Spine and Thoracic Cage
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
How many vertabrae are there?
33
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
How many sacral vertebrae are there? (forming the sacrum)
5 (fused)
How many coccygeal vertebrae are there? (forming the coccyx)
4 (fused)
What are the most common variations in vertebrae distribution?
shifts between adjacent groups with the same total number (ex. L5 sacralized)
What are the common elements of the presacral (un-fused) vertebrae?
body, vertebral arch, spinous (dorsal) process, vertebral foramen
vertebral canal
all the vertebral foramina of all vertebrae articulating together, contains spinal cord
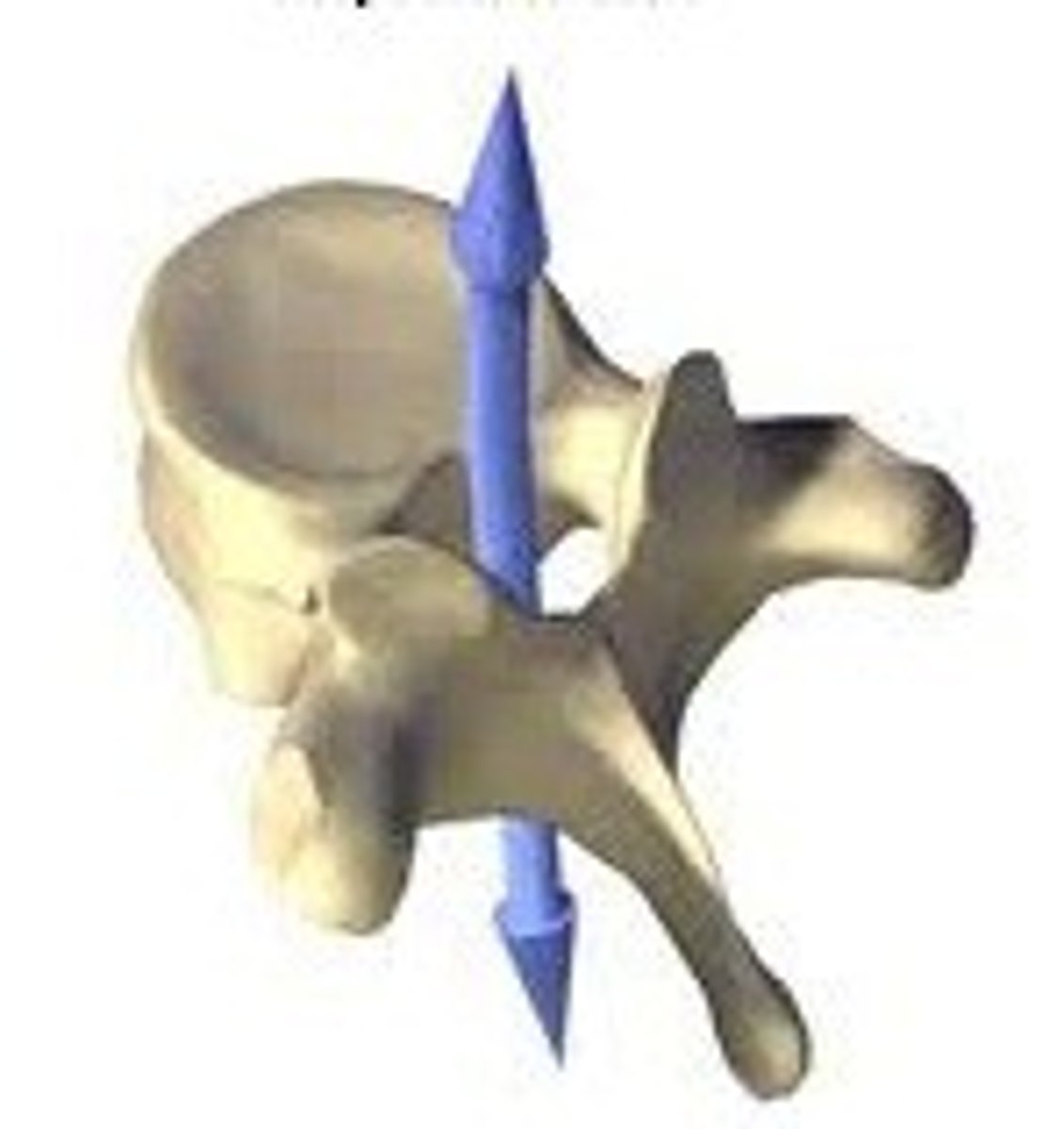
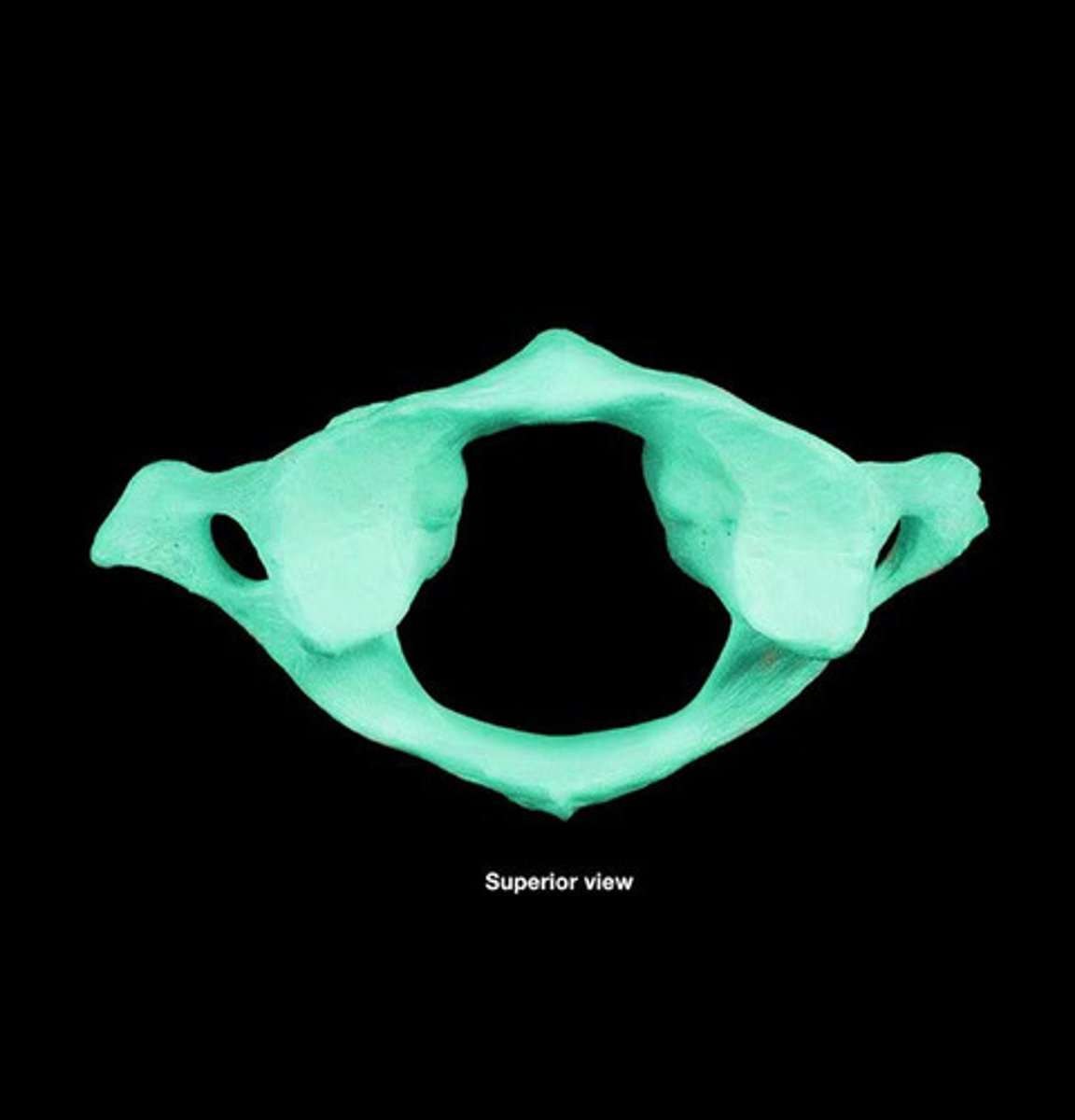
C1 (the atlas)
lacks body and spinous process, allows head to nod
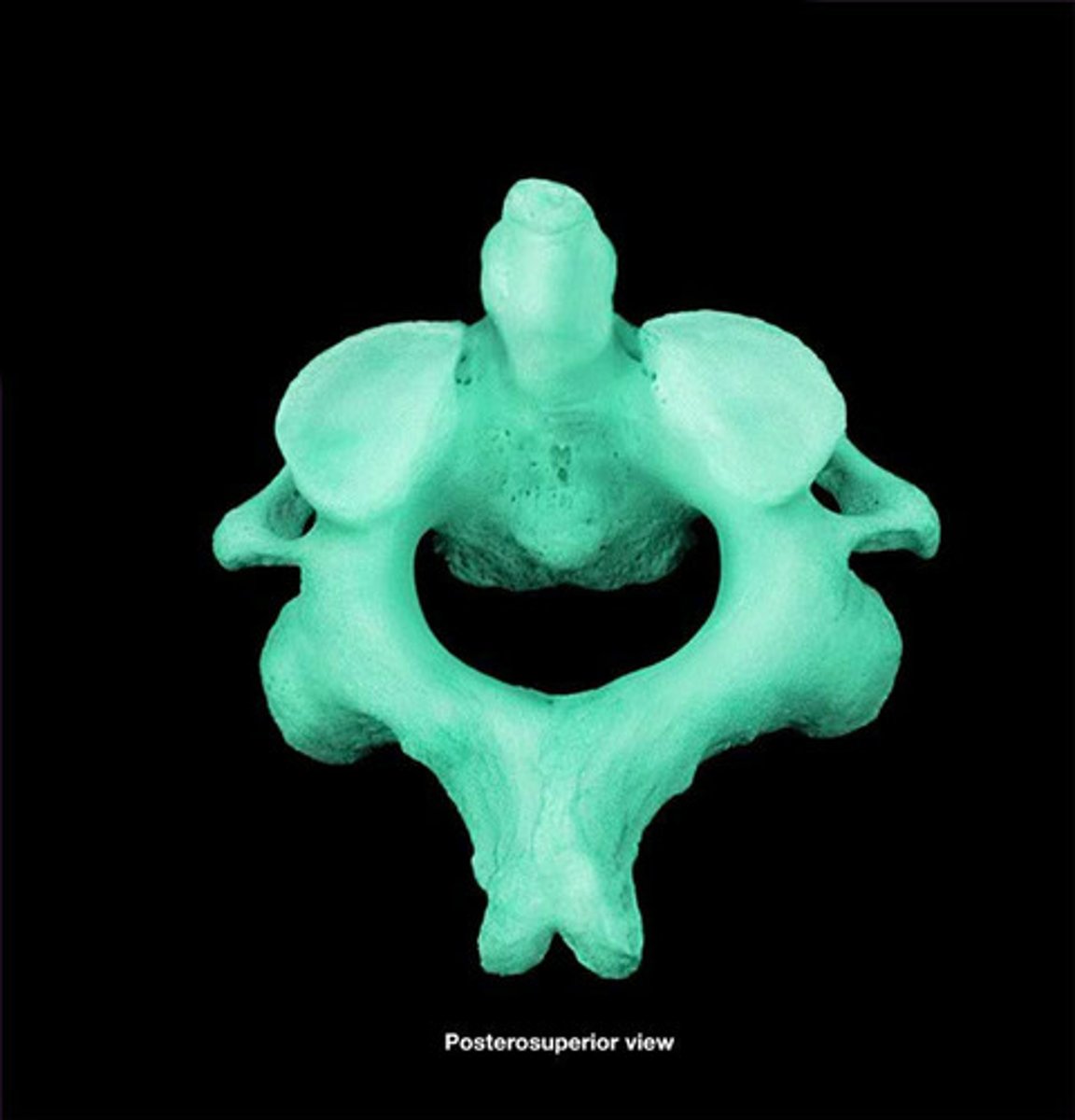
C2 (axis)
Has a dens/odontoid process projecting superiorly from the body, allows head to rotate
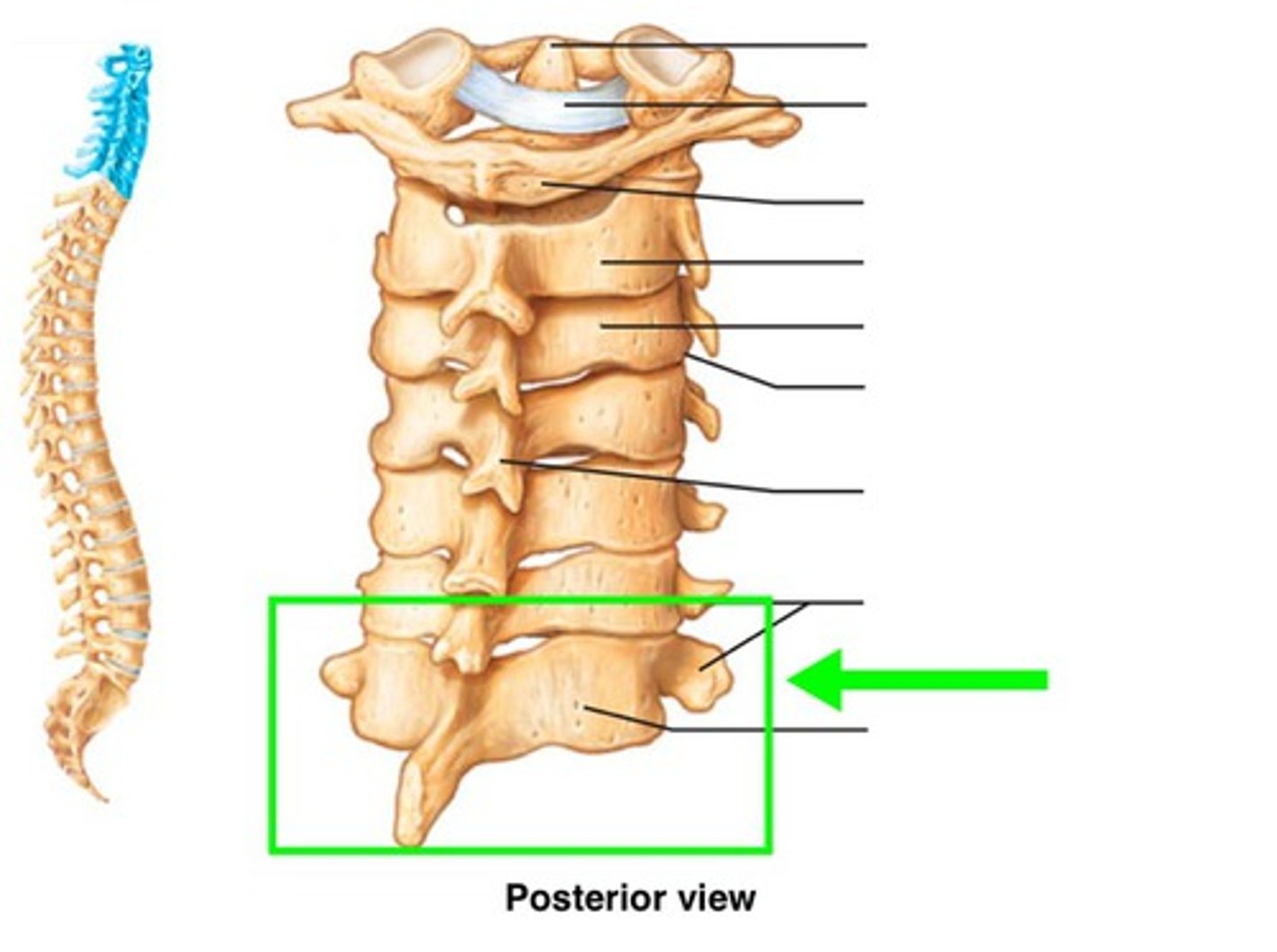
C7 (vertebra prominens)
Long sloping non-bifid spinous process, palpable when neck is in flexion
L4
ankle dorsiflexion
S3
third heart sound, a fused portion of the sacrum
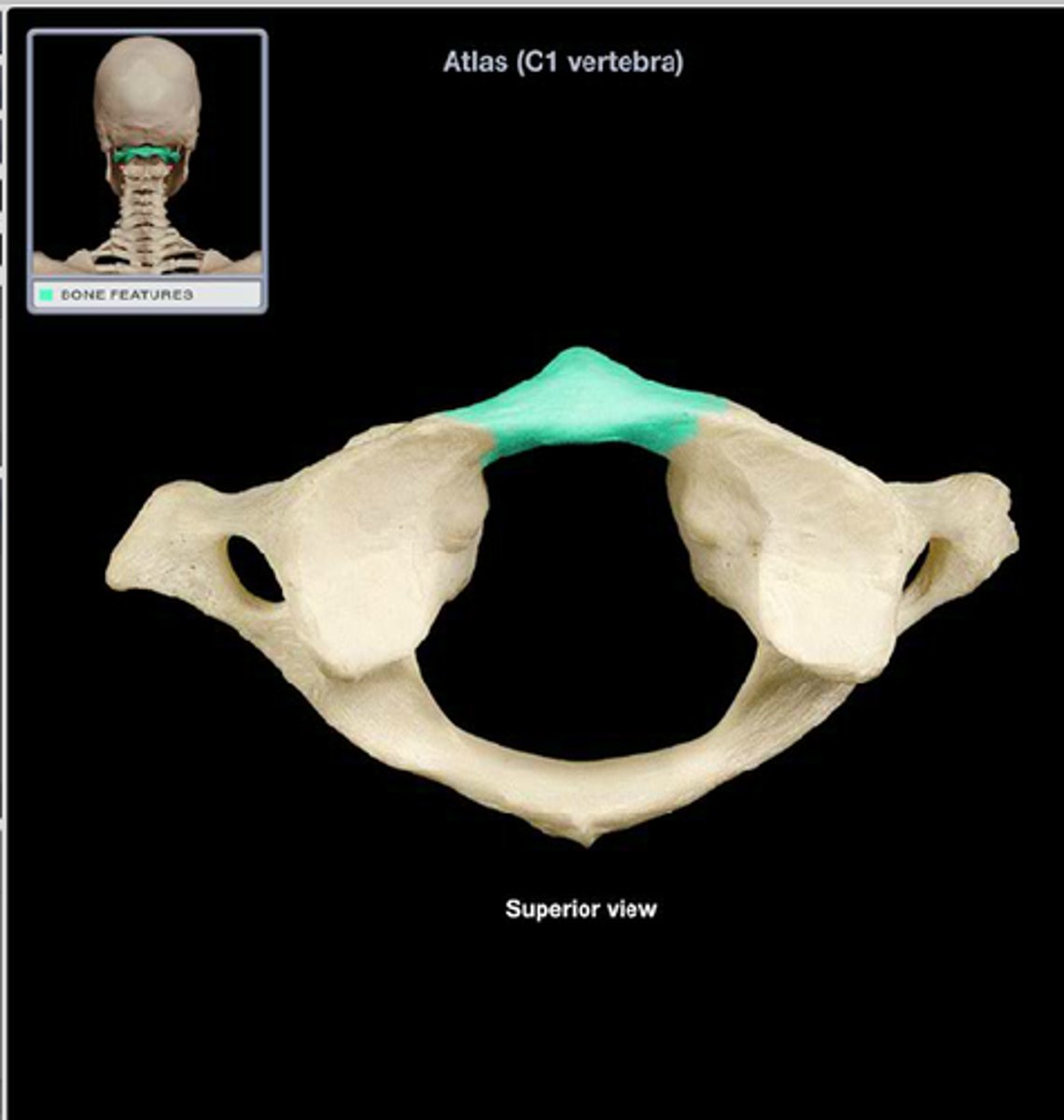
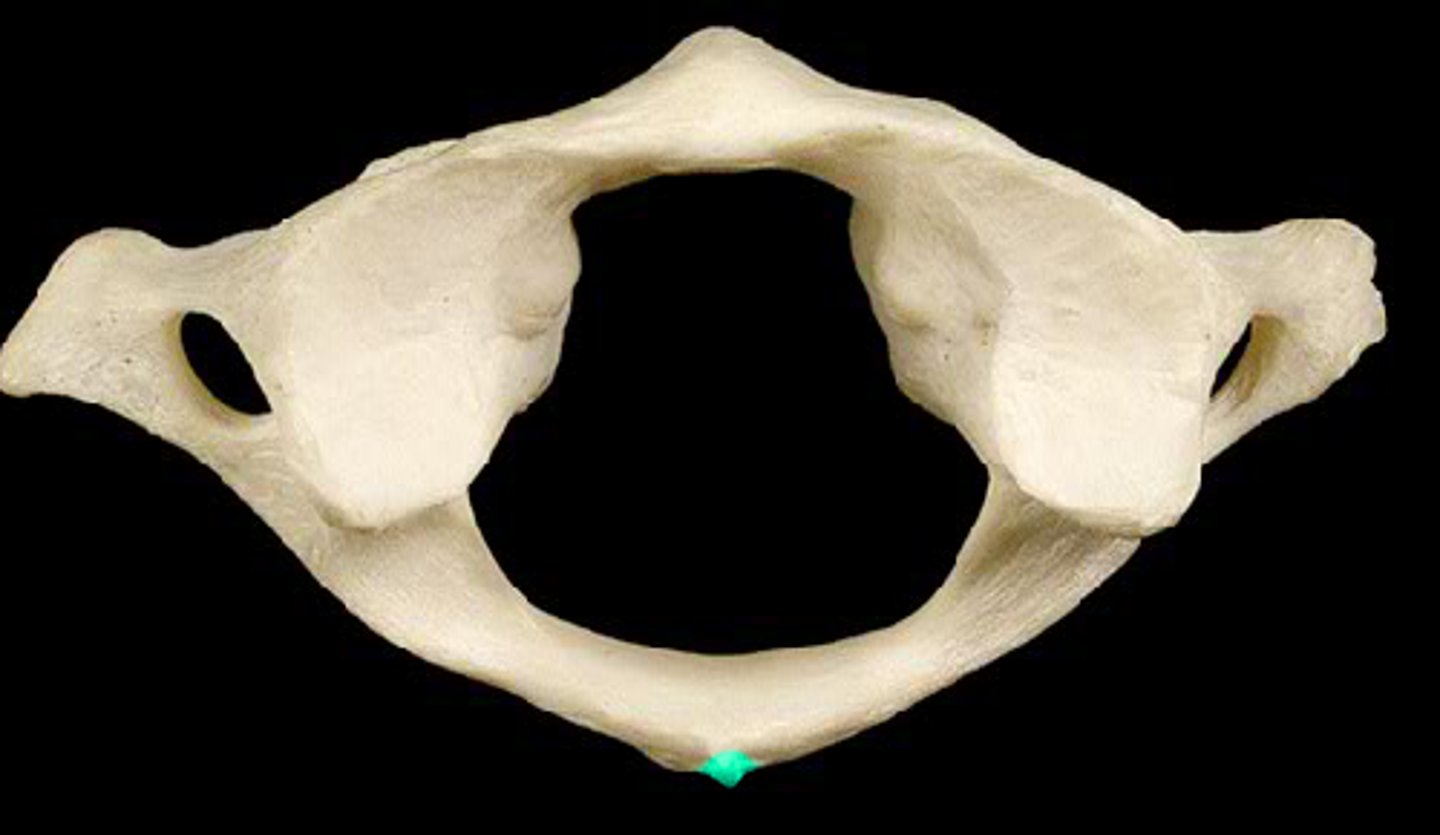
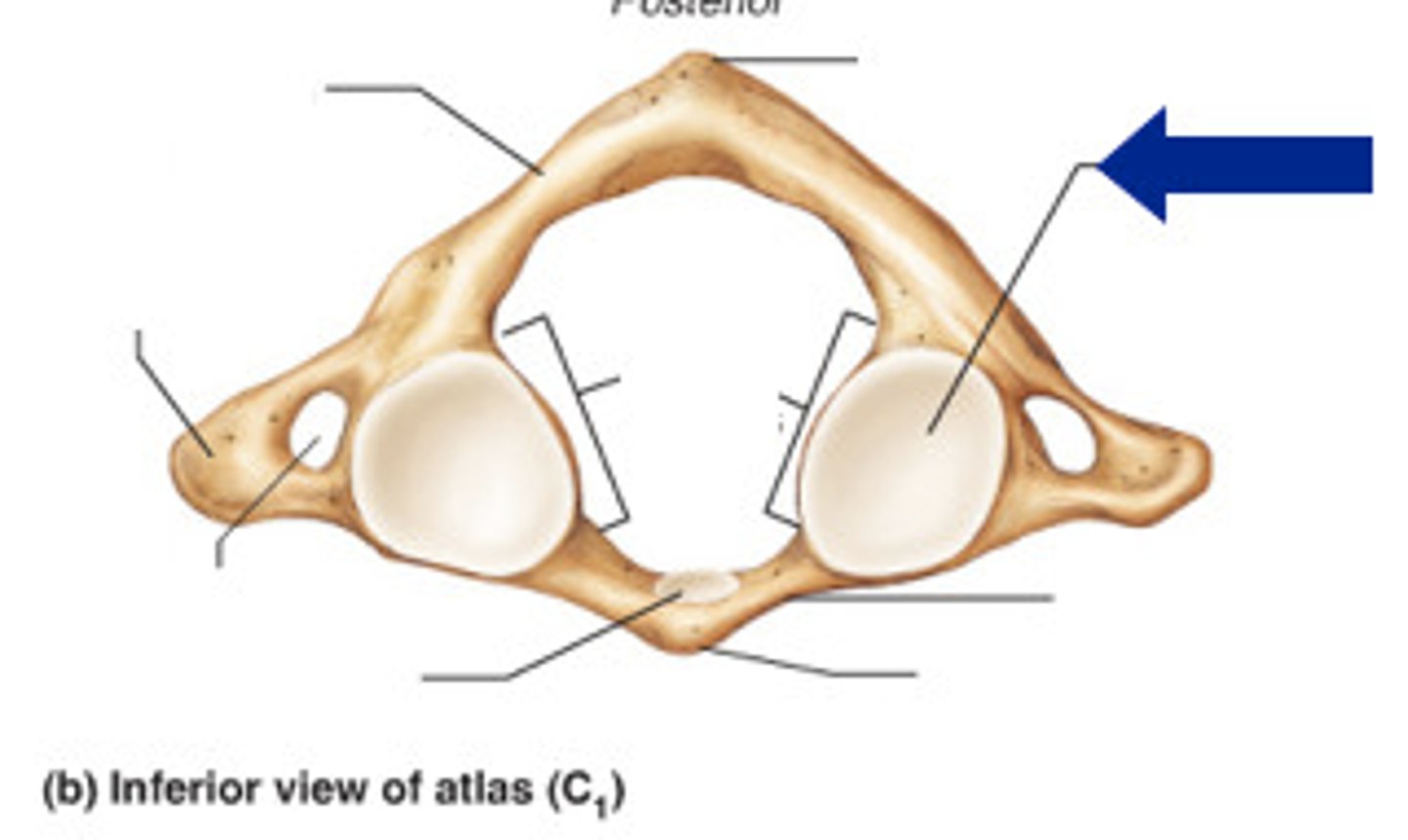
anterior arch of atlas
A small arch on the atlas that would be in the ventral most part of the body. Allows for a ventral articulation with the Dens.
