Ancient Egyptian and Mesopotamian Architectural Structures: Zoser, Giza, Karnak, Ur
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
The Funerary Complex of King Zoser was primarily constructed from _____ brick.
Limestone
What material originally encased the limestone bricks of Zoser's Funerary Complex?
Polished Limestone topped with Gold
What is the architectural term for a wall capped at its end by a column, as seen in Zoser's complex?
Stubbed Wall
A column that is connected to a wall, like those in Zoser's Funerary Complex, is called an _____ column.
Engaged
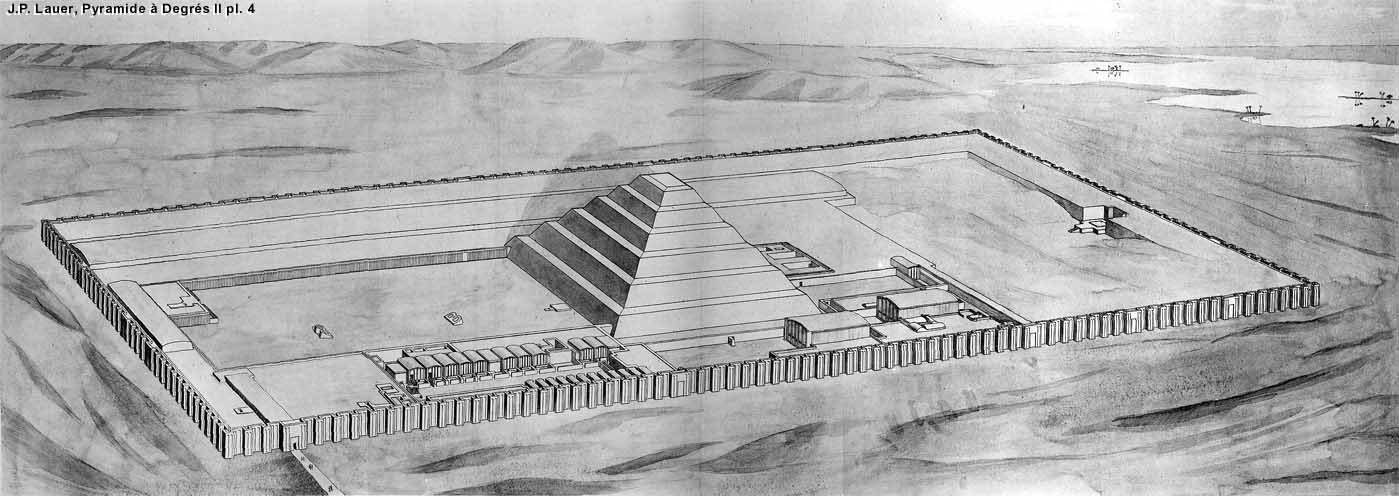
What was the primary function (Utilitas) of the Funerary Complex of King Zoser?
King Zoser's tomb
The distinctive form (Venustas) of King Zoser's pyramid is known as a _____ pyramid.
Stepped
The ribbed columns in Zoser's Funerary Complex were designed to imitate what natural material?
Bundles of Reeds
In the North Palace of Zoser's complex, a column represented a Papyrus plant, showing a stem and a _____ as its capital.
Blooming Flower
King Zoser's pyramid is considered an architectural evolution of what earlier tomb structure?
