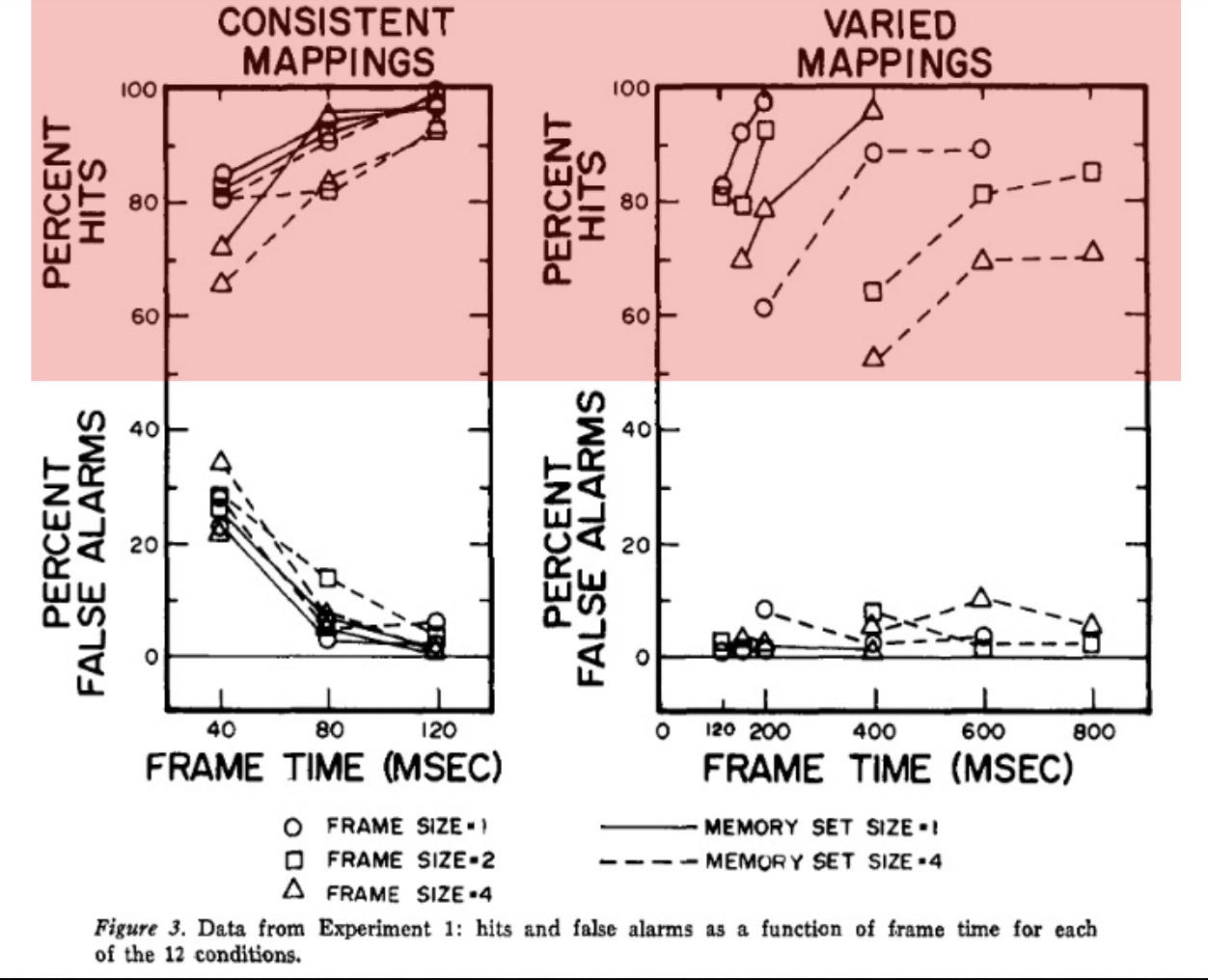
Four independent variables
Varied vs consistent
Varied - the target in the current trial could become a distractor in another trial
Consistent - the target won’t become a distractor in another