Mechanical, Thermal, and Chemical injuries of the cornea - lim
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
basal cells cornea
single layer of columnar mitotic layer
secretes VM
zonula occludens
tight jxns
prevent intercellular movement of substances from tear film
prevents pathogens from getting into cornea
gap jxns and desmosomes
1, joins wing cells to each other and to surface and basal cells
hemidesmosomes
anchor basal cells thru BM, bowmans, and anterior stroma
corneal nerves
V1
enteres via peripheral stroma and branches thru mid stroma towards epi
3 nerve plexus
intraepithelial
subepithelial
mid stromal
NO NERVES IN POSTERIOR STROMA, DESCEMENTS, ENDO
bowmans
dense fibrois sheets of randomly arranged collagen 1 fibrils
resistant to damage but does not regenerate - forms scar tissue
normal epi regeneration
regenerates in 7-10 days
constant shedding of surface cells into tear film (flattened non keratinized squamous cells)
wing cells move up to replace those cells
basal cells move up to become wing cells
limbal stem cells constantly renew basal cells
at Palisade of Vogt
slow migration of basal cells occurs fro the periphery toward center of cronea
wounded ep regeneration
damaged ep secretes cytokines (IL 1 and TNF alpha) and growth factors (TGF B)
exposed corneal nerves release neuropeptides that helps w wound healing process
basal cell mitosis stops
hemidesmosomes near injury disapperas and adjacent ep cells flatten and shift to form a single layer to cover defect
Once defect is covered, Basal cell mitosis resumes, and proliferation fills in the defect and tight adhesions are established
With proper regeneration, hemidesmosomes are reestablished.
needs this for propper healing
*Healing is quicker if basement membrane remainw ________
intact
*With basement membrane damage, complete healing may take 8 week.a
corneal abrasion symptoms
10/10 sharp pain,
foreign body sensation
and light sensitivity.
It is worse with blinking. I
t started when my baby scratched my left eye.
My left eye is watering, and it is red.
corneal abrasion cause
Result of superficial trauma to the eye
• Ex. Fingernail, paper, tree branches, makeup brush
who does corneal abrasion effect more (epi)
males - bc of occupation
and contact lens wearers
pathophys of corneal abrasion
Mechanical trauma to corneal surface result in:
• Epithelial cell loss
Subsequent activation of dynamic and complex wound-healing process (see physiology review)
clinical presentation of corneal abrasion
usually unilateral
INJURY
swollen eyelid w conj injection
SLE
corneal ep defect
ABSCENCE of underlying opacification = NO infiltrate
meausre it
Mild AC rxn
positive Na/Fl stainging
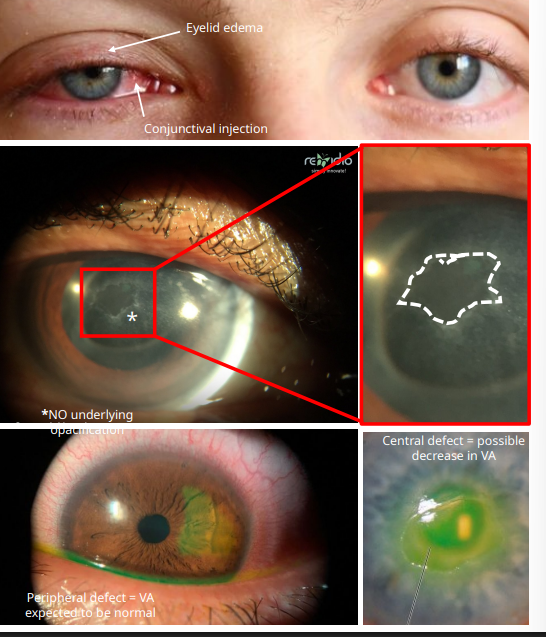
what does positive NaFl staining indicate
defects in corneal ep
focal defects = punctate staining
abrasion = (larger staining)
corneal abrasion management MANDATORY
antibiotic to prevent infection
what od you prescribe for a corneal abrasion for a Non contact lens wearer
erythromycin 0.5% ung QID affected eye
what od you prescribe for a corneal abrasion for injury from organic material (fingernail or vegetative matter) or CL wearer
NEED TO COVER PSEUDOMONAL GRAM -
Fluroquinolone QID affected eye
2 nd Generation
Ciprofloxacin 0.3% Ciloxan
Ofloxacin 0.3% Ocuflox
4 th Generation
Moxifloxacin 0.5% Vigamox
Moxeza Besifloxacin 0.6%
Besivance Gatifloxacin 0.3% Zymar
why are oral FQ bad
blow out tendons (tendonitis)
bad in pregnancy
how do we treat pain w corneal abrasion
with anterior chamber rxn
cycloplegic
cyclopentolate 1% BID affected eye
topical NSAID
Ketorolac 0.4% QID affected eye
can cause corneal toxicity if used excessively
oral NSAID
OTC Ibuprofen 400 mg every 6 hours PO
should we rx topical anesthetic (proparacaine) for pain control?