Mastabas
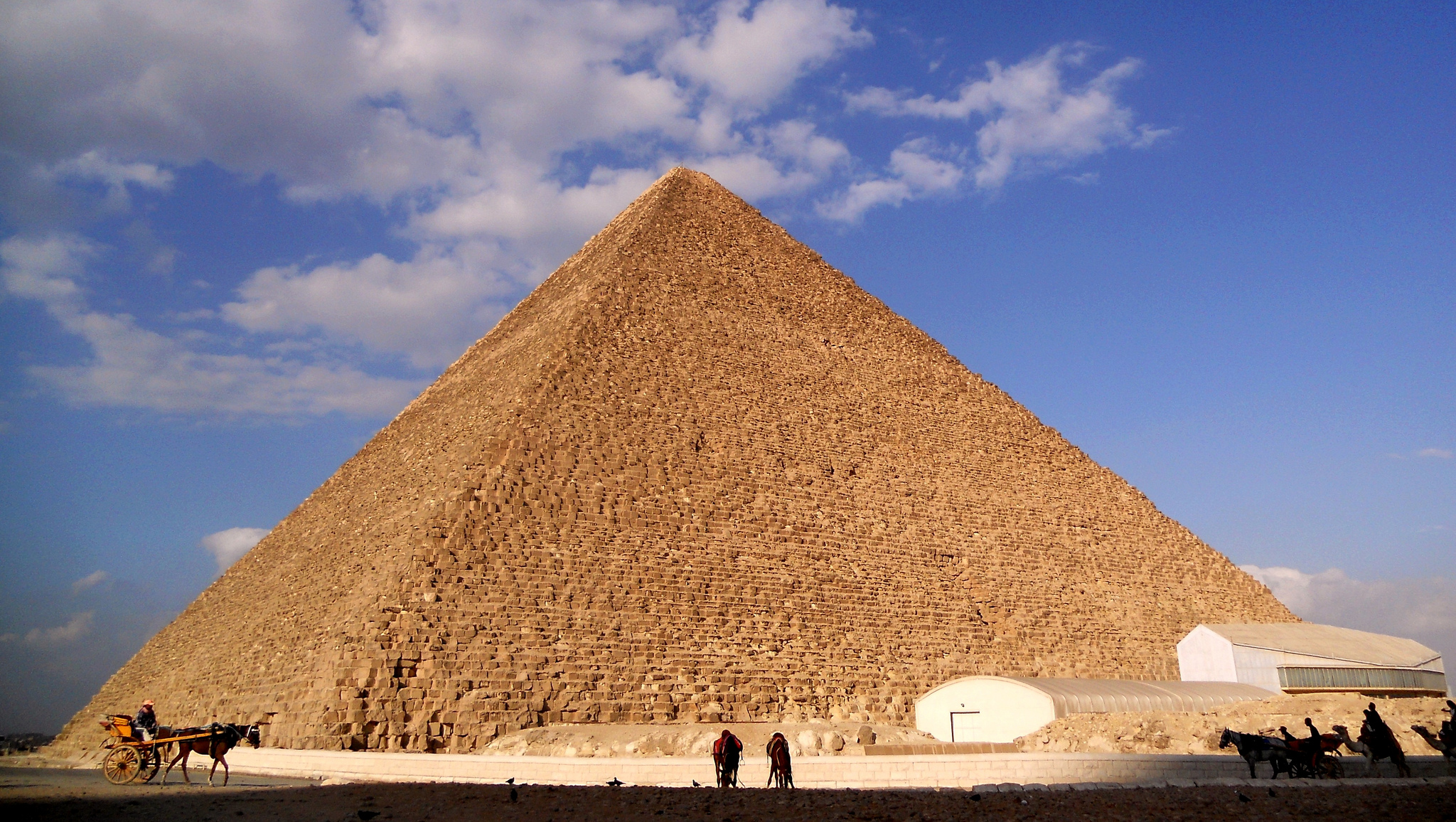
The Pyramid of Khufu is more commonly known by what name?
The Great Pyramid of Giza
What structural element was built above the King's Chamber in the Great Pyramid to protect it from the weight above?
Five granite relief chambers
The Great Pyramid of Giza's base was ____
Almost a perfect square
The Great Pyramid of Giza was part of a larger complex that included a Valley Temple, a Mortuary Temple, and a connecting _____.
Causeway
What was the primary function (Utilitas) of The Great Pyramid of Giza?
King Khufu's tomb
Which of the Giza pyramids still has some of its original polished limestone casing at its peak?