trial (because they are different types: letter vs number)
the other 3
Frame size (e.g. size of crowd) - # of letters/numbers in each display
Frame time (duration) - 20-800ms
Memory set size - number of targets
Study
Consistent mapping - ONLY thing that matters is frame time
Varied mapping - all variables have an affect
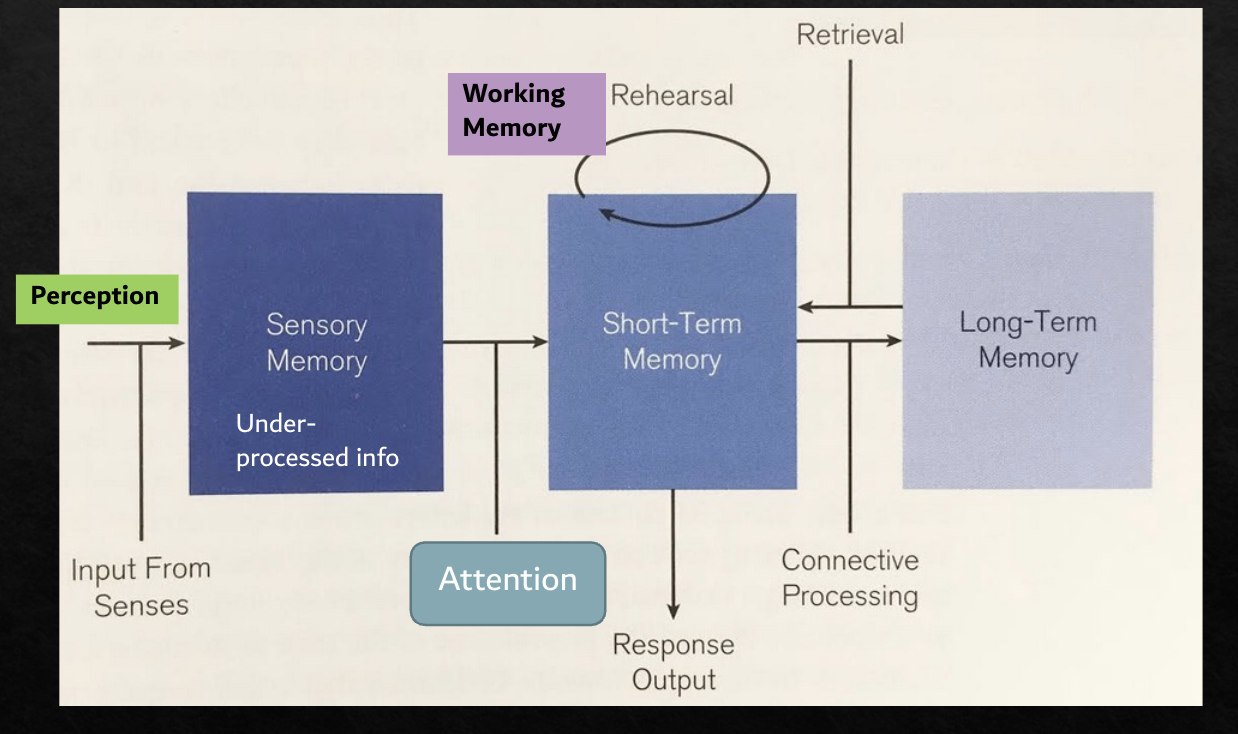
Sensory memory
Initial and brief storage of (under-processed) sensory input
Testing processing and short-term storage capacity
