Forensic Radiology: Identification and Injury Analysis
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Radiology
Used for identifying remains and injuries.
Radiologic Identification
Depends on antemortem and postmortem images.
Antemortem Radiographs
Images taken before death for comparison.
Postmortem Radiography
X-rays taken after death for identification.
Biological Profile
General information from skeletal remains.
Skeletal Identification
Most durable tissue used for identification.
Frontal Sinuses
Unique to individuals, like fingerprints.
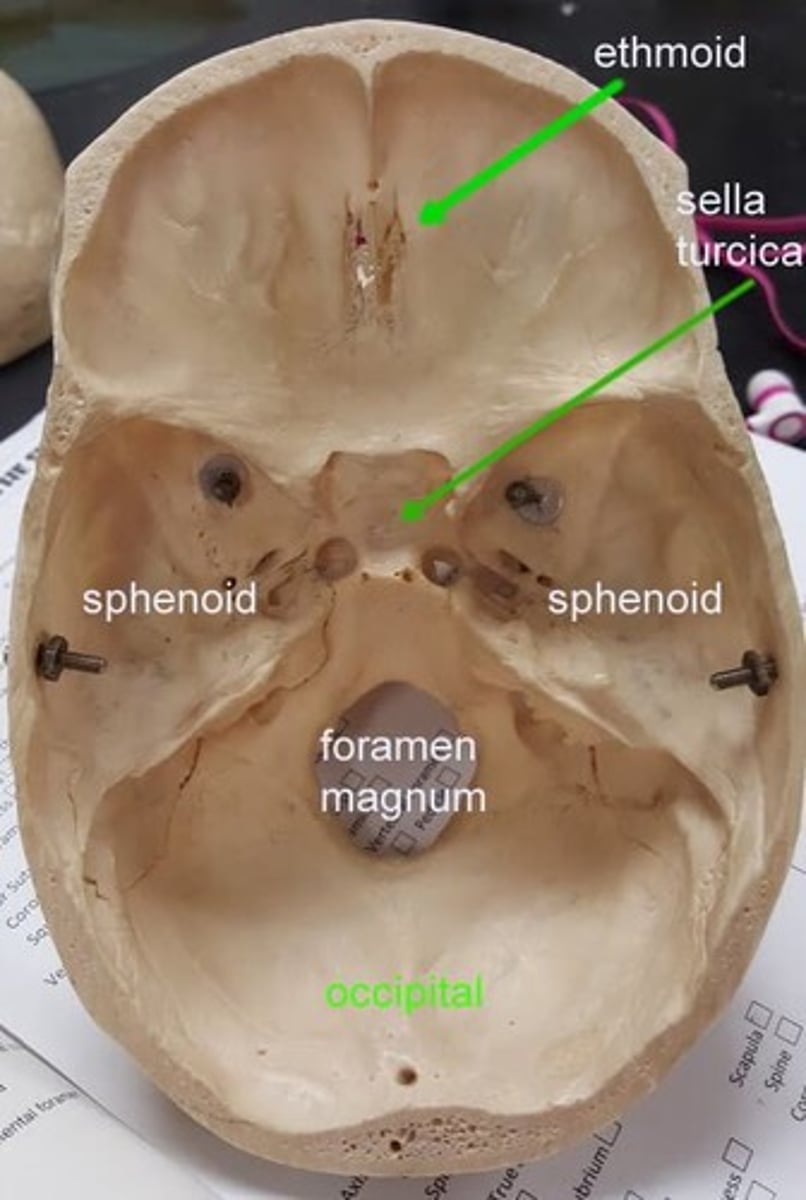
Cliniod Processes
Structures aiding in skull identification.
Sella Turcica
Deep skull structure often survives trauma.
Chest Radiography
Most frequently radiographed body area.