Pyramid of Khafre
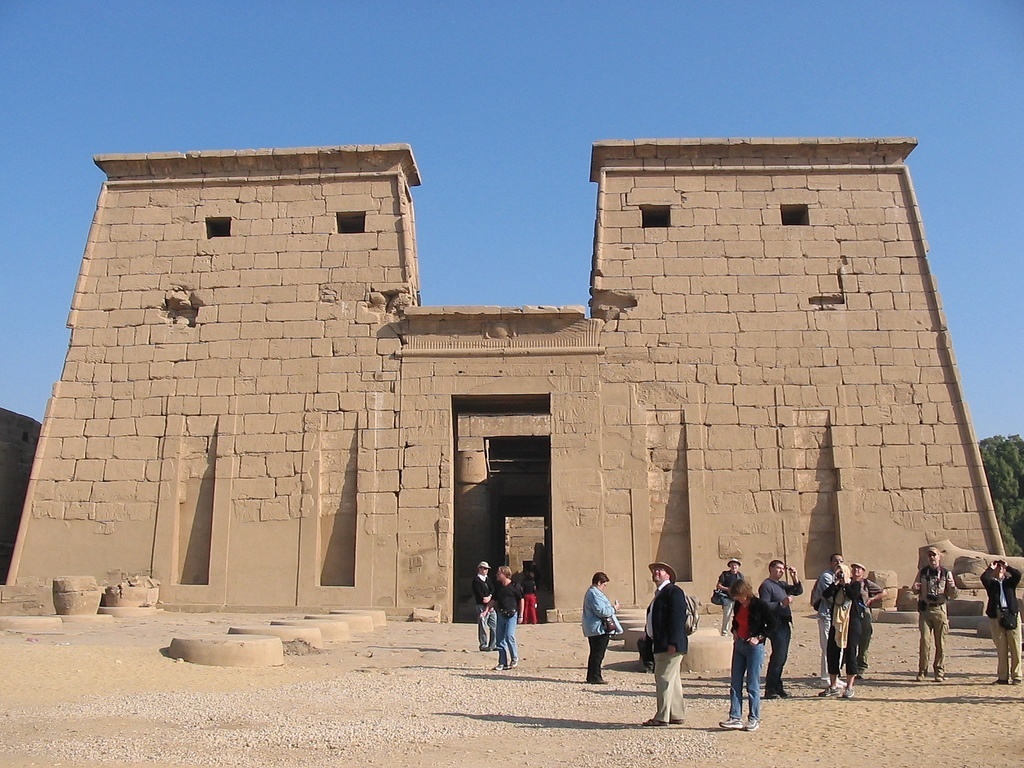
List the four main parts of the Temple of Khonsu in order from the entrance.
Pylon, Courtyard, Hypostyle Hall, Sanctuary
A hall with a roof supported by columns; from the Greek 'hypo' meaning 'under'
Hypostyle Hall
What type of construction, featuring vertical supports and horizontal beams, was common in the Temple of Khonsu?
Post and lintel construction
What is the term for the massive gateway of an Egyptian temple, like that at the Temple of Khonsu?
Pylon
The pylons of the Temple of Khonsu have _____, meaning their walls are sloped on all four sides.
Battered walls
A decorative molding that protrudes horizontally, crowning a vertical member of a structure.
Cornice
The columns in the Courtyard of the Temple of Khonsu were shaped like Papyrus stems with _____ for capitals.
Buds
How did the capitals of the columns in the Hypostyle Hall of the Temple of Khonsu differ from those in the courtyard?
They were shaped like open Papyrus flowers instead of buds
The Temple of Amun at Karnak was dedicated to Amun, the father of which god?
Khons
The Temple of Khonsu had missing ___ & ___ in front of the pylon
Sphinxes and Obelisks
The exterior of the Temple of Khonsu used to be ___ & have ___
Painted, flags
How many pylons did the Temple of Amun have
Eight
The Temple of Amun now only contains ___ obelisk and the other was gifted to ___
One, France
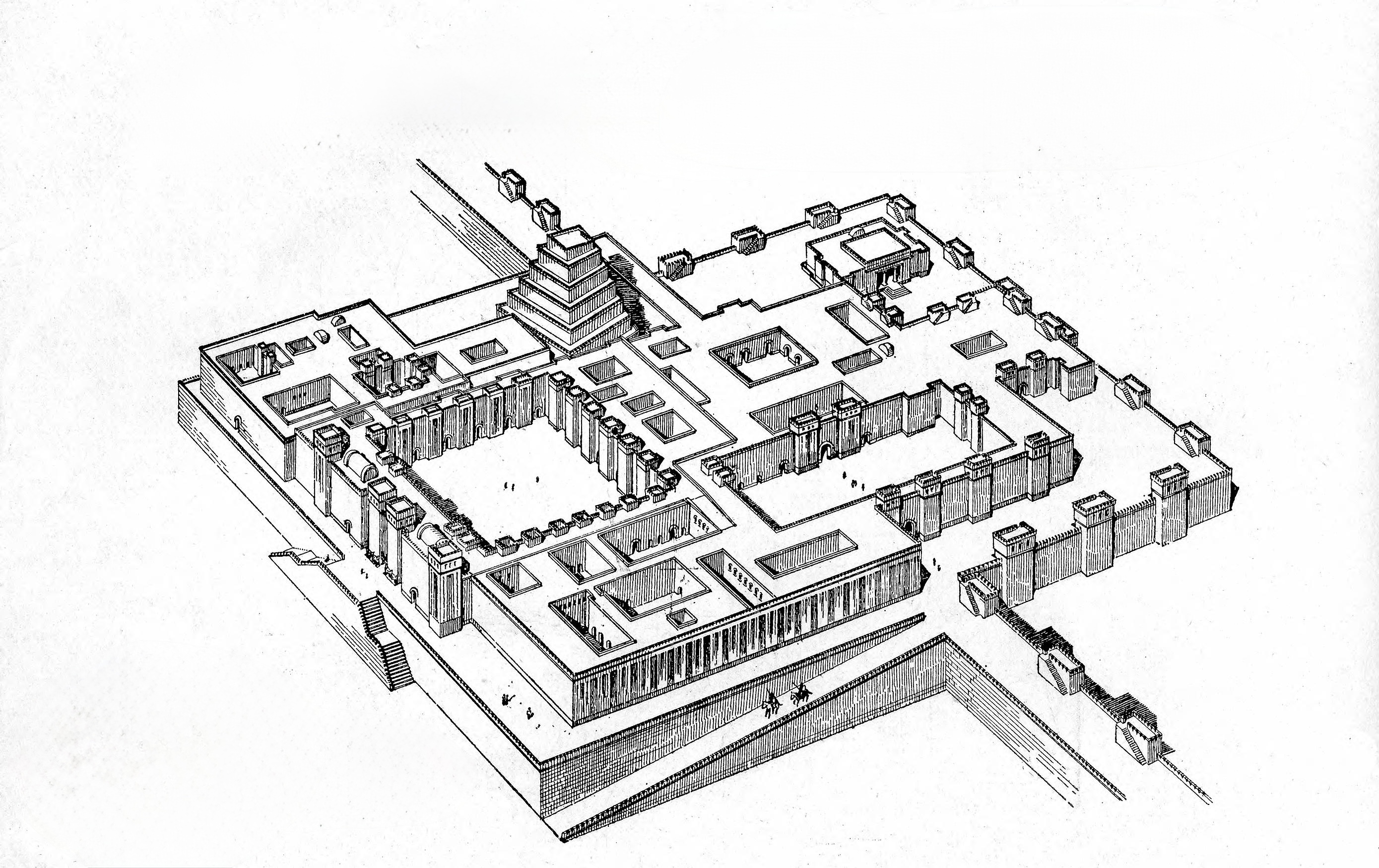
The interior of the Ziggurat at Ur was made of mud brick, while the exterior veneer was made of _____.
Baked brick
What was the function of the 'Weep Holes' in the Ziggurat at Ur?