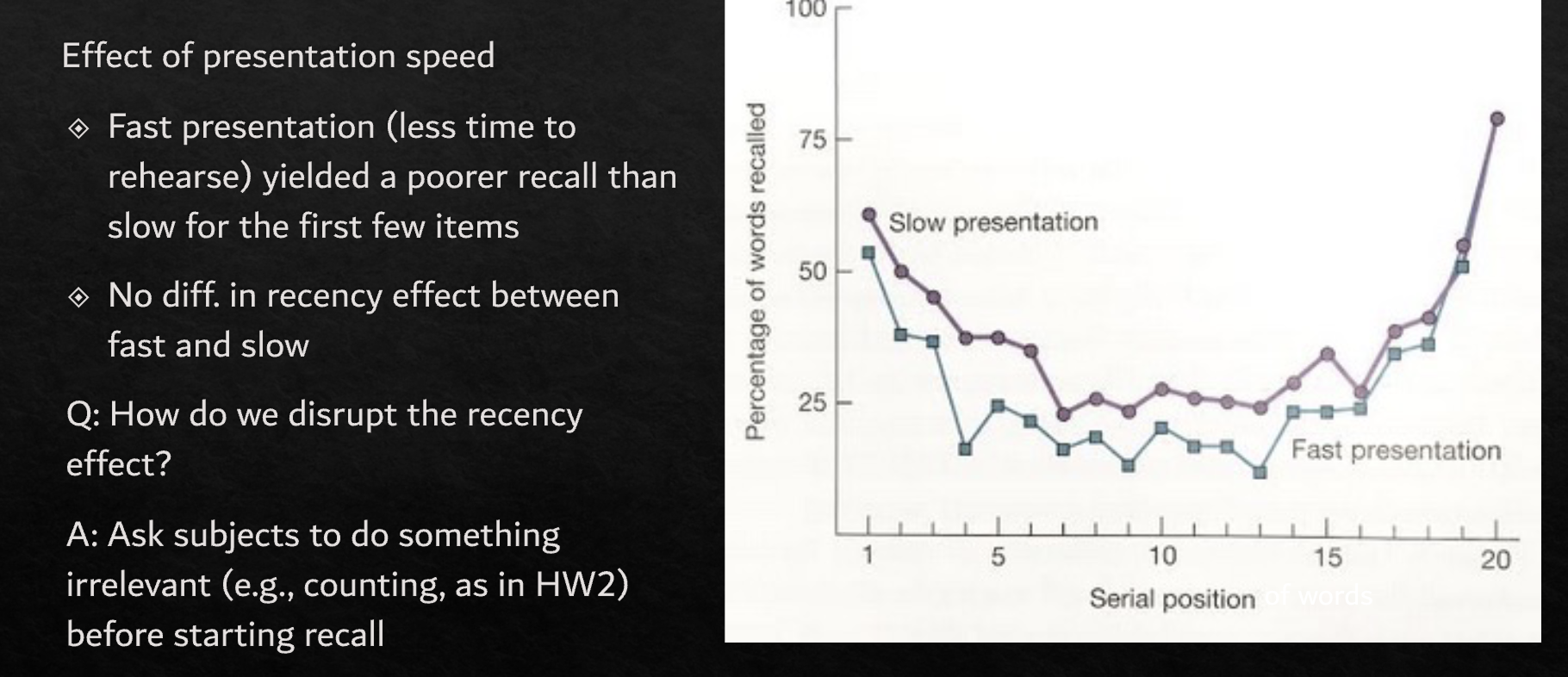
Forgetting
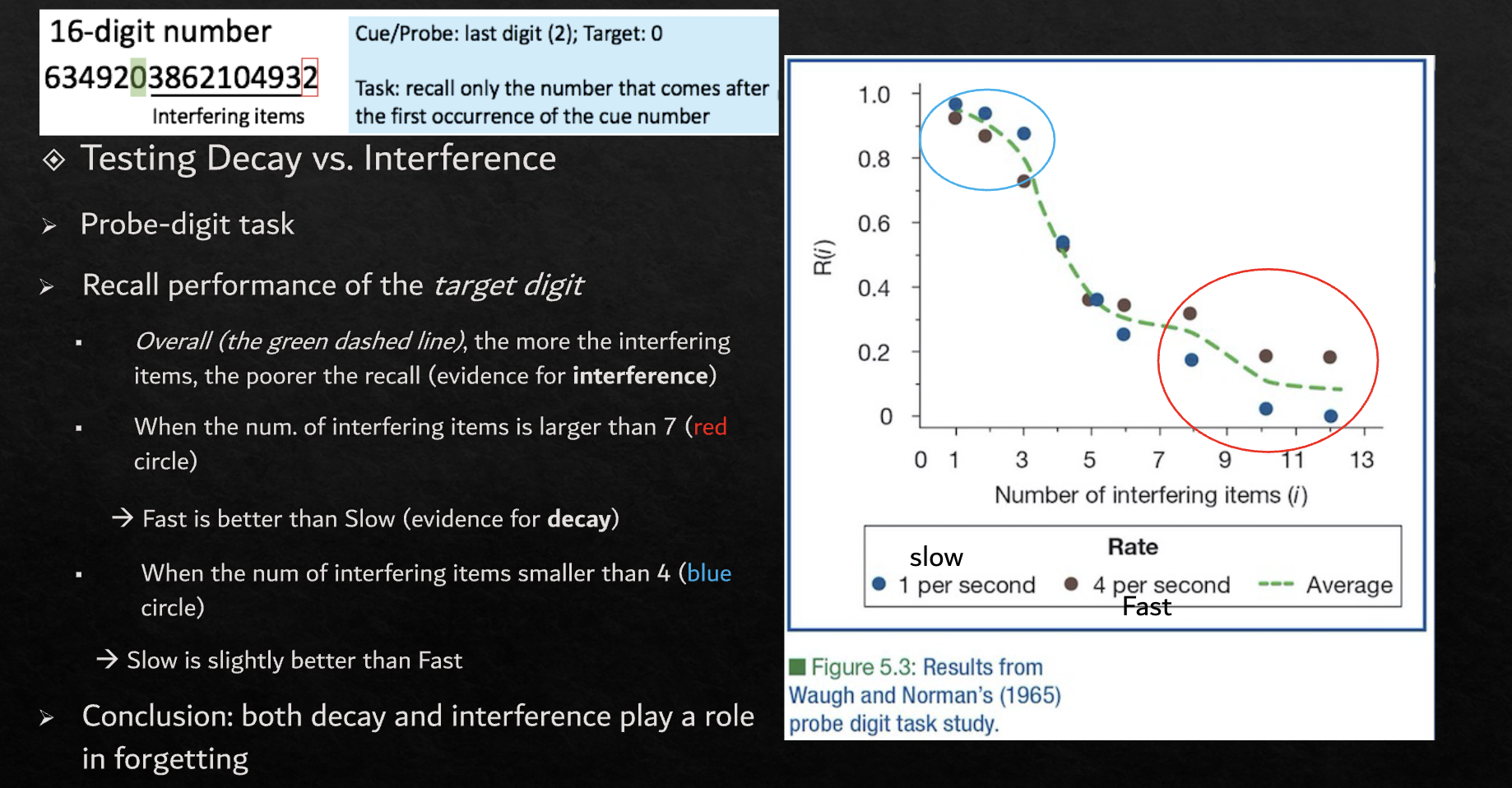
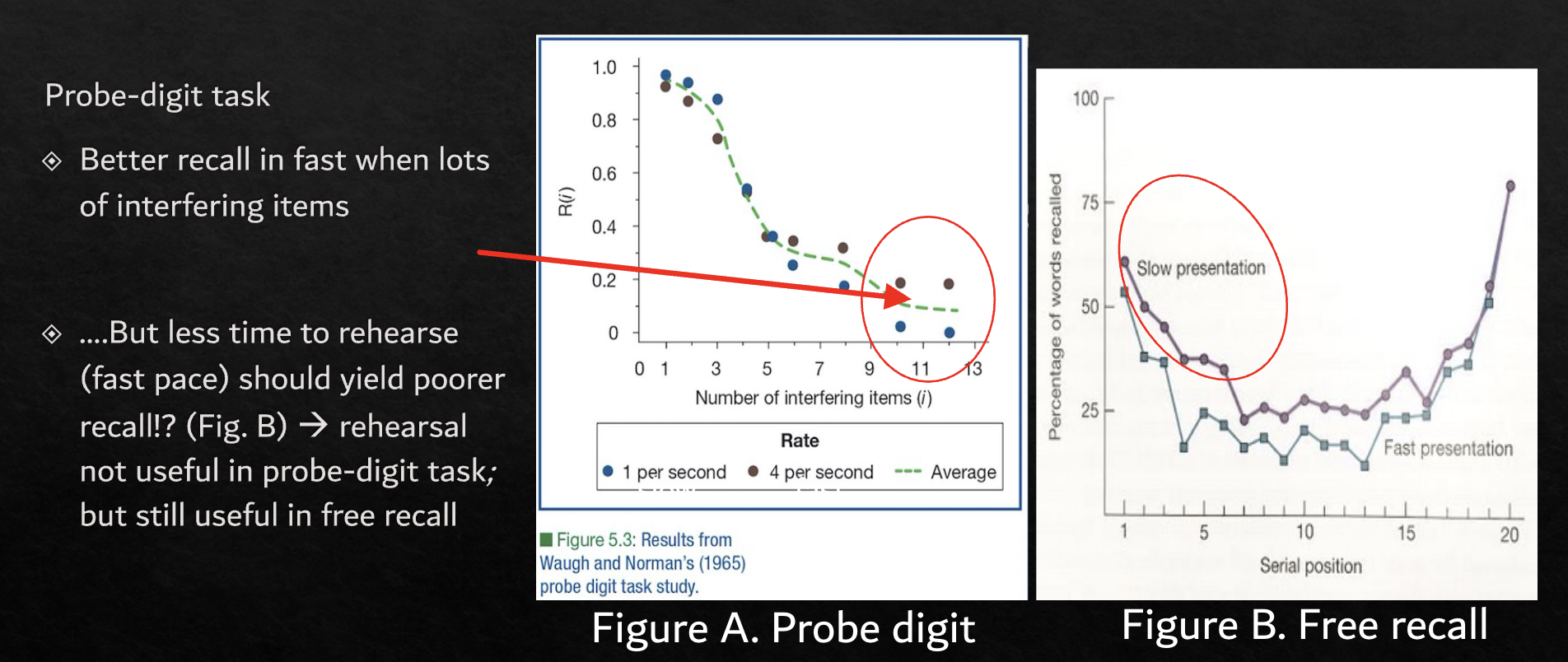
Is rehearsal useful in all tasks? Not necessarily
In probe digit - slower presentation hindered performance
