General chemistry 3: bonding and chemical interactions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
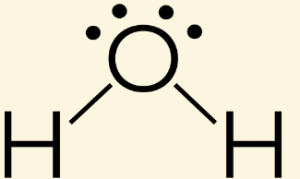
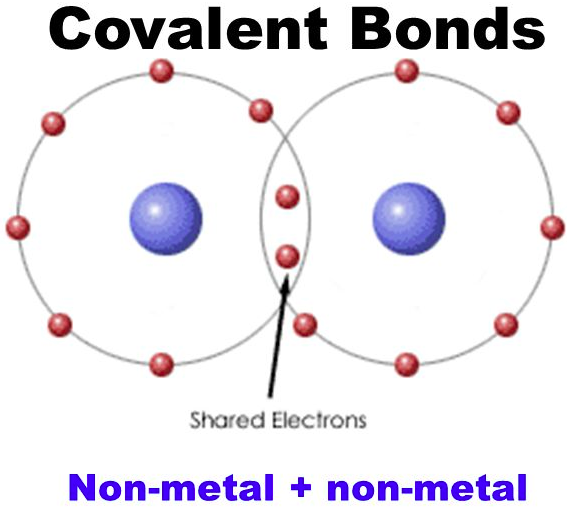
A/an [...] bond is the sharing of electrons between two elements
covalent
between same element
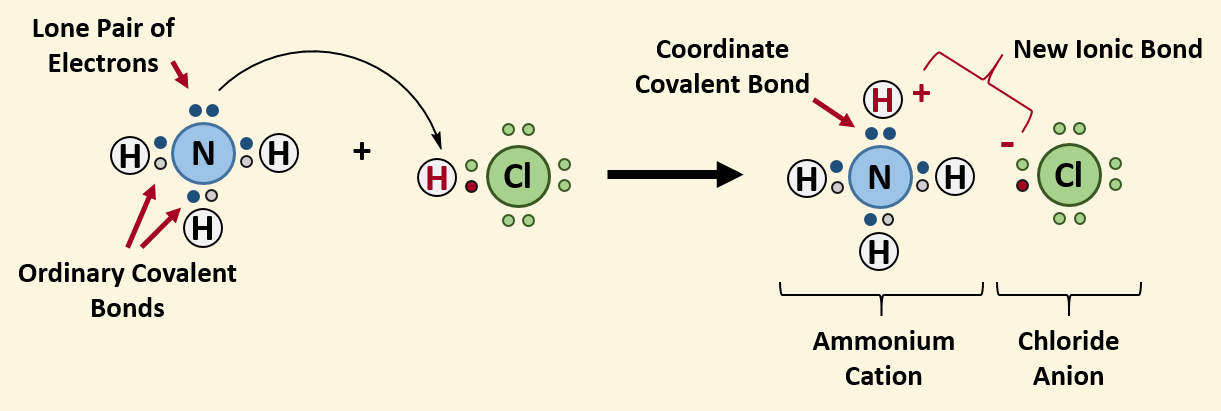
[...] bonds are when a single atom provides both bonding electrons
coordinate covalent
most often found in lewis acid-base chemistry
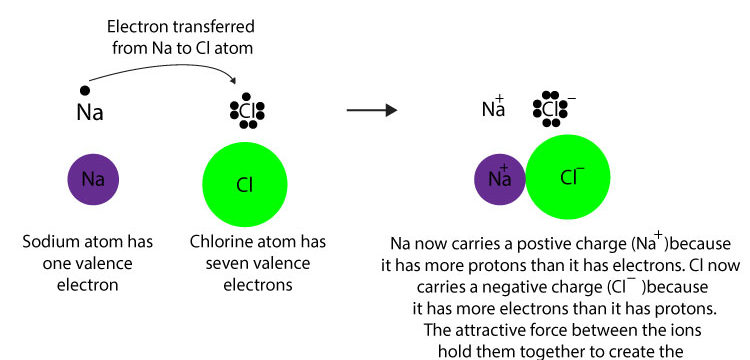
[...] bonds are formed by the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms
ionic
usually formed between an element with a low ionization energy and an element with a high electron affinity
[...] refers to the number of bonds between two atoms (single, double, or triple bond)
bond order

The greater the number of bonds (bond order) the [higher or lower] the bond strength and the [longer or shorter] the bond
higher, shorter bond length

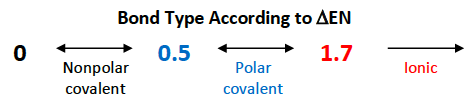
Non-polar bonds have a △EN that is [...]
less than 0.5
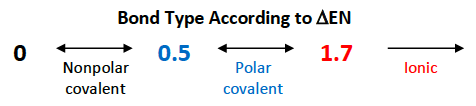
Polar bonds have a △EN that is between [...] and [...]