To release trapped moisture from between the bricks
What was believed to be located at the top of the Ziggurat at Ur?
A temple for the moon goddess
The Ziggurat at Ur was surrounded by a _____, which is a sacred wall enclosure.
Temenos
Why was the Ziggurat at Ur believed to be elevated?
To be closer to the heavens
What was the primary building material for the Palace of Sargon?
Mud brick and stone
The corners of the Palace of Sargon were deliberately oriented to face the _____.
The cardinal directions
Why was the Palace of Sargon abandoned shortly after its construction?
King Sargon II died in war and his body was never found
The bottom of the walls in the Palace of Sargon were decorated with sculptures and carvings made of what stone?
Alabaster
What are the guardian figures at the Palace of Sargon, depicted as winged bulls with human heads, called?
Lamassus
What feature of the Lamassu figures symbolized their divine status?
horned crowns, which were reserved for gods
The Ishtar Gate was the main northeast entrance into what ancient city?
Babylon
The Ishtar Gate had a mudbrick core and was faced with what decorative material?
Deep blue glazed brick
What is the architectural term for the square-shaped notches at the top of a fortified wall, like those on the Ishtar Gate?
Battlements or crenellations
The lion reliefs on the Ishtar Gate were symbolic of which goddess?
Ishtar
What was the form of writing used in Babylonia at the time of the Ishtar Gate's construction?
Cuneiform
What is the translated meaning of the inscription on the Processional Way leading to the Ishtar Gate?