NO
delays corneal healing and can cause corneal melt
how do we allow for smoother healing in corneal abrasion
bandage contact lens
keeps eyelids from disrupting healing
ep debridement
copious lubrication
OTC preservative free artificial tears Q1H to Q2H affected eye
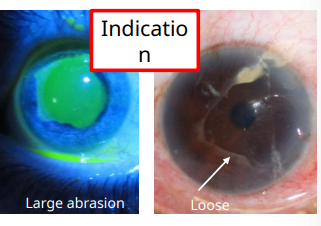
what does this indicate
debridement
irregular edges
when do we follow up for corneal abrasions - large and central OR bandage CL used
1 day
when do we follow up for corneal abrasions - small or peripheral
2-5 days to make sure the ep defect is improving
corneal FB symptoms
“I have 7/10 sharp pain,
foreign body sensation
and light sensitivity.
It is worse with blinking.
I think something flew into my left eye; I don’t wear safety glasses at work. I work in construction”
epi for corneal FB
males
workign age group
high risk activities - grinding, hammering, welding, woodworking
with high velocity FB what do we worry ab
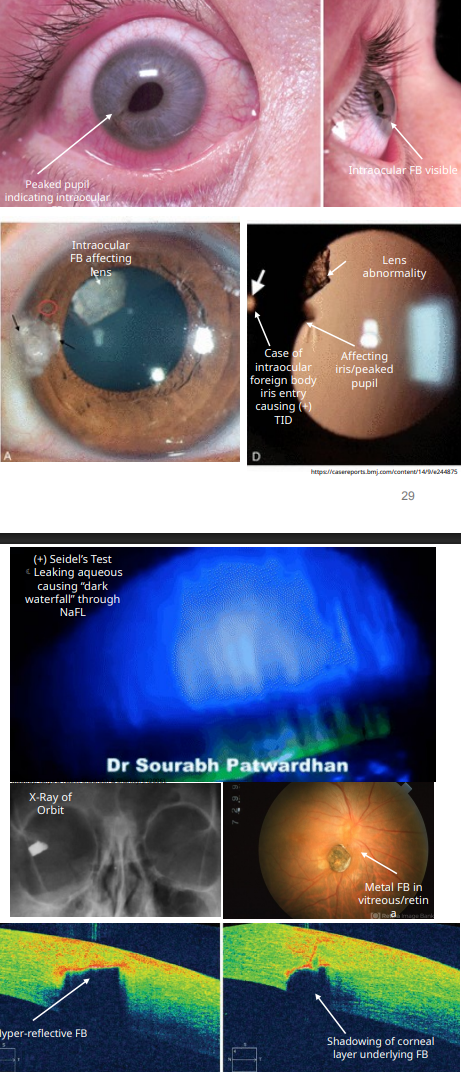
intraocular FB
pathophys of corneal FB
FB lodged in any 5 layers of cornea •
High velocity object more likely to pierce through bowman’s and into stroma
1. FB disrupts epithelium and triggers strong inflammatory response: release inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and TNFα )
Organic material
Higher risk for microbial colonization *
Inorganic material (metal)
Can oxidize and leave deposits
2. Inflammation triggers corneal edema, and cellular infiltration (Neutrophils & monocytes)
3. If FB is retained, chronic inflammation leads to stromal scarring and visual compromise
what do you see in SLE for corneal FB
the FB itself
could have or not a rust ring
mean metallic FB
mild AC rxn
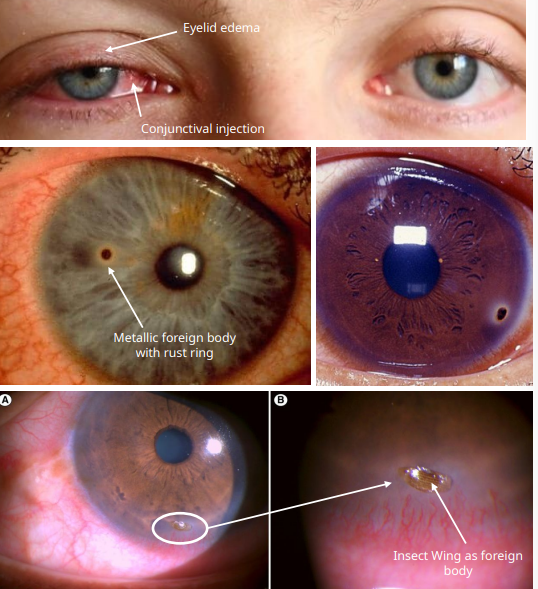
what do we look for in an intraocular FB
look for
pupil irregularities
iris tears adn transillumination defect
lens abnormalities
check for
+ Seidel Test = dark waterfall effect of NaFl being washed away
aq is coming out
DFE to see if it made it to vitreous or retina
OCT shows depth of FB
ORBITAL XRAY
how do we remove corneal FB
get informed consent
Instill topical anesthetic
2. Remove using spud, forceps, small-gauge needle at slit lamp
remove rust ring
flick away deposit w needle
Alger brush —> stops at Bowmans
oscilaring burr knocks off corneal ep to get rust ring off
if it is deep - leave it along and let it migrate up
reattempt to remove 1 day f/u
measure size of ep defect
TREAT LIKE CORNEAL ABRASION
when do you f/u for FB
1 day if rust ring remains
if you cant get it all out and its peripheral its ok
when do we refer to ophthalmology urgently
if intraocular FB
deeper stroma is affected
recurrent corneal erosion symp
“Remember me?
I came in a few months ago because my baby scratched my left eye, and it healed since then. But I woke up this morning with
10/10 sharp pain,
foreign body sensation and
light sensitivity in that same left eye!
It is worse with blinking.
My left eye is watering, and it is red…