0.5 and 1.7
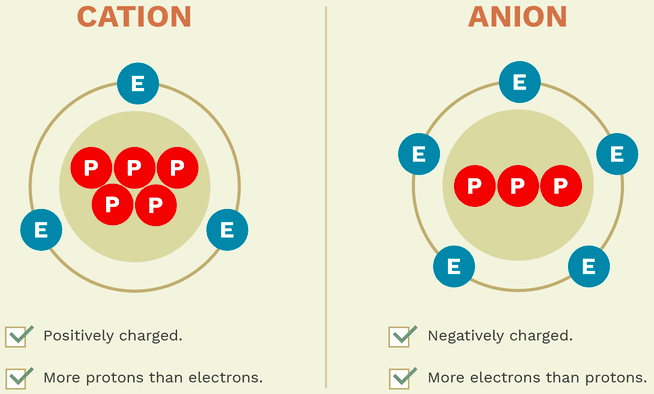
Cations are ions with a [...] charge
positive
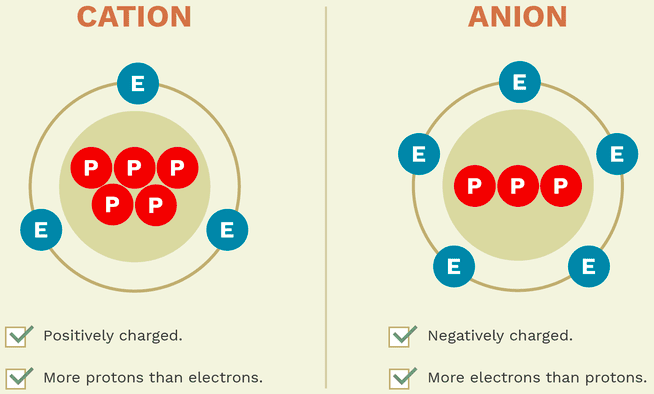
Anions are ions with a [...] charge
negative
[...] are large, organized arrays of ions
crystalline lattices
ex: solid carbon

Hydrogen bonds are most often formed between hydrogen and the following elements: [...]
O, N and F
O-H, N-H, F-H