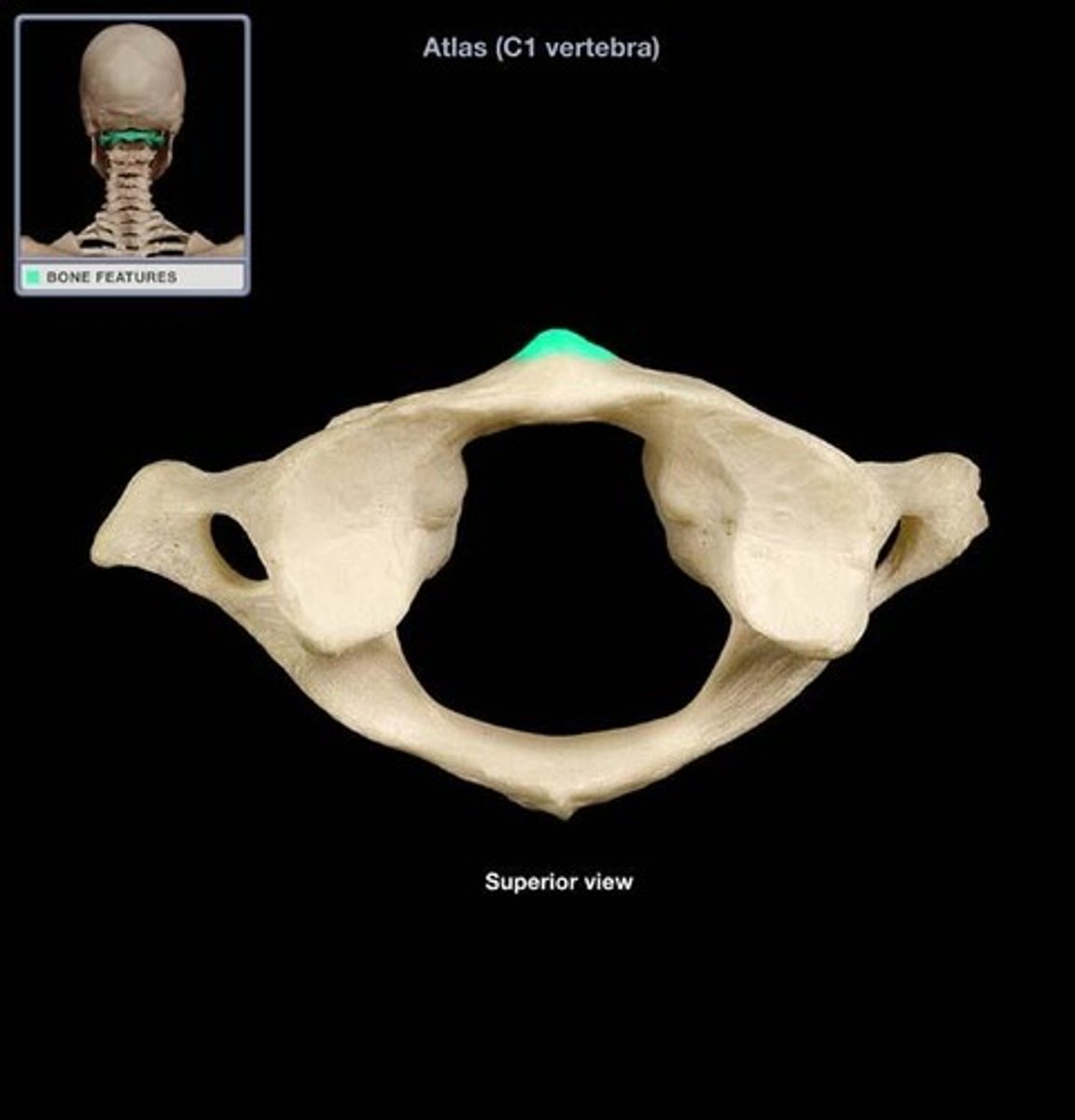
anterior tubercle of atlas
serves as site of attachment for cervical ligaments and muscles
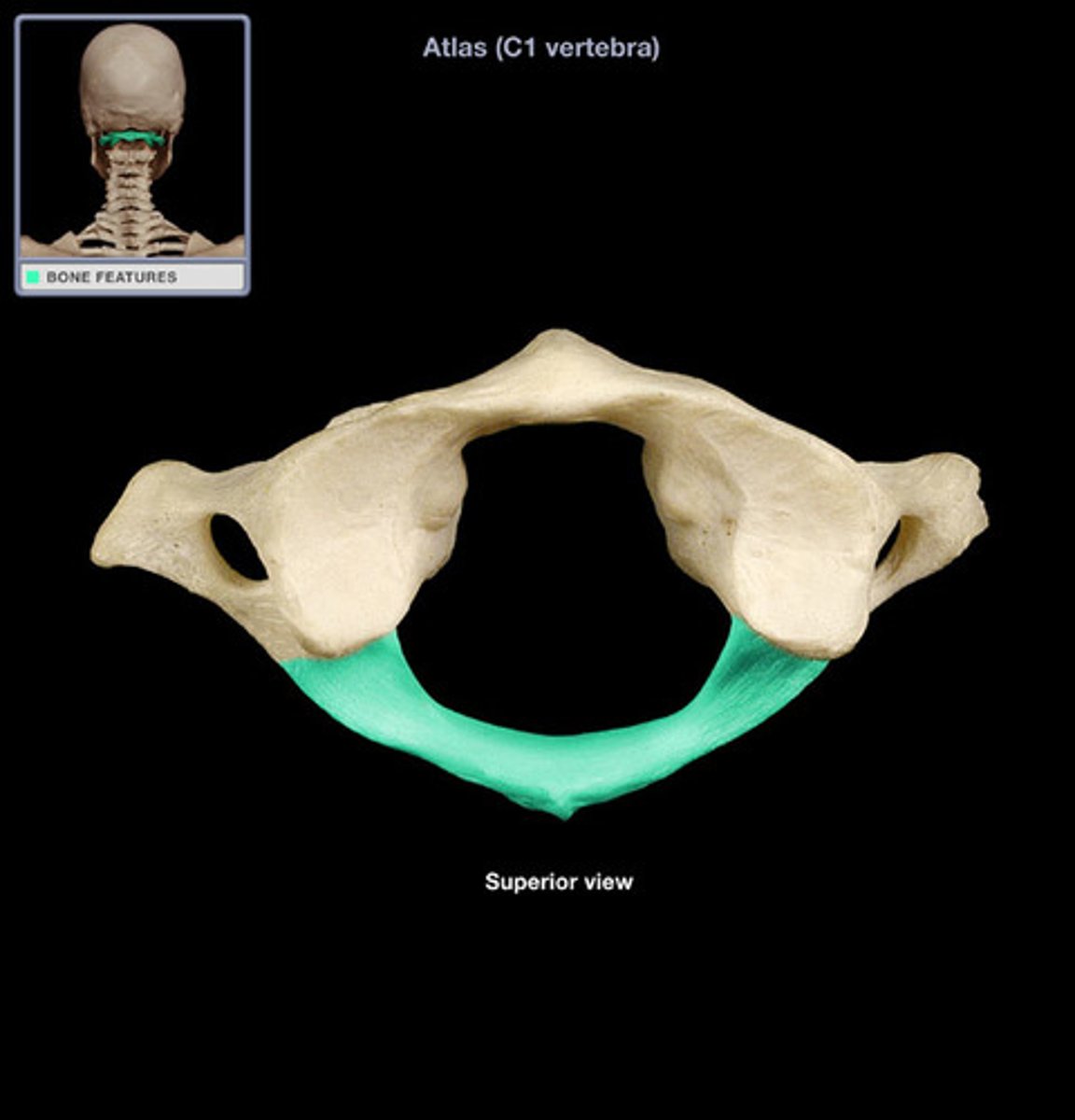
posterior arch of atlas
ID the landmark and bone
posterior tubercle of atlas
Where nuchal ligament attaches
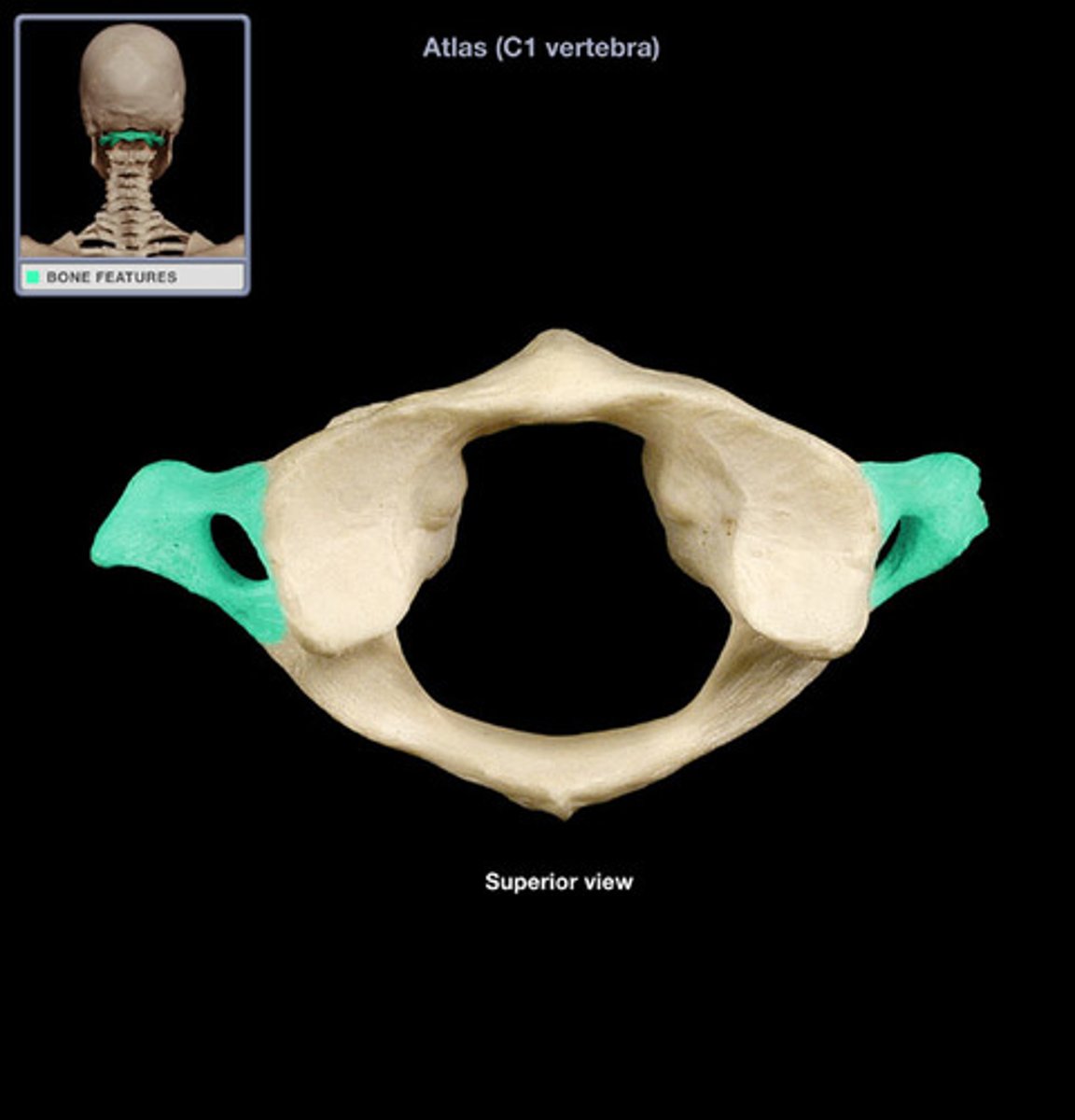
transverse process of atlas
insertion of obliquus capitis inferior
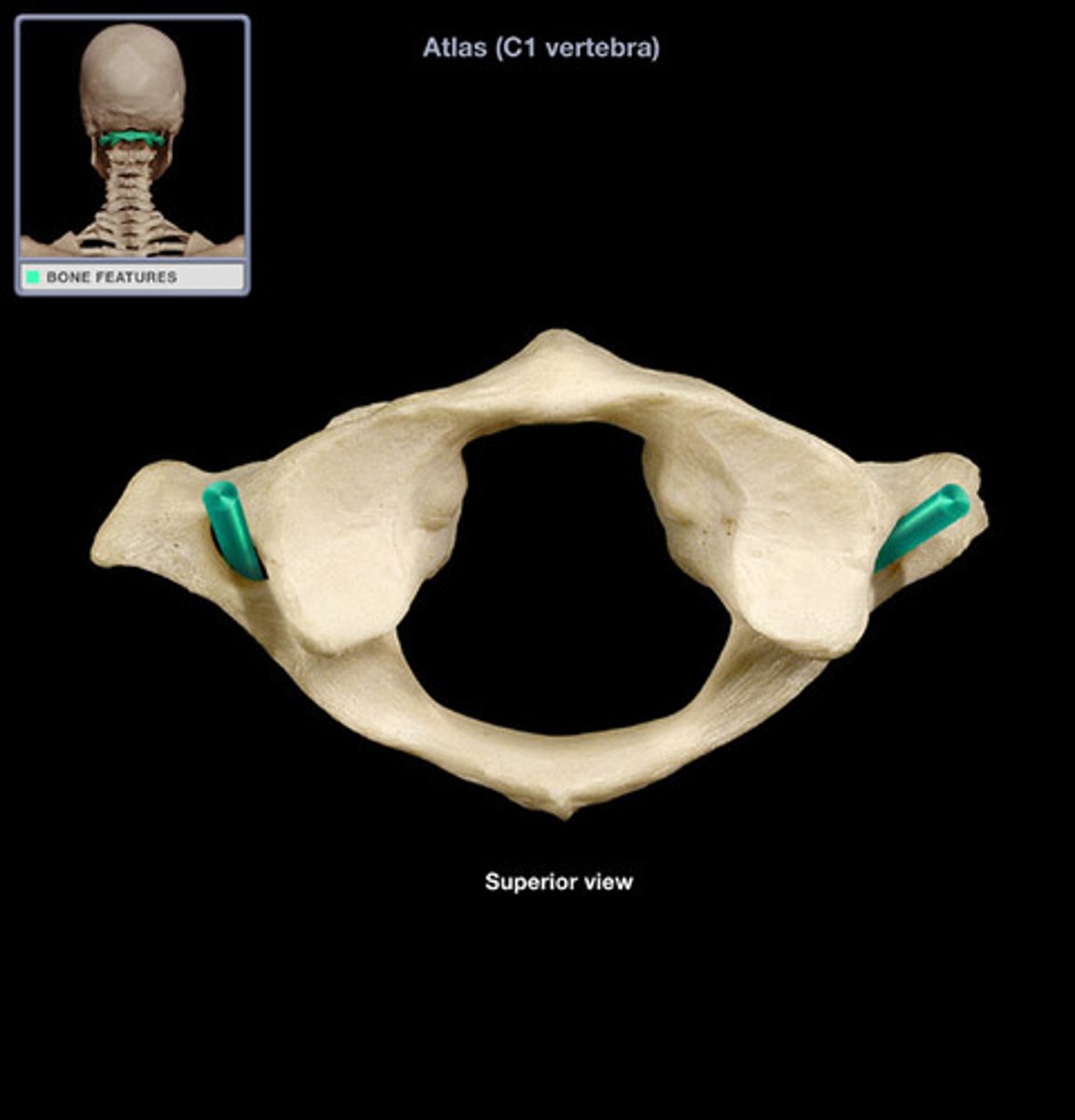
transverse foramen of atlas
ID the opening and bone
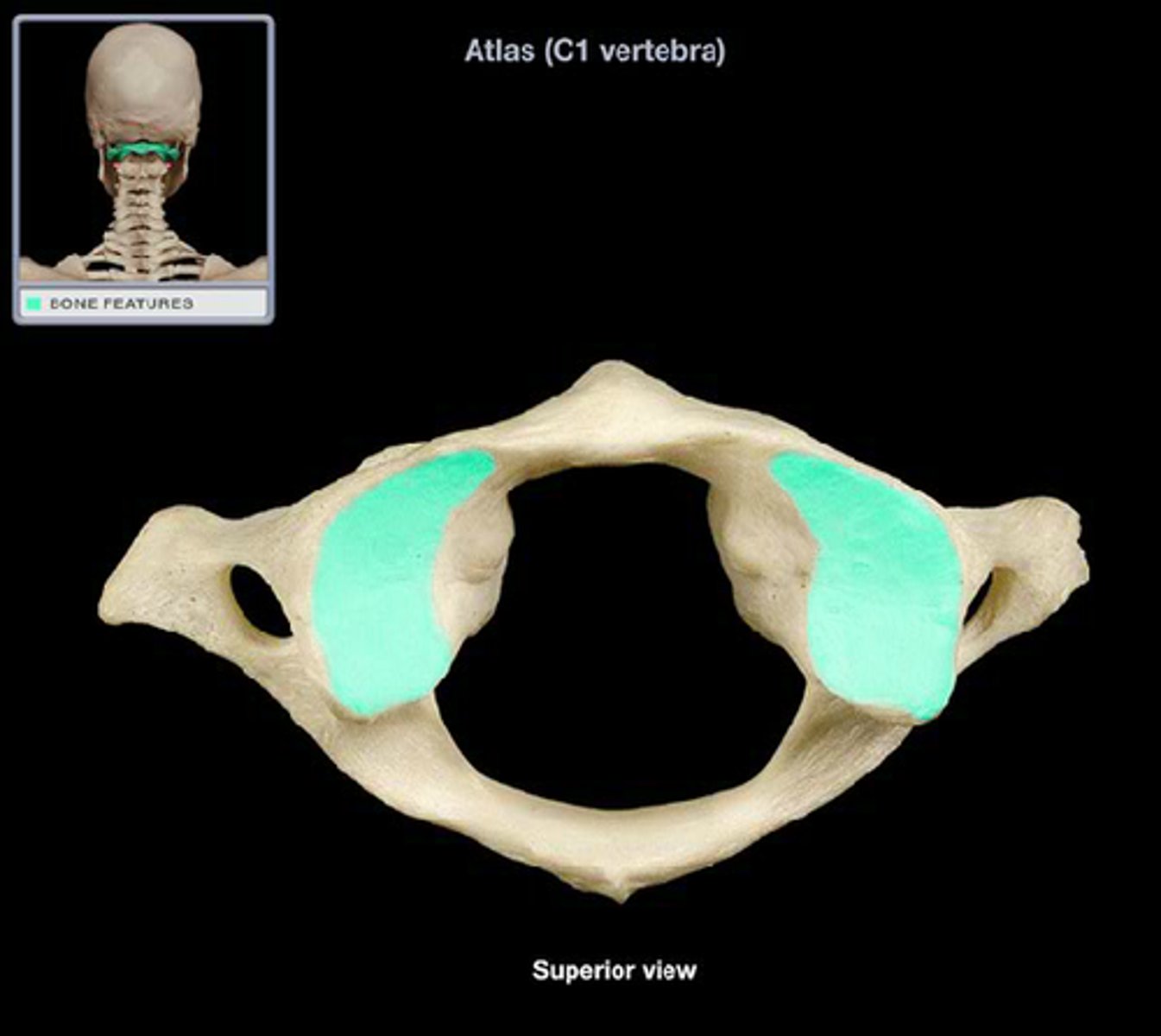
superior articular facet of atlas
articulates with occipital condyle
inferior articular facet of atlas
articulates with axis (C2)
body of axis
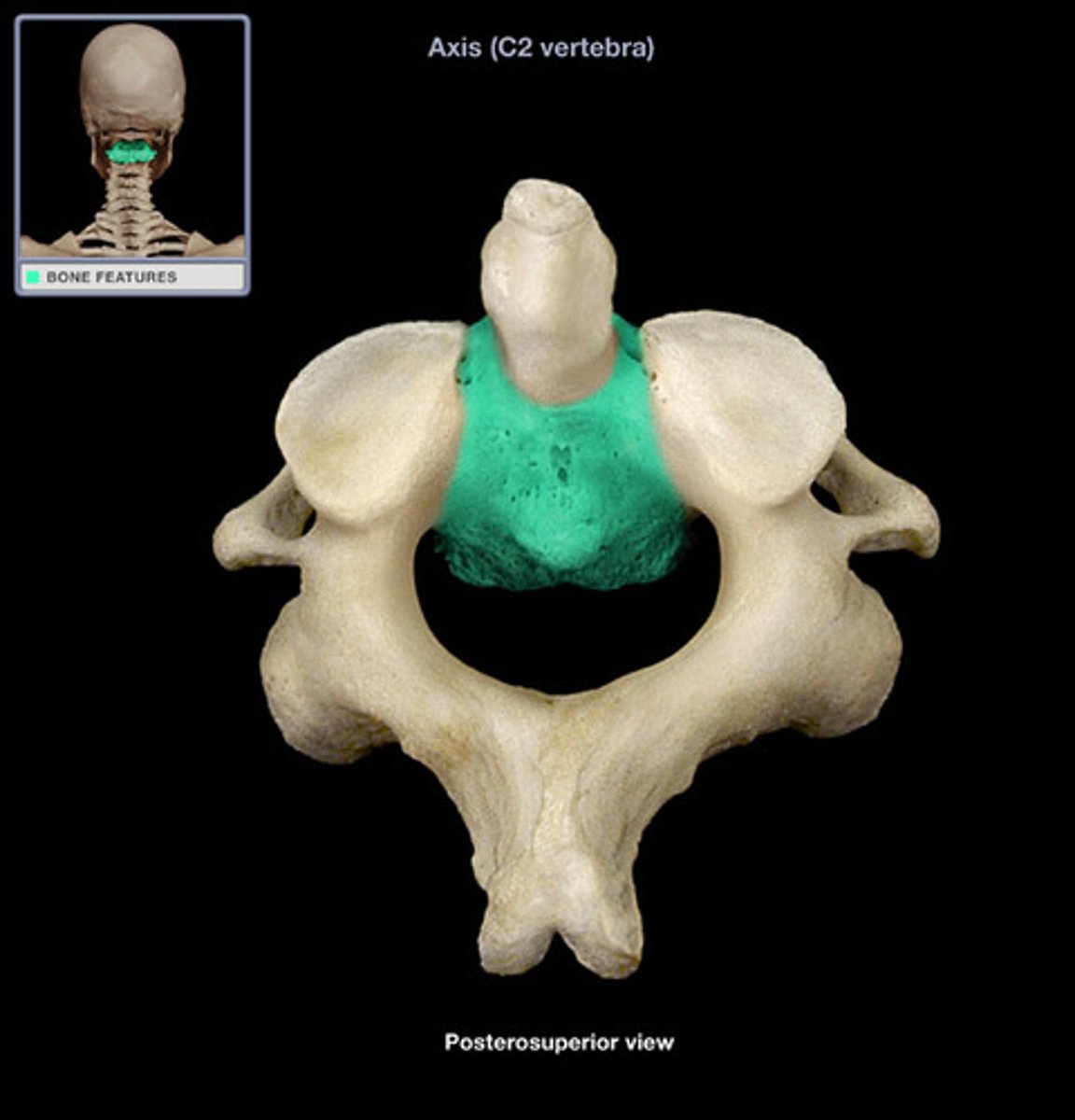
dens of axis (odontoid process)
large toothlike process projecting between articulating facets
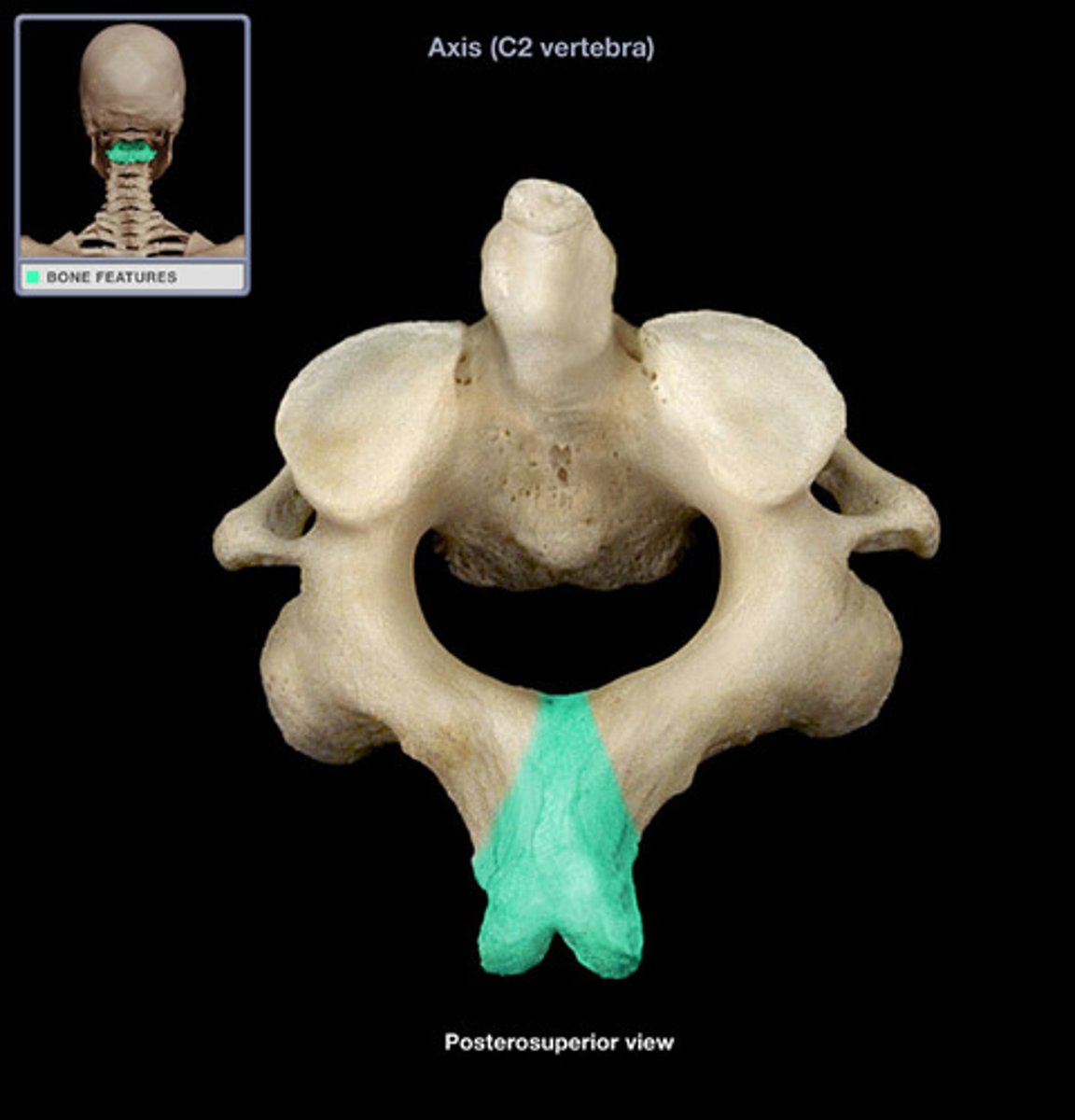
spinous process of axis
origin of rectus capitis posterior major
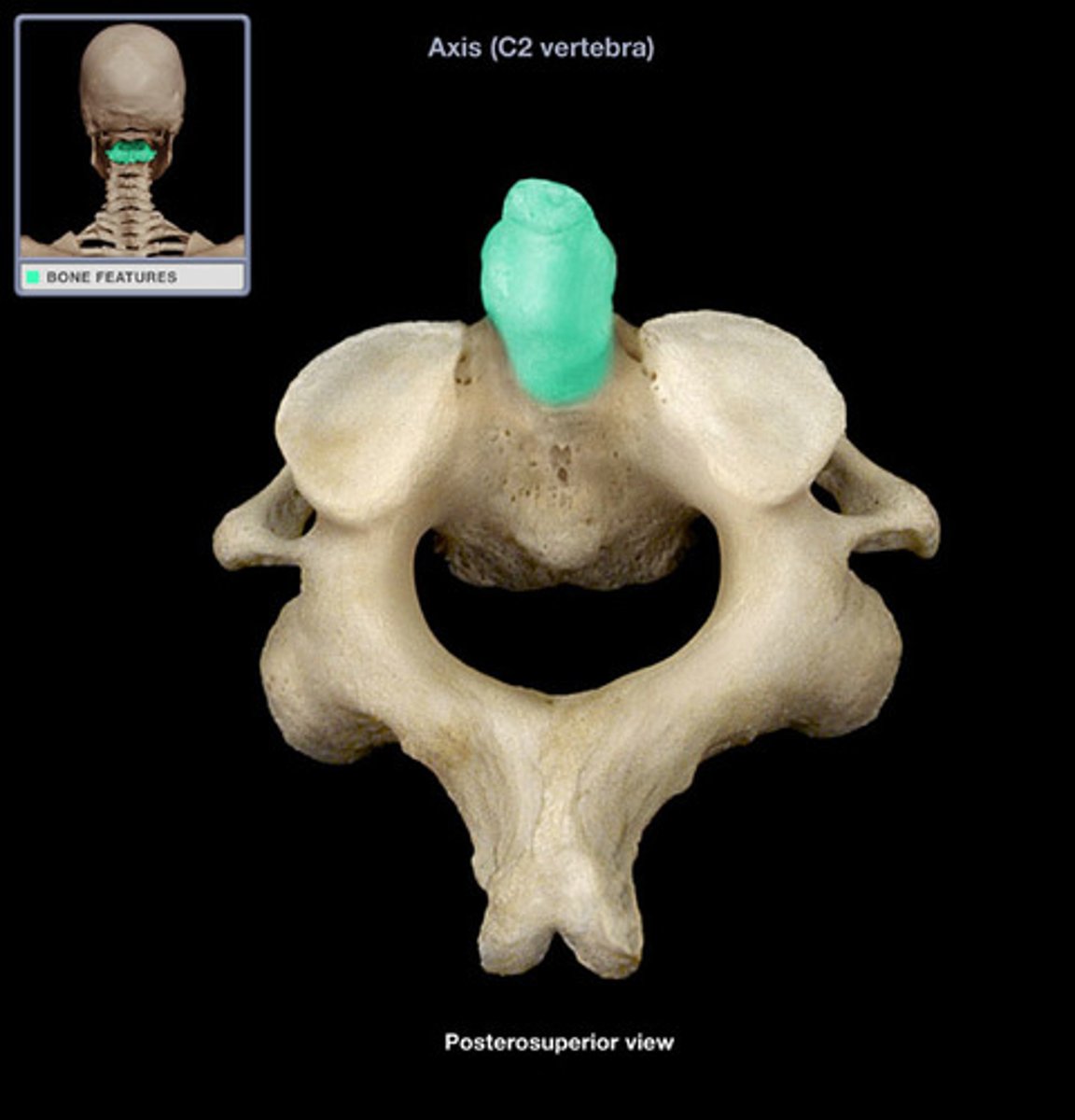
transverse process of axis
What is this?
