Cell Cycle & Chromosome anatomy
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12-Pro '24'25. Made by Nathan G.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Interphase
Nondividing phase & longest phase in cell cycle
Cell grows
a. DNA replicates
b. Nutrients accumulate
- Nuclear envelope still visible
Gap/Growth 1 (G1)
Rapid growth & attains normal size
Organelle duplication starts
Longest phase within interphase
- Muscle & nerve cells stay at this phase for whole life
Synthesis (S)
DNA replicated in the nucleus
Chromosomes double, gain 2 sister chromatids
Centrosome duplicated
Gap/Growth 2
Restores energy, grows, & creates proteins for mitosis
Organelle duplication ends
Mitosis/M-phase
Cell division done by somatic/body cells for:
Asexual reproduction
Growth & development
Tissue renewal
Prophase (Prepare)
Chromatin condense into chromosomes
Centrosomes move apart
Spindle fibers begin to form between centrosomes
-Chromatin microscopically visible
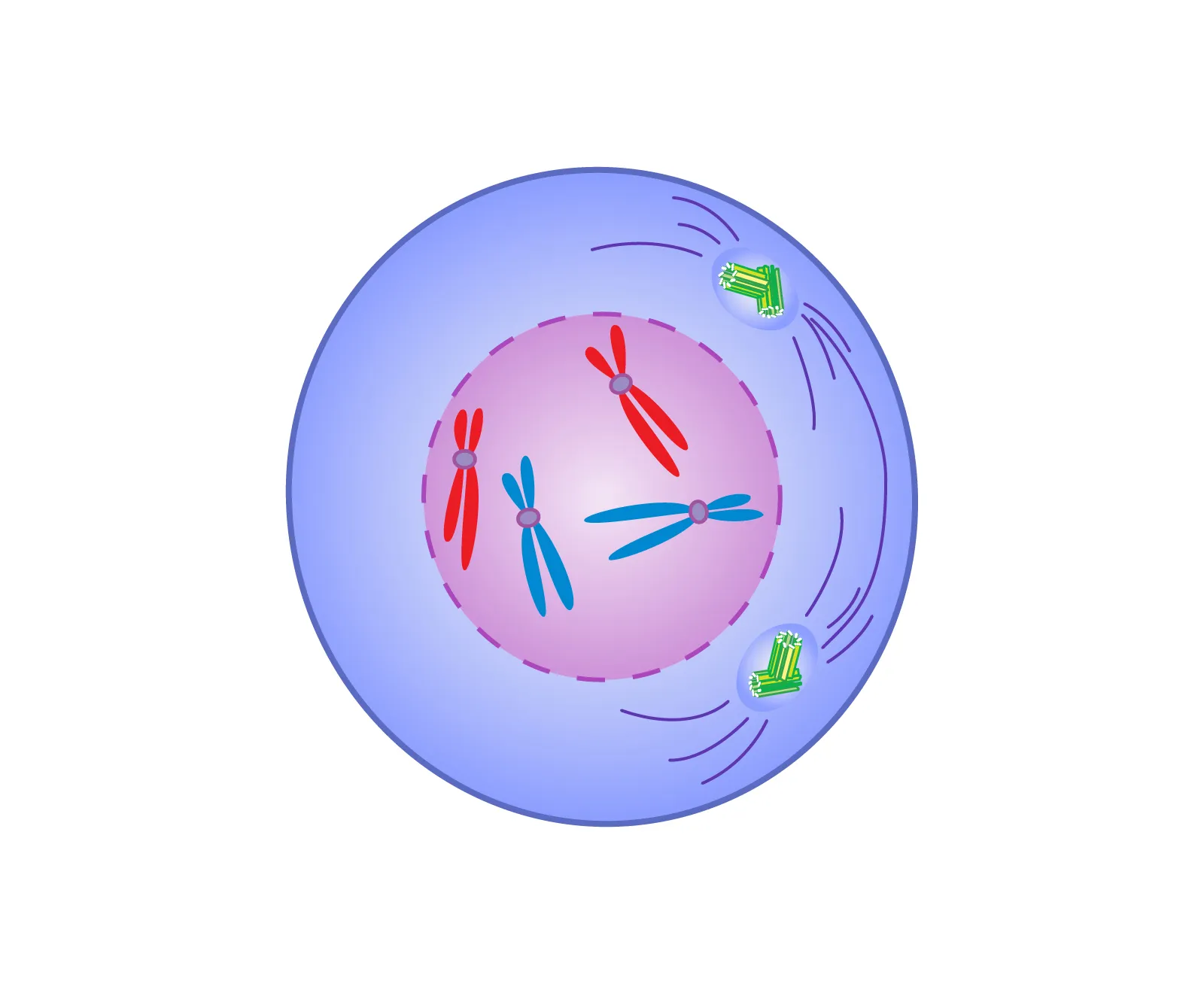
Metaphase (middle)
Chromosomes align on Metaphase plate
Nuclear envelope dissapears
Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores
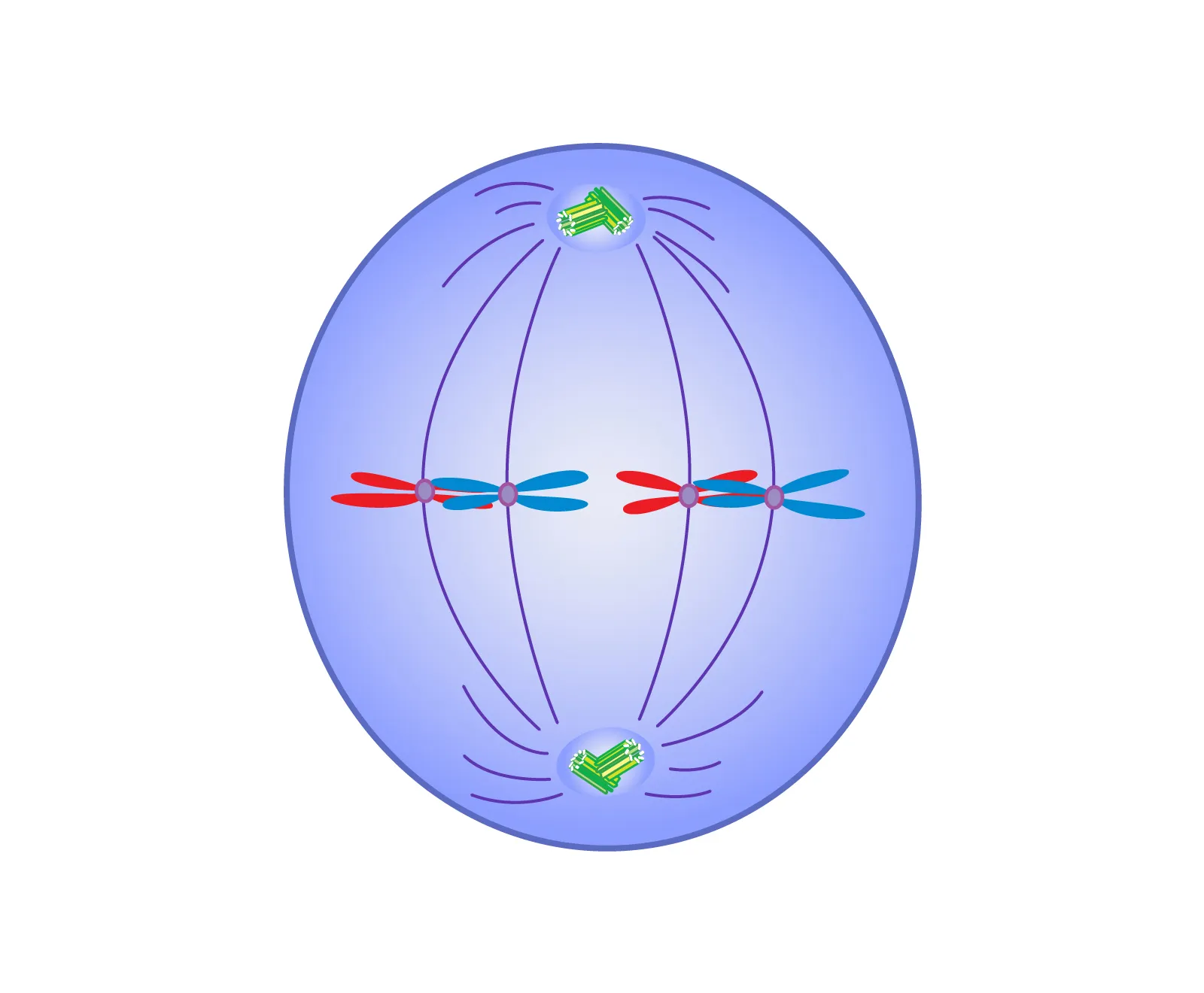
Anaphase (away)
Spindle fibers each pull a sister chromatid apart
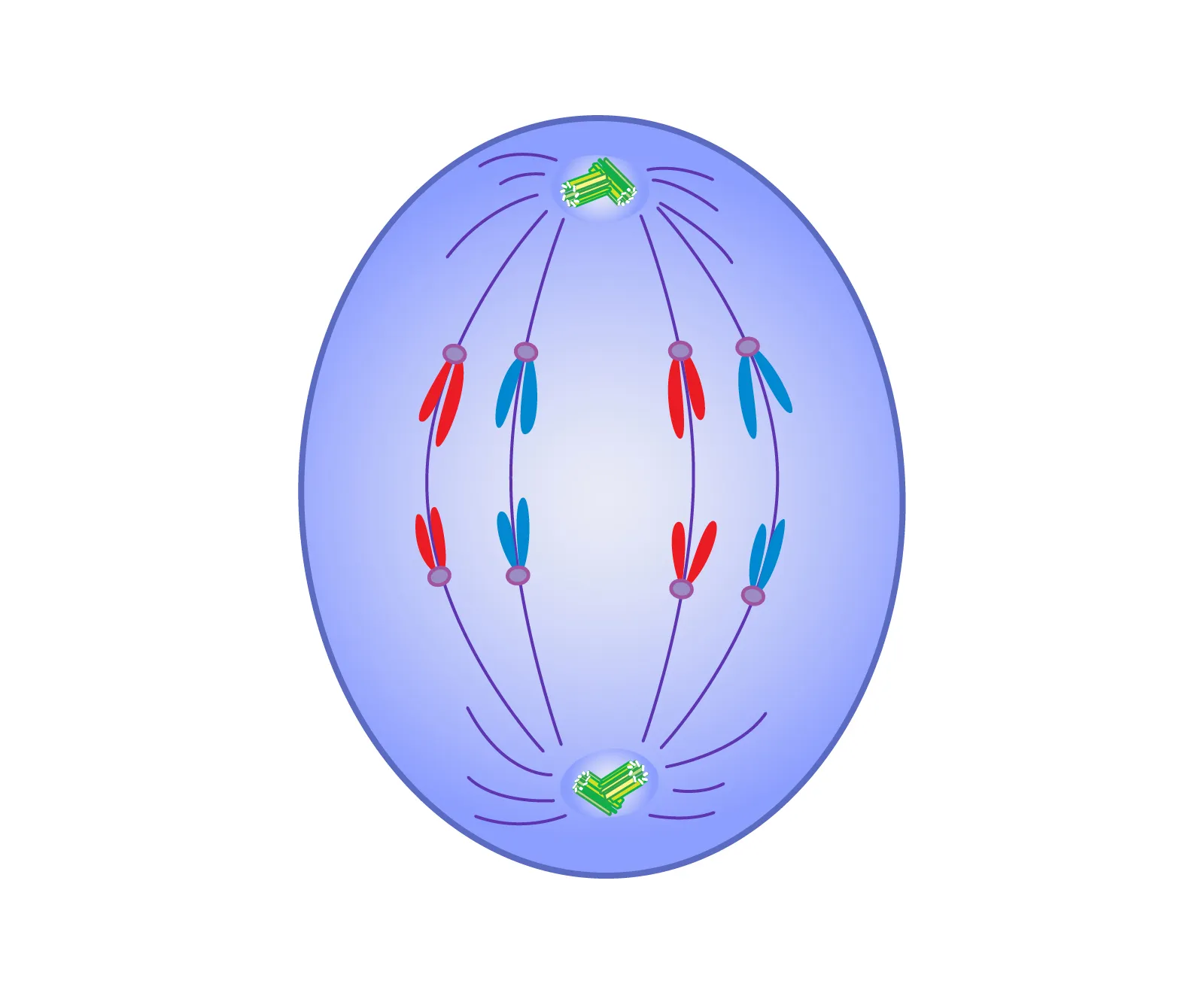
Telophase (together)
Nuclear membrane forms around each pole
Chromosomes decondense into chromatin
Spindle fibers breakdown
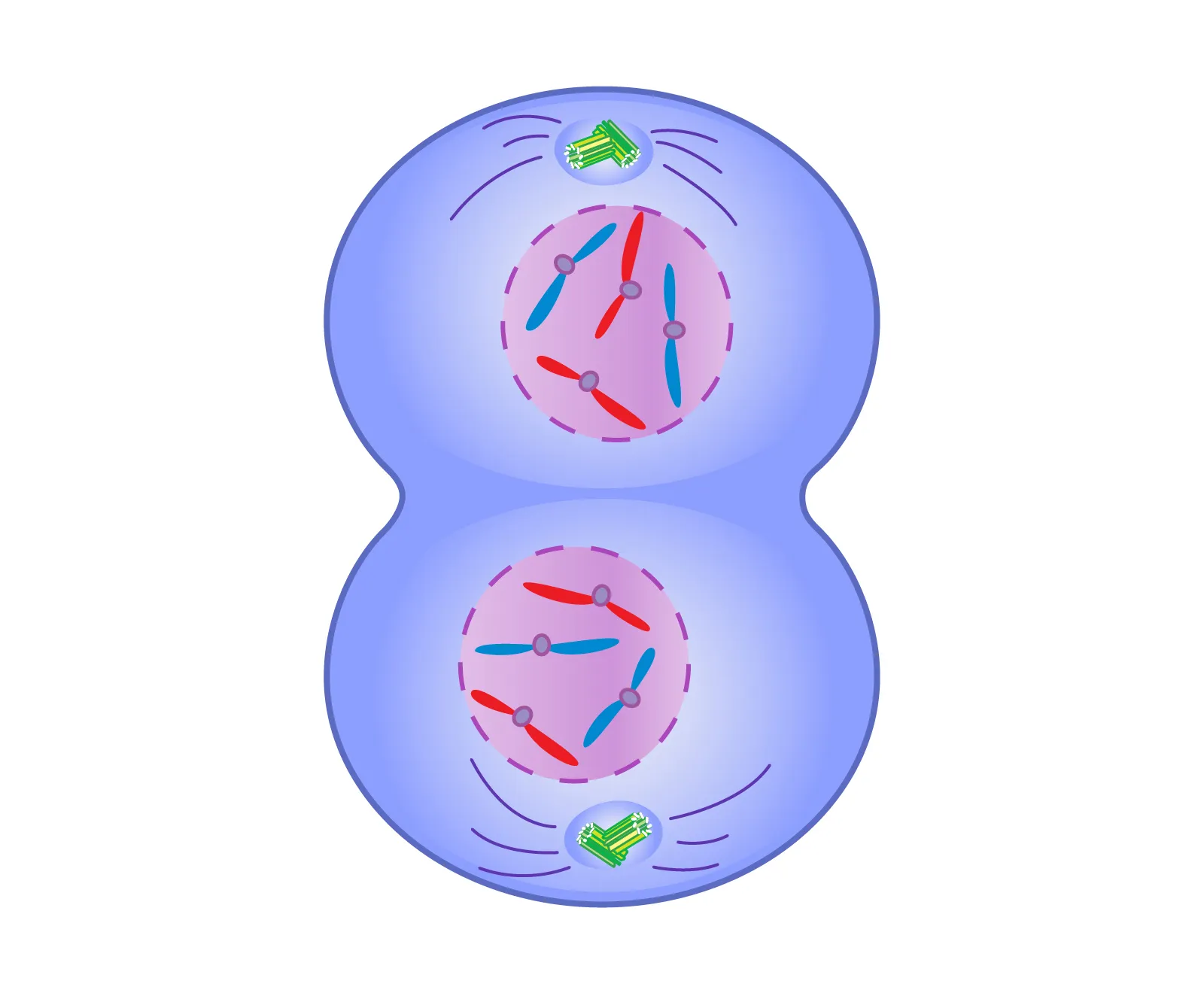
Post-mitosis
Cytokinesis
Both cells enter interphase
Cells are genetically equal w/ same ploidy