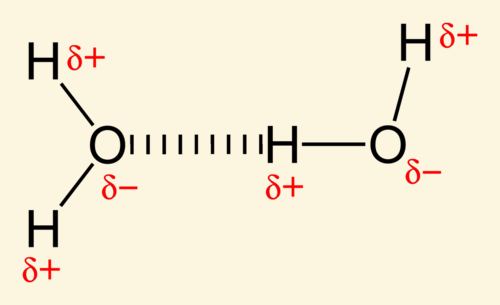
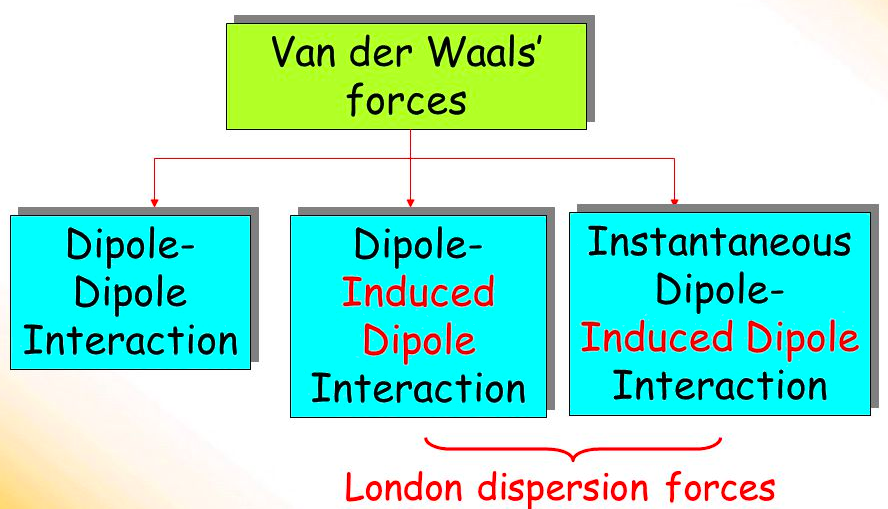
Van der Waals Forces is a general term that includes [...] forces and [...] forces
dipole-dipole forces
london dispersion forces
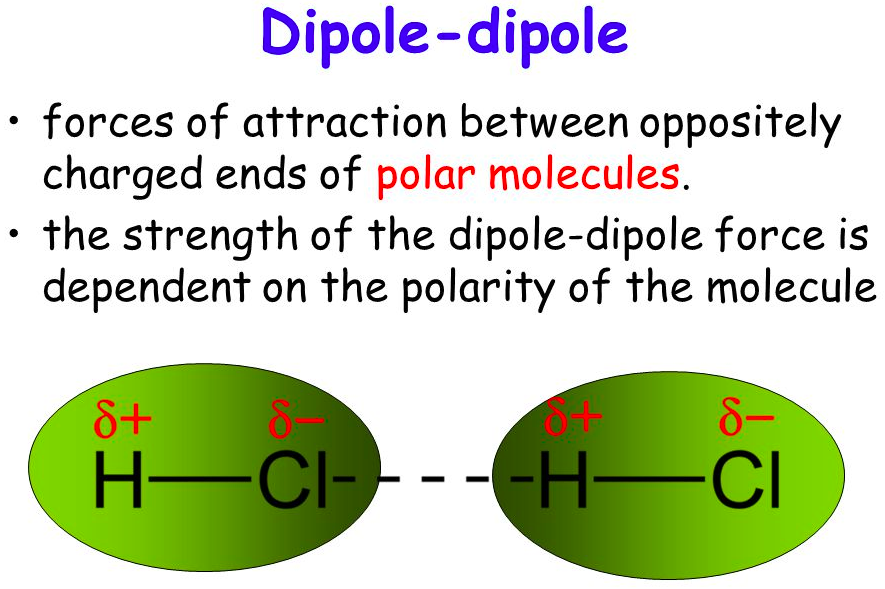
[...] forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule
Dipole-dipole
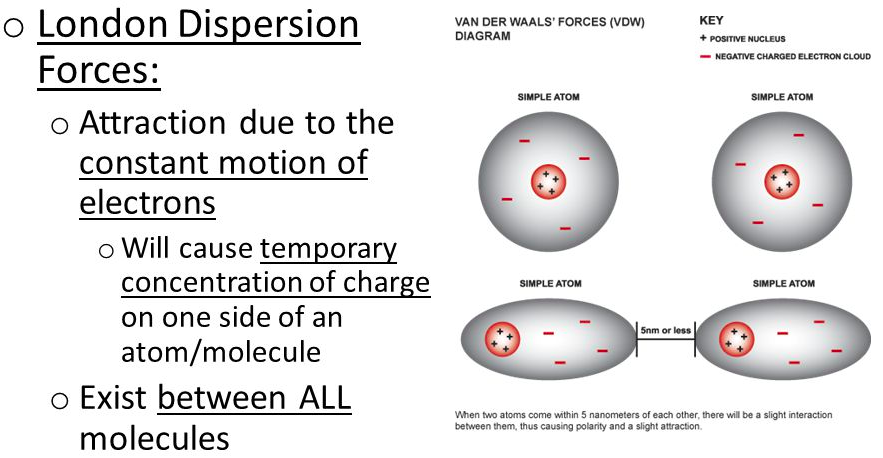