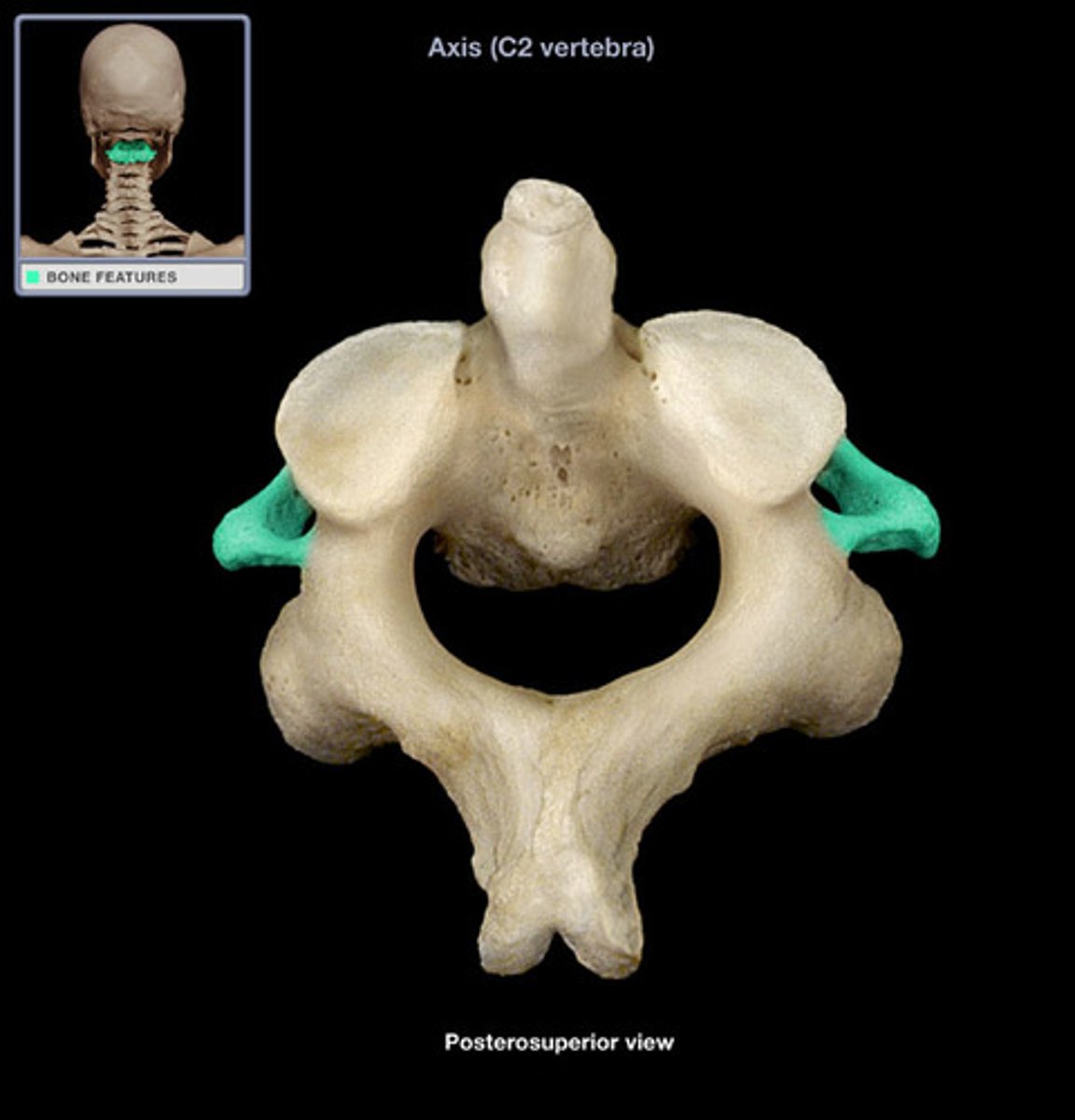
transverse foramen of axis
ID the opening and bone
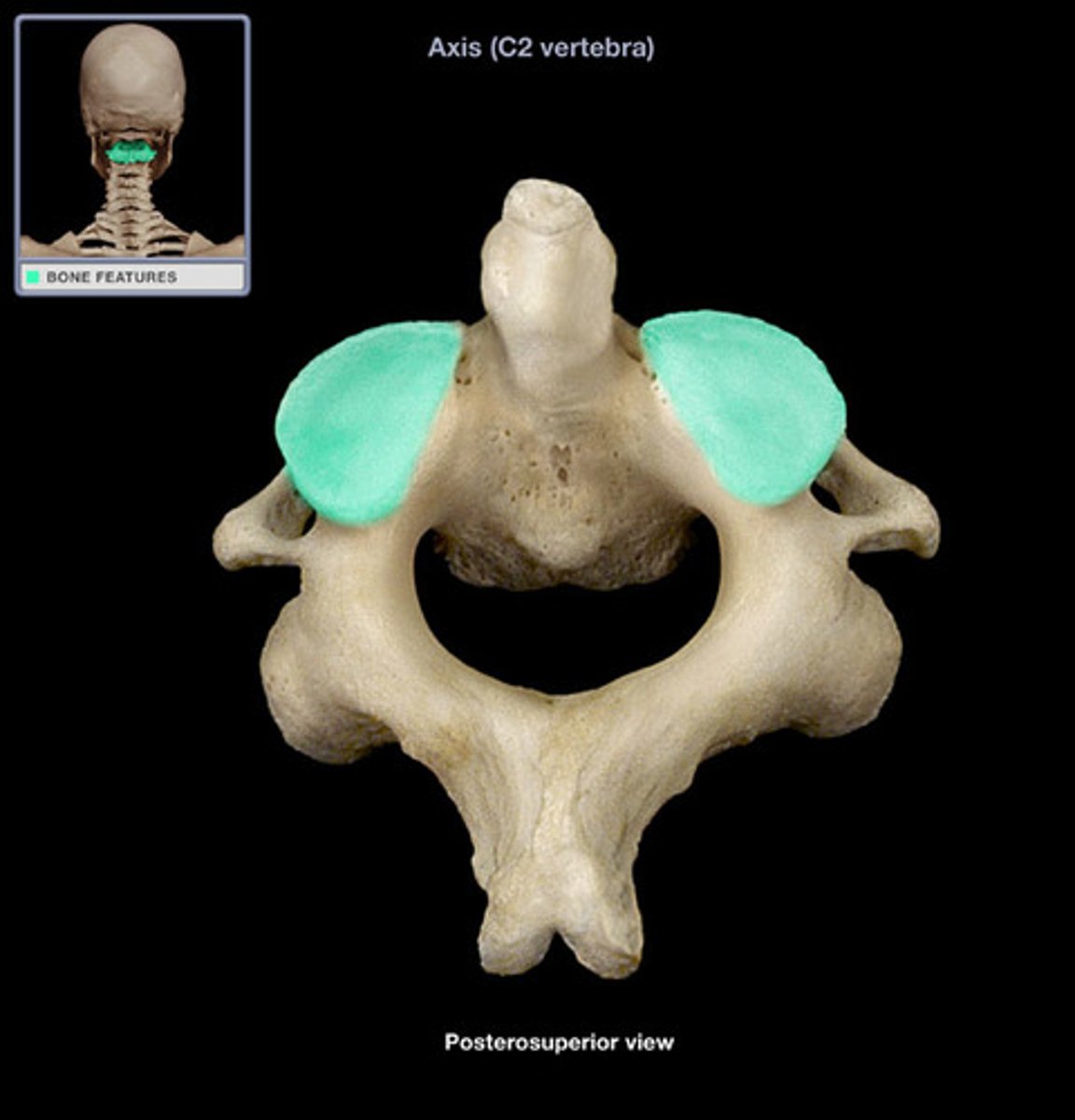
superior articular facet of axis
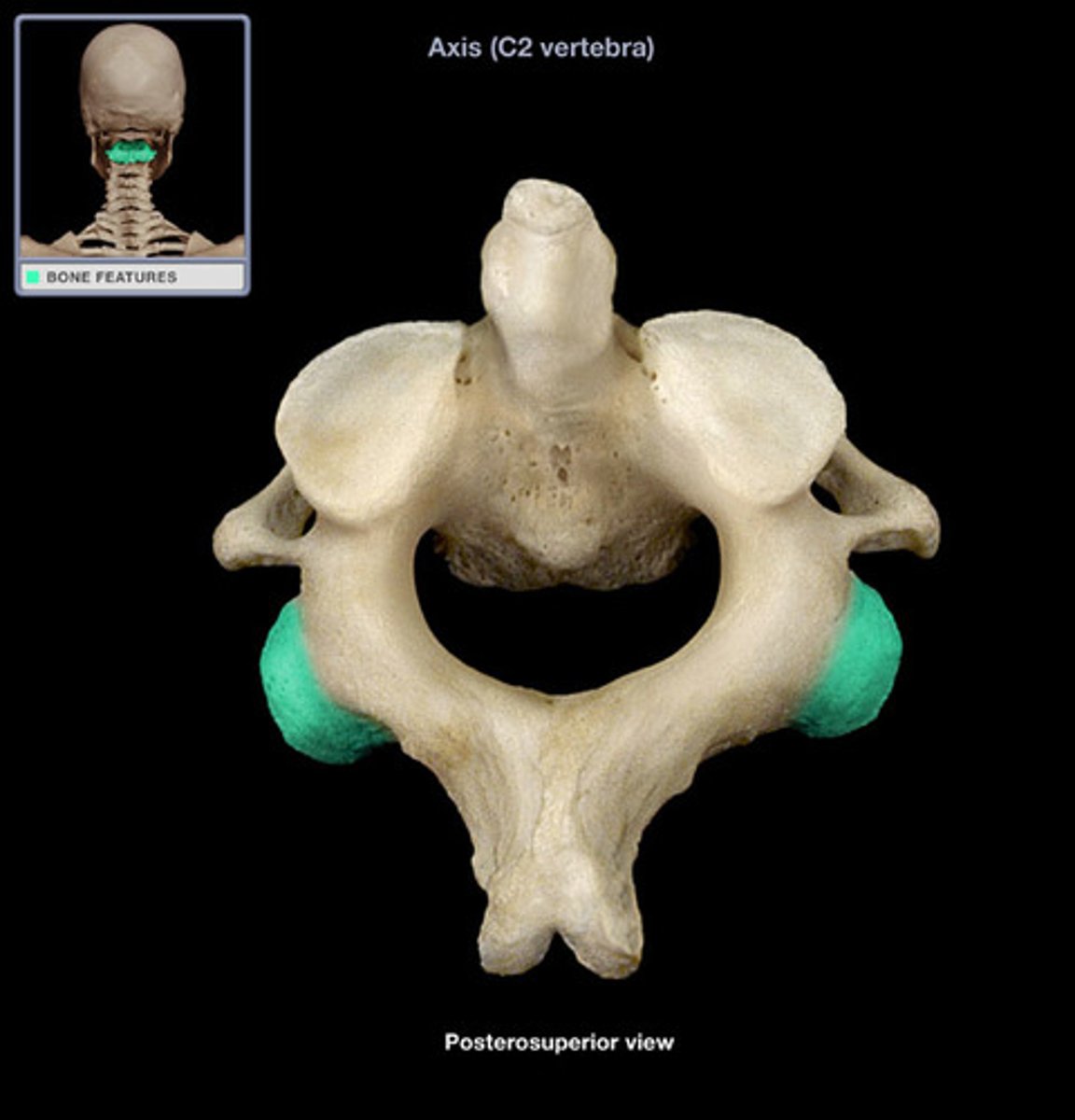
inferior articular facet of axis
What are the characteristics of typical cervical vertebrae?
small bodies, transverse processes with foramina
What feature do C2-C6 have?
short, bifid (divided by notch into 2 parts) spinous processes
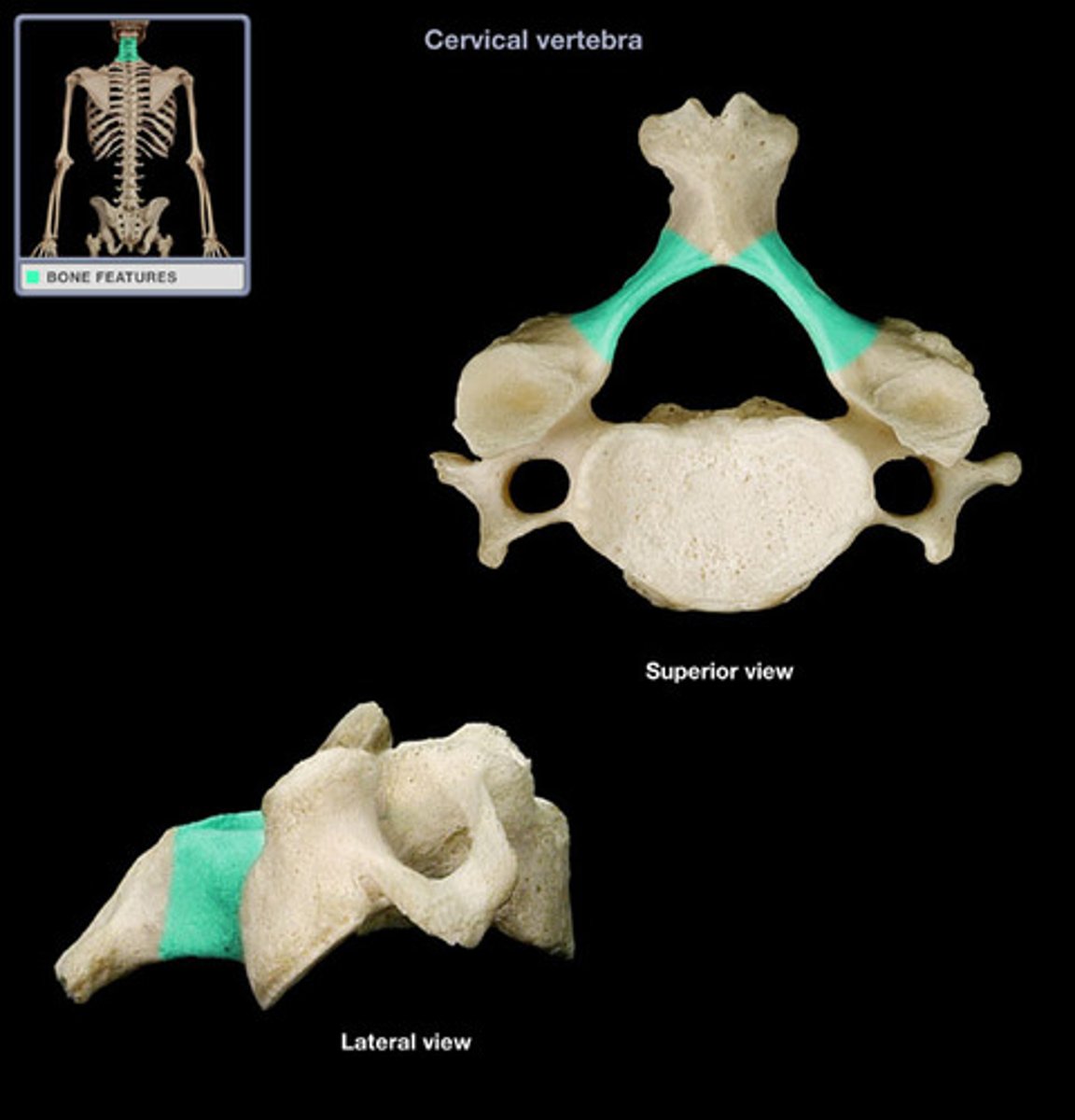
cervical pedicle
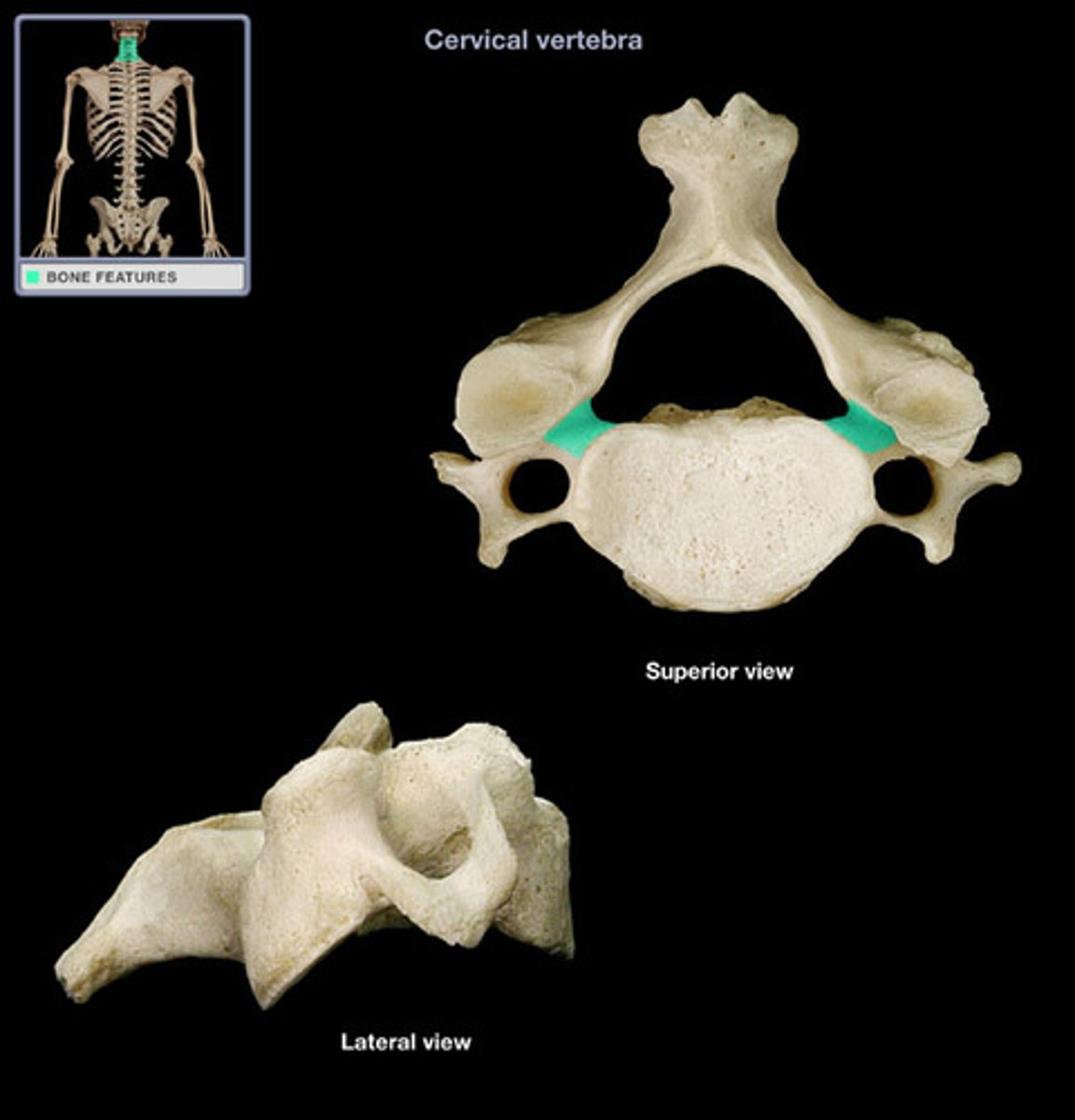
cervical lamina
bony region between the transverse process and the spinous process
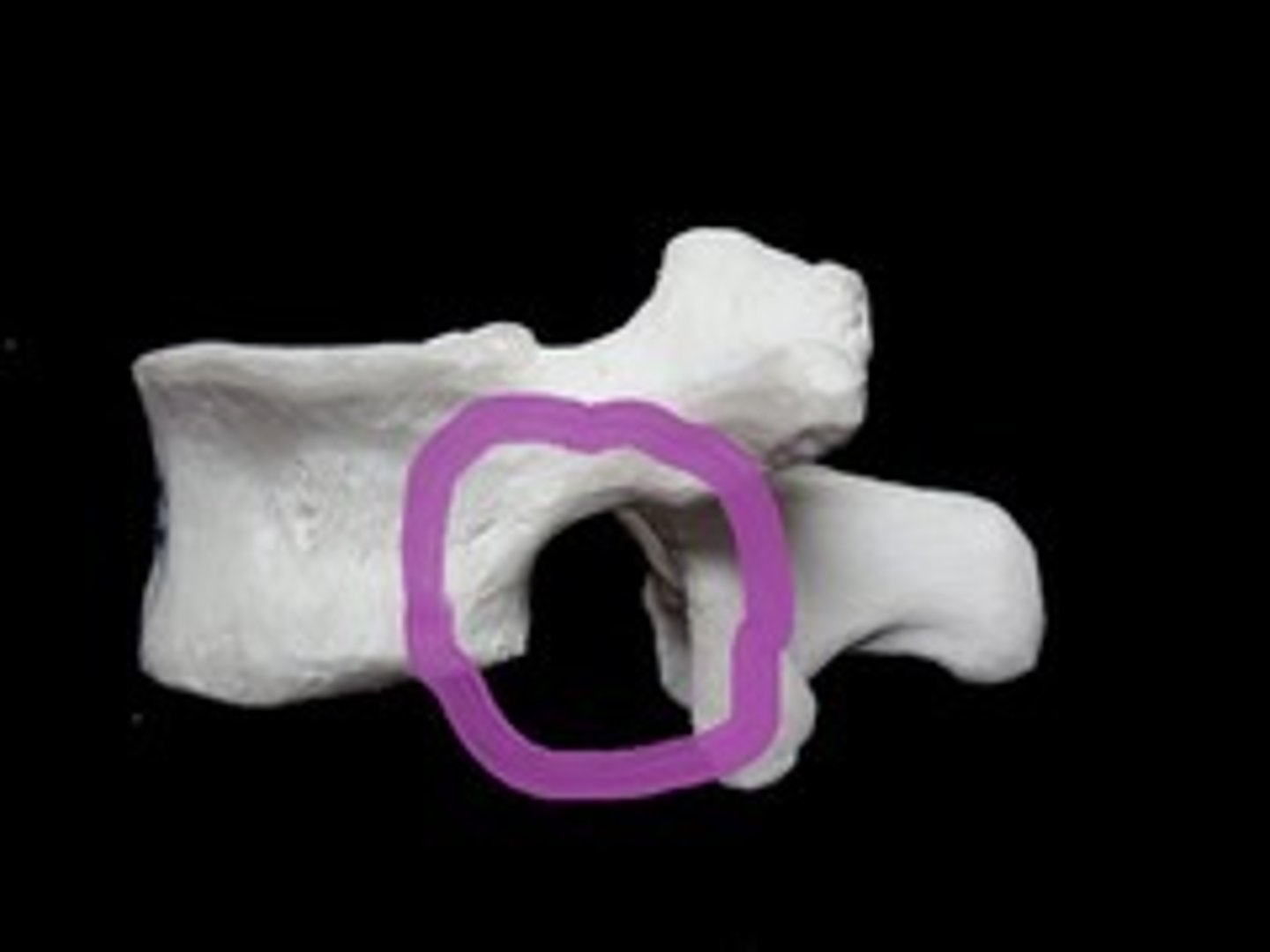
inferior vertebral notch
space for nerve passage
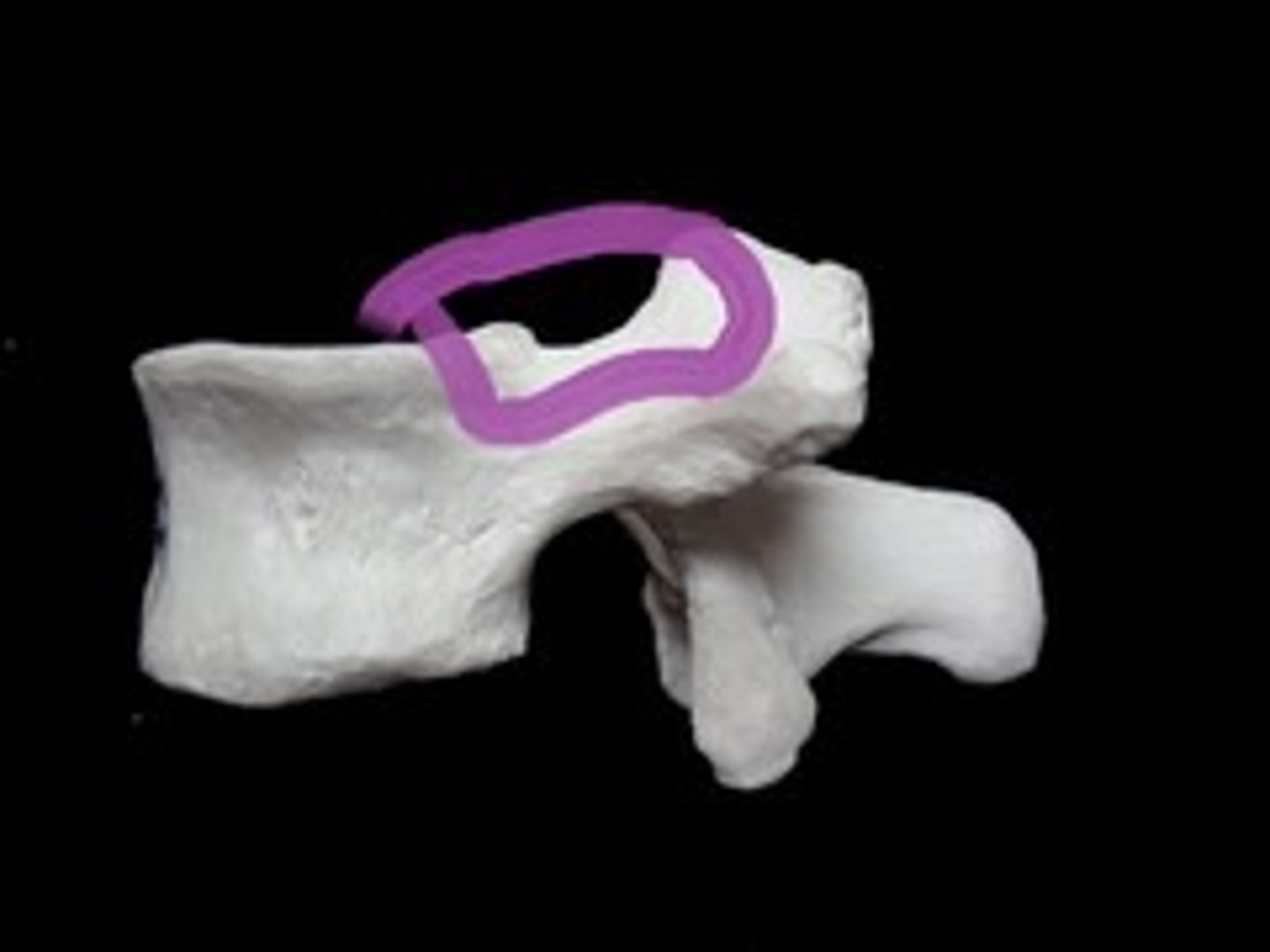
superior vertebral notch
indentation of the body and superior articular process
What are the distinct features of thoracic vertebrae?