In free recall - it helped performance
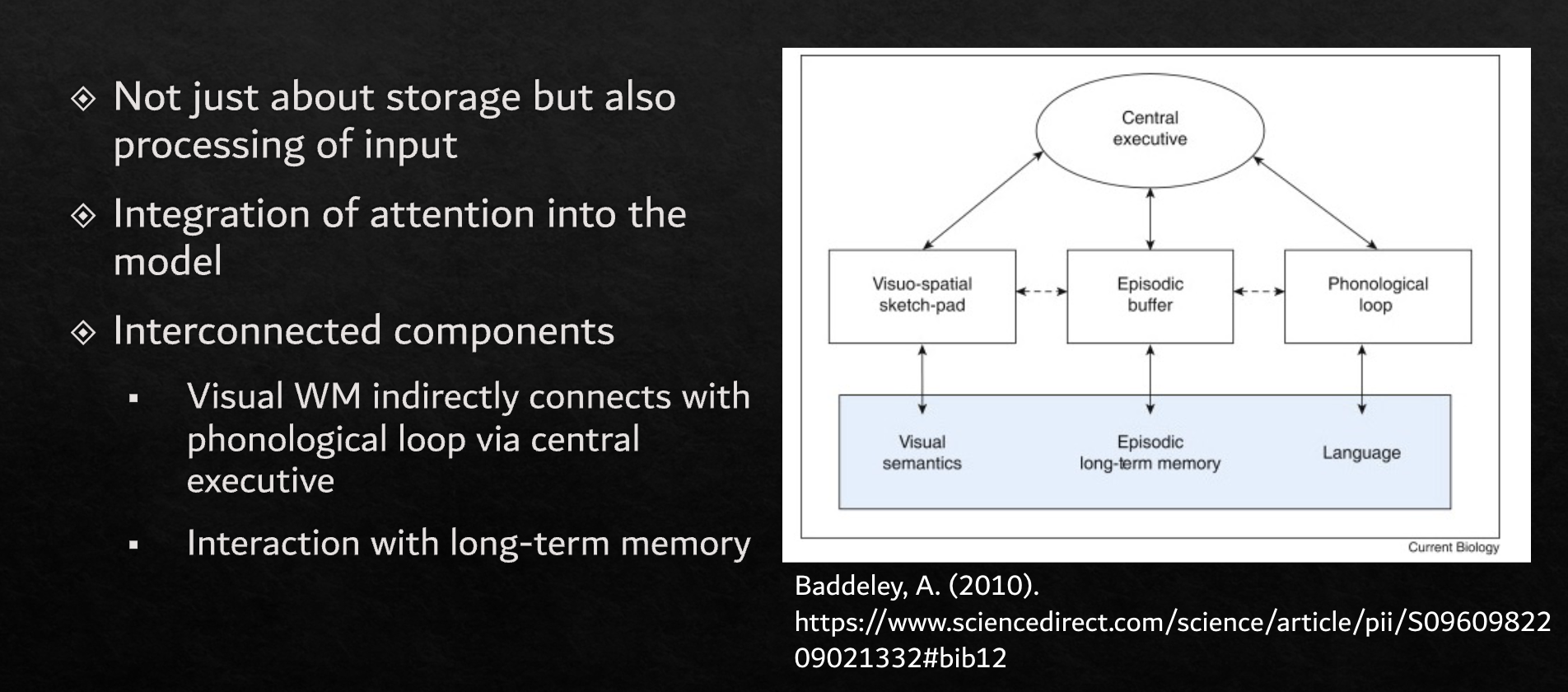
Working memory
Visio-spatial sketch-pad → visual semantics
Episodic buffer → episodic long-term memory
Phonological loop → language