[...] forces are temporary attractive forces created when a temporary dipole induces a dipole in a neighboring molecule
london dispersion forces
the weakest intermolecular force
Place in order of strength:
hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole forces, and London dispersion forces

[...] bonds are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals
sigma
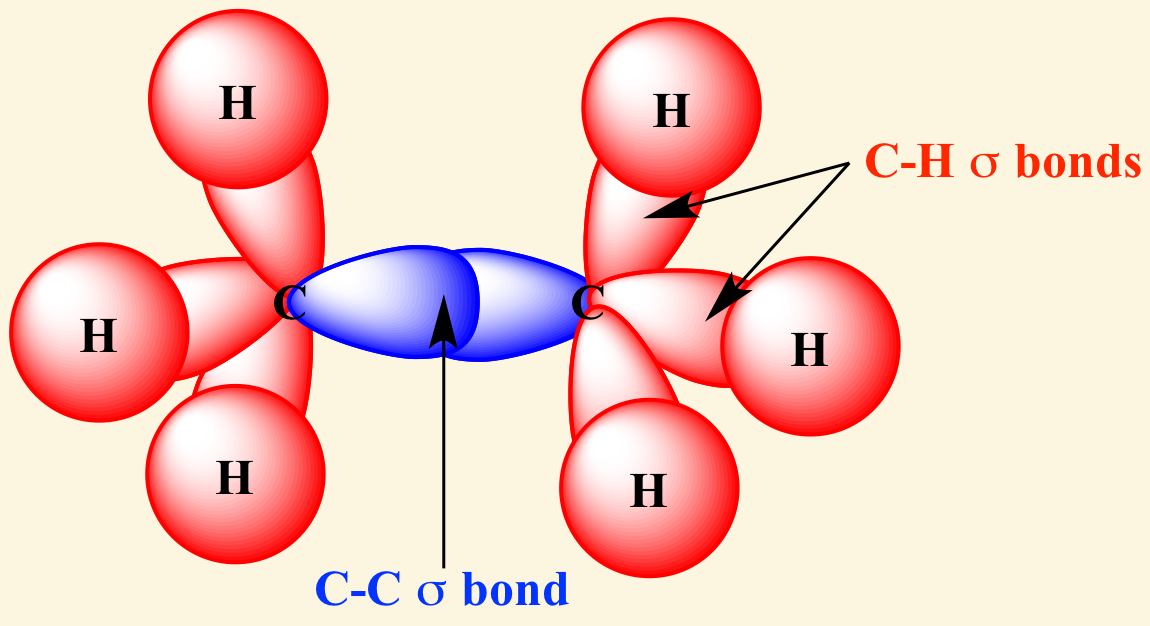