demi-facets for heads of ribs (superior and inferior on body), transverse process with costal facets for rib tubercles, long, inferiorly sloping spinous processes that overlap with vertebra below
costal facet of transverse process
Provides articulation of tubercles of ribs (1-10)
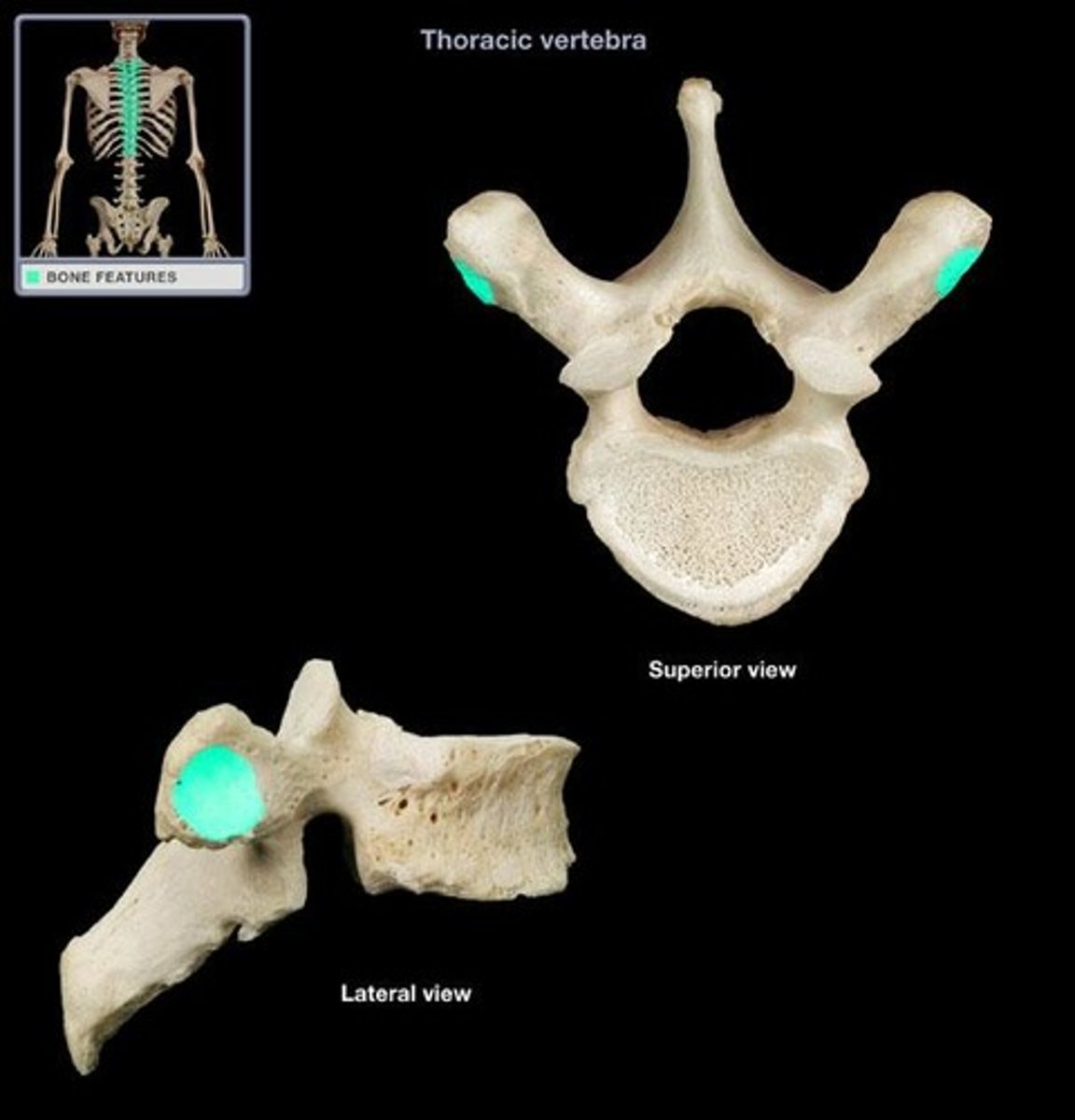
superior costal facet of thoracic vertebrae
receive the head of the ribs on the superior side; only in thoracic vertebrae
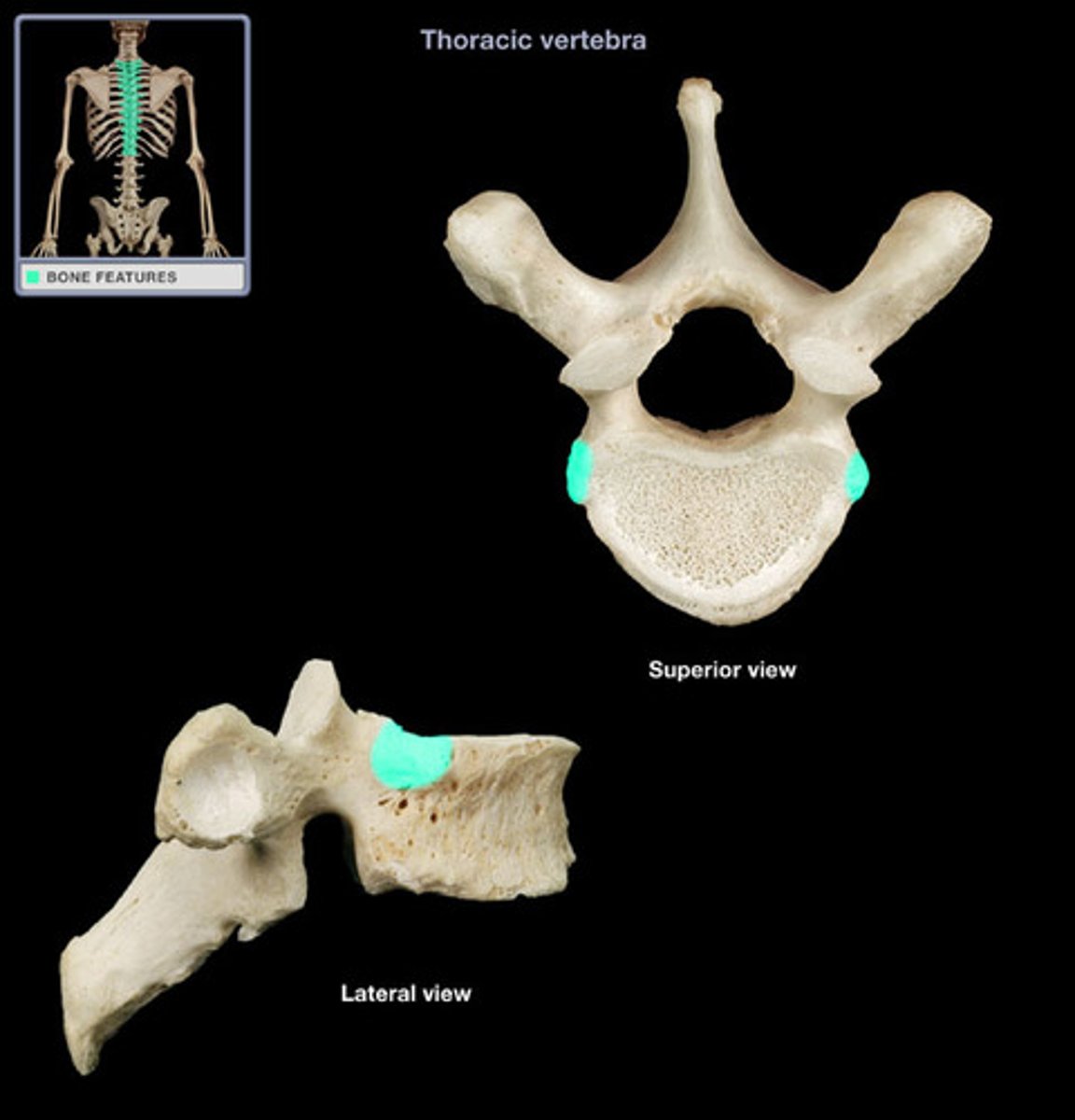
inferior costal facet of thoracic vertebrae
Present on T1-T8, where the inferior articular facet of the ribs sit connecting to the facet of the superior. Absent on T9-T12
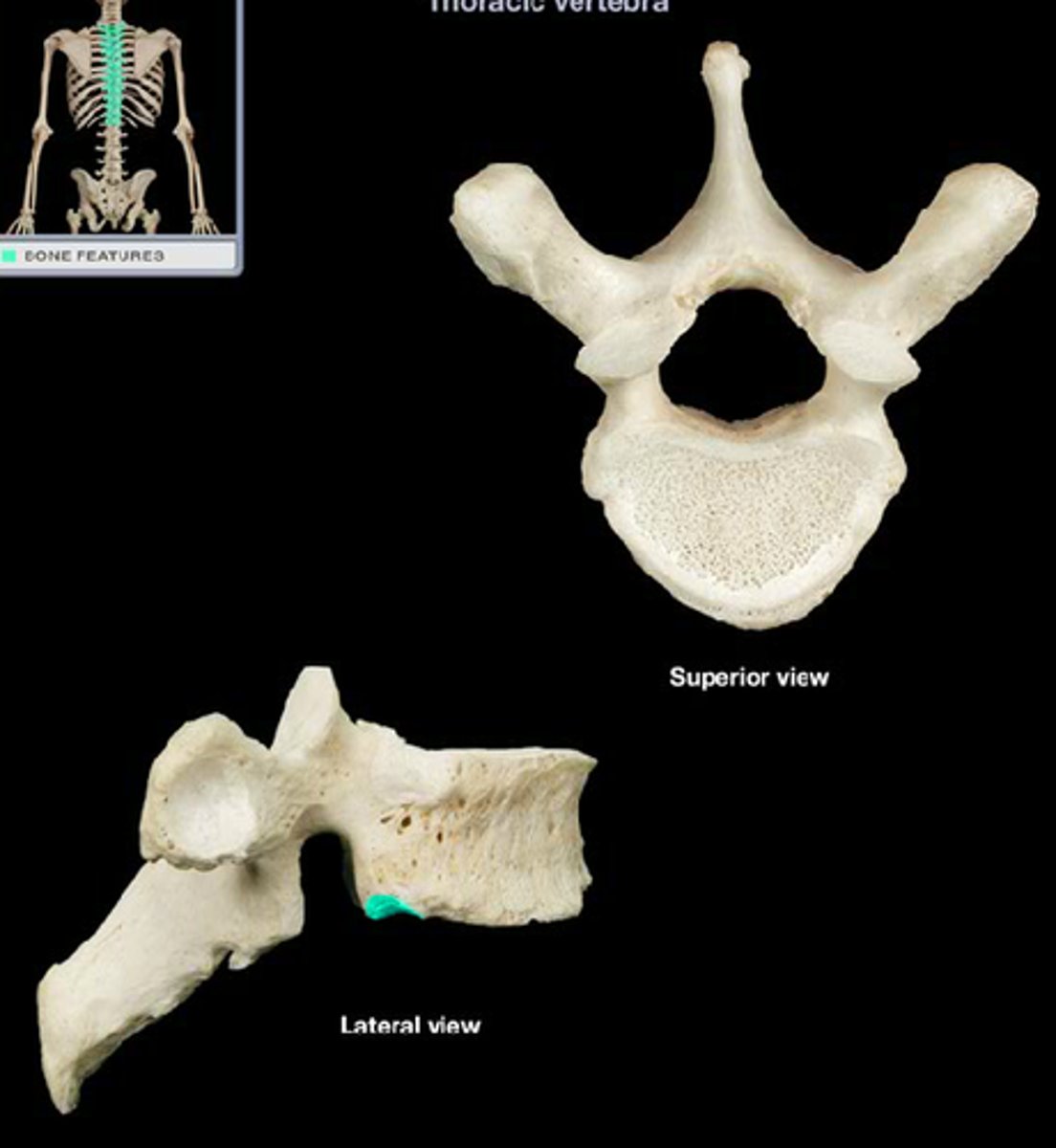
What are the unique features of the lumbar vertebrae?
built for support, have large bodies, large/squared spinous processes projecting almost horizontally
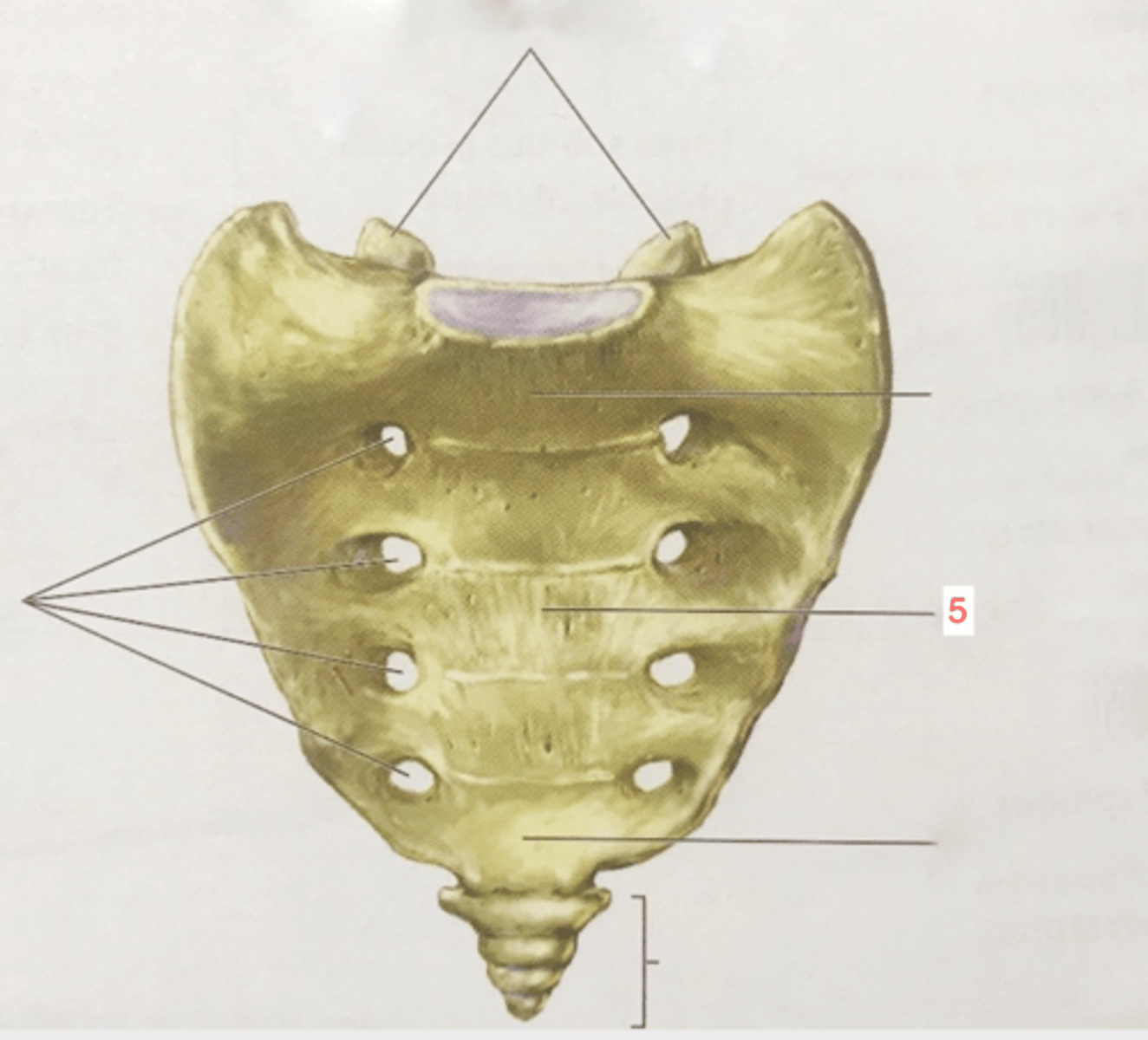
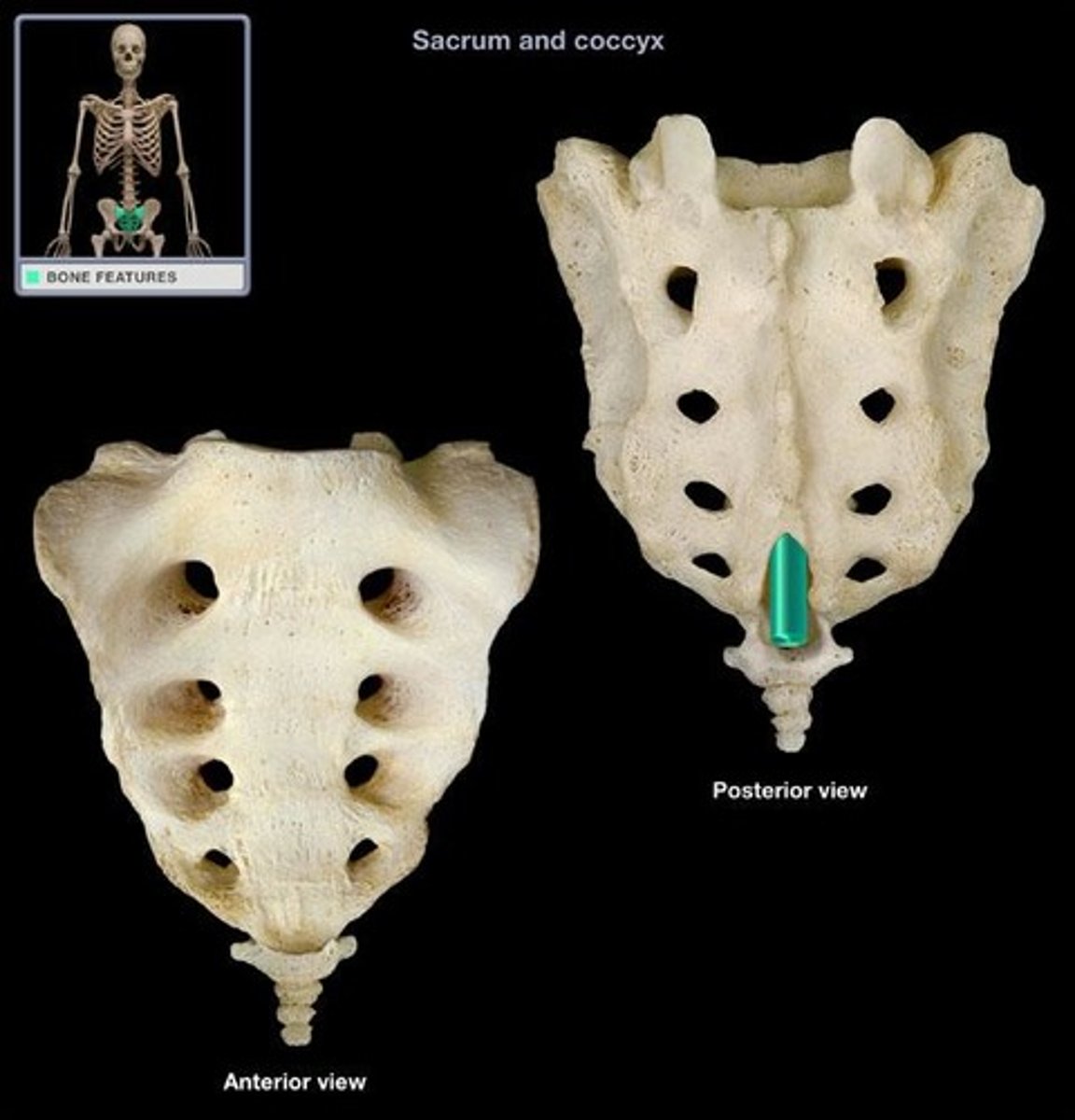
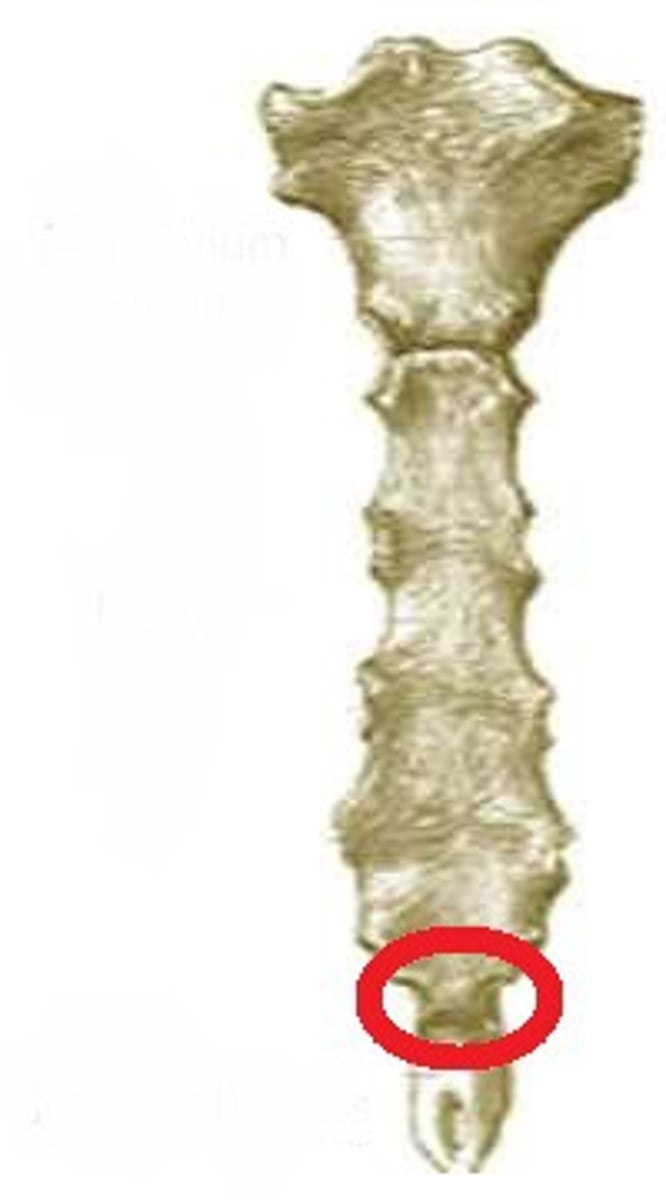
What is unique about the sacrum?
varies in curvature, sexual dimorphism varies in length (so does coccyx)
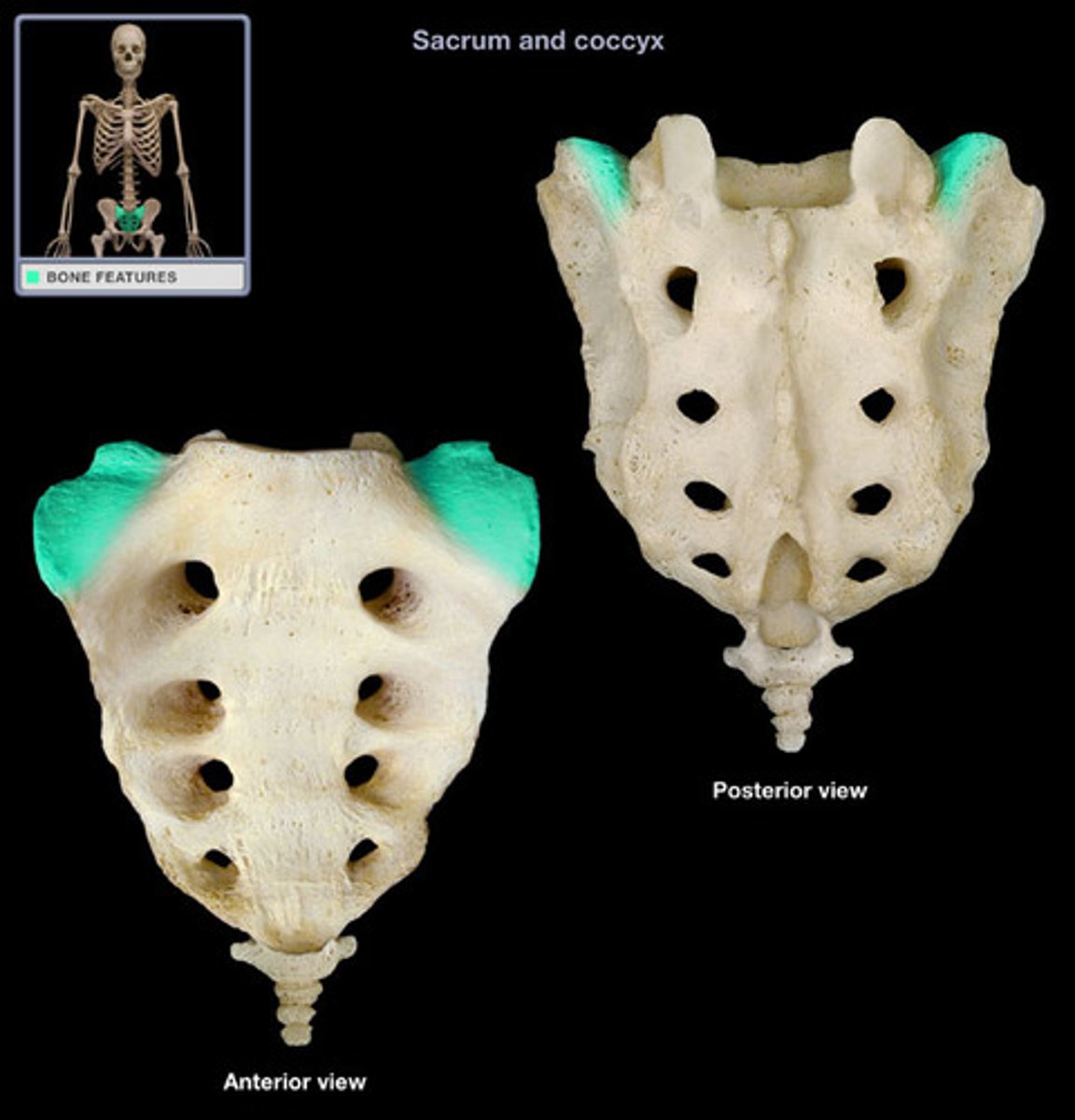
ala of sacrum
Wing-like masses of the sacrum
sacral promontory
Where the first sacral vertebrae bulges into pelvic cavity
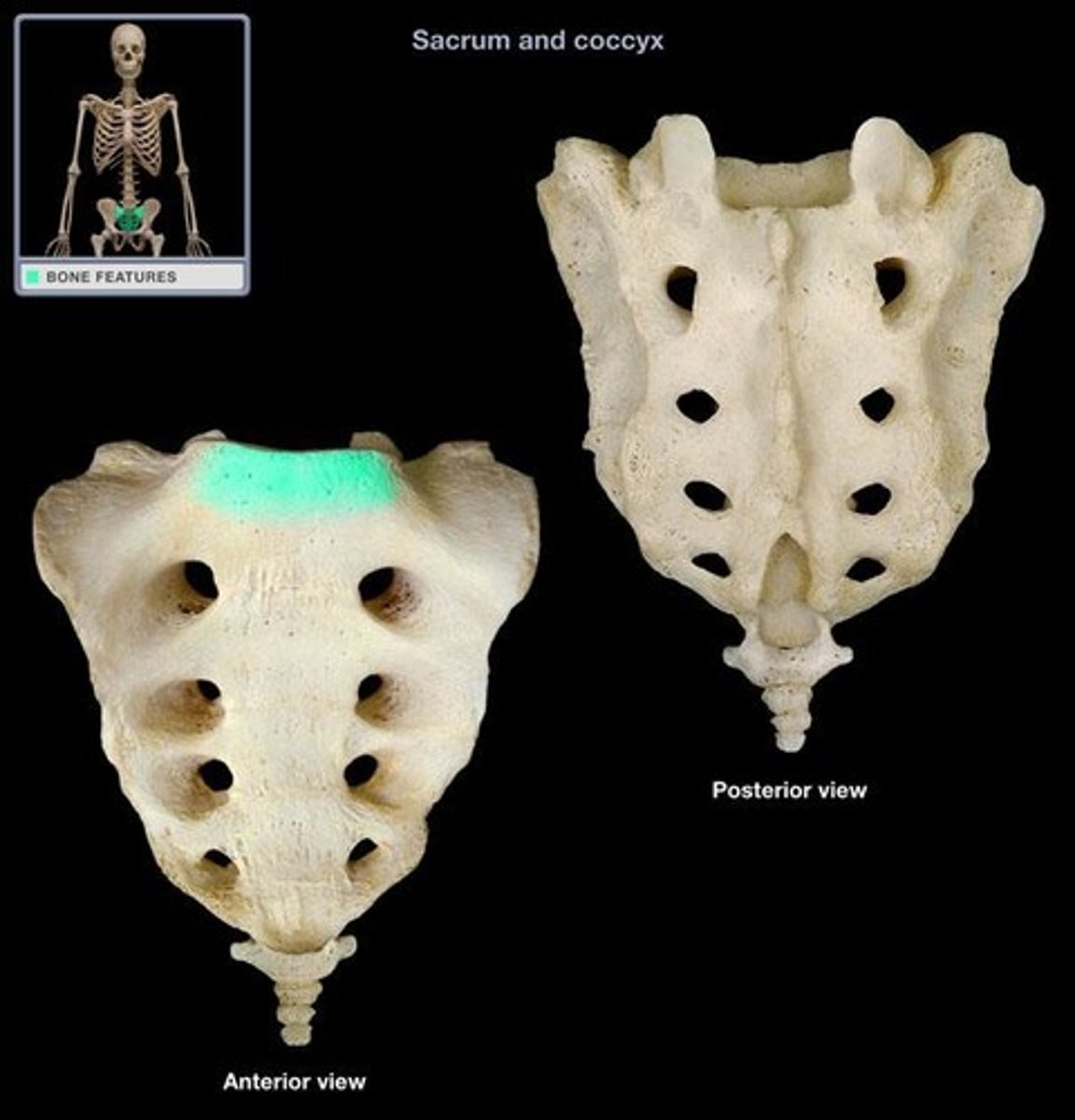
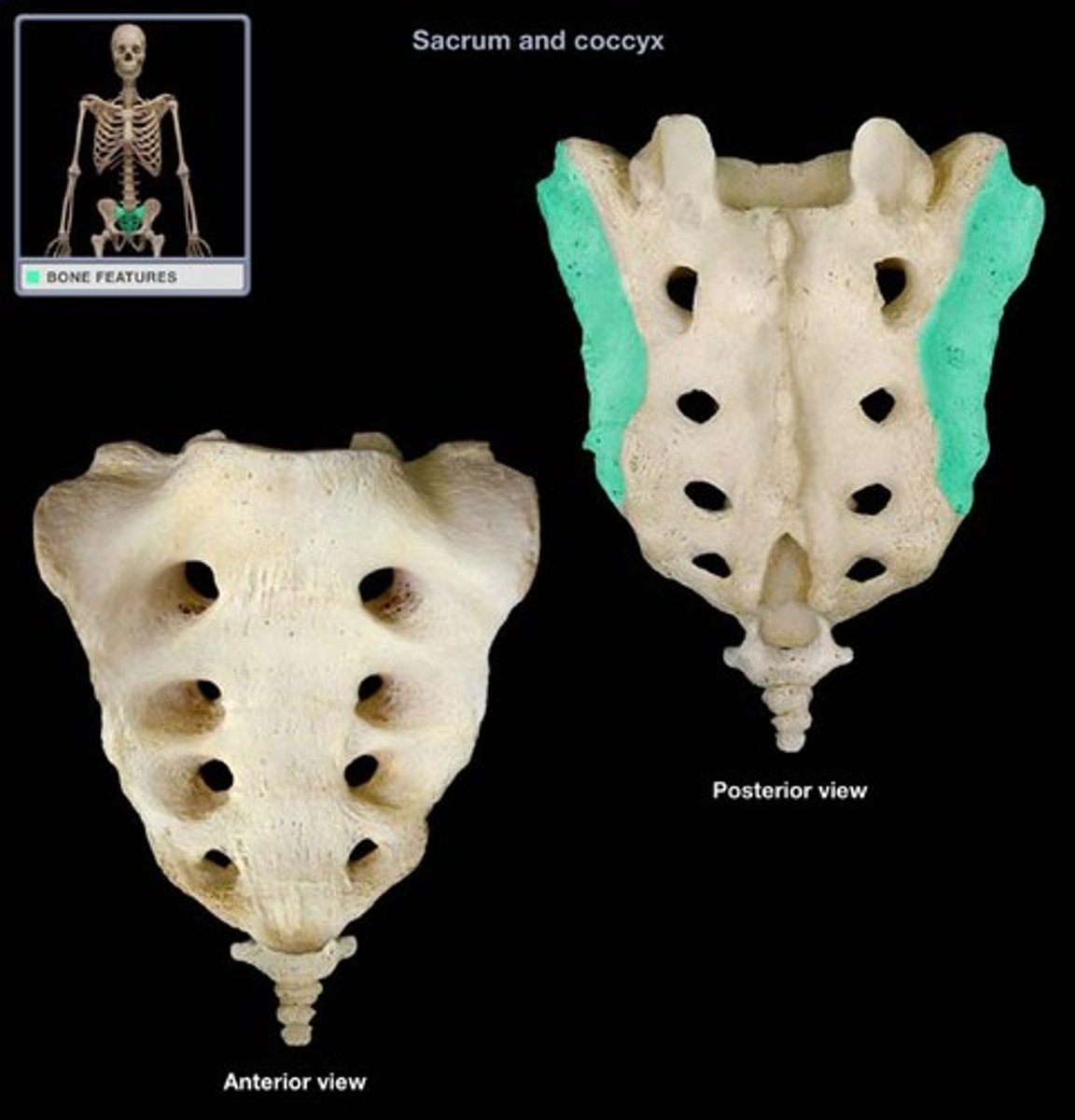
auricular surface of sacrum
Can only be seen from posterior view, articulation with ilium
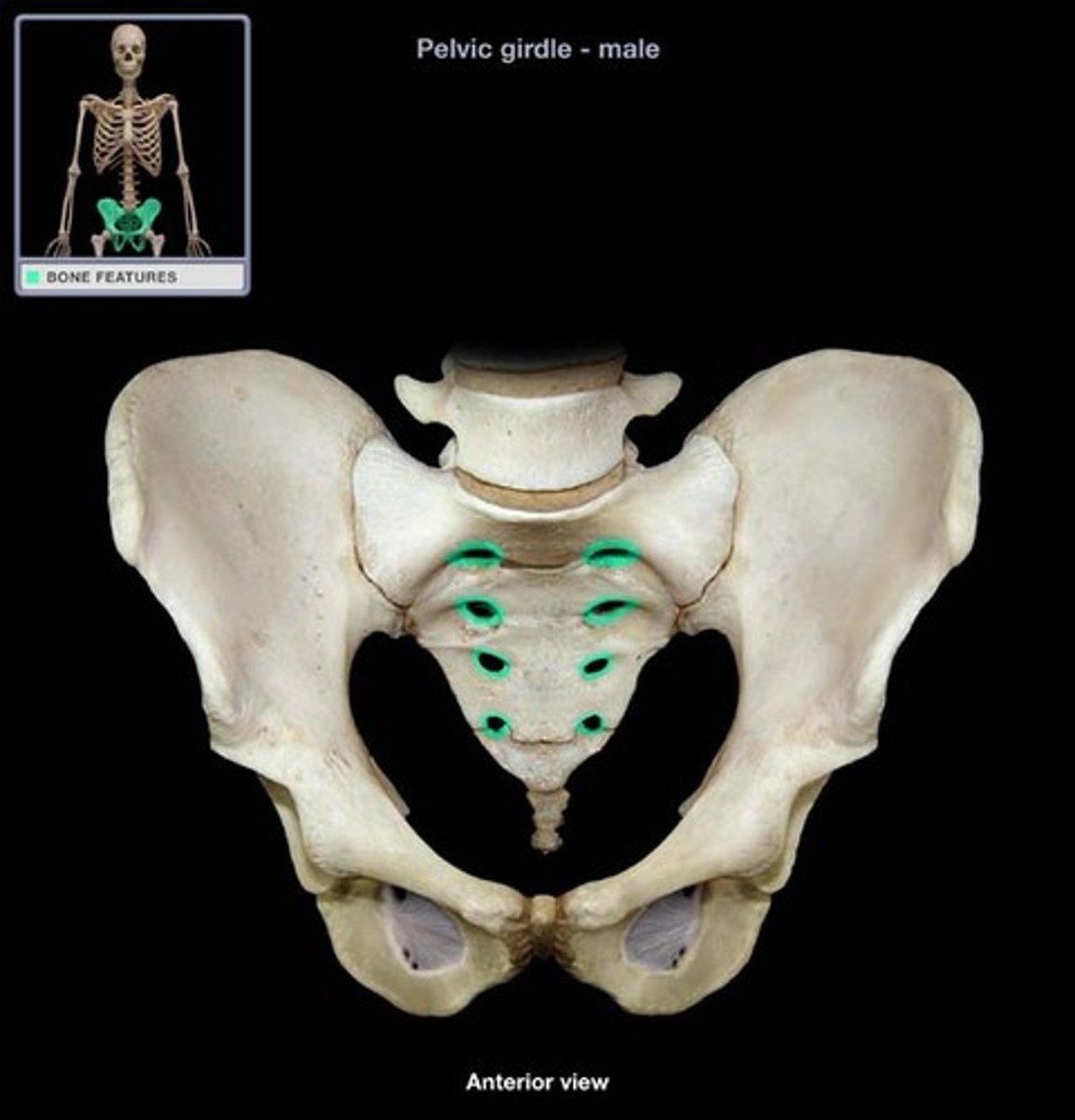
anterior sacral foramina
openings on the anterior side of the sacrum
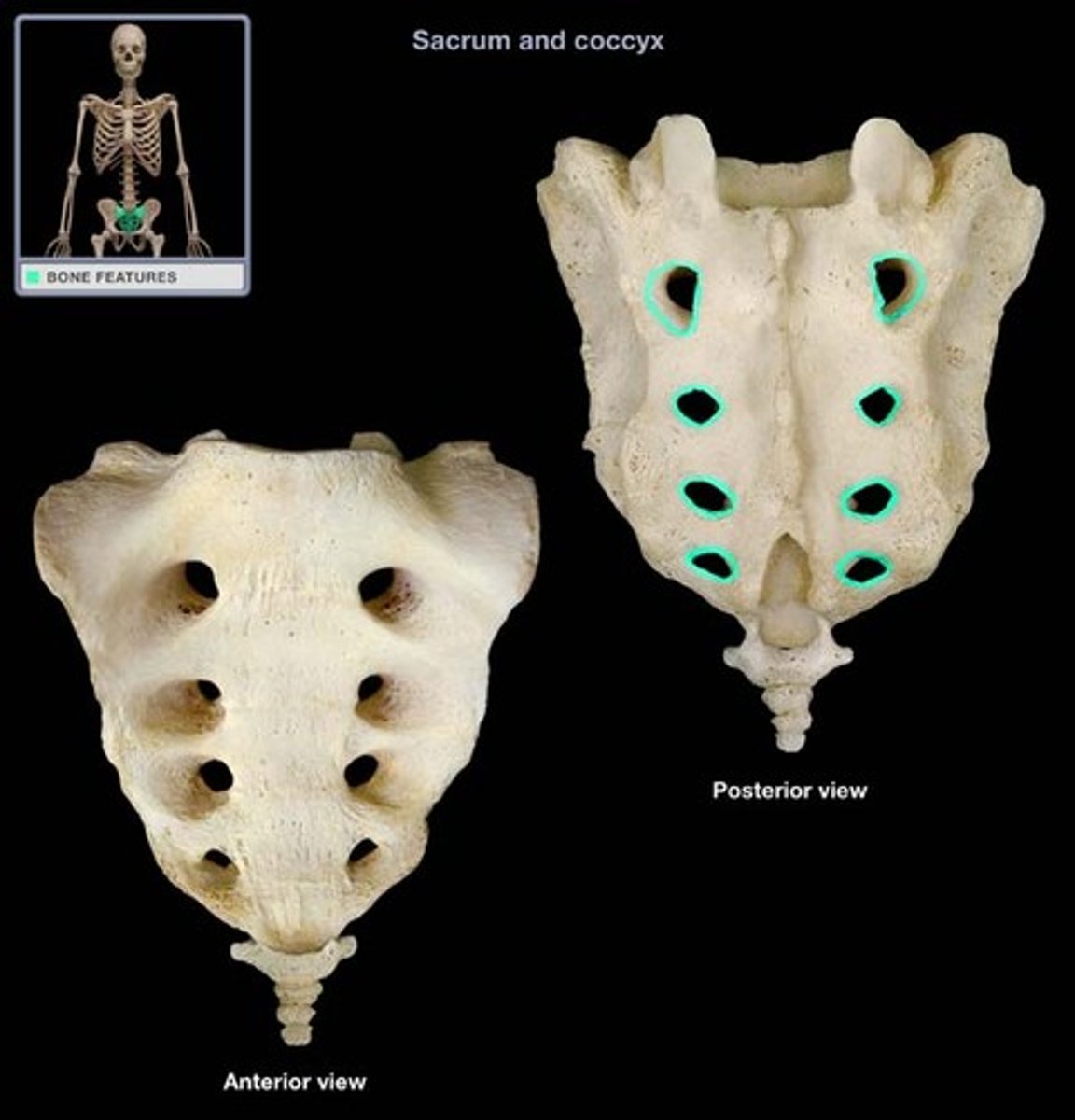
posterior sacral foramina
openings on the posterior side of the sacrum
sacral canal
continuation of vertebral canal
