Unit 6: Classification of Matter, Periodic Table and Atomic Theory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Matter
Particles
Pure substance
1 type of particle
Can’t be physically separated
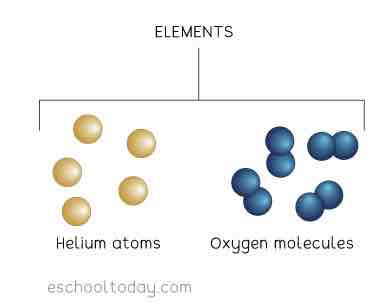
Element
1 type of particle
1 type of atom
Diatomic element
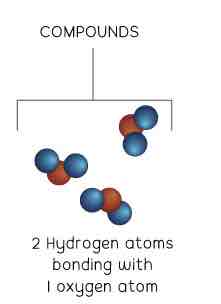
Compound
1 type of particle
More than 1 type of atom bonded to another atom
Mixture
2 or more different types of particles
Cab be physically separated
Heterogeneous
Unevenly mixed
Can identify different particles
Homogeneous
Evenly mixed
Can’t identify difference particles

Atomic number
Number of protons
Atomic mass
Average of atomic mass exiting
Protons + neutrons
Democritus
First to suggest the existence of atom
Invisible
Dalton’s Model
All elements are composed of tiny indivisible and indestructible particles called atoms
Atoms of the same element are identical.
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed.
Atoms of different elements can combine in whole number ratios to form compounds.
What is wrong with Dalton’s Model?
Atoms of the same elements are identical is wrong because there are isotopes
Cathode Ray tube experiment
Evidence: When a magnetic field was brought near the cathode ray tube, the beam was deflected
Conclusion: The subatomic particles making up the beam must be negatively charged
The cathode ray tube experiment involved a sealed glass tube with a vacuum, where high voltage was applied across two metal electrodes. This produced a beam of cathode rays traveling from the negative electrode to the positive electrode (anode). Thomson observed that the rays were deflected by electric and magnetic fields, proving they were negatively charged particles.
Ernest Rutherford
Predicted that if Thomson’s model was correct the a particle would go straight through atoms
Conducted gold foil experiment
Rutherford’ Gold Foil Experiment
a beam of positively charged alpha particles was directed at a thin sheet of gold foil. Surrounding the foil was a photographic film, which would emit light when struck by the particles. By observing the flashes of light, Rutherford’s team tracked the paths of the alpha particles, noting whether they passed straight through, deflected at small angles, or bounced back. It showed atoms have a small, dense, positively charged nucleus, as most alpha particles passed through the foil while some were deflected at large angles.
James Chadwick’s Model of Nucleus
Model: discovered the neutrally charged neutronlocated in the nucleus
Mass Spectroscopy
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. It works by ionizing chemical compounds, separating the ions based on their mass and charge using electric and magnetic fields, and detecting them.
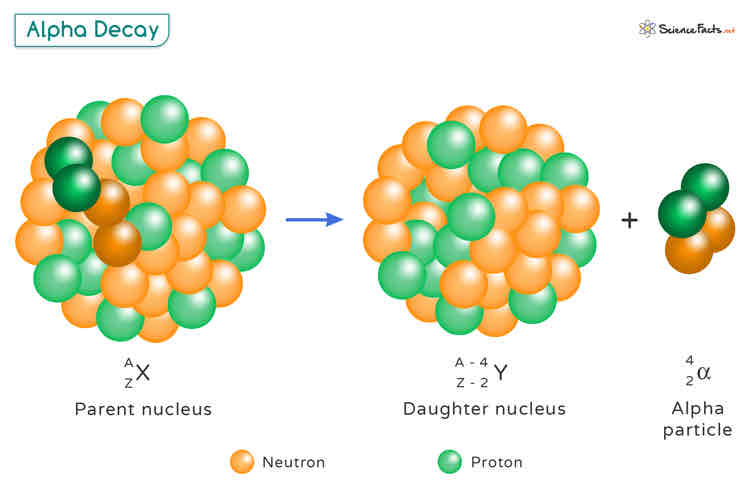
alpha decay