May the arrogant not flourish/prevail
How many layers did the Ishtar Gate have
Two
Which side of the city was the Ishtar Gate on
East of the Euphrates
Three Greek Orders
Doric
Ionic
Corinthian
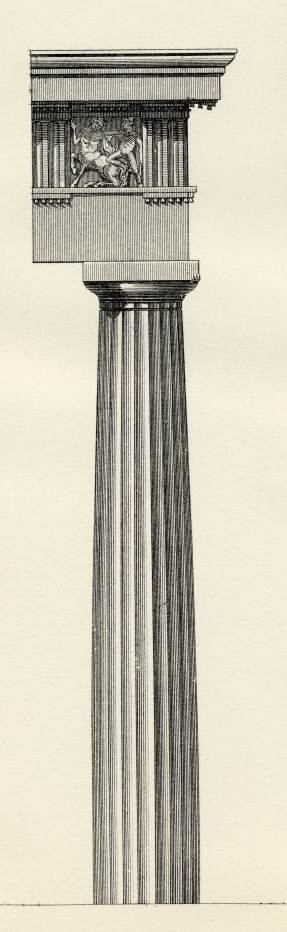
Doric
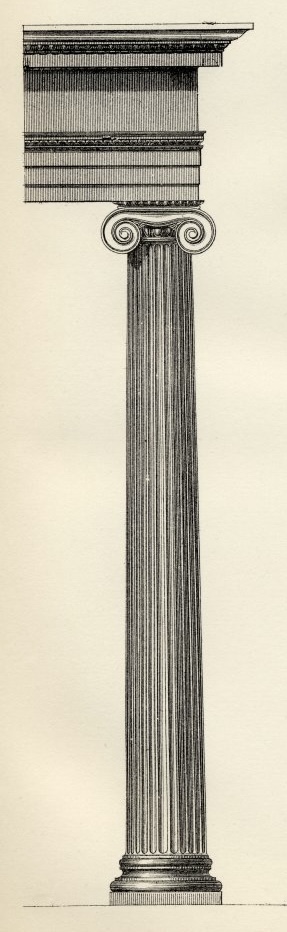
Ionic
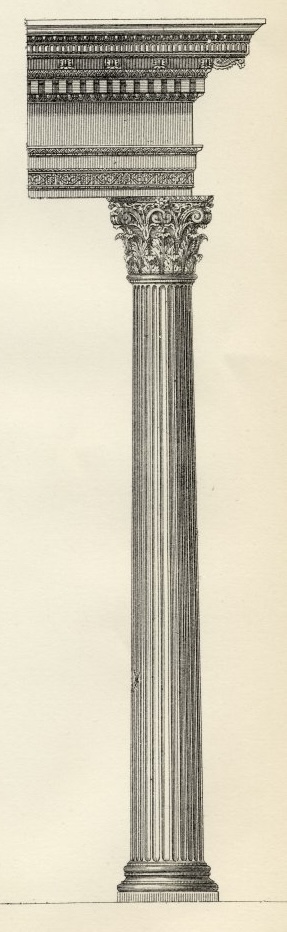
Corinthian
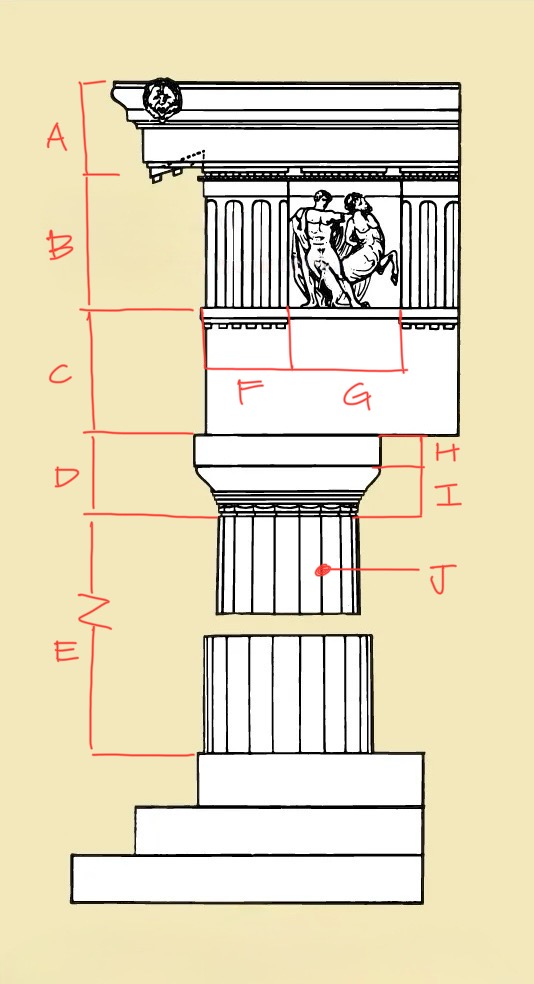