but my baby didn’t scratch me ag
cause of recurrent corneal erosion
Damage to corneal epithelium and/or basement membrane from the following:
• Previous injury (abrasion)
Most common reason
• Corneal dystrophies
2 nd most common reason:
• Epithelial Basement Membrane Dystrophy (EBMD)*
• Corneal degenerations
• Band-Keratopathy
• Corneal surgeries
pathophys of recurrent corneal erosion ******************************** missing info
RCE almost always have a predisposing condition that ”loosens” epithelium
1. Corneal dystrophies or degenerations result in change to cell-matrix interface and epithelium to basement membrane complex
2. Previous corneal abrasion/epithelial injury or surgery
• In normal: Deepest basal layer adheres tightly to underlying basement membrane via hemidesmosomes
• After injury: Weakened hemidesmosomes due to trapped damaged epithelial cells
• Nocturnal desiccation (closed eyelid state)
• Adhesion of tarsal plate to epithelium
Upon awakening (openingofeyelids)
recurrent corneal erosions clinical presentation
unilateral - corneal abrasion hx to eye
bilateral (not at the same time)- corneal dystrophy
could impact vision
swollen eyelid and conj injection
SLE
corneal ep defect or punctate defects
NO infiltrate
loose/irregular ep
NaFl staining
how do you acutely manage recurrent coreal erosion (normal)
treat like corneal abrasion
how do you acutely manage a RCE if medical management is inefefctive or its chronic:
sx management - CORNEAL SPECIALIST
what are some sx managements for RCE
ep debridement w diamond Burr superficial keratectomy
smooths bowmans membrane
phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK)
laser ablation of surface irregularities
doing what diamond burr does w a laser
anterior stromal puncture w needle or NdYAG
scarring effect
whats the long term preventative management once the acute episode of RCE has been resolved
5% NaCl soln QID and 5% NaCl ointment QHS of affected eye for 3-6 m —> MURO 128
osmotic action of NaCl on tear film to reduce corneal edema
SALT DRAWS OUT FLUID
burns on instillation
artificial tears QID and artificial tear ointment QHS of affected eye for 3-6 mo
prevent dessication of ep and protects from eyelid forces
barrier from eyelid to cornea
Rx doxycyline 50 mg BID PO for 4 weeks
decreases MMP to promote collagen production and corneal healing
anti inflammatory action
topical corticosteroid - FML 0.1% BID for 4 weeks
f/u for long term preventative management of RCE
3 mo to confirm no recurence
1 month if on corticosteroid
chemical burn treatment
immediately start
DO THIS BEFORE YOU ASSESS ANYTHING
copious irrigation w saline
EVERT EYELID AND SWEEP FORNIX
Morgan lens - ER eye irrigating system
how long do you irrigate in chemical burns
until ocular surface pH becomes normal 7 - 7.4
may take 10L of soln and 30 mins
how do you assess a chemical burn once you irrigate
what chemical
how long was it in eye
mech of injury
high pressure?