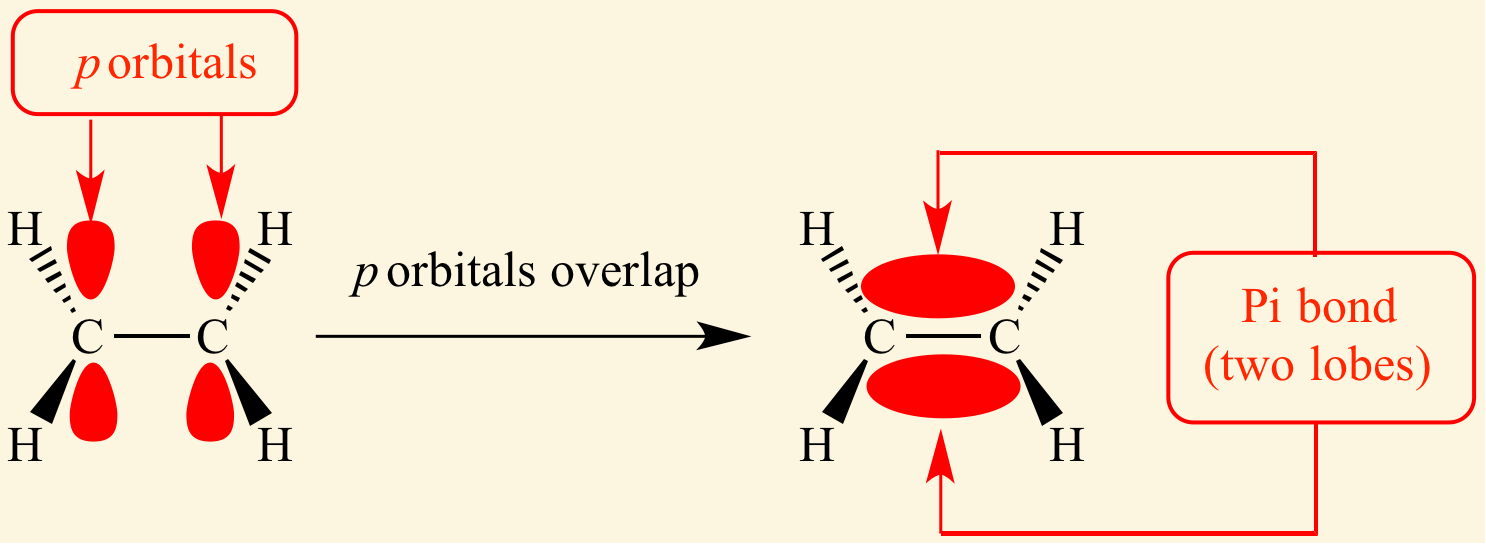
[...] bonds are formed by lateral (side-by-side) overlap of atomic orbitals
pi
the 2nd and 3rd bond in double and triple bonds are pi bonds
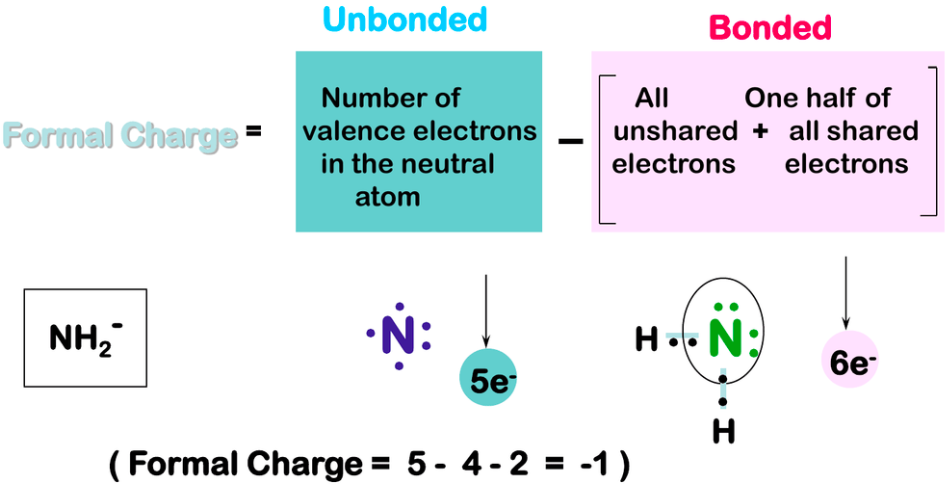
[...] is the charge given to an individual element within a molecule
formal charge
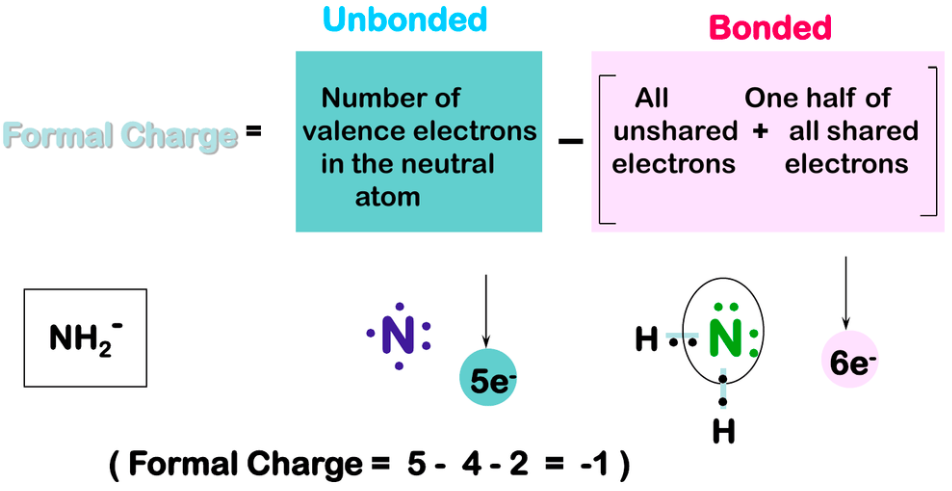
Give the formula for formal charge
Formal Charge = [...]
