APHUG | Unit 1
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
terms idrk
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Cartography
map-making
projection
method of flattening the round earth
ALL distort (shape, area, distance, and direction) but MOST accurate on center
simplification
what information is relevant to the map being created
aggregation
collection/gathering of things together
reference map
helps you see where things are
where certain places are being put
choropleth map
use COLORS to show value
graduated/proportional symbol map
use different sized symbols to show value
cartogram
distorts LAND area based on the particular variable
Remote Sensing
Gathering data through sensors/photos (satellites)
Application:
Land use change
Farms
Study of uninhabitable places
Impact of disasters

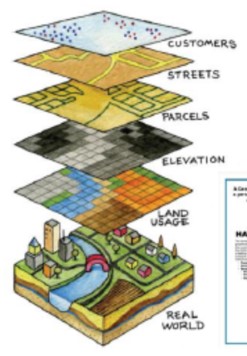
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
combines hardware and software to create detailed maps with layers and analyze spatial data.
Application:
Location of remaining natural resources over time
Where to open the next Chipotle
Satellite Navigation Systems (like GPS)
precise location
primary purpose is navigation
distribution
arrangement of something over a given area
concentration
spread of something over a given area
diffusion
spread of a feature from one place to another over time
cluster
group into a set
dispersal
distribute/spread over a wide area
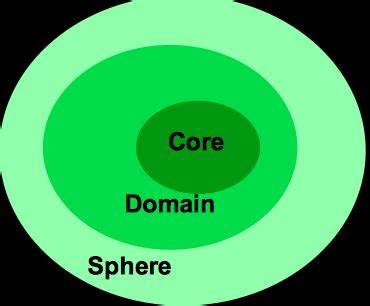
core-domain sphere model
a model that shows how cultural traits are strongest in the core, less intense in the domain, and weakest in the sphere.
space-time compression
world feels smaller due to advancements in technology
reduction of time it takes for people, goods, and information to travel between places
local scale
county
city
district
sub-national scale
state
province
national scale
country
ecological perspective
relationships between living things and their environment
friction of distance
the longer a journey is, the more time, effort, and cost it will involve
region
an area of earth’s surface with certain characteristics that make it distinct from other areas
formal region
area that has one or more shared traits
physical (mountain range, climate area)
cultural (language, religion)
data (population, income, ethnicity)
functional region
center of an interest or activity
node
focal point of a functional region
perceptual/vernacular region
defined by people’s perceptions of the area
topographic map
map that uses contour lines to display the terrain and elevation changes in an area
toponym
a name given to a place or location
absolute direction
exact direction a person is heading
fixed points of reference on the Earth's surface
ex. north, south, east, west
relative direction
direction depends on location of other places
absolute distance
exact distance between 2 places
ex. miles, kilometers
relative distance
approximate measurement between two places
ex. 23 hrs travel
remote sensing
collection information about earth’s surface from satellite orbiting the earth
helps us understand changes over time
help create thematic system

Global positioning system (GPS)
network of satellites used to determine location of something on the Earth’s surface
concentration
how things are spread out
refers to the degree of closeness or clustering
distance decay
the larger the distance the less interaction