did they have on eye protection
what are acid burns
sulfuric acid - car bateries
acetic acid - vinegar
sulforous acid, hydrochlloric acid - pool
alkali burns
ammonia
lye
potassium hydroxide
magnesium hyroxide - fireworks
lime = cement and plaster
whats worse for the eye — acid or alkali burns
alkali
pathophys of acid burns
LESS severe than alkali burns
• Acid binds and denatures proteins on ocular surface and cause precipitation in corneal epithelium and stroma
• Precipitated protein act as barrier and prevent further penetration
alkali burn pathophys
MORE severe than acid burns
• Alkali is lipophilic and saponifies fatty acids in cell membrane leading to cell death
• Penetrates deeper stroma and destroys ground substance and collagen
clinical presentation of chemical burn
Severity of clinical signs depend on chemical type and contact time
• Corneal epithelial defect
• Ranging from small punctate keratopathy to large defects
• Possible blanching (whitening) of limbus and conjunctiva
• Possible anterior chamber reaction
• Possible corneal edema
• Possible increase in IOP
DONT MEMORIZE THE GRADING SCALE FOR CHEMICAL BURN
how do we manage mild burns: to promote re ep
OTC preservative free Artificial Tears Q1H affected eye.
how do we manage mild burns: control pain
Cyclopentolate 1% BID affected eye.
how do we manage mild burns: dec inflammation
Prednisolone Acetate 1% QID affected eye.
how do we manage mild burns: prevent infection
Erythromycin 0.5% ung QID affected eye
how do we manage moderate burn: promote re ep
OTC preservative free Artificial Tears Q1H
how do we manage moderate burn: control pain
Atropine 1% BID affected eye.
how do we manage moderate burn: decrease inflammation
Prednisolone Acetate 1% Q1H affected eye with rapid taper at day 10-14
how do we manage moderate burn: prevent infection
FQ QID
what do we do if IOP is elevated in a chemical burn (rx)
acetazolamide 250 mg PO QID for duration of IOP spike
NOT IN SULFA ALLERGY
not well tolerated by pt
what do we do for severe burn (grade 3/4)
corneal specialist
they are getting an amniotic membrane (grade 3) or surgical options (grade 4)
how do we f/u for chemical burns
1 day to look for improvement
re ep may take 10-14 days
>21 days suggests permanent stem cell injury and permanent vision loss from ulceration and scarring is likely —> CORNEAL SPECIALIST
UV keratitis symptoms
“I have 7/10 pain
and both of my eyes
red and watery that started today. They’re also sensitive to light
and have foreign body sensation.
I am a welder, and I am supposed to wear this mask, but I forgot. I was welding yesterday.” —> delayed onset = symptoms worsen 6-12 hours after exposure
UV keratitis cause
sunburn to eye
exposure to UV rays
pathophys of uv keratitis
Transparent cornea transmits visible light spectrum (400nm to 700nm) but absorbs UV spectrum (10nm to 400nm) • 100% of UV-C (<290nm) absorbed by corneal epithelium • Protects stroma and endothelium • Damages epithelium and causes epithelial cell apoptosis
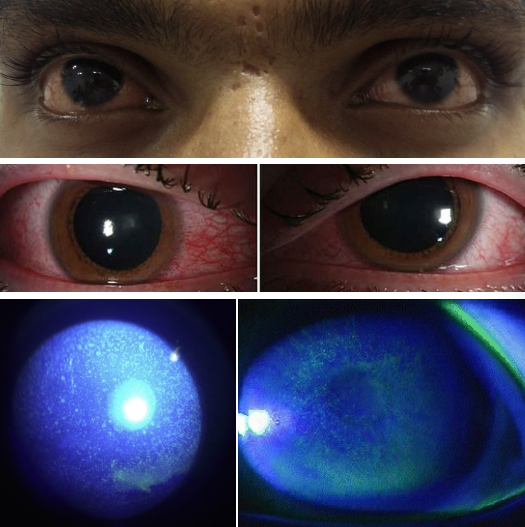
clinical presentation of UV keratitis
Bilateral •
Mild eyelid edema, conjunctival injection
Assessment through slit lamp •
Dense, confluent, punctate epithelial defects
• (+) NaFl Staining •
Mild to moderate corneal edema possible
treating UV keratitis
will get better in 1-3 days = self limiting
OTC preservative free Artificial Tears PRN use.
Erythromycin 0.5% ung QID OU.
Cyclopentolate 1% QD OU.