Formal Charge = valence electrons − dots − sticks
"Dots" are nonbonding electrons
"Sticks" are pairs of bonding electrons
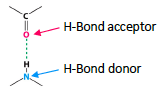
![<p>O is the hydrogen bond <span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[acceptor or donor]</strong></span></p><p>N is the hydrogen bond <span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[acceptor or donor]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/54bf54b7-2276-46a6-b0ab-42cb57d5bf05.png)
O is the hydrogen bond [acceptor or donor]
N is the hydrogen bond [acceptor or donor]
acceptor
donor
the acceptor mist possess a lone electron pair
the donor is usually strong electronegativity
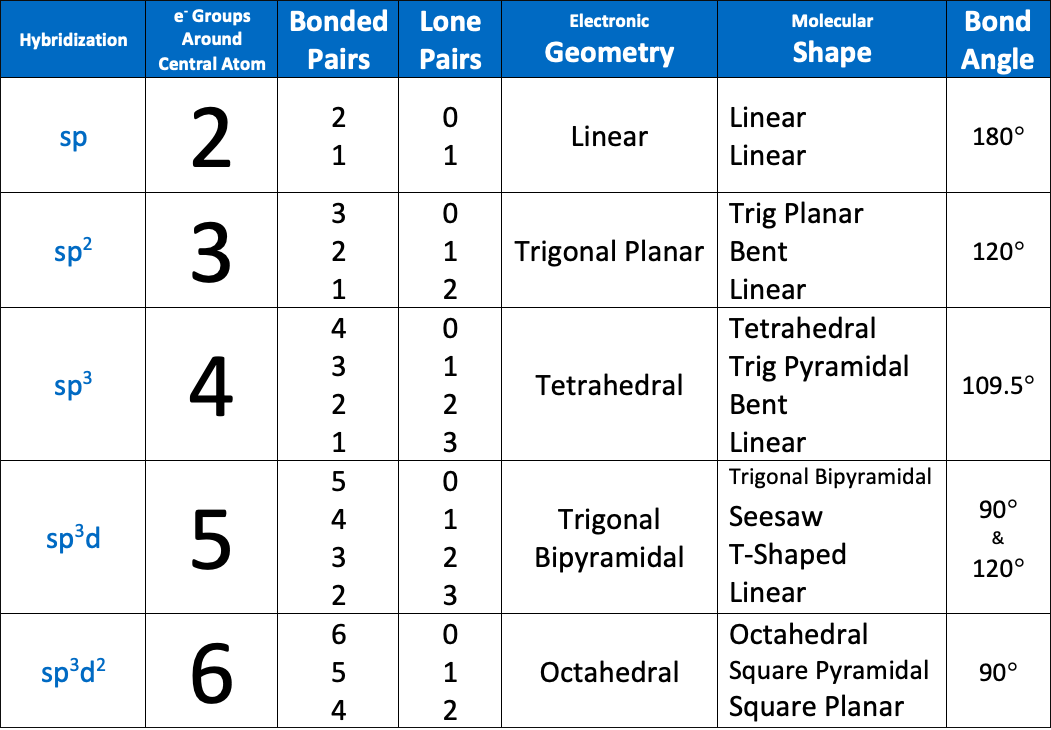
The bond angle of an sp hybridized atom is [...]
180
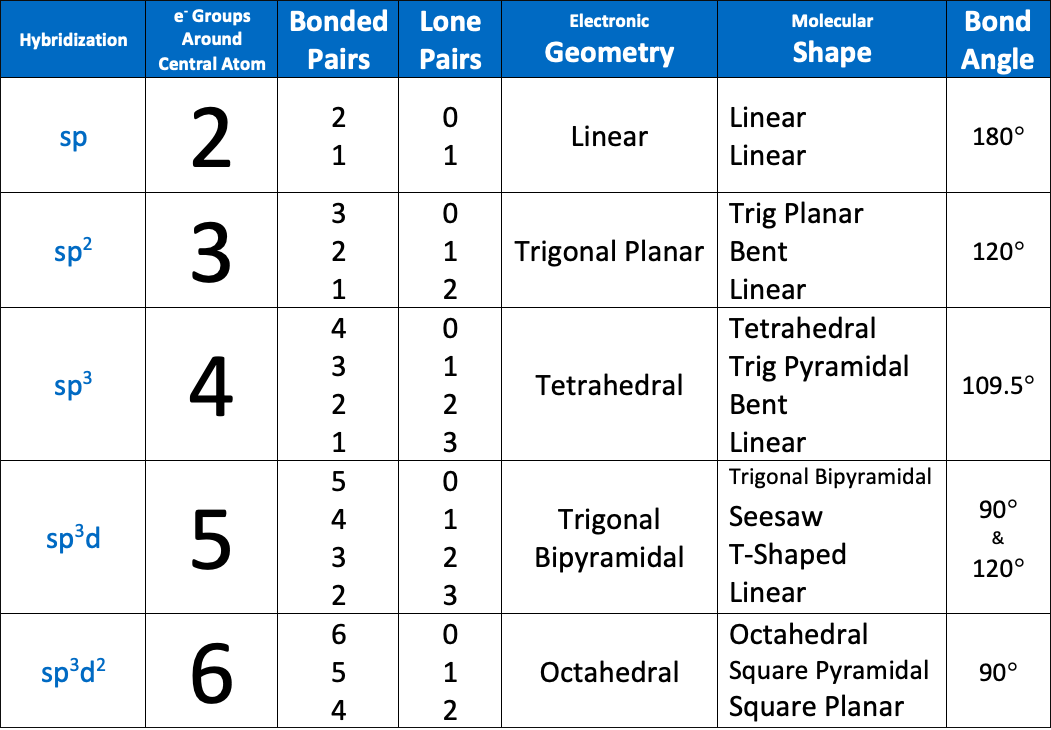
The bond angle of an sp2 hybridized atom is [...]
