5.3- Explaining & Classifying Psychological Disorders
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
3 Ds
Dysfunction, Distress, Deviance from norms
Dysfunction
Behavior interferes with daily functioning
Distress
Personal suffering disturbing to self
Deviation from Norms
Behaviors and emotions that differ significantly from what is considered appropriate or typical for a social group
Stigma
The perception that a certain attribute makes a person unacceptably different from others
Racism
Discrimination based on race
Sexism
Discrimination based on gender
Ageism
Discrimination based on age
Discrimination
Unjustifiable negative behavior toward a group and its members
Culture-Bound Disorder
Abnormal syndromes found only in a few cultural groups
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
Classifies and describes disorders (APA)
International Classification of Mental Disorders (ICD)
Mental & physical health coding on global scale (WHO)
Eclectic Approach
An approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the client's problems, uses techniques from various forms of therapy
Behavioral Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive learned associations between or among responses to stimuli
Psychodynamic Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on unconscious thoughts and experiences, often developed during childhood
Humanistic Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on a lack of social support and being unable to fulfill one's potential
Cognitive Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive thoughts, beliefs, attitudes, or emotions
Evolutionary Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on behaviors and mental processes that reduce the likelihood of survival
Sociocultural Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on maladaptive social and cultural relationships and dynamic
Biological Perspective on Disorders
The causes of mental disorders focus on physiological, neurotransmitter, or genetic issues
Biopsychosocial Model on Disorders
Assumes that disorders are influenced by genetic predispositions and physiological states (biological), inner psychological dynamics (thoughts), and social and cultural circumstances (environment)
Diathesis-Stress Model
States that the onset of mental illness involves the interaction of two key factors: a genetic predisposition and an environmental stressor of some kind
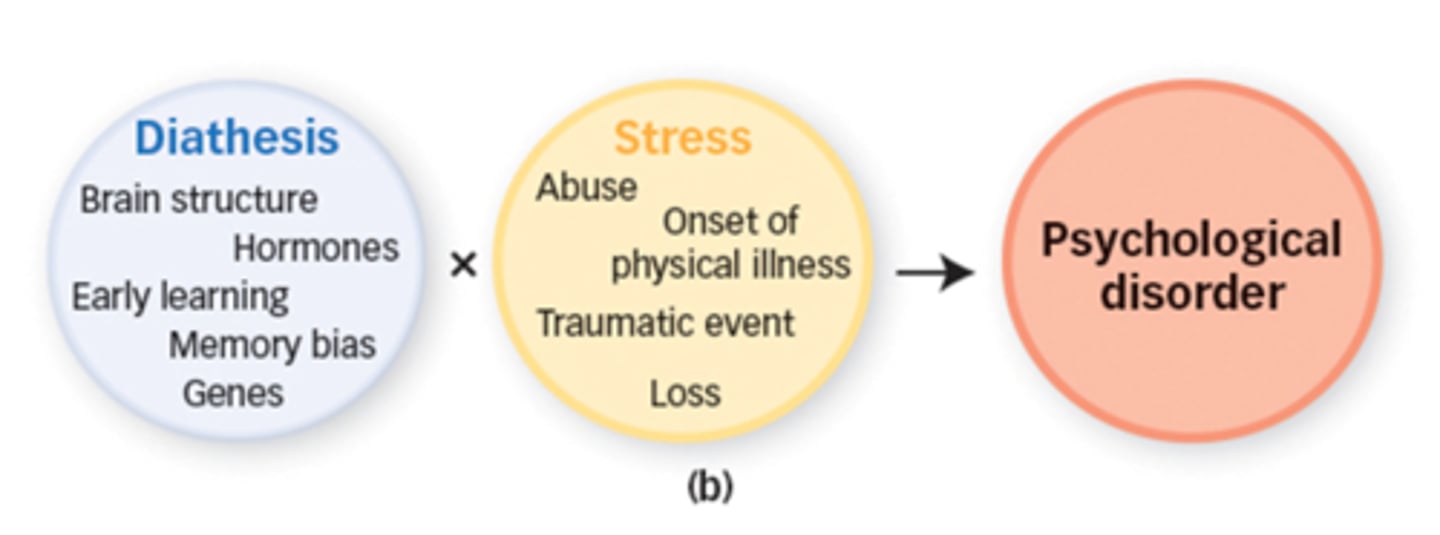
Diathesis
Predisposition for a certain disease
Stress (Diathesis-Stress Model)
Environmental stress or trauma