Cornice
Frieze
Architrave
Capital
Shaft
Triglyph
Metope
Abacus
Echinus
Flute
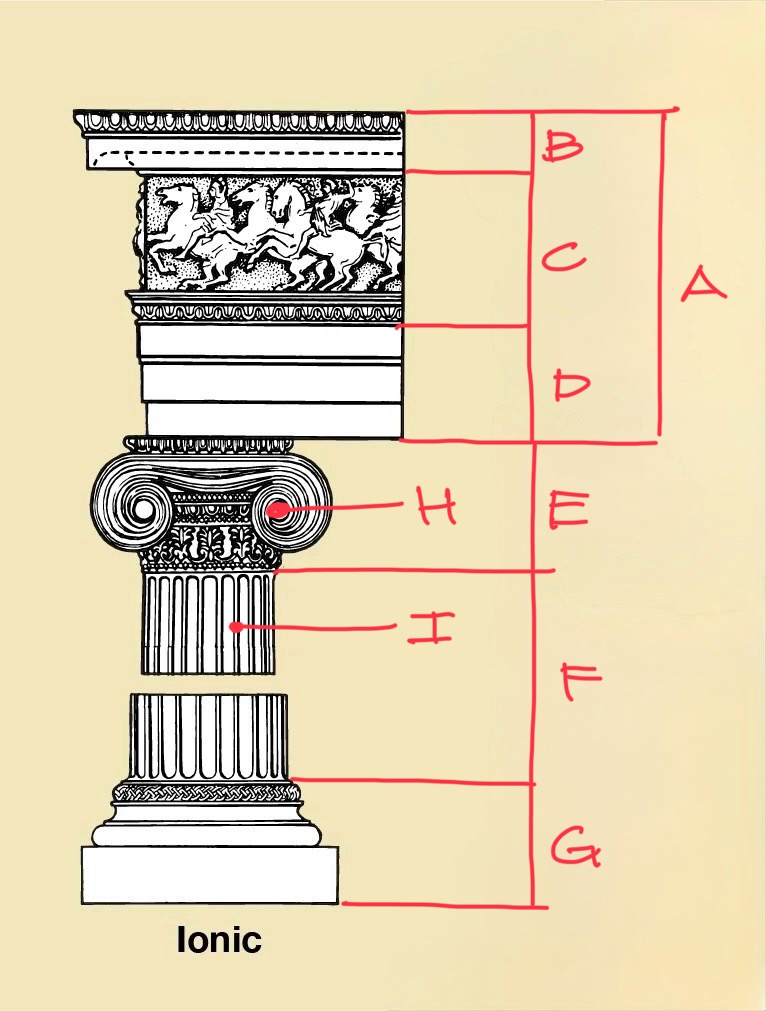
Entablature
Cornice
Frieze
Architrave
Capital
Shaft
Base
Volute
Flute
Tapering/bowing of column
Entasis
How much smaller the top diameter is from the base
Diminution
name
time
location
arch
client
Funerary complex of King Zoser
Old kingdom
Saqqara, egypt
Imhotep
King Zoser