120
The bond angle of an sp3 hybridized atom is [...]
109.5
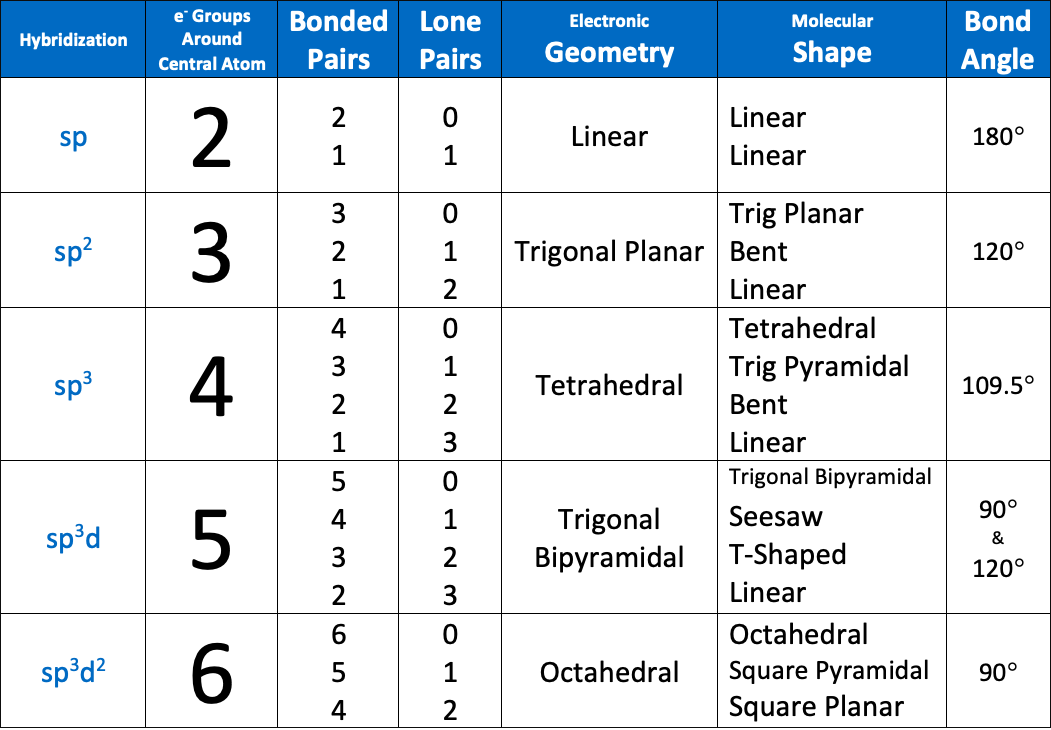
Bond angles of an sp3d hybridized atom are [...] and [...]