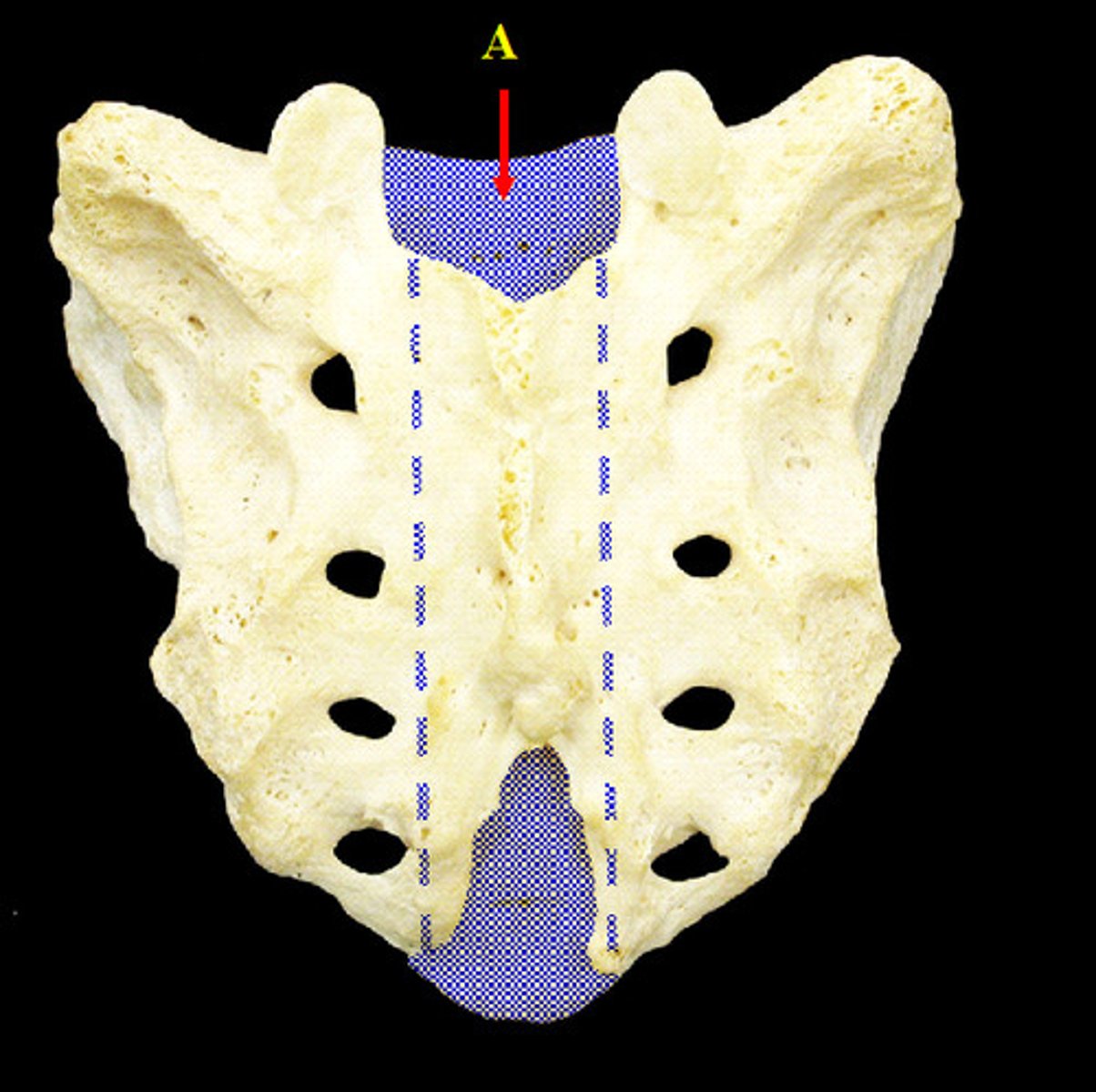
sacral hiatus
inferior opening of the sacral canal
What makes up the thoracic cage?
sternum, ribs, and thoracic vertebrae
What is the function of the thoracic cage?
Protects heart, lungs, trachea, esophagus, and other thoracic organs, support upper limbs and provide muscle attachments
Which are the true ribs and what makes them "true" ?
1-7, attach directly to sternum via costal cartilage
head of rib
Articulates with the costal facet of a thoracic vertebral body.
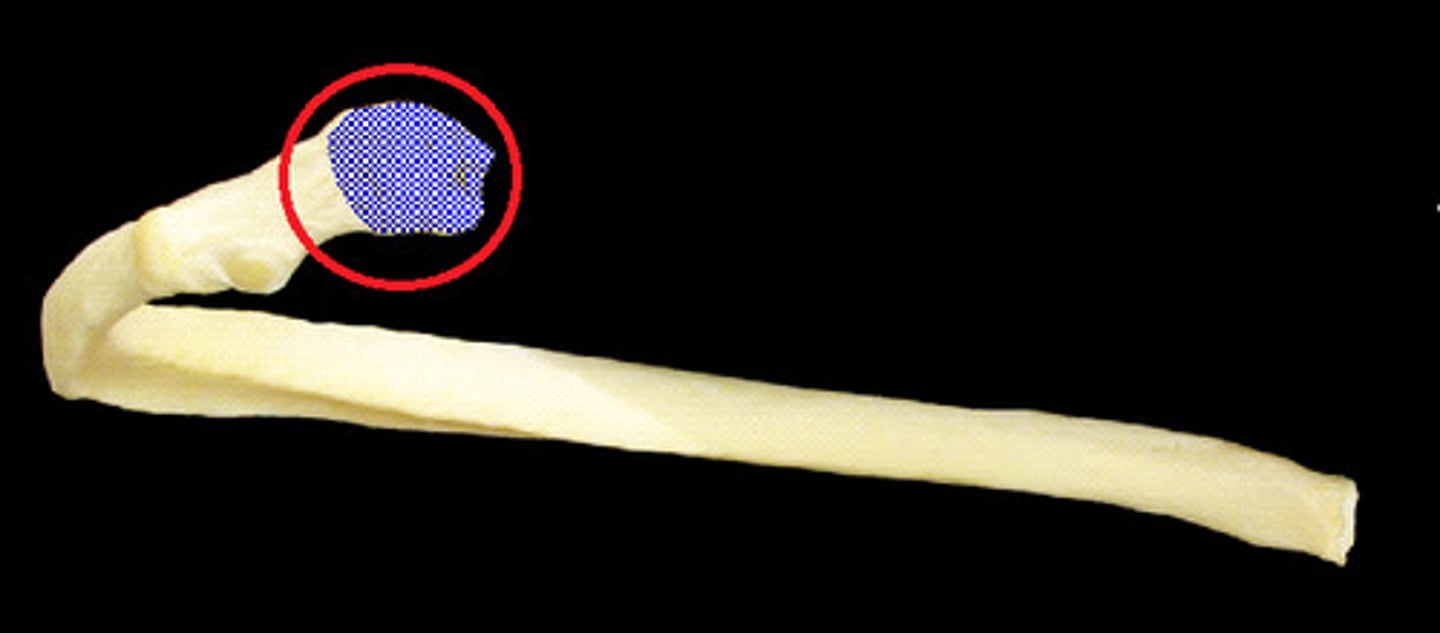
neck of rib
between head and tubercle
tubercle of rib
A structure in the neck of the rib that articulates with the costal facet of a thoracic vertebra's transverse process.
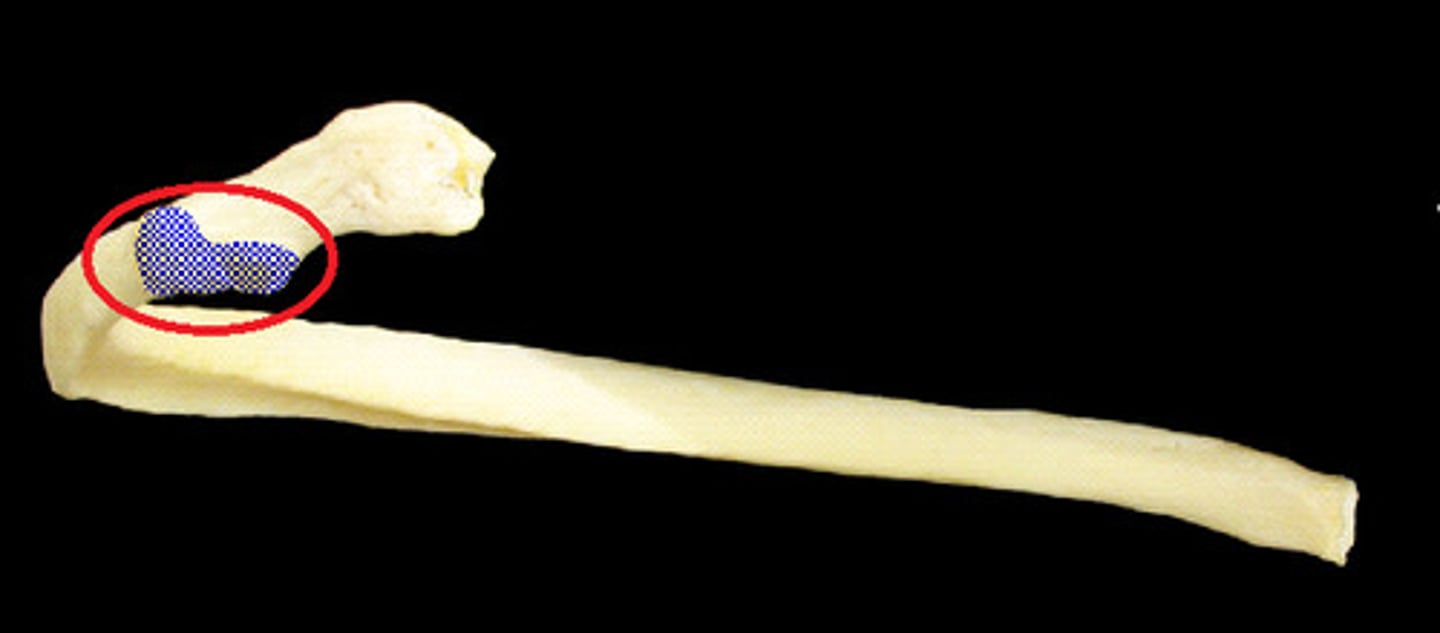

groove for subclavian vein
Rib 1
Just anterior to the scalene tubercle of the first rib
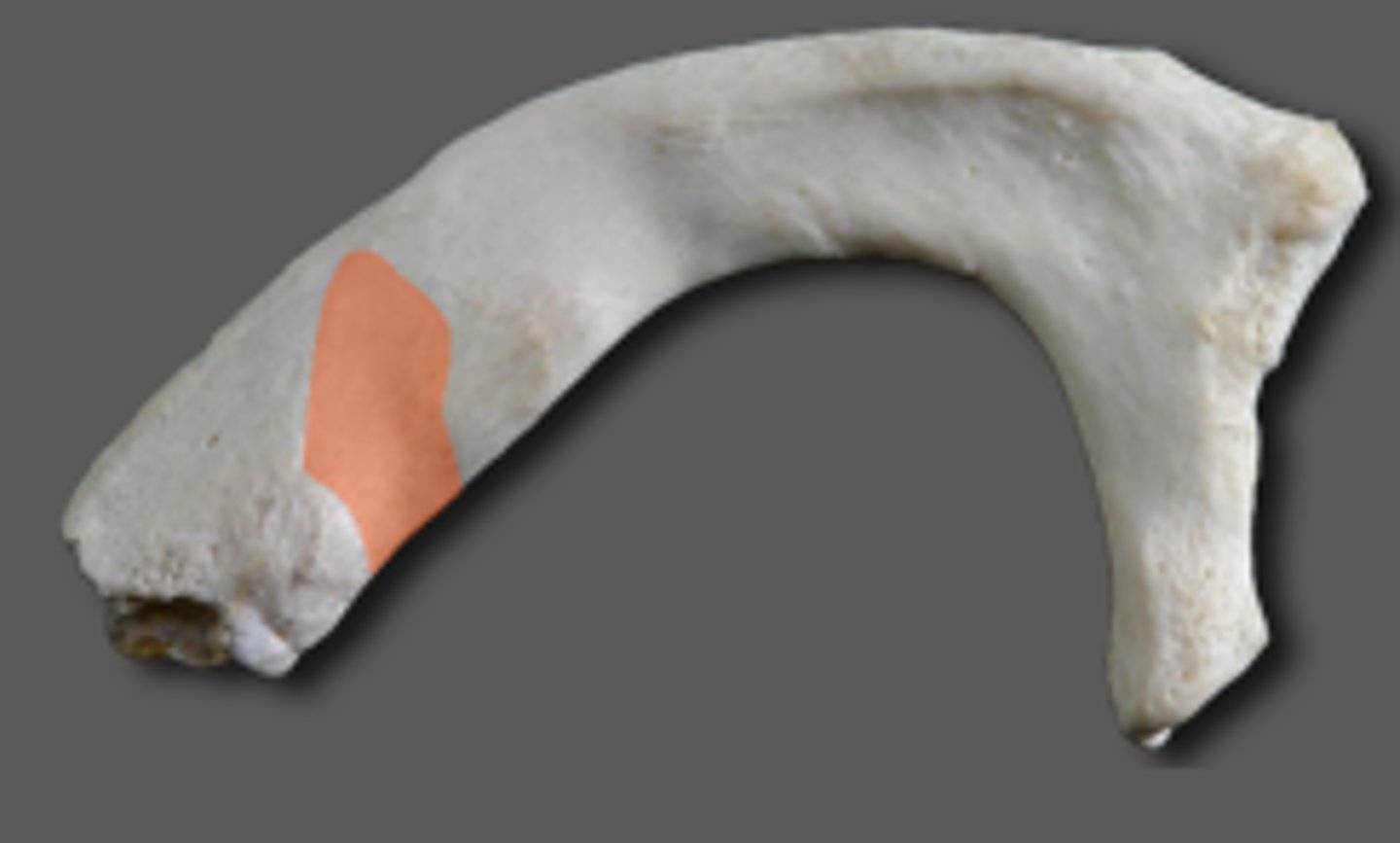
groove for subclavian artery
Rib 1
Immediately posterior to the scalene tubercle on the upper surface of the first rib
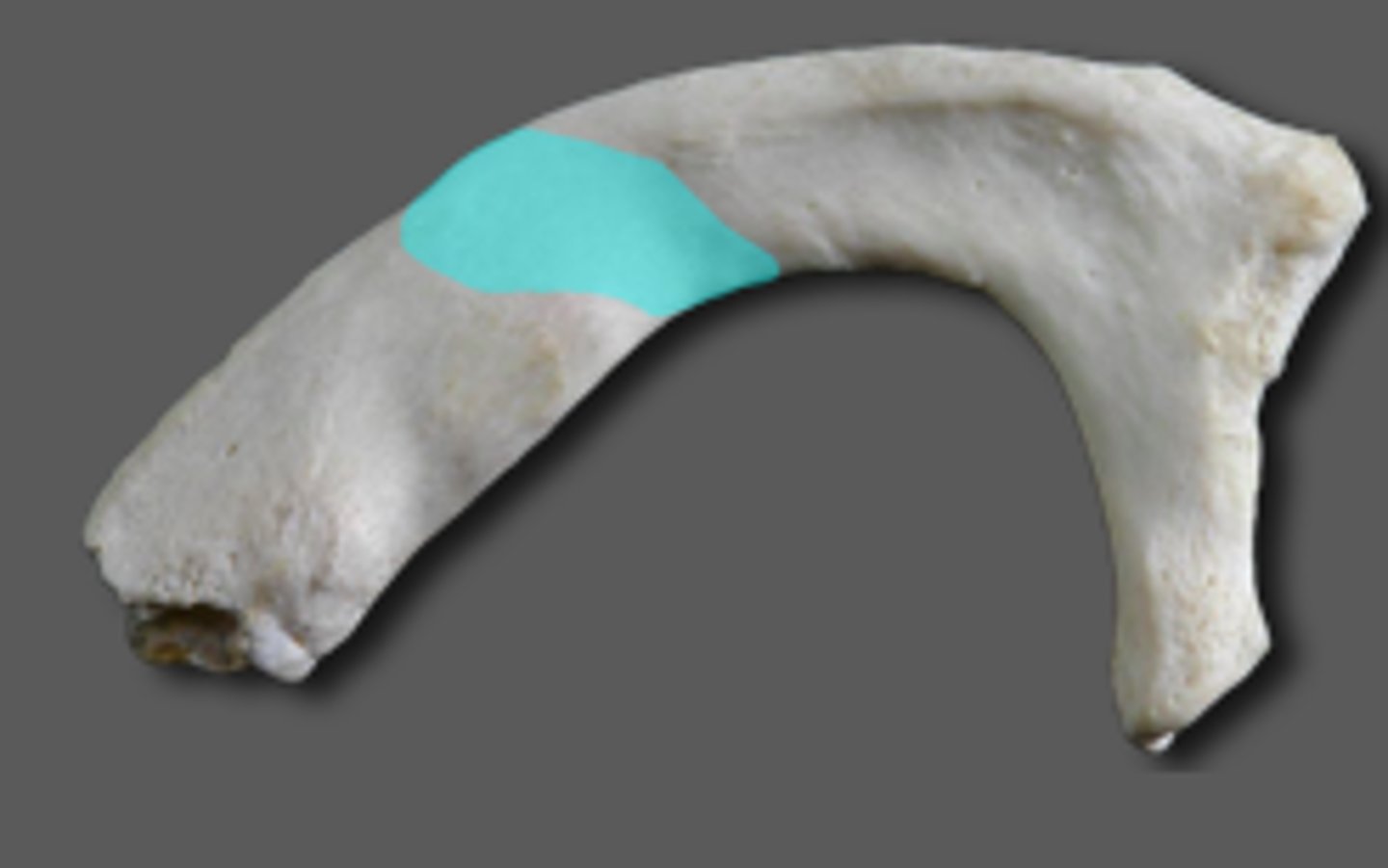
scalene tubercle of the first rib
anterior scalene insertion
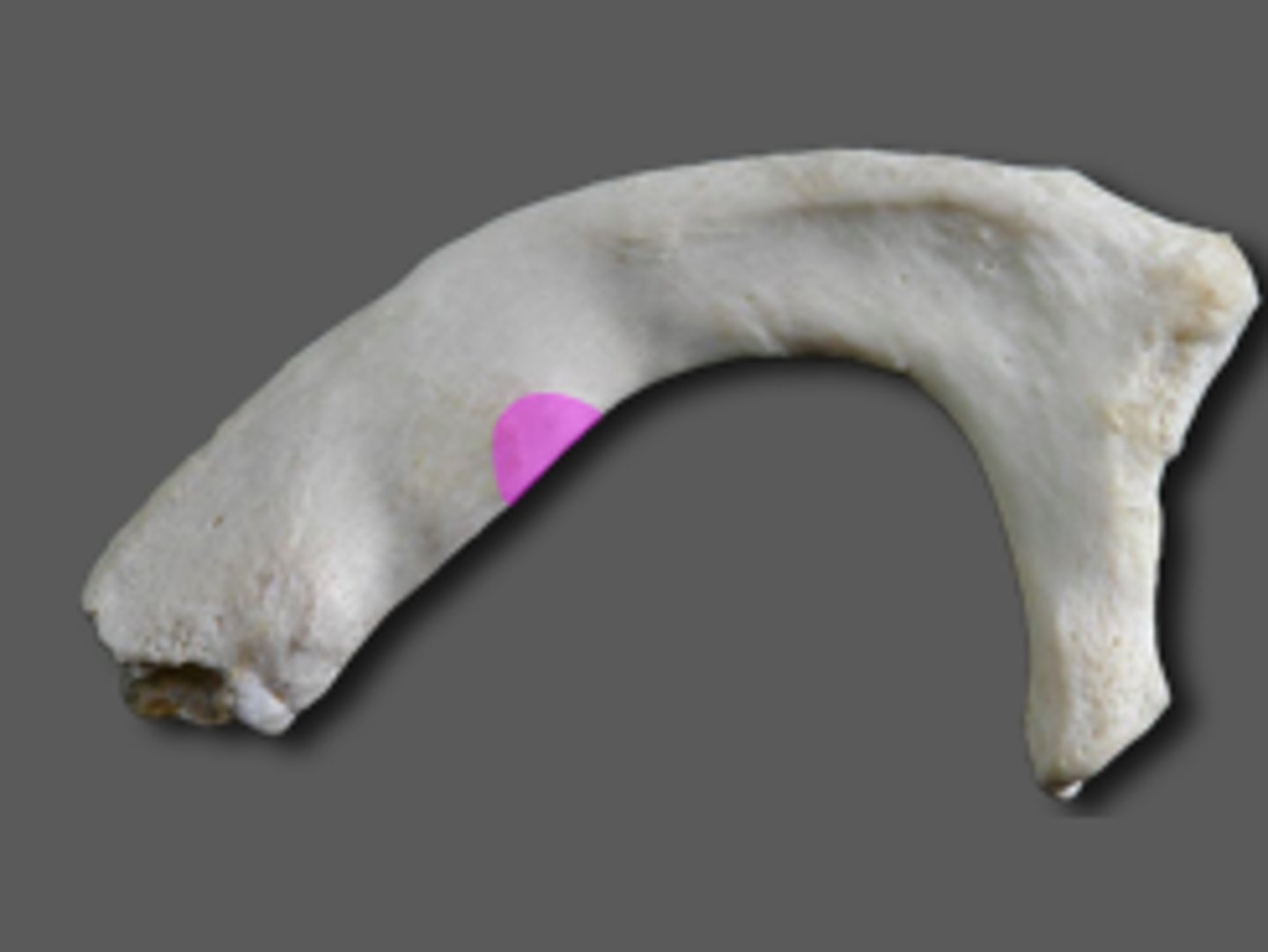
angle of rib
curve of rib
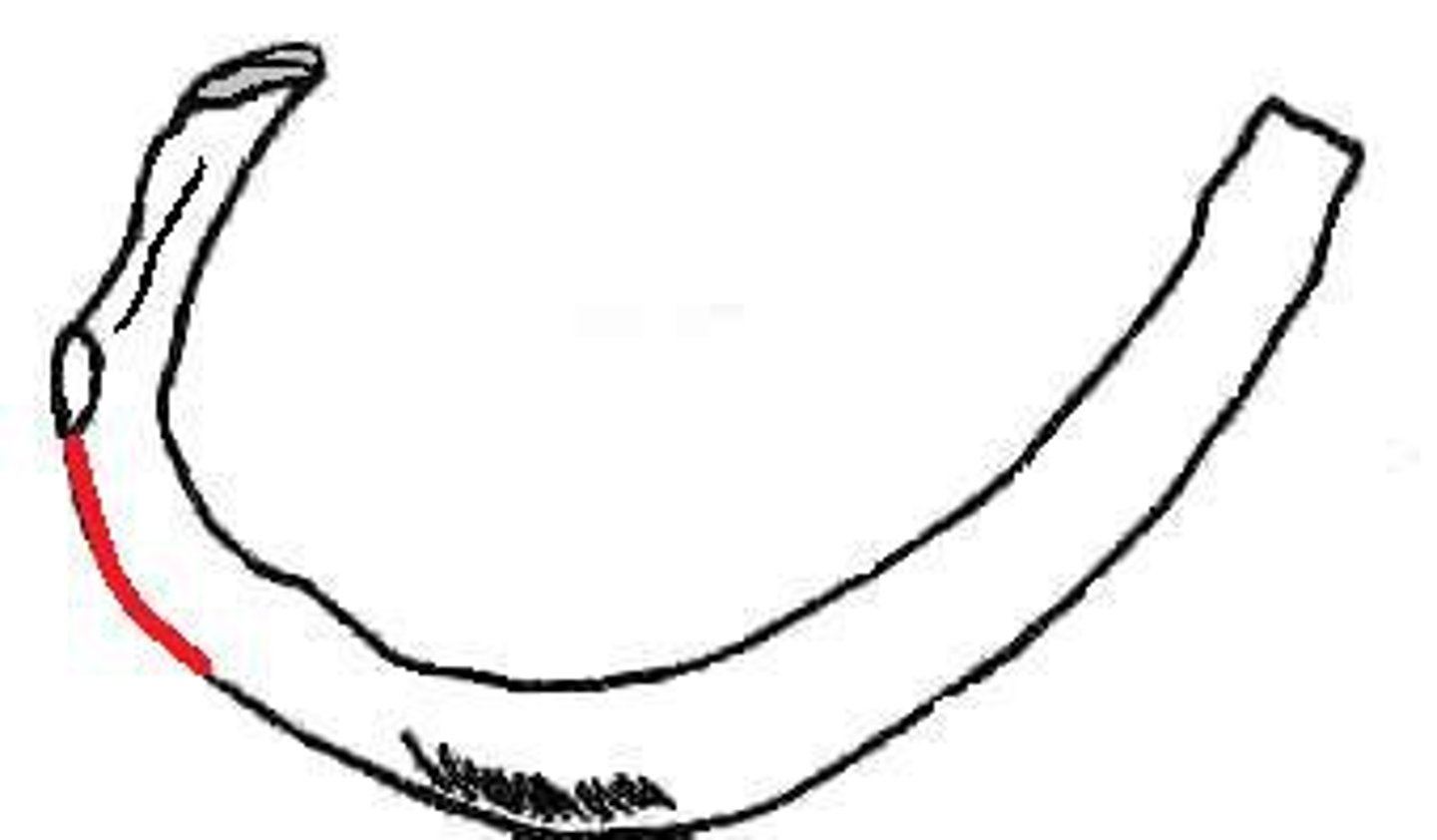
serratus anterior tuberosity
A bulbous bony protrusion found centrally but on the superior anterior facing region of rib of 2nd rib only
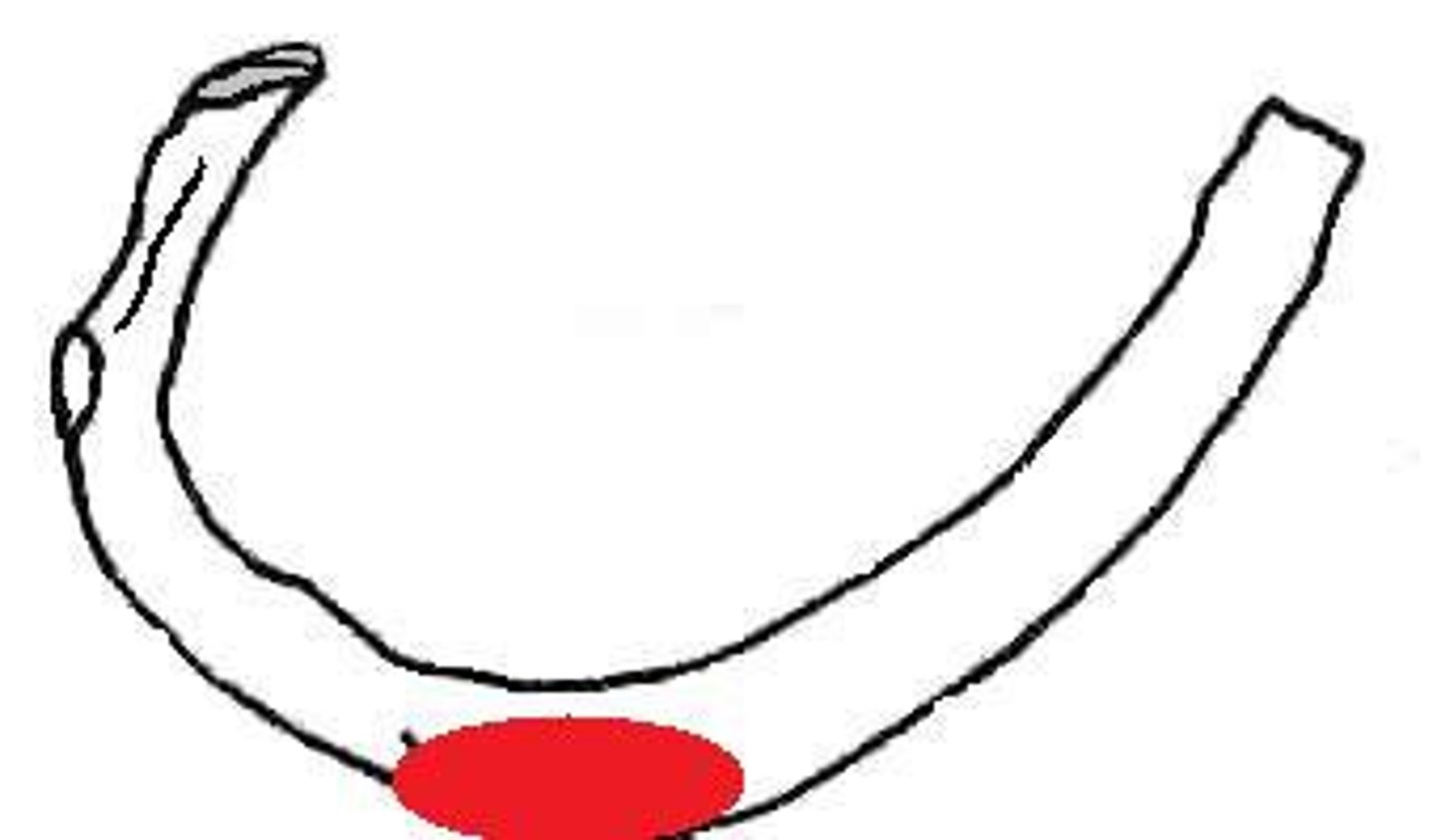
superior articular facet of rib
articulates with inferior costal demifacet of the thoracic vertebral body one numeric segment superior
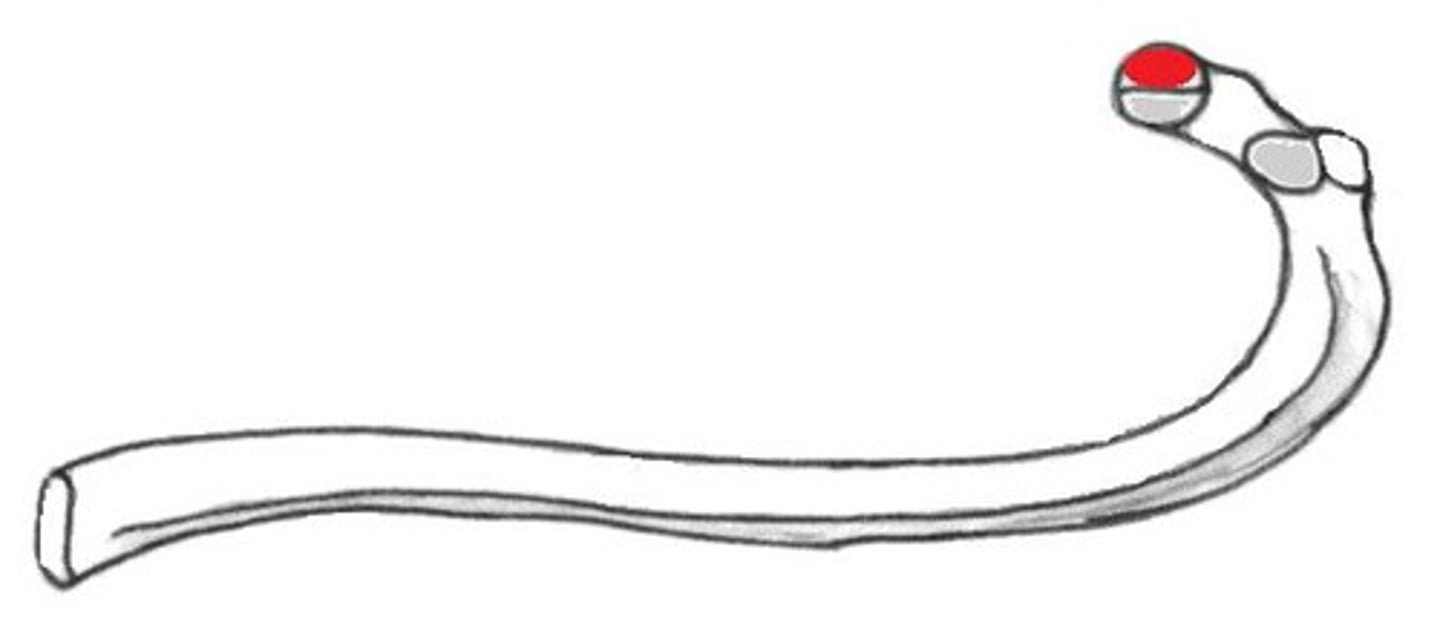
inferior articular facet of rib
Articulates with the superior costal facet of a thoracic vertebral body.
