Topic 3 - Graphs
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the types of graphs?
Undirected → The edge set is an unordered pair of vertices
Directed/diagraph → All edges have associated numerical values
Weighted → All edges have associated numerical values
Define a simple graph:
A graph that does not have more than 1 edge between any 2 vertices and no edge starts and ends at the same vertex.
What is a degree sequence?
A non increasing sequence of the vertex degrees (the number of edges attached to the vertex → deg(v))
What symbols define minimum and maximum degree?
Minimum degree → δ(G)
Maximum degree →Δ(G)
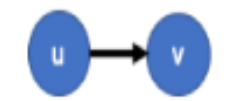
Define incidence for the edge (u,v) in a graph G = (V,E) for it being directed and undirected:
Undirected graph → (u,v) is incident on vertices v and u.
Directed graph → (u,v) is incident from vertex u and incident to vertex v.
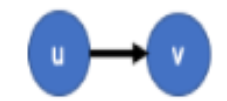
Define adjacency for the edge (u,v) in a graph G = (V,E) for it being directed and undirected:
Undirected graph → the adjacency relation is symmetric, the 2 vertices are mutually adjacent.
Directed graph → vertex v is adjacent to u if there is an edge that leaves u and enters v.
For a weighted graph, what is the entry for the adjacency matrix?
The weighted edges.
What is a walk?
Visiting K vertices in any order, with repeititons allowed, with the only restriction being that you can only transition between vertices if an edge exists between the pair.
What is a trail?
A walk where the edges are distinct (no repetitions).
A set of trails is a subset of all walks.
What is a (simple) path?
A walk where the vertices are distinct.
A set of paths is a subset of all trails.
What is graph geodesic/distance?
The number of edges in a shortest path connecting 2 vertices. If 1 vertex cannot be reached from another path made of edges, the distance is infinity and the path is disconnected.
What is the length of a cycle/circuit?
The number of edges.
What are eulerian trails?
Visit each edge exactly once.
How is a graph defined to be traversable?
If you can draw a trail between all the vertices without retracing the same path.
What are hamiltonian paths and cycles?
Path → A path that visits every vertex once.
Cycle → A path that ends at the initial vertex.
What is a subgraph?
A graph where vertices and edges are subsets of the vertices and edges of another graph.
What is a clique (complete subgraph)?
A subgraph where all vertices are adjacent to eachother
What is graph isomorphism?
Graphs are isomorphic if there is a bijection between the vertex sets.
2 graphs are connected in the same way with the same number of vertices, they may be labelled differently or have different spacial locations.
What is an acylic graph?
A graph with no cycles.
What is a tree?
An undirected, connected, acylic graph. Any vertex pair is connected by a single path.
Give 2 examples of where trees are used:
→ A directionary structure on a computer file system
→ A decision tree in AI
What is a depth-first traversal?
Start at the root vertex and explore as far along 1 path as possible before backtracking.
What is a breadth-first traversal?
Start at the root vertex and explore all of the adjacent vertices at the present depth before moving to the next depth level.
What is Cayley’s formula for the number of trees?
Counts for all trees within isomorphisms. The number of non-isomorphic trees (NIT) is smaller.
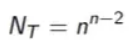
What is the relationship between vertices and edges?
m = n - 1 where m = #E and n = #V
What is a rooted tree?
A tree with a special vertex at the top called a root.
What is a spanning tree?
A tree that is a subgraph of another tree containing every vertex
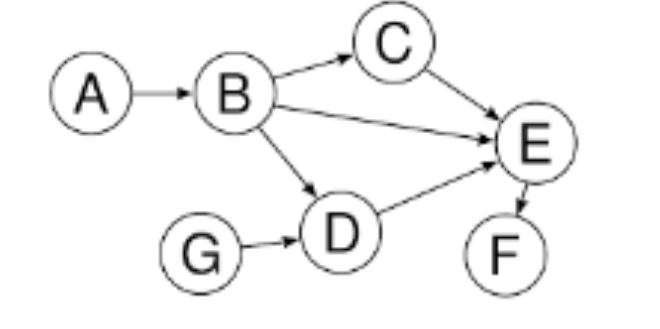
What are source vertices and sink vertices in terms of a Directed Acylic Graph, and name them for this graph:
A source vertex → All of the edges are indicent from it. A and G.
A sink vertex → All of the edges are incident to it. F.