90 and 120
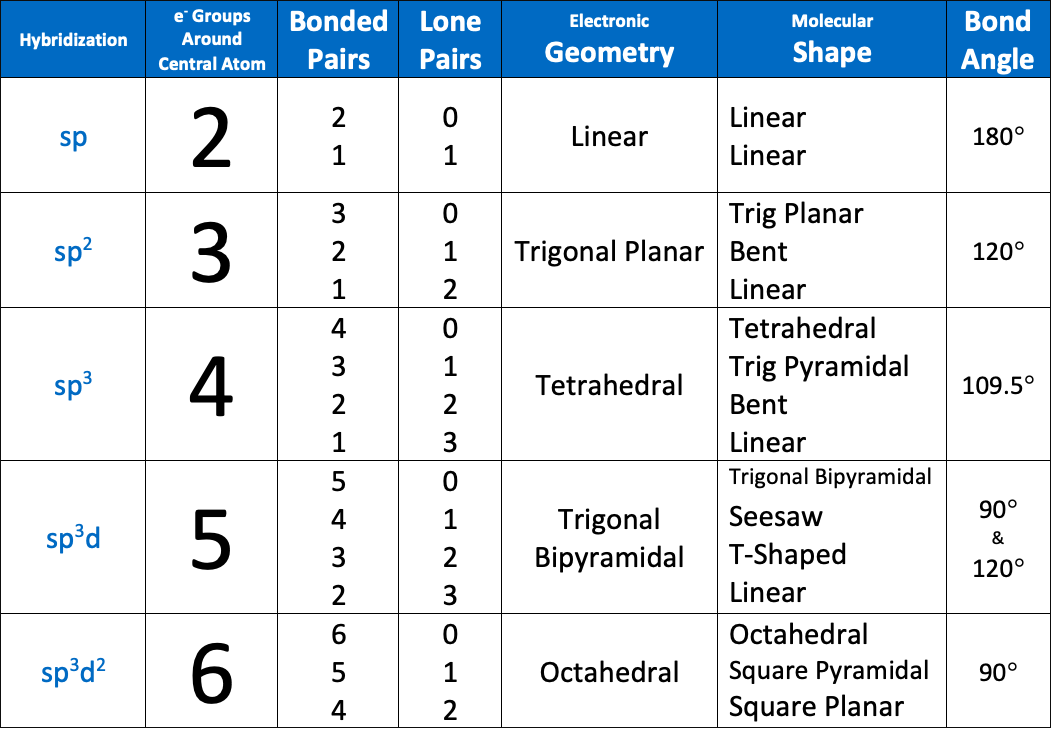
The bond angle of an sp3d2 hybridized atom is [...]
90
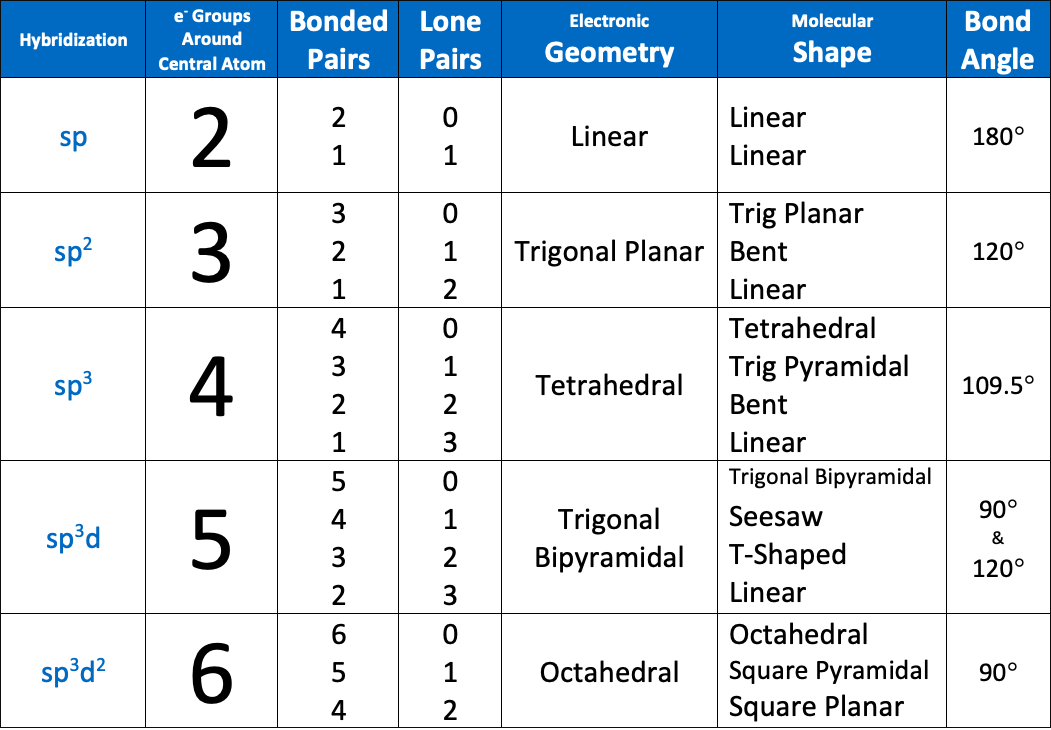
An H2O molecule is a bent because [...]
the lone pair of the electrons repulse each other and push the H atoms away