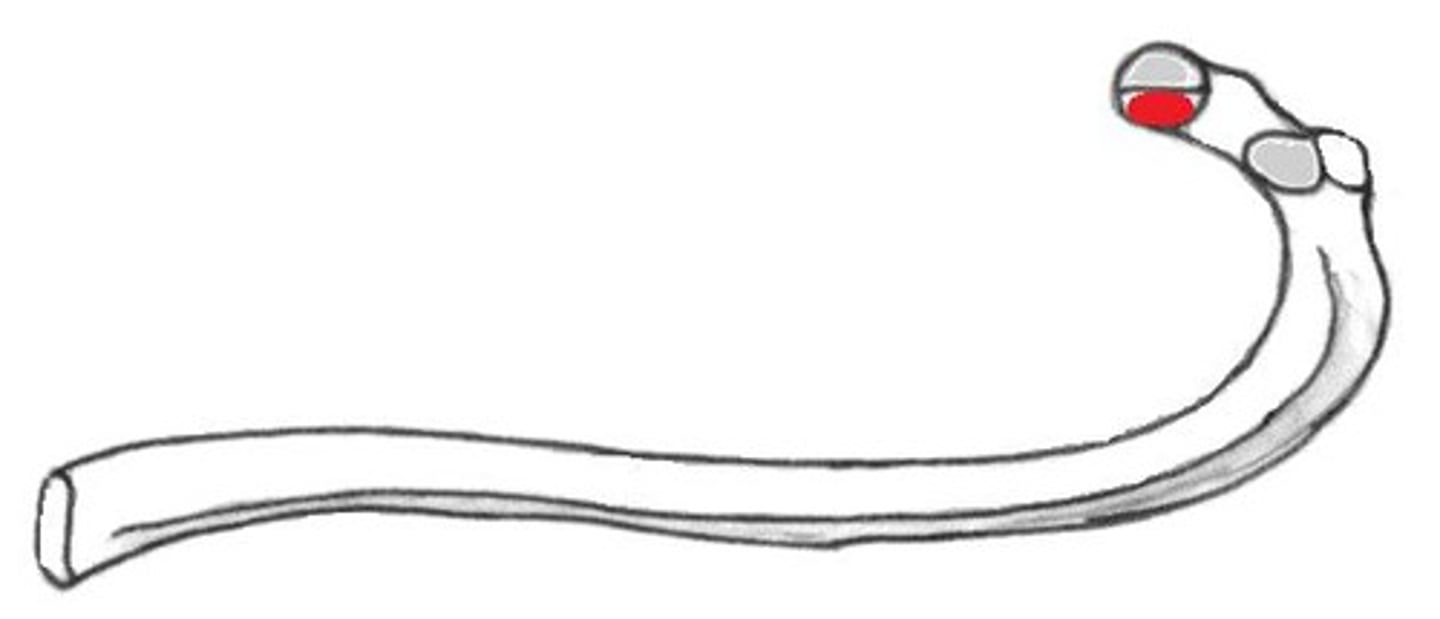
costal groove of rib
muscle attachment; arteries, veins, and nerves run in the groove
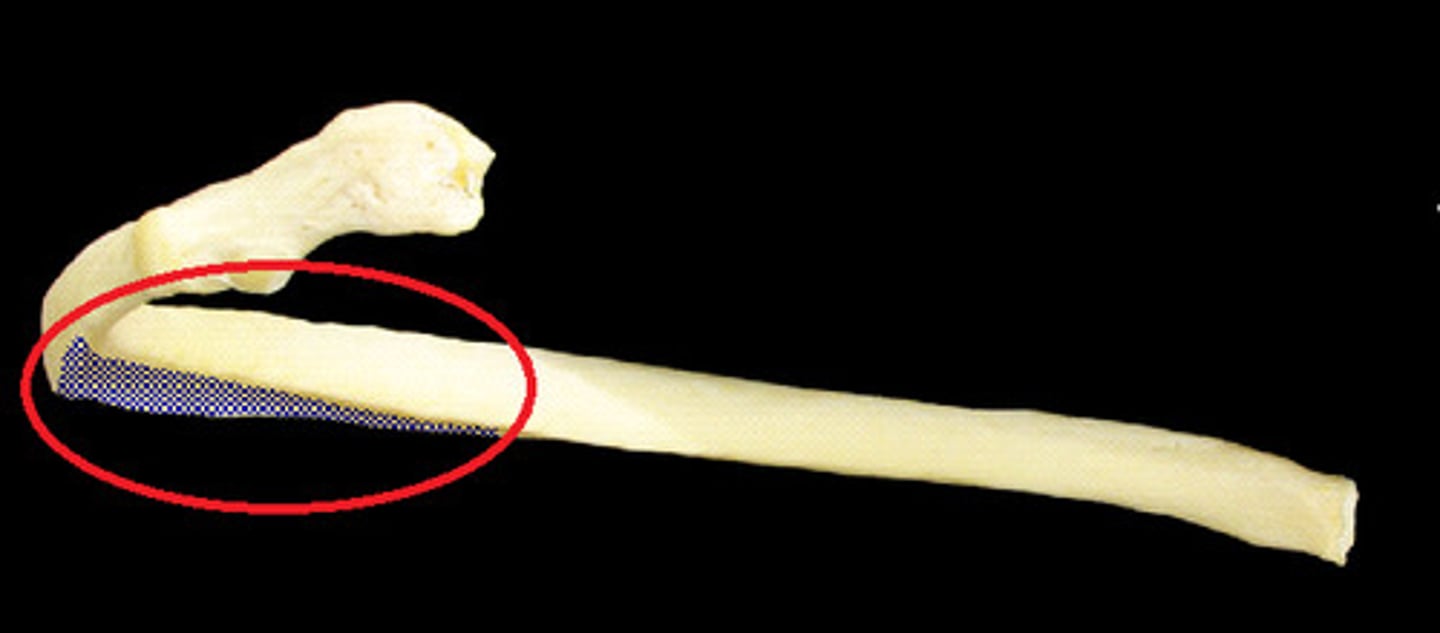
Which are false ribs? Why?
ribs 8, 9, 10 (usually), attach directly to sternum but by the cartilage of the superior rib
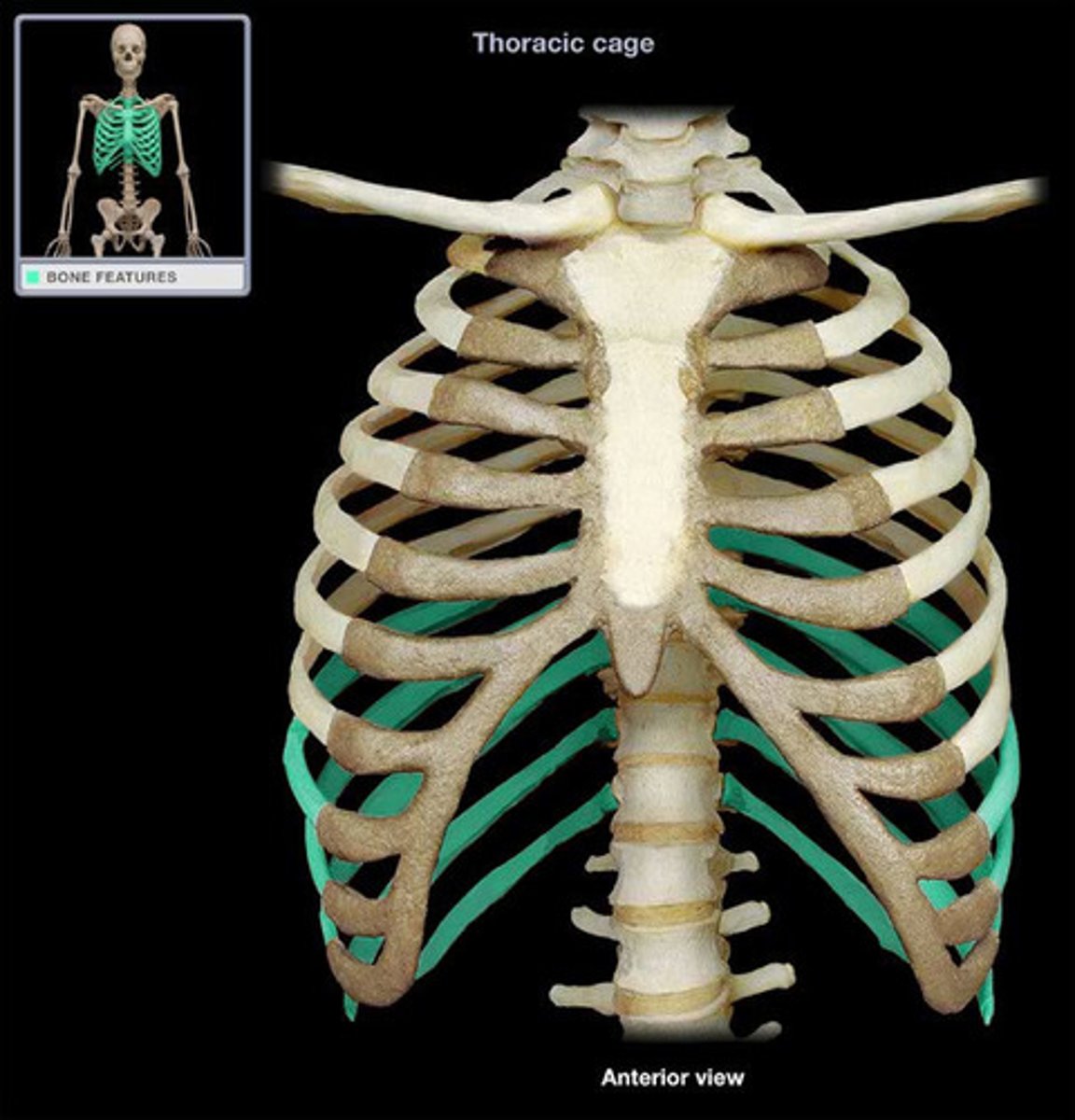
Which are the "floating ribs" and why?
11-12, Don't attach in any way to sternum
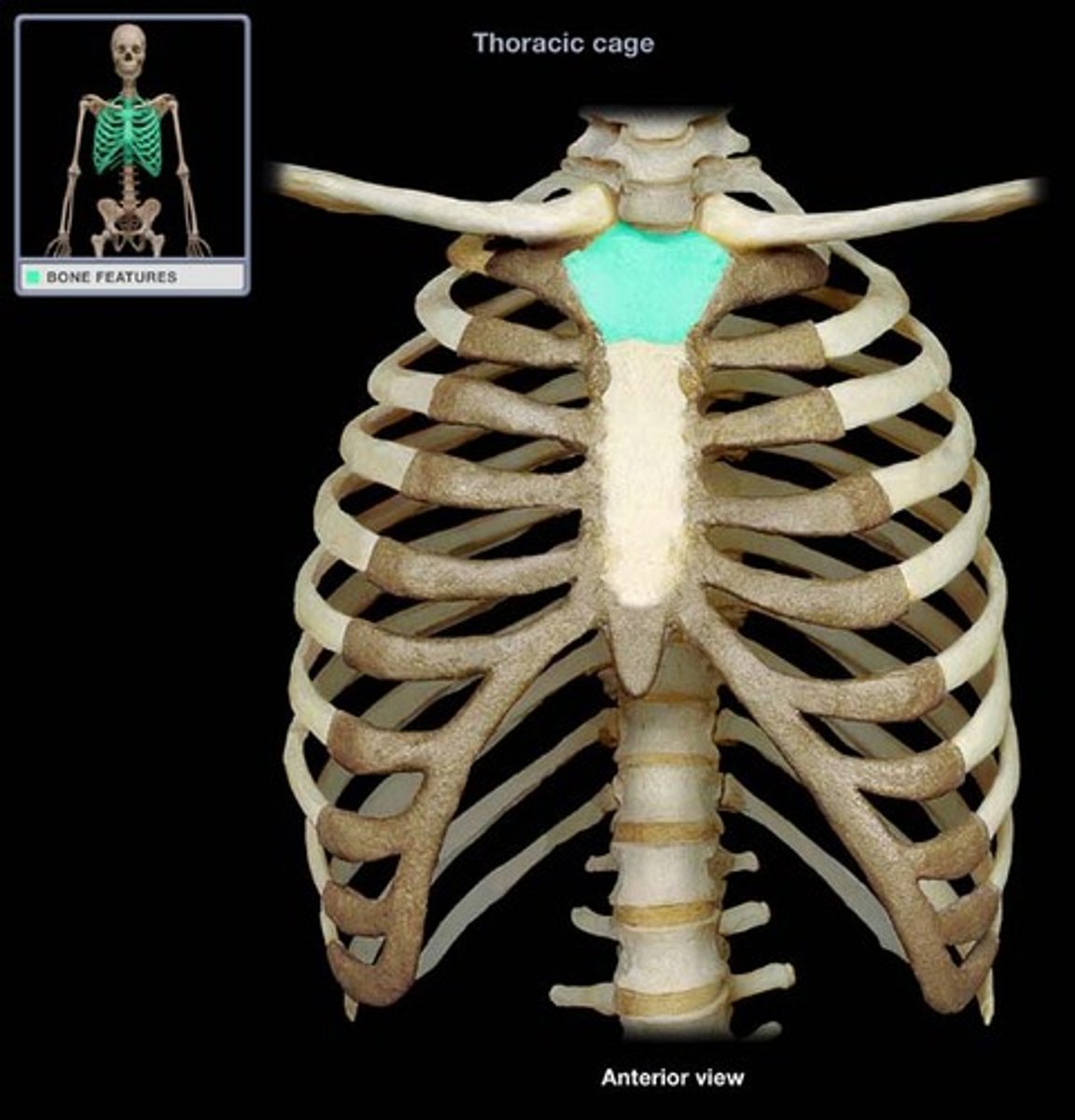
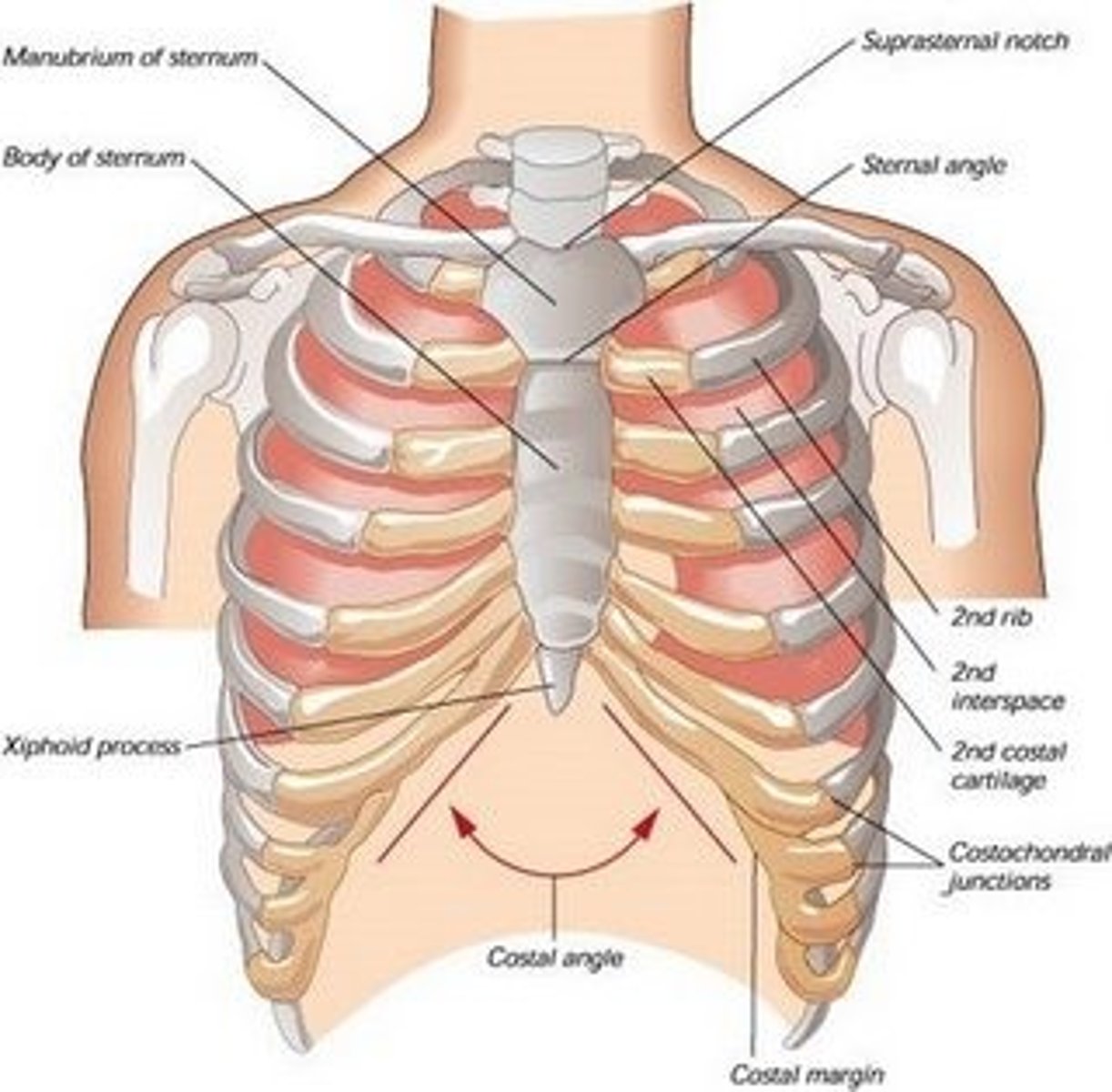
manubrium of sternum
Articulates with ribs 1, 2, & clavicles. Sternocleidomastoid muscles also attach here.