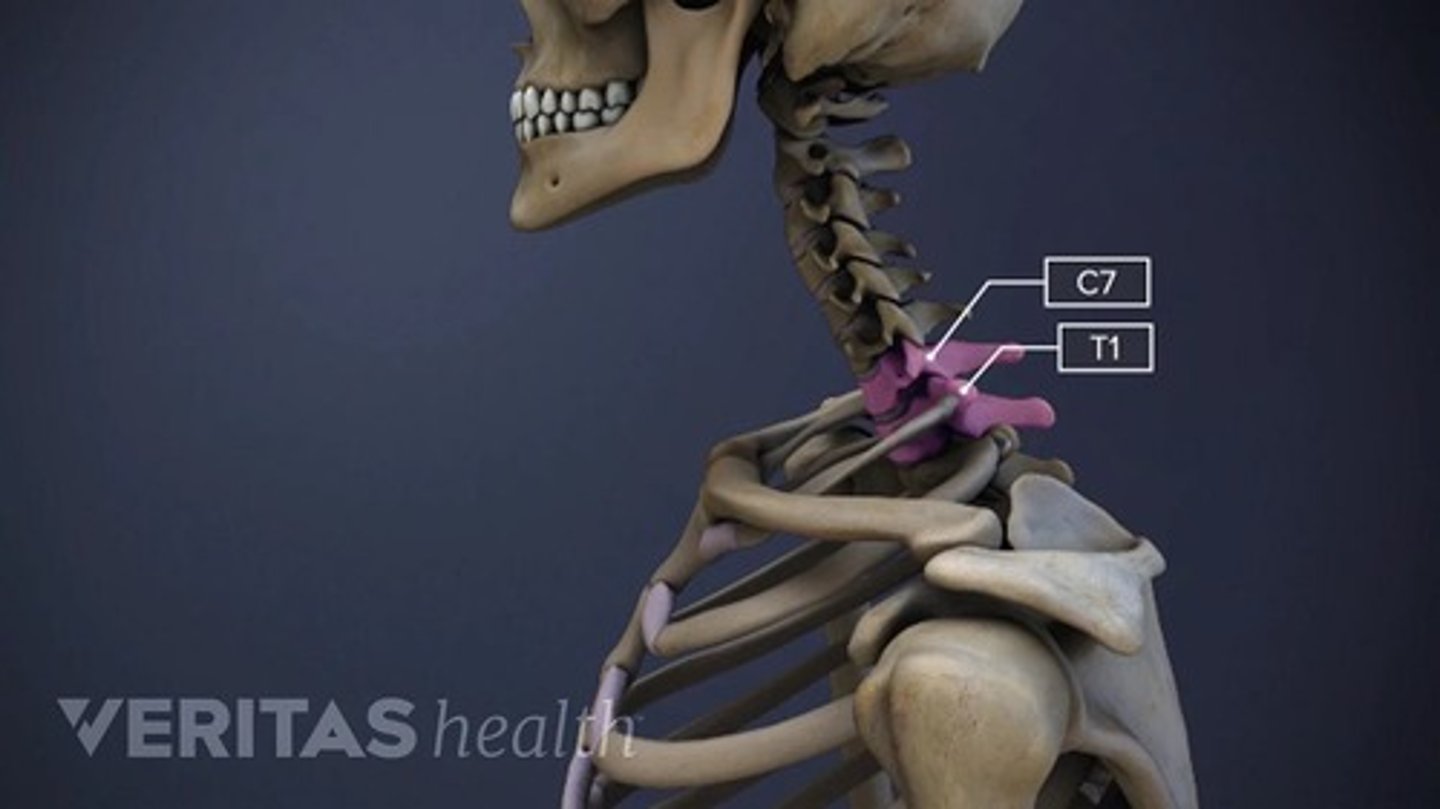
Cervicothoracic Junction
Survives calamity, aiding in identification.
General Information
Data without antemortem studies.
Specific Information
Derived from individual skeletal peculiarities.
Gallstones
Useful for radiological comparisons in identification.
Surgical Sutures
Aid in comparative identification of remains.
Paranasal Sinuses
Distinctive features for skull identification.
Mastoid Air Cells
Unique structures aiding in identification.
Thrombi
Useful in radiological comparisons.
Parasitic Infections
Can be identified through radiology.
Soft Tissues
Similar density, less useful for identification.
Water Density
Characteristic of non-skeletal soft tissues.
X-ray Tube Positioning
Varies between clinical and postmortem films.
Comparative Identification
Matching patterns in antemortem and postmortem images.
Postmortem chest films
X-rays taken of deceased in supine position.
Cervicothoracic junction
Area where cervical spine meets thoracic spine.
Costal cartilage calcification
Calcium deposits in rib cartilage aiding identification.
Pleural calcification
Calcium buildup in pleura, useful for identification.
Pulmonary calcification
Calcium deposits in lungs, can indicate pathology.
Sternal configuration
Shape of sternum, occasionally aids in identification.
Scapular configuration
Shape of scapula, useful in rare identification cases.
Clavicle changes
Alterations in clavicle assist in positive identification.
Abdominal wall survival
Abdomen often survives incineration or trauma.
Lumbar spine anomalies
Variations in lumbar spine useful for identification.
Degenerative spurring
Bone growths indicating degeneration, useful in identification.
Iliac artery calcifications
Calcium deposits in iliac arteries may indicate pathology.
Vascular grooves
Distinct patterns in bones aiding identification.
Trabecular patterns
Unique bone structures useful for identification.
Single bone identification
Identifying remains based on a single bone's features.
Iatrogenic interference
Health issues from medical treatment affecting identification.
Cause of death
Determined through radiologic examination and historical data.
Osseous injury
Bone damage from trauma or repetitive stress.
Fracture analysis
Examining fractures to determine injury cause.
Skull fracture examination
Studying fracture lines reveals injury sequence.
Sharp force injury
Penetrating wounds often undetectable on X-ray.
Foreign bodies in radiology
Metallic objects visible; narcotics packaging detectable.