name
time
location
arch
client
Pyramid of Khufu or Great Pyramid of Giza
Old kingdom
Giza, egypt
unknown
King Khufu

name
time
location
arch
client
Temple of Khons
new kingdom
karnak, egypt
unknown
King Ramesses III
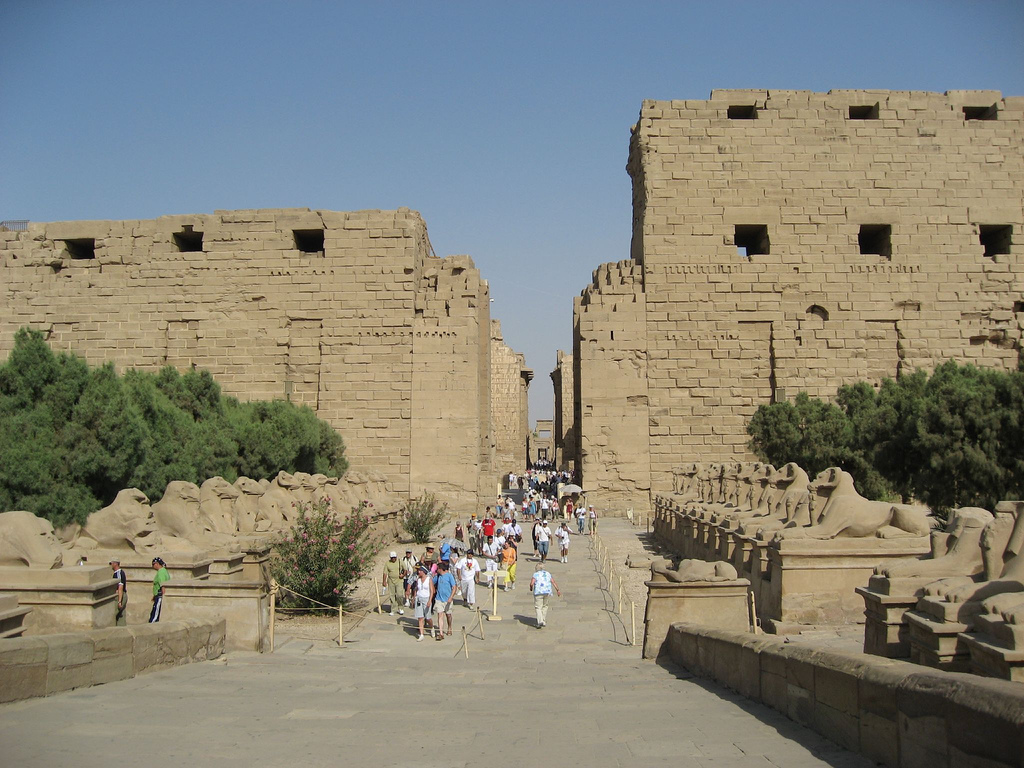

name
time
location
arch
client
temple of Amun
new kingdom
karnak, egypt
unknown
King Seti I and King Ramesses II