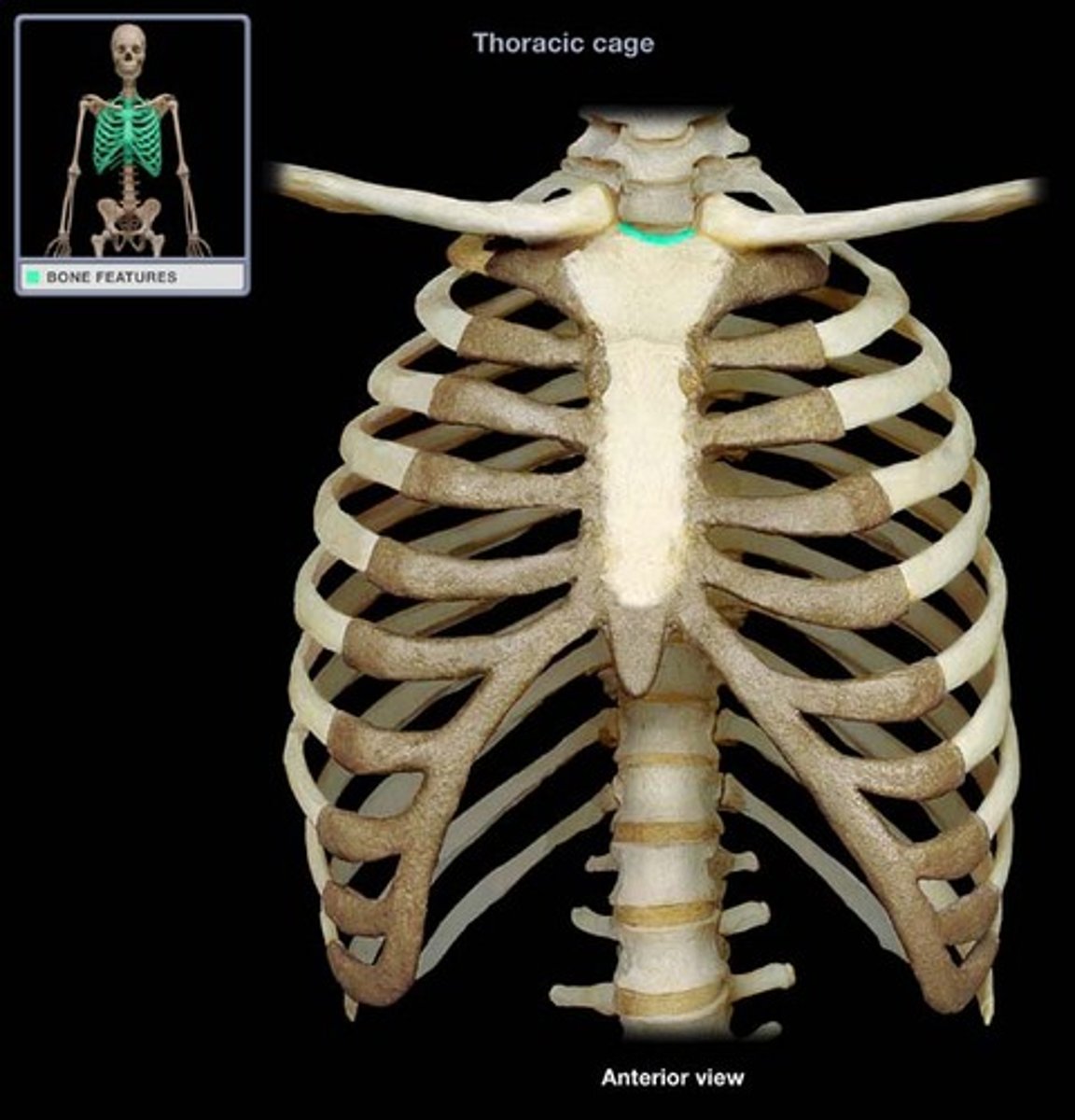
suprasternal (jugular) notch
superior surface of manubrium; u shaped notch
clavicular notch of sternum
Site where manubrium articulates with the clavicles

costal notches of sternum
indentations on sternum where costal cartilages from the ribs articulate
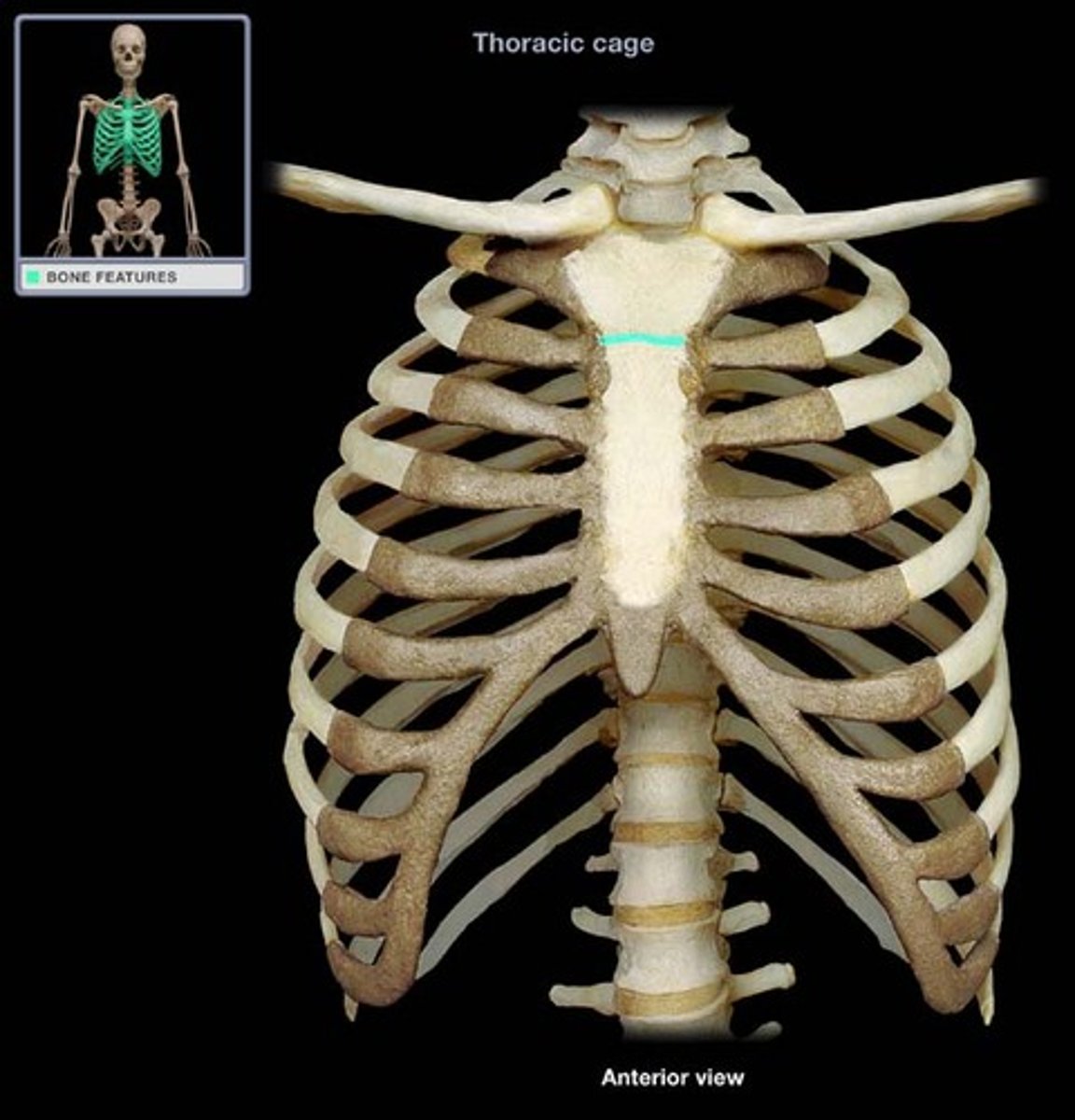
sternal angle
Ridge between manubrium and body at second rib
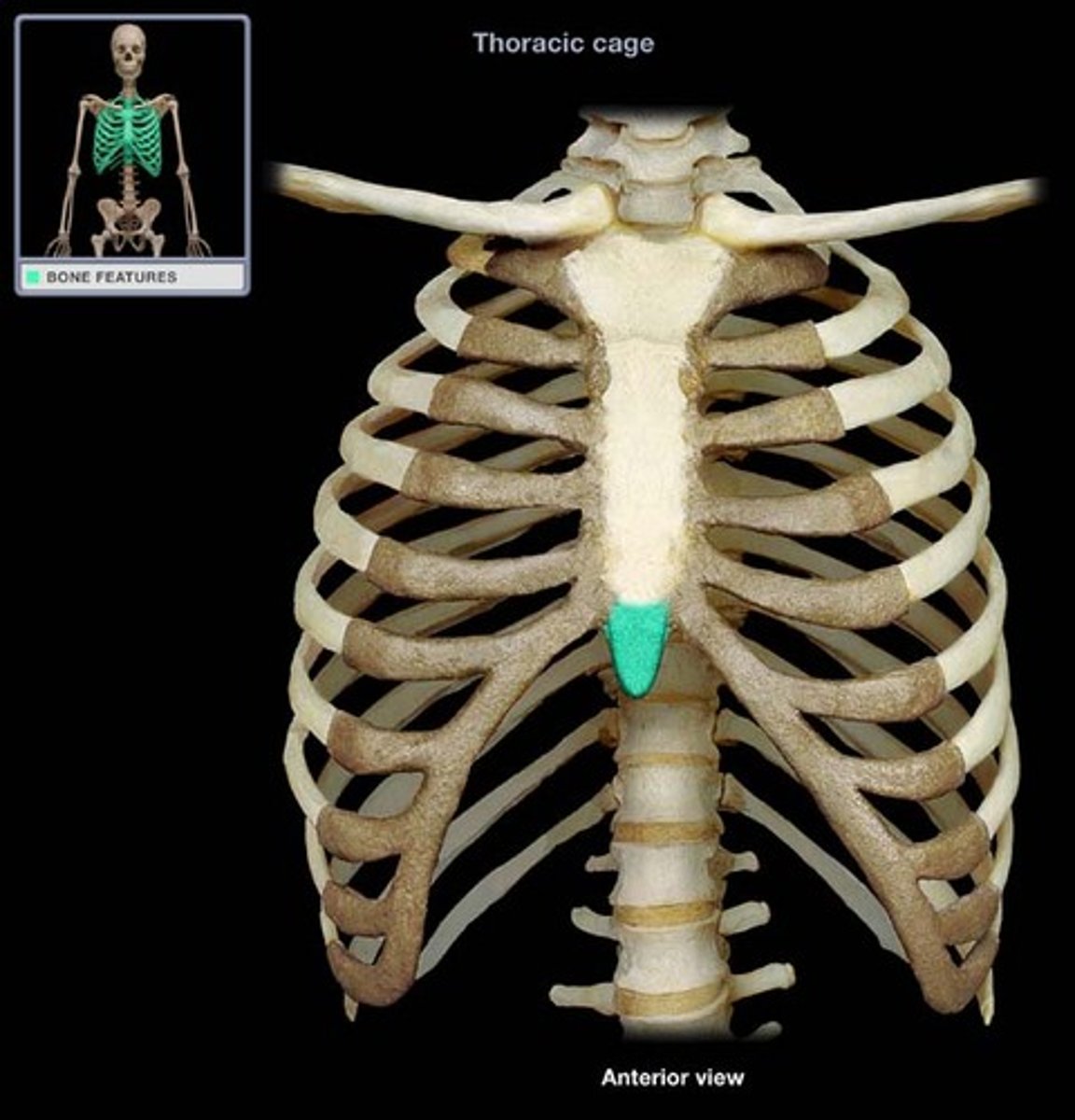
Xiphoid process of sternum
(T10)
Midline marker for superior level of liver, central tendon of diaphram
inferior border border of heart
cartilaginous in young people. Bone after 40.
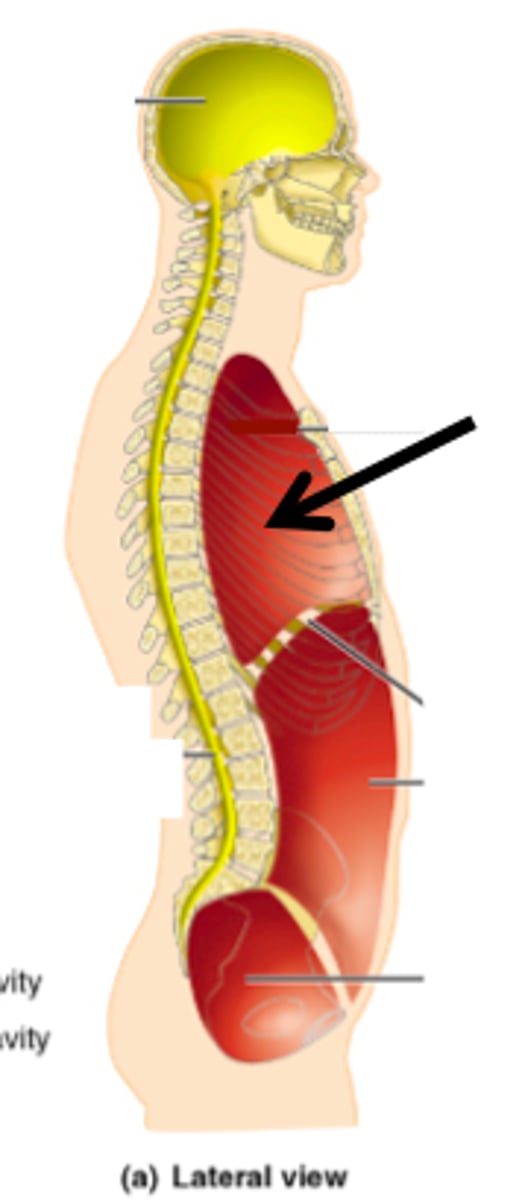
thorax
between neck and abdomen, divided at diaphragm
chest
colloquial term for anterior upper thorax

thoracic cage
ribs, sternum, thoracic vertebrae, encloses organs and moves for ventilation
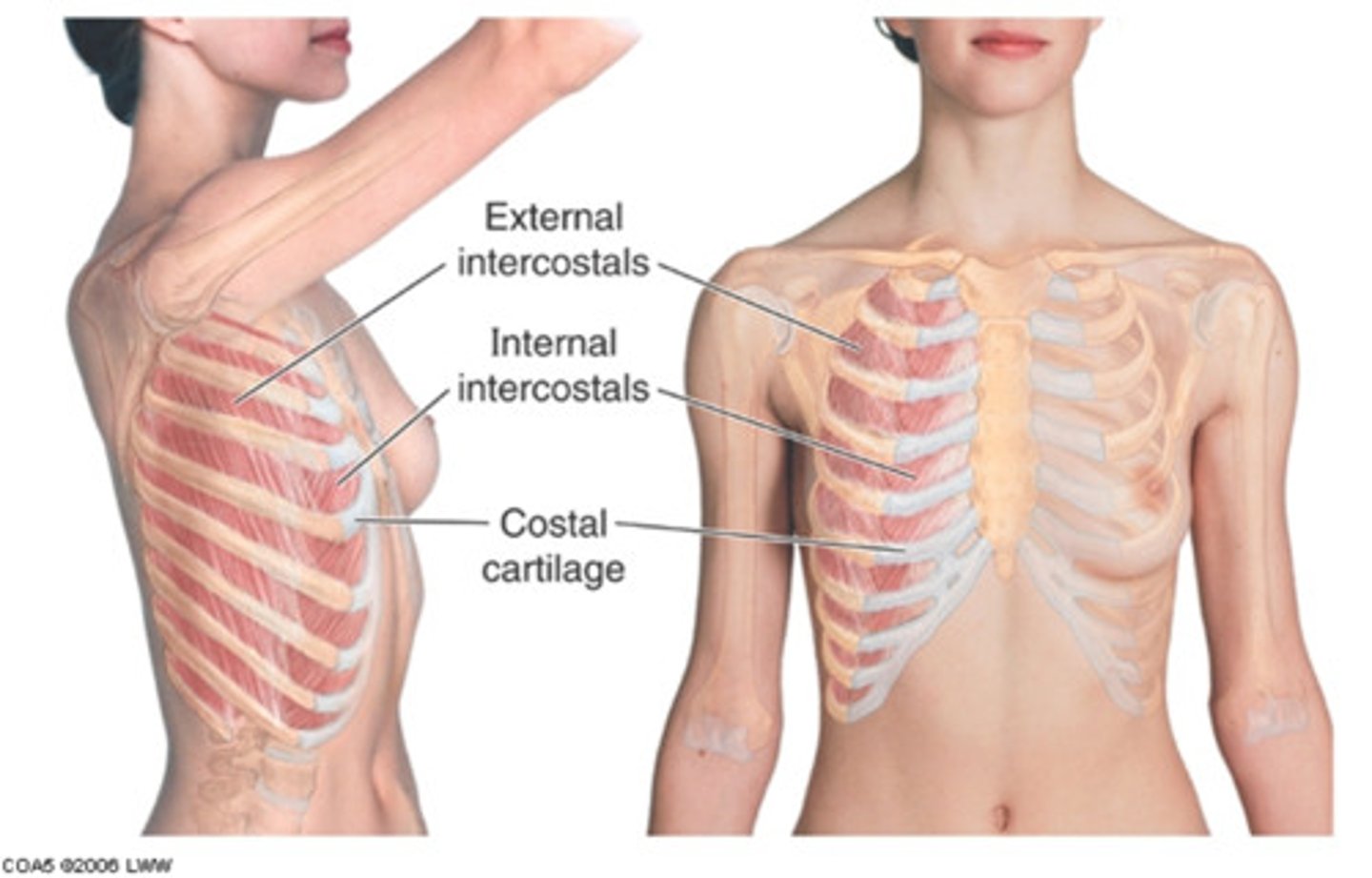
thoracic wall
thoracic cage, skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, IC muscles
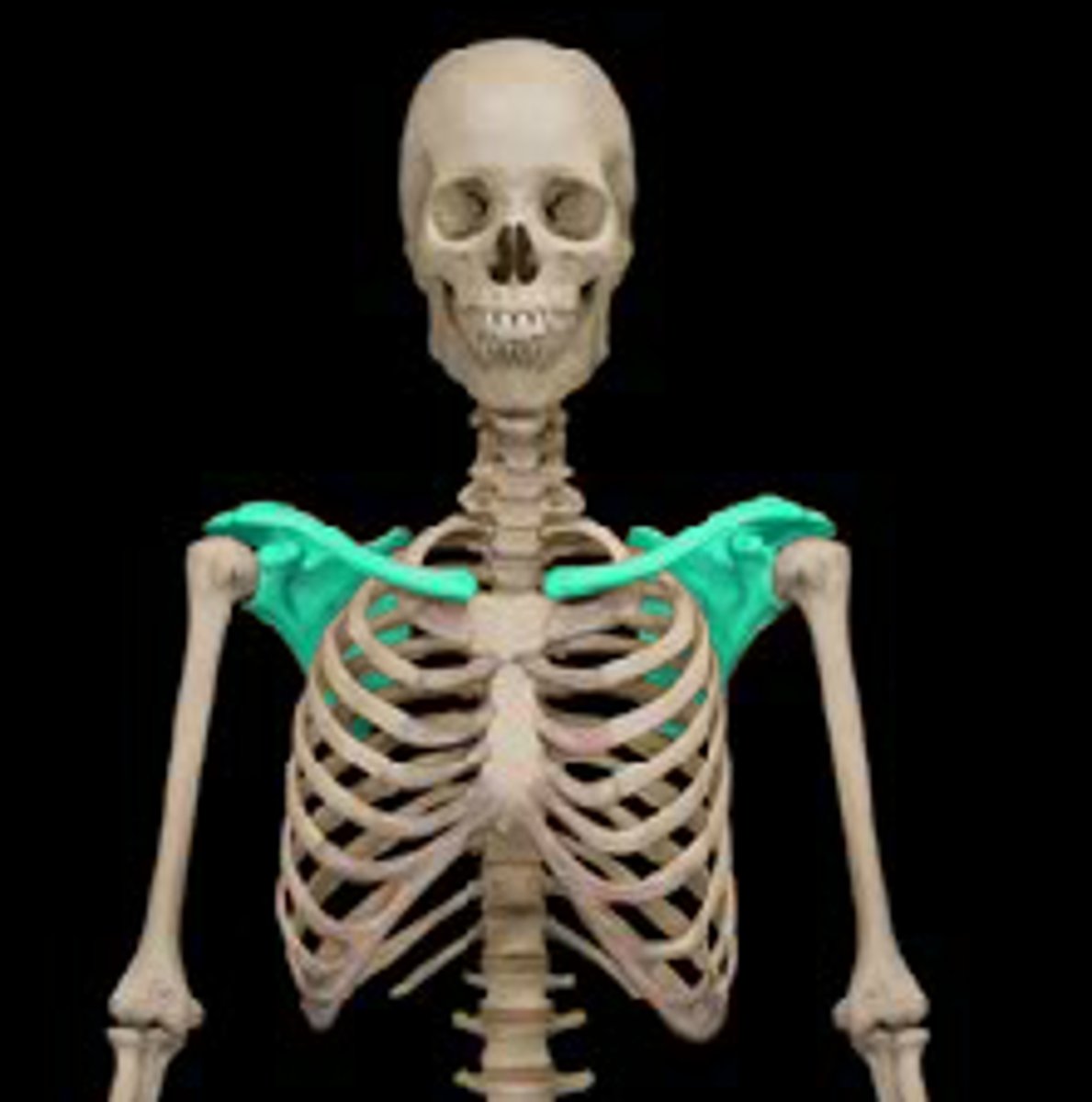
pectoral girdle
clavicle and scapula
thoracic cavity
mediastinum, pleural cavity, pericardial cavity
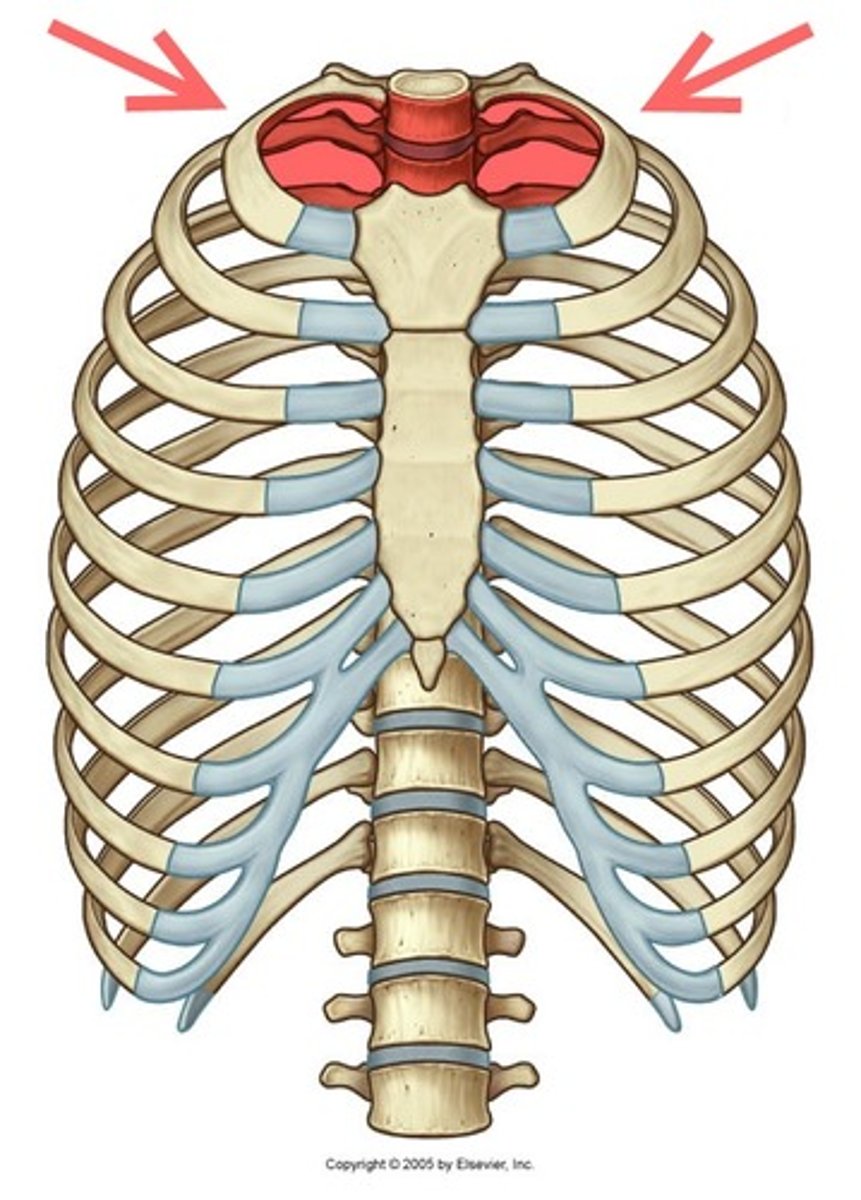
superior thoracic aperture
Continuous with the deep neck and upper limb.
Densely packed with vasculature and viscera. (rostral border)
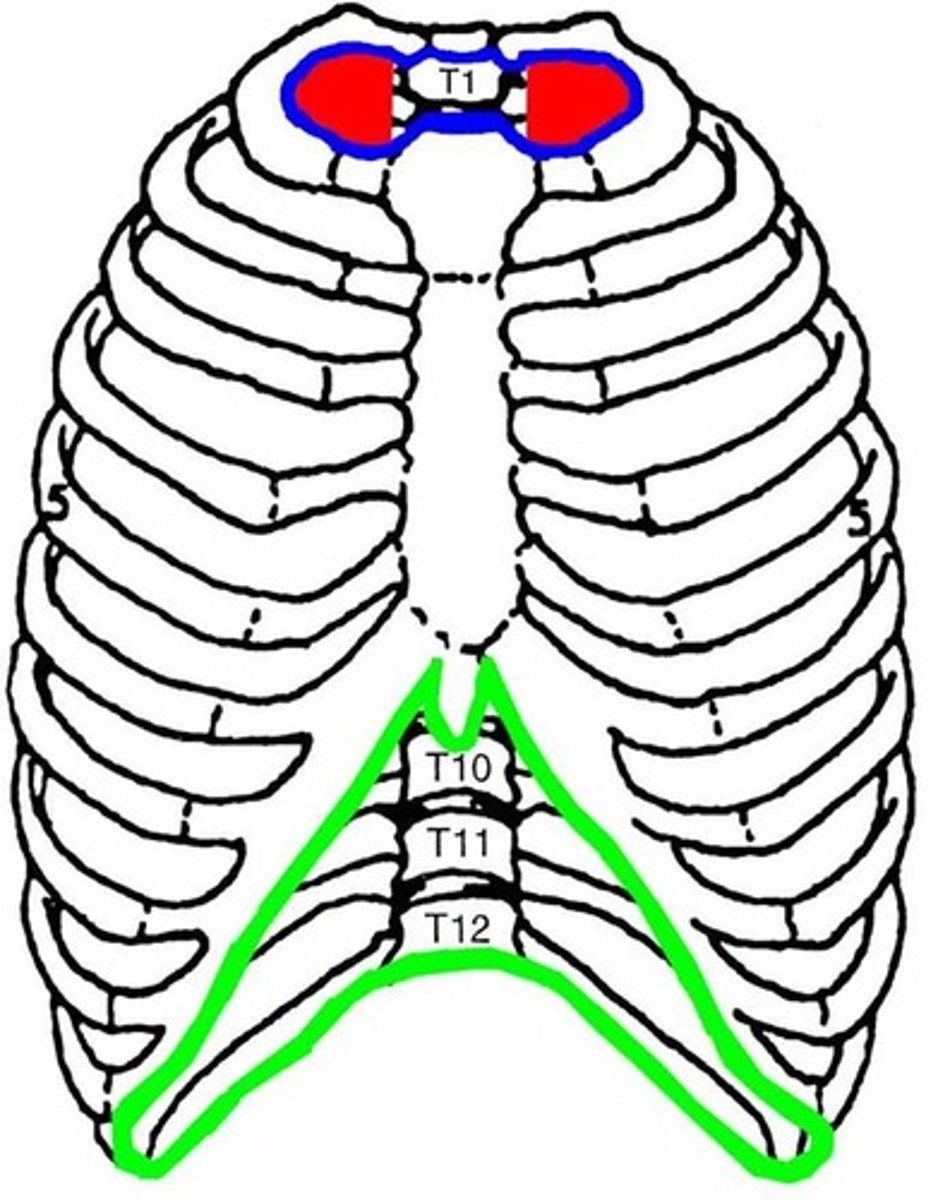
inferior thoracic aperture
plane created by diaphragm (enclosed inferiorly), xiphoid process, costal margin, edge of ribs and T12 (caudal border)
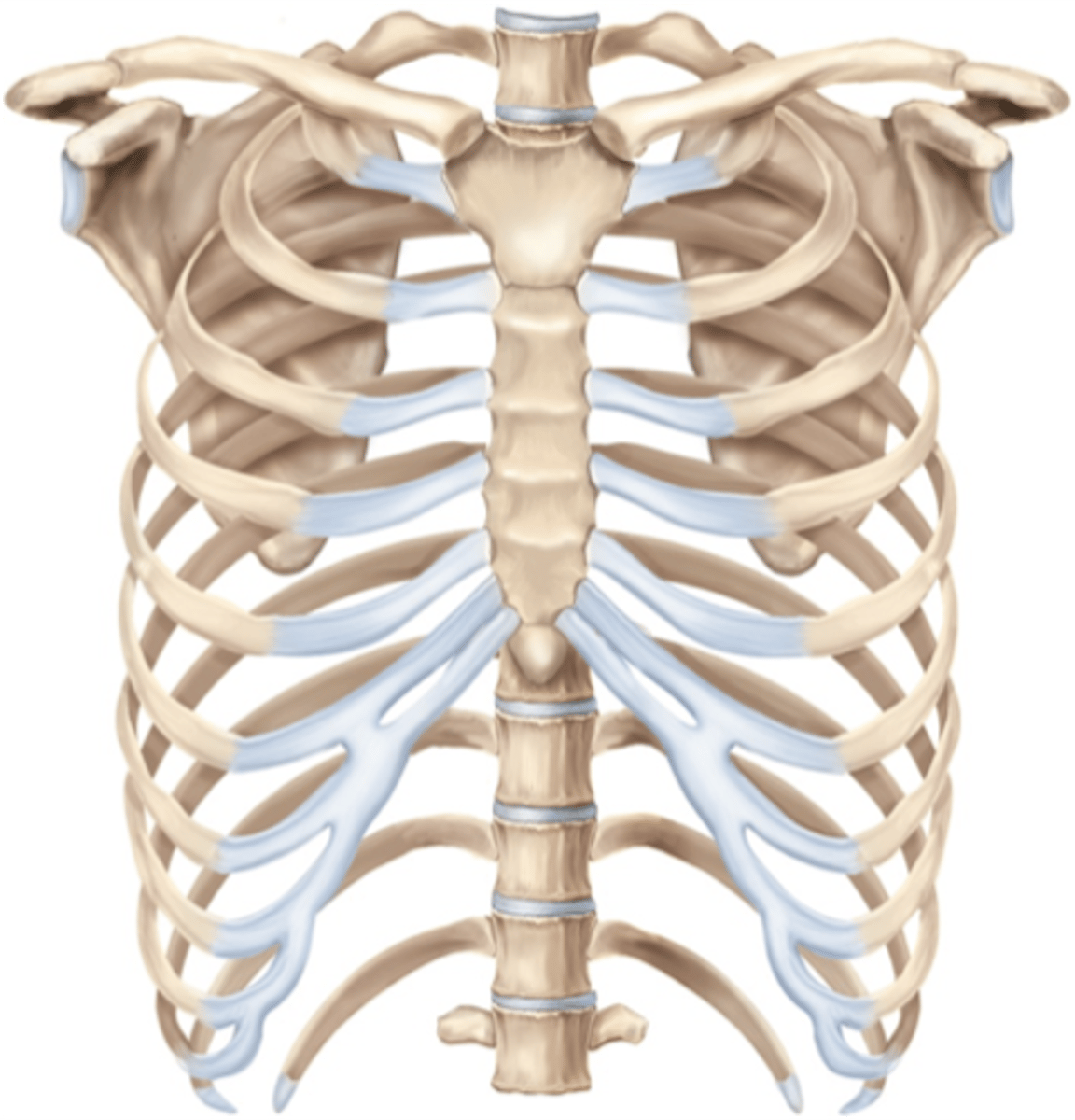
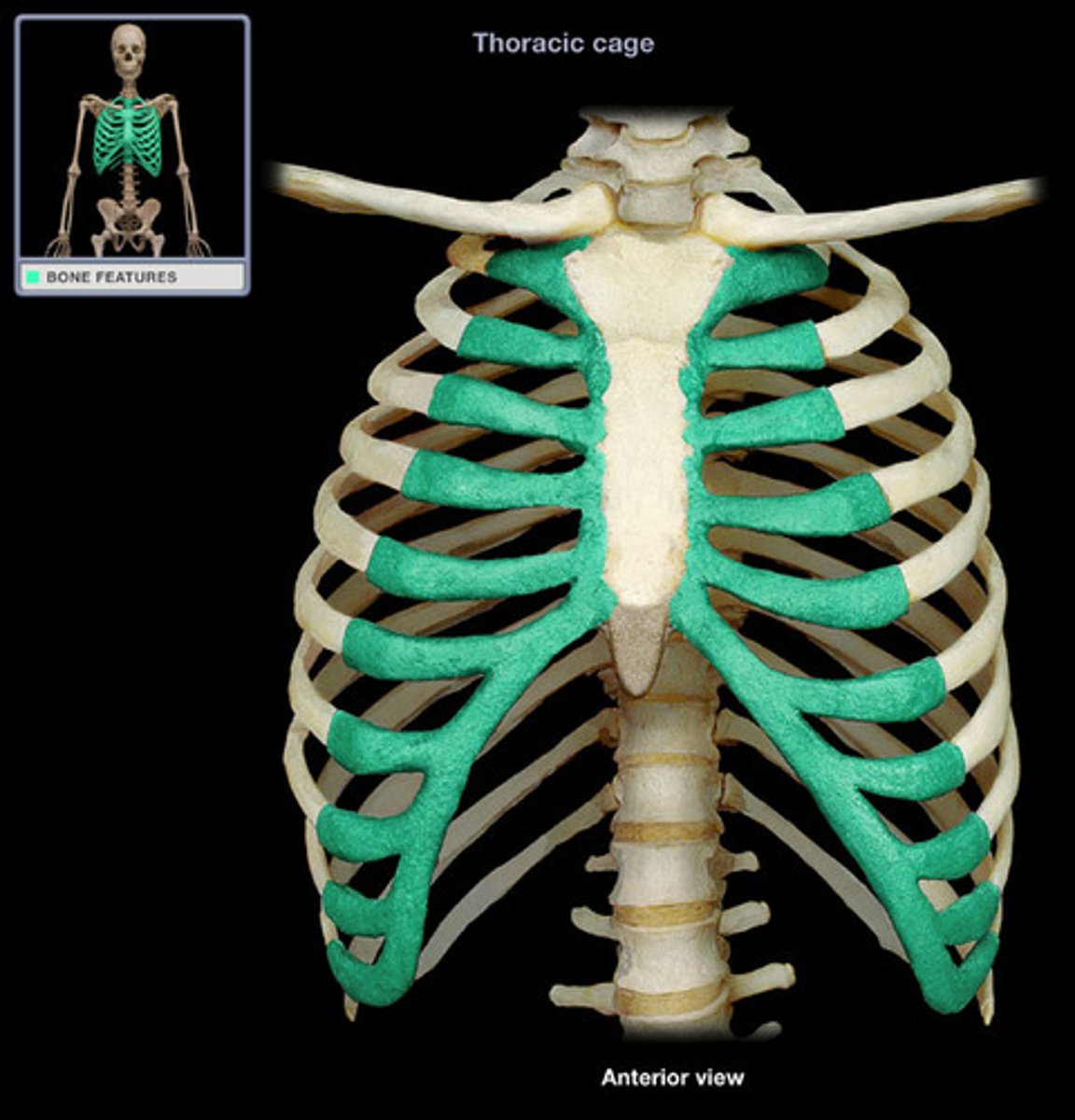
How is the costal cartilage numbered?
