Midterm 2 OB Chapter 5
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is motivation?
The extent to which persistent effort is directed towards a goal.
4 Characteristics of Motivation
Effort, persistence, direction, goals.
What is effort?
The level of resources put into a job.
What is persistence?
Individual's determination and dedication for the job.
What is direction?
The direction of a person's work-related behavior.
What are goals?
Enhancement in organizational objectives/goals.
2 Types of Motivation
Intrinsic + Extrinsic
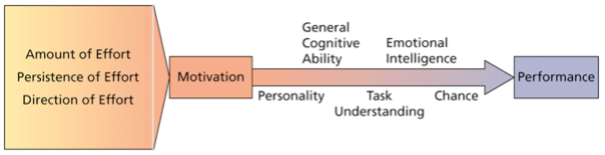
What is Intrinsic Motivation? What type of performance does it impact?
Internal motivation stemming from direct relationships with workers and the job.
Impacts quality of performance
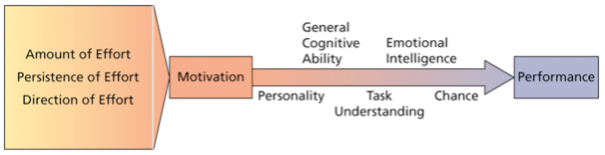
What is Extrinsic Motivation? What type of performance does it impact?
External motivation stemming from the work environment to the job.
Impacts quantity of performance
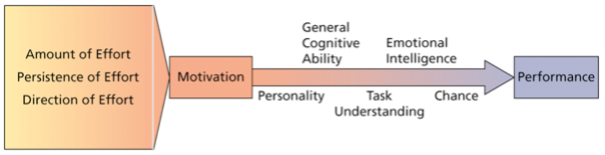
What is Performance?
The extent to which an individual contributes to achieving the organizational objective.
5 Factors Predicting Performance
General Cognitive Ability
Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Personality
Chance
Task Understanding
What is General Cognitive Ability?
An individual's basic information-processing capacities and cognitive resources.
What is Emotional Intelligence (EI)?
Ability to understand and manage one's own and others' feelings/emotions.
What are Need (content) Theories?
Theories concentrating on what motivates people.
Needs —> Behaviour —> Incentives and Goals
4 Types of Need Theories
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Alderfer’s ERG Theory
McClelland’s Theory of Needs
Self-determination
5 Maslow's Hierarchy Needs
Humans have 5 sets of needs arranged in a hierarchy:
Self – actualization: needs regarding development to their truest potential
Self – esteem: needs for feelings of adequacy and confidence
Belongingness: needs for social interactions
Safety: needs for security and stability
Physiological: basic survival needs
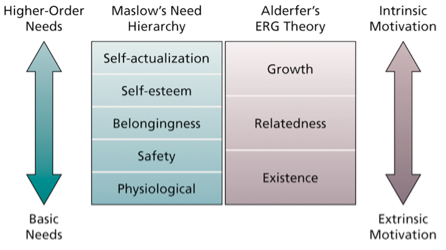
3 Needs in Alderfer's ERG Theory
Three-level hierarchal need theory.
Growth – needs that’s fulfilled by strong personal involvement in the work setting
Relatedness – needs satisfied by open communication/exchange of thoughts/feelings with others
Existence – needs satisfied by materialistic substance/conditions (food, pay, safety)
3 Needs in McClelland's Theory
Non-hierarchal need theory outlining the conditions under which needs result in particular patterns for motivations.
Need for Achievement (Ach): Desire to perform challenging tasks
Preference for situations in which personal responsibility can be taken for outcomes.
A desire for performance feedback.
A tendency to set moderately difficult goals that provide for calculated risks.
Need for Power (Pow): Desire to influence others
Need for Affiliation (Aff): Desire to establish/maintain interpersonal relationships
What is Self-Determination Theory (SDT)?
Motivation theory that considers whether people's motivation is autonomous or controlled.
3 Basic Psychological Needs are met —> autonomous motivation, otherwise controlled motivation:
Components: Competence, Relatedness, and Autonomy
Autonomous Motivations: Self-motivated/intrinsic motivation that occurs when people feel they control their motivation (eg. interesting task)
Controlled Motivation: When people are motivated to obtain a desired consequence or extrinsic reward
What is the Job Characteristics Theory?
Core characteristics of a job that has psychological impacts on workers.
Components:
Skills variety
Task identification
Task significance
Autonomy
Feedback
Psychological Impression: Meaningful work, increased responsibility, evaluation on work performance
Outcome: High Intrinsic motivation, high quality-performance, increased satisfaction, decreased turnover and absenteeism
Moderators: Knowledge and skills, Growth Need Strength, context significance
2 Implications of Need Theories
Appreciate Diversity:
A tendency to set moderately difficult goals that provide for calculated risks.
eg. Best salesperson is not the best manager, The needs of a college graduate differ from those of an employee about to retire
Intrinsic motivations
Ensure that low-level needs (poor pay, job insecurity, and unsafe working conditions) are met so that employees can focus on higher order outcomes
Enrich jobs to be more stimulating and challenging
What are Process Theories?
Theories concentrating on how motivation occurs.
Name the 4 Process Theories
Expectancy Theory
Equity Theory
Goal-setting theory
Organizational Justice Theory
What is Expectancy Theory?
Motivation is determined by the outcomes that are expected from actions on the job.
3 Implications of Expectancy Theory
Boost expectancies: increasing self-efficacy
eg. Employees might not understand what the organization considers to be good performance or see how they can achieve it.
How likely is it that you will do the action causing the outcome?
Boost instrumentality: clarify reward contingencies.
Fair rewards system
Provide stimulating, challenging tasks for those interested
How likely is the outcome?
Boost valence of outcomes:
How important is the outcome to you?
eg. Design personalized motivation packages
What is Equity Theory?
Motivation stems from comparing inputs to outcomes received and comparing them to others.
3 Implications of Equity Theory
Avoid under or over payment
Making relevant inputs and outcomes clear
Have fair procedures
What is Goal-Setting Theory?
Goals are motivational when they are specific and challenging, and feedback is provided. Uses SMART Goals.
What is Organizational Justice Theory?
3 types of Organizational Justice Theory.
Employees' overall fairness of their organization.
Distributive
Procedural
Interactional
What is Distributive Justice?
People receive the outcomes they think they deserve.
What is Procedural Justice?
Occurs when the process used to determine outcomes is reasonable.
What is Interactional Justice?
Perceived fairness of interpersonal communication.
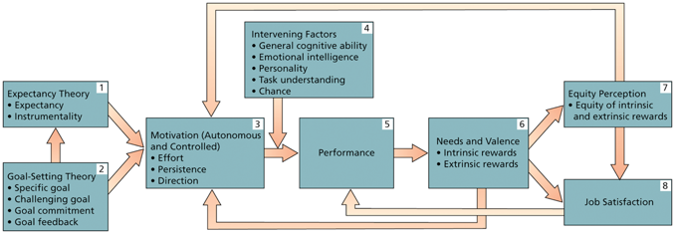
Integration of Theories of Work Motivation
What is Goal Orientation?
An individual’s preference for a goal.
3 Types of Goal Orientation
Learning Goal Orientation: Process goals that are complex as it requires individuals to master to learn to accomplish the goal
Performance Goal:
Ongoing goals that are typically simple task
Performance-Prove Goal Orientation: Successfully completing a task by seeking favourable judgement about the outcomes
Performance-Avoid Goal Orientation: Avoiding negative judgment about the outcome their performance
2 Types of Goal Proximity
Short-term and distal goal (long-term goal)
Prefer short-term goals