Drowning radiographs
Lung density from pulmonary edema in drowning victims.
Air embolism in diving
Air bubbles in blood from scuba diving accidents.
Pugilistic Attitude
Muscle shrinkage causing wrist and ankle fractures.
Cremation Temperature
2012°F increases bone shrinkage during cremation.
Thermal Fractures
Longitudinal fractures in de-fleshed dry bones.
Gunshot Wound Path
Bullet travels straight until energy loss.
Exit Wound
Opening where bullet exits the body.
Radiography
Imaging technique to locate bullets in body.
Bullet Count Correlation
Number of bullets matched with entry/exit wounds.
Jacketed Bullets
Bullets that may separate from projectiles.
Caliber Differentiation
Identifying bullet calibers indicates multiple shooters.
Range of Fire
Determined by inspection of body and clothing.
Subdural Hematoma
Blood collection between skull and brain surface.
Cerebral Edema
Brain swelling due to fluid accumulation.
Metaphyseal Fractures
Injuries to the growing plate of long bones.
Diaphyseal Fractures
Fractures from twisting and torsion forces.
Transverse Fractures
Fractures caused by grabbing or swinging.
Facial Fractures
Common in assaults, especially in battered women.
Le Fort Fractures
Facial fractures classified into three types.
Le Fort I Fracture
Horizontal fracture across maxilla, below the nose.
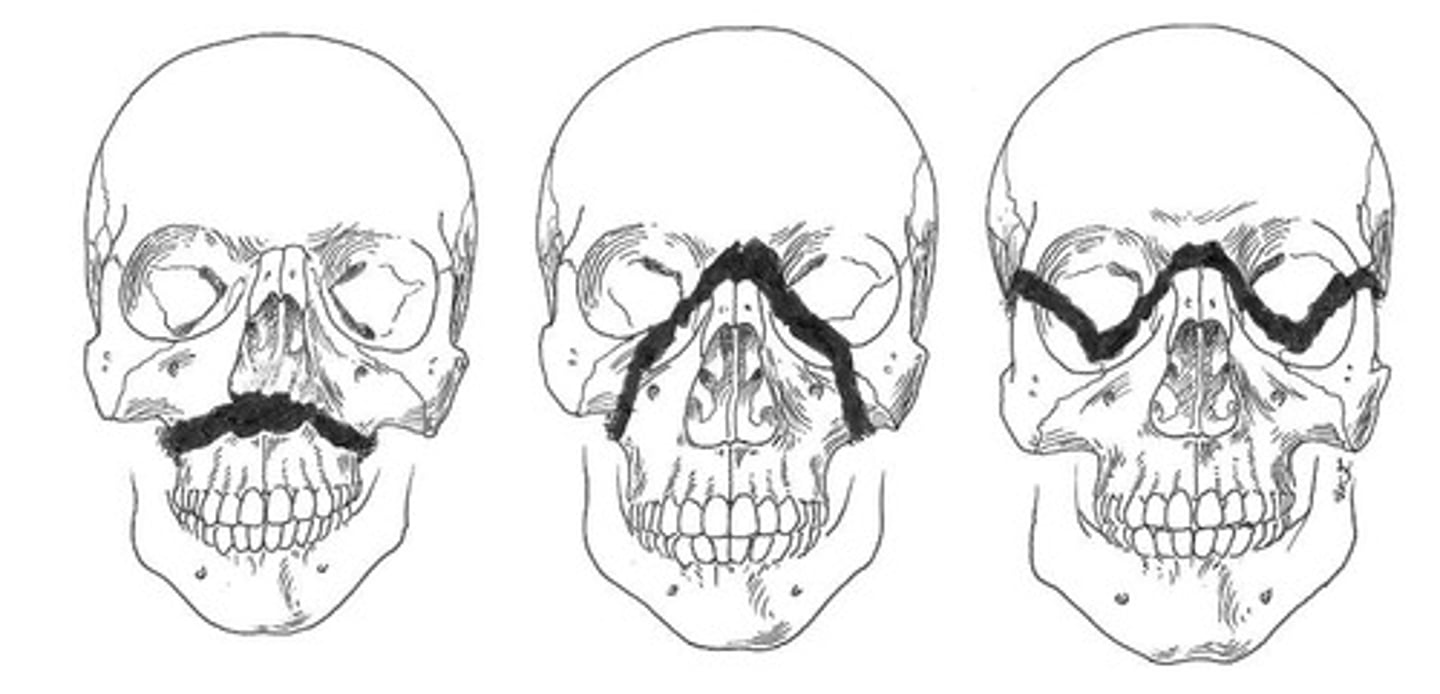
Le Fort II Fracture
Fracture involving midsection of the face.
Le Fort III Fracture
Complete separation of face from skull base.
Elderly Abuse
Increasing recognition of physical maltreatment in elderly.
Maxillofacial Injuries
Injuries to the face, often from abuse.