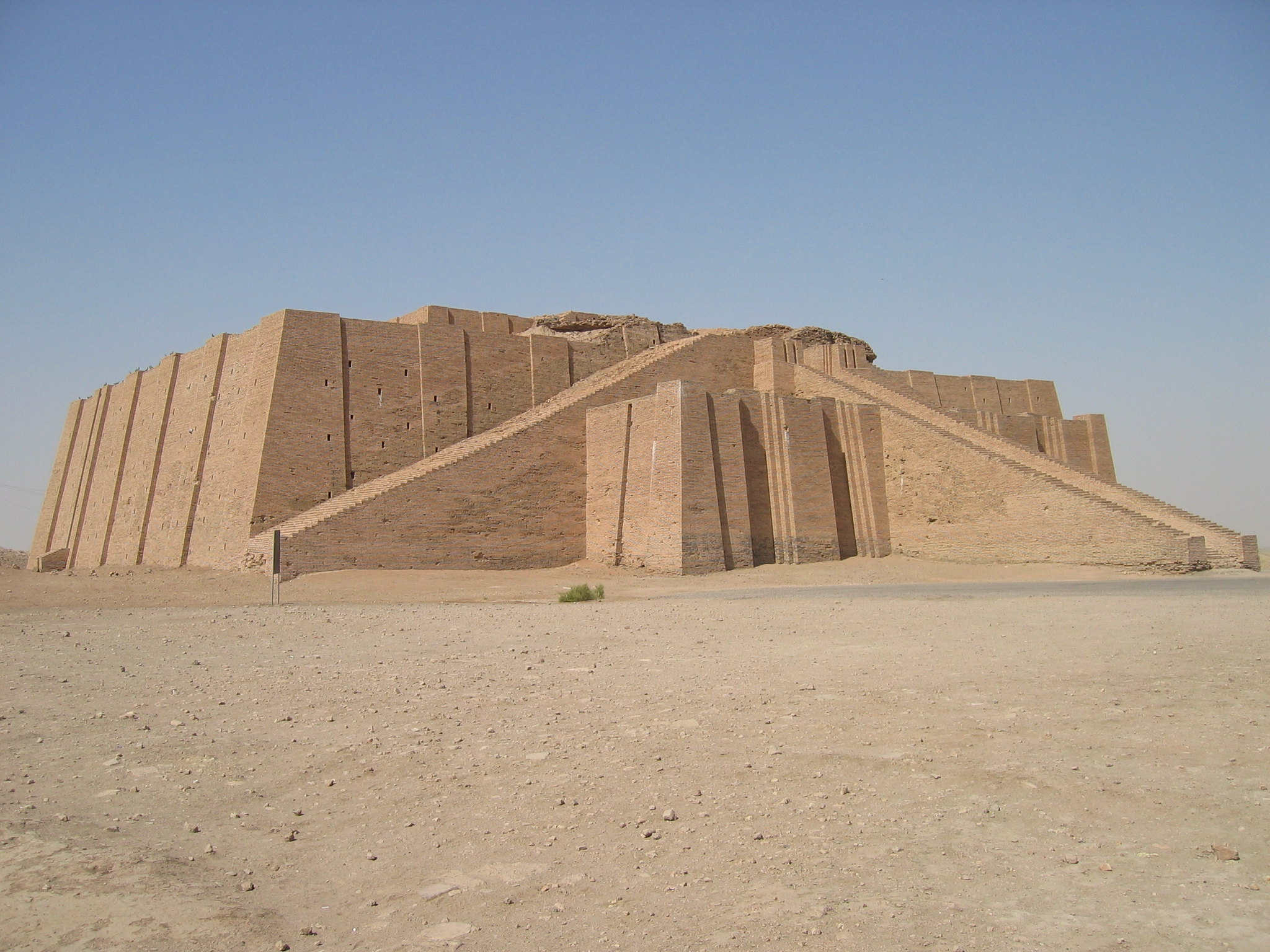

name
time
location
arch
client
Ziggurat at Ur
22nd century bce
Sumer, iraq
unknown
king ur-nammu
name
time
location
arch
client
Palace of Sargon
8th century bce
khorsabad, Iraq
unknown
king sargon II
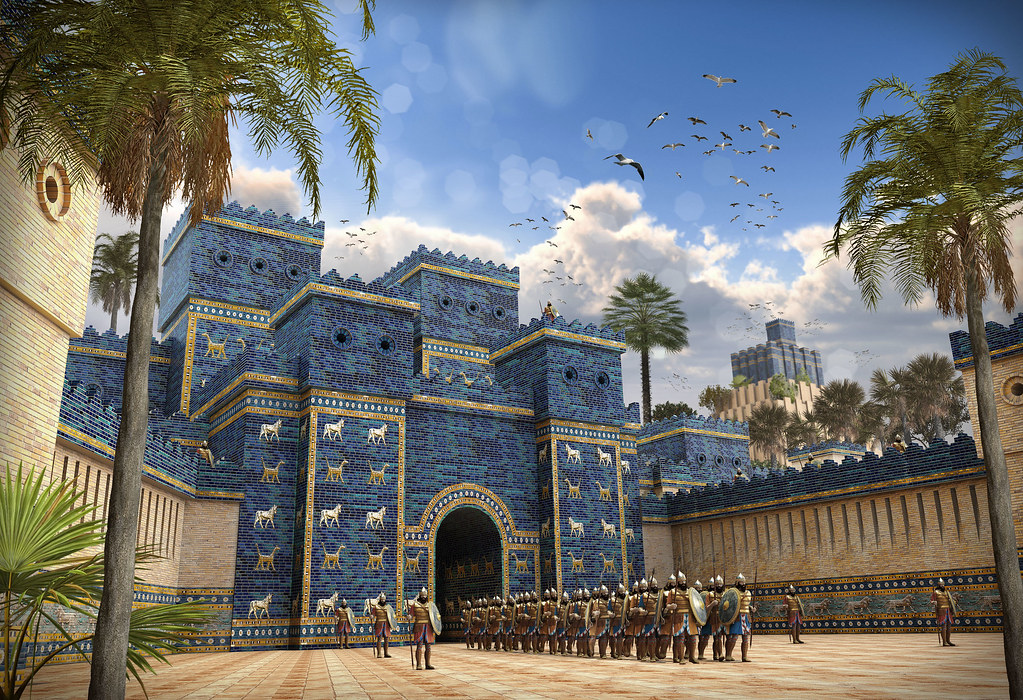

name
time
location
arch
client
Ishtar Gate
6th century BCE
Babylon, Babylonia
Unknown
King Nebuchadnezzar II