by the rib it articulates with
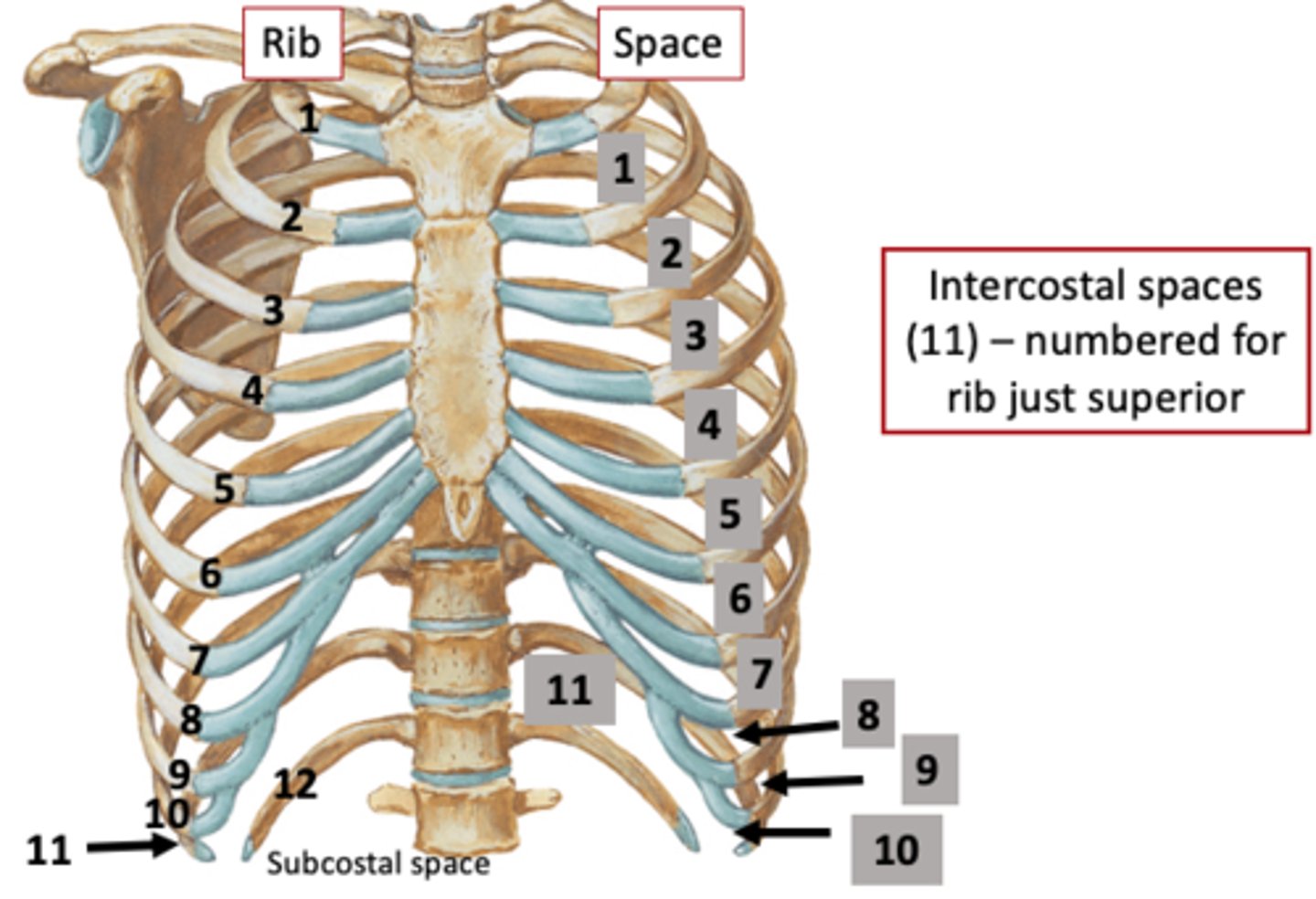
How are intercostal spaces numbered?
According to the rib superior to the space
At what part of the sternum is the left ventricle just inferior to?
if arms down, inferior to mid sternum. If arms up, inferior to lower sternum
Why are the palpable dorsal spinous processes caudal to the middle of their corresponding bodies?
the processes project inferiorly
What is the suprasternal notch level to?
T2-T3
What is the sternal angle (manubriosternal joint) level to?
T4-T5
What is the xiphisternal joint level to?
T9
What are subglandular implants and what are the pros and cons?
implants over the PM, less natural looking but less invasive
What are submuscular implants and what are their pros and cons?
implants deep to the PM, look more natural but more invasive
What does the sternum articulate with at its joints?
clavicles, ribs 1-7
1st sternocostal joint
synarthrosis and synchondrosis - starts off cartilaginous and fuses in adulthood
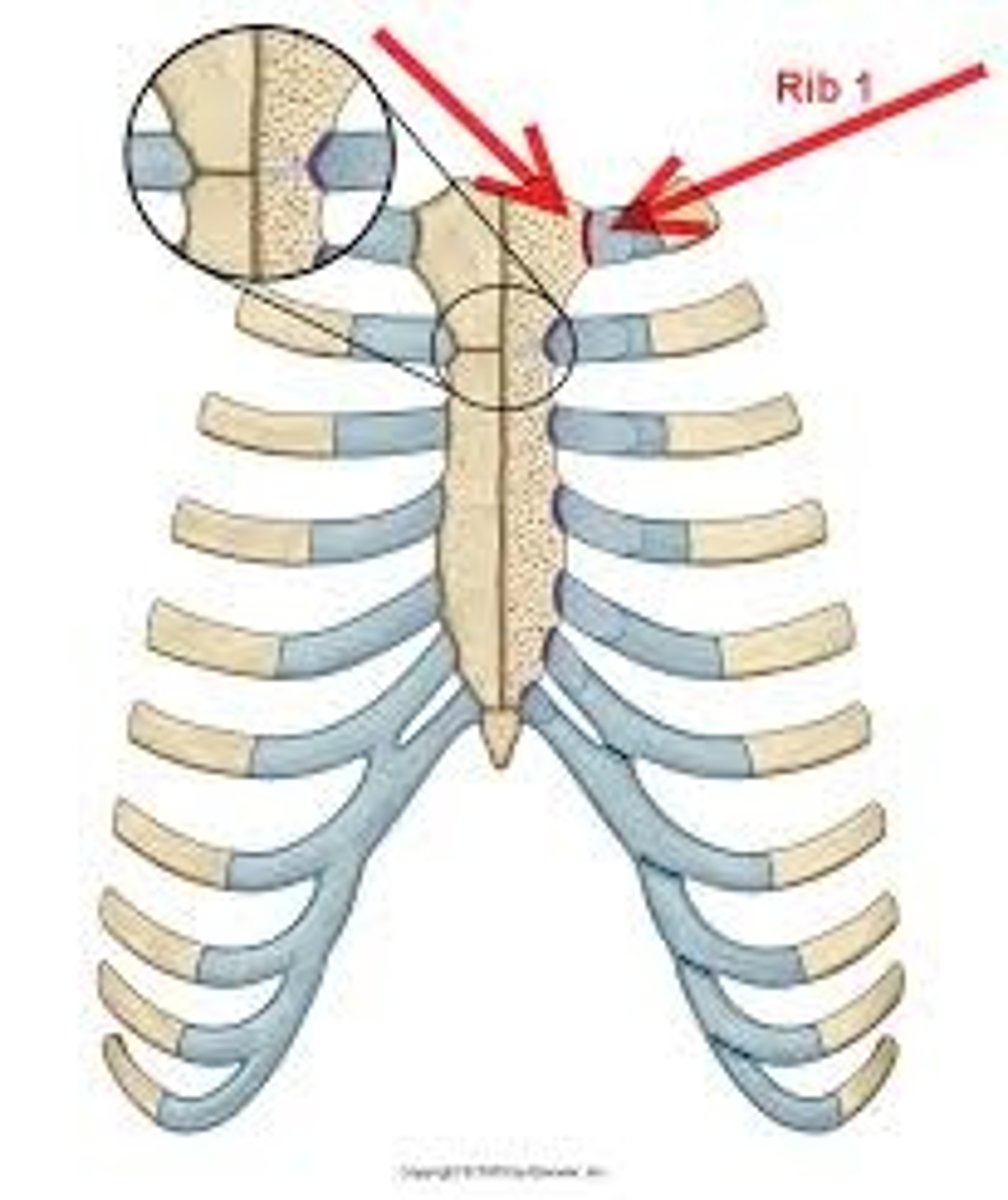
2nd-7th sternocostal joints
Synovial, diarthrodial, plane (gliding)
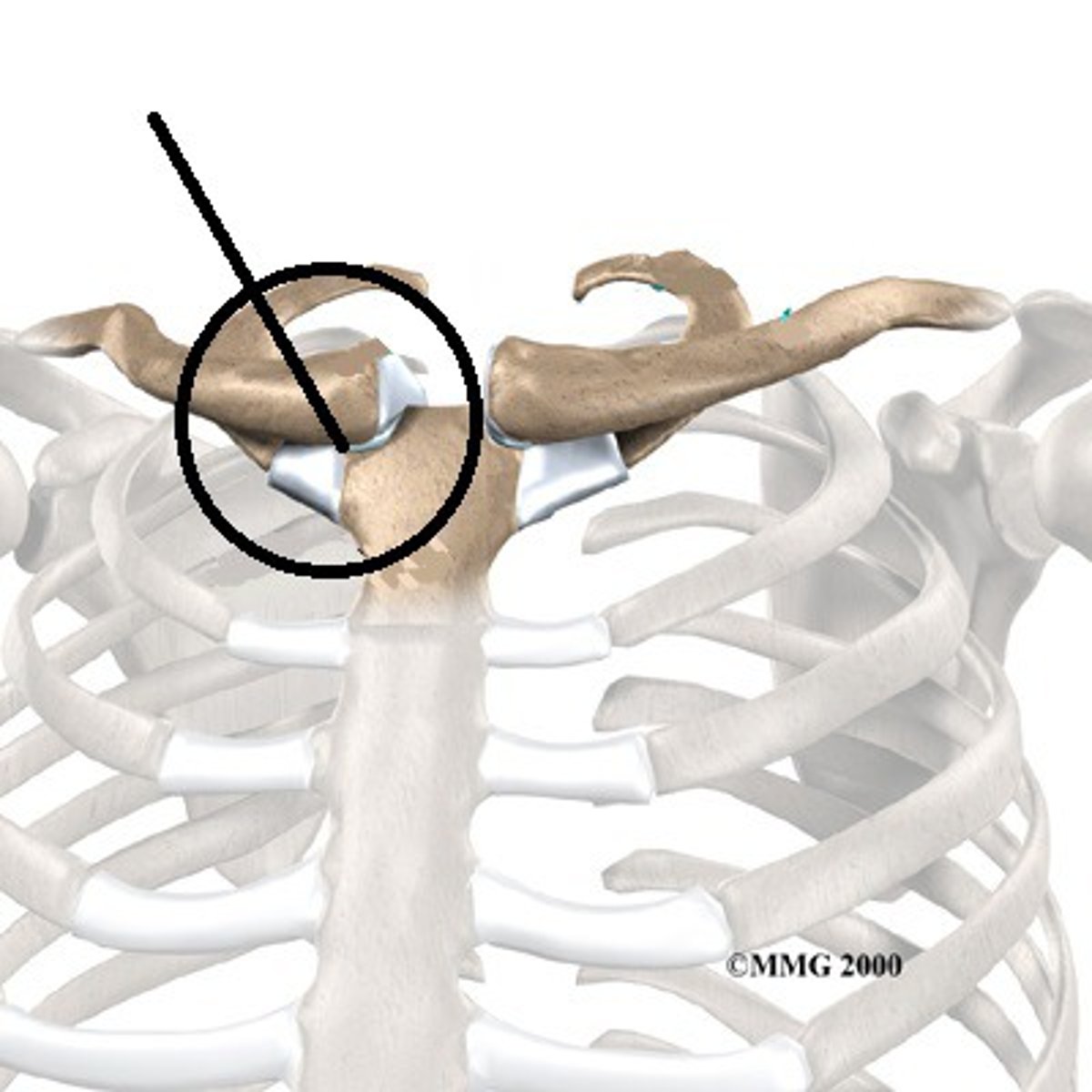
sternoclavicular joint
Articulation between the clavicle and the sternum, synovial joint
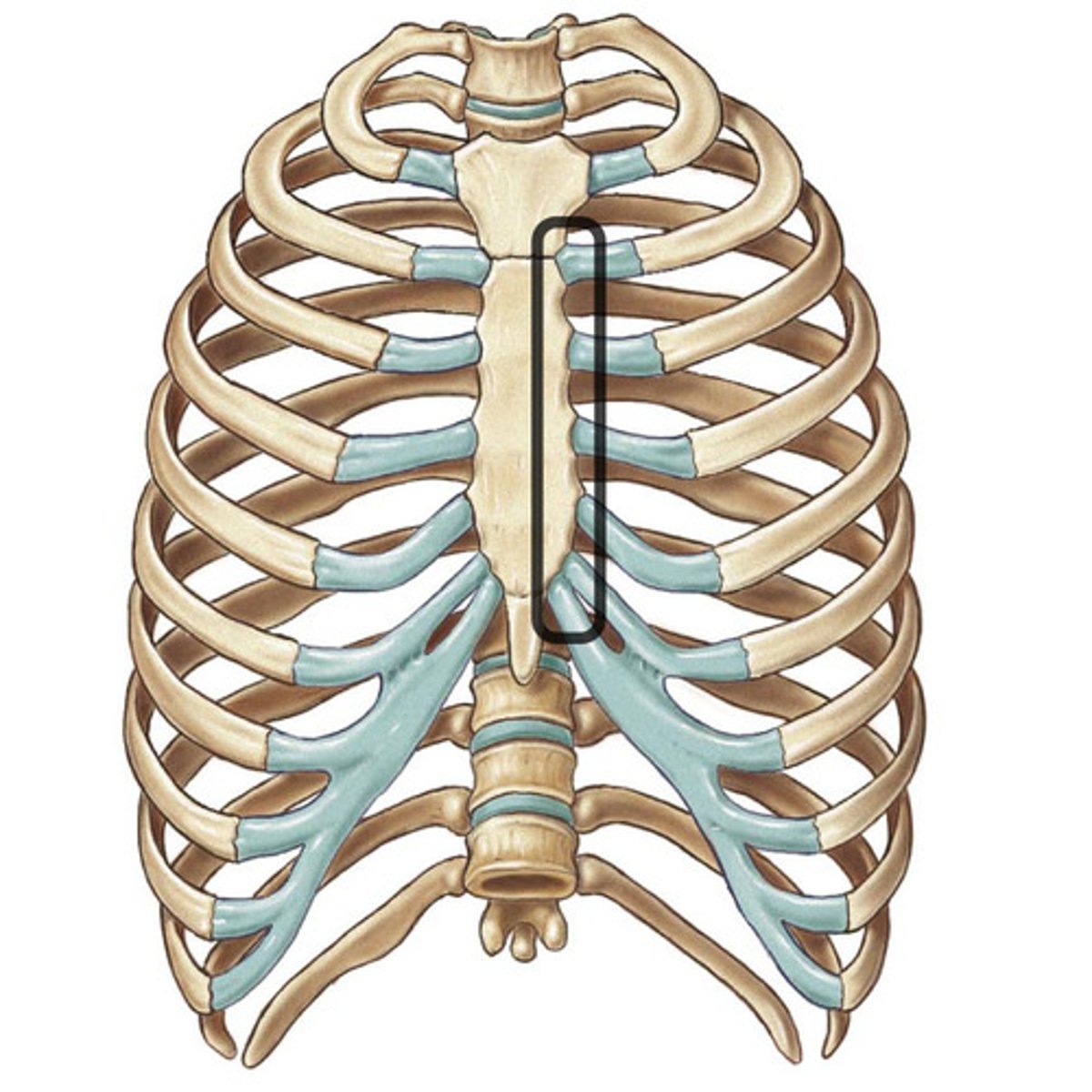
manubriosternal joint
symphysis between manubrium and body of sternum
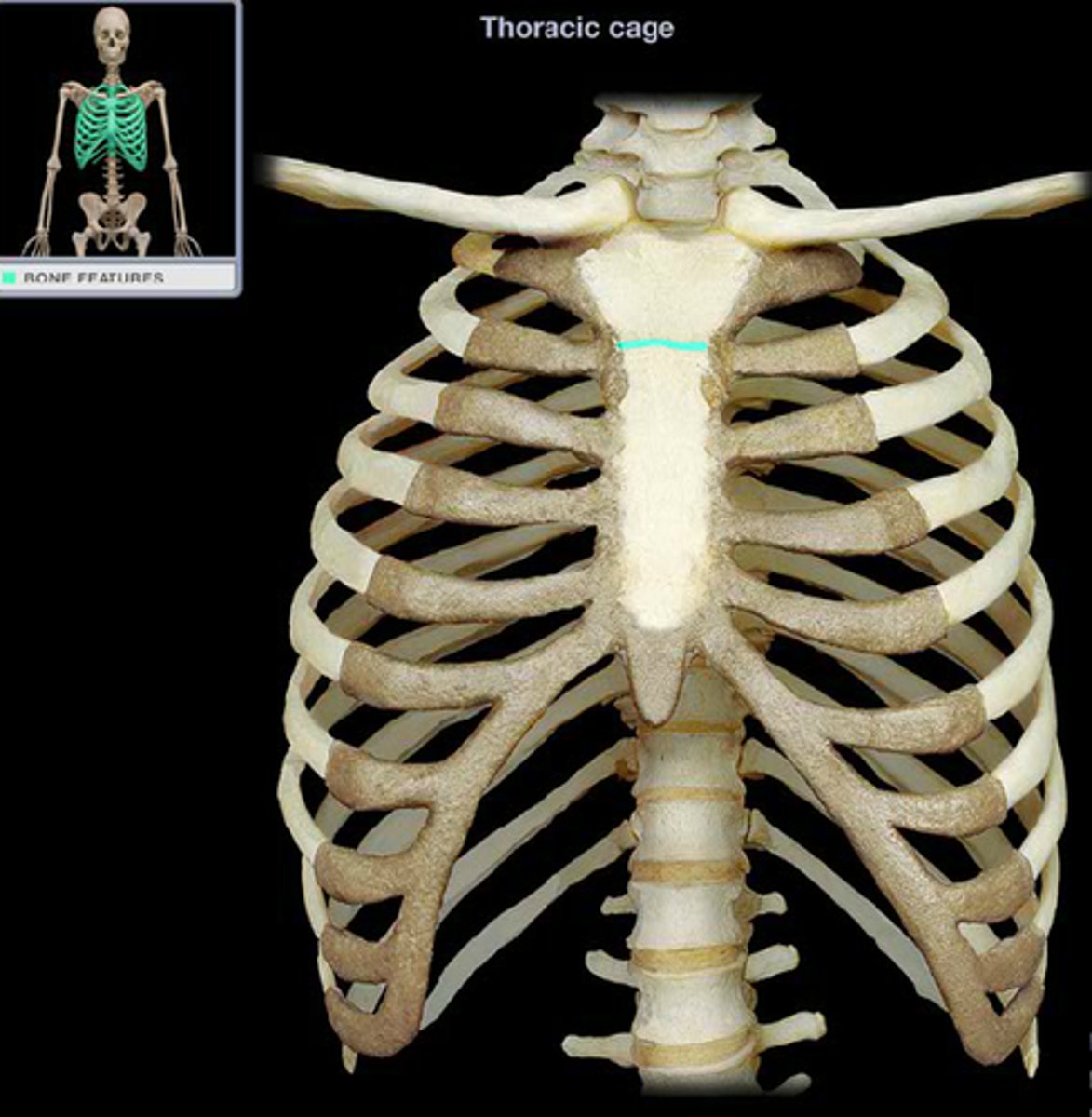
xiphisternal joint
point where sternal body and xiphoid process fuse, symphysis
What is the general frequency and size of thoracic wall joint movements?
they are frequent but small
costovertebral joint
pertaining to the joint between a rib and a vertebra, synovial, vulnerable to sprain

costotransverse joint
The point of articulation between the tubercle of a rib and the transverse process of a vertebra, synovial
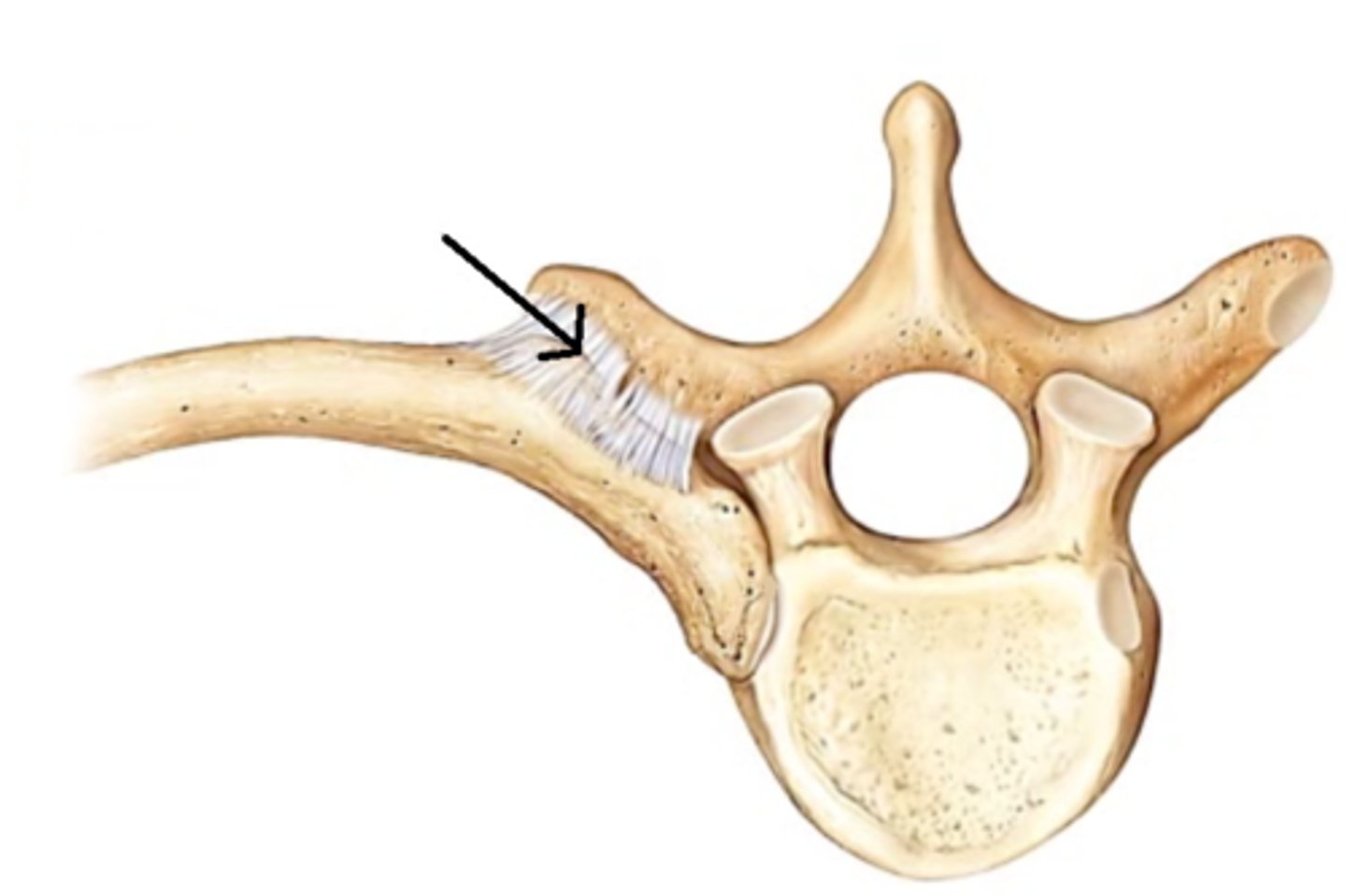
Which vertebra(e) does a rib articulate with at a costovertebral joint?
the vertebra one above and its own
Which vertebra(e) does a rib articulate with at a costotransverse joint?
only its own
What is the movement of a costotransverse joint and why?
mostly rotational, anterior movement in sagittal plane (pump handle), since the articular surfaces on the 1-6 ribs are convex
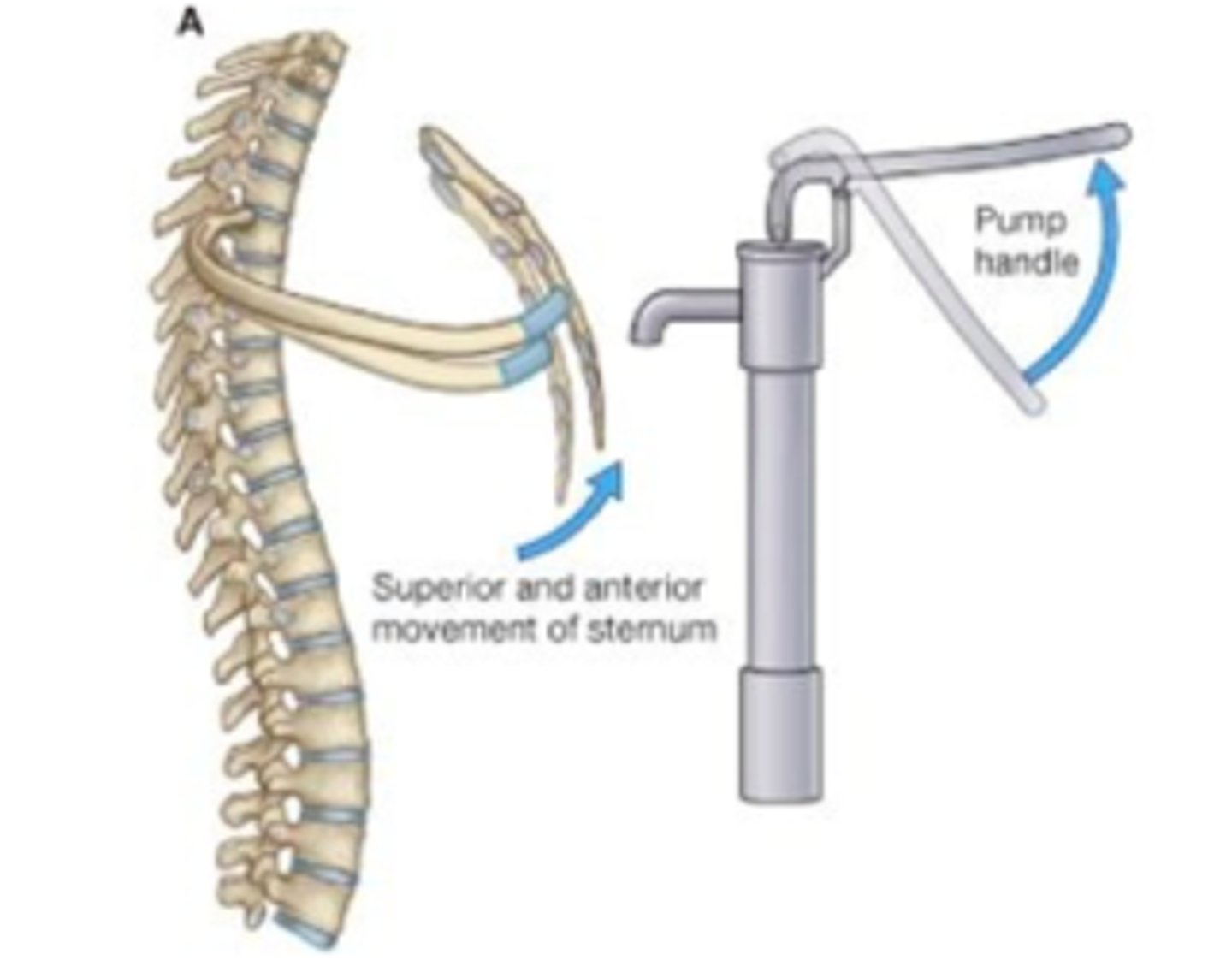
What is the movement of costovertebral joints and why?
gliding movement of lateral expansion in transverse plane (bucket handle), since the articular surfaces on tubercles of ribs 7-10 are flat