Cell cycle checkpoints
G1 - checks cell readiness for S phase
G2 - checks cell readiness for M phase
Spindle checkpoint (M) - checks spindle fiber attachment before anaphase
Meiosis
Cell division for sexual reproduction
Uses sex/haploid cells
Meiosis 1
Reductional
Halves chromosome count to haploids
Meiosis 2
Equational
Equivalent to mitosis
Prophase 1 (Meiosis)
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
a. Pairs homologous chromosomes (Synapsis)
b. Does crossing over of genetic material at telomeres
Metaphase 1 (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes align on metaphase plate
Anaphase 1 (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes pulled away via spindle fibers
Nucleoli appear
Telophase 1 (Meiosis)
Separated chromosomes enclosed in different nuclei
Cytokinesis occurs after
Daughter cells become haploid
Prophase 2 (Meiosis)
Daughter cells’ chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form
Move towards metaphase plate
Metaphase 2 (Meiosis)
Daughter cells’ chromosomes align with each other, connect to spindle fibers
Anaphase 2 (Meiosis)
Daughter Cells’ chromosomes separate into sister chromatids
Telophase 2 (Meiosis)
Daughter cells have separated into 2, 4 total haploid cells
Fully separate via Cytokinesis after
Protein Kinase
Phosphorylation: Pass down phosphate group causing cellular response
CDK
Cyclin-dependent Kinase
Activity rises & falls w/concentration of cyclin in cell
Activates other kinases
e.g. MPF starts Mitosis
Centrosome
2 perpendicular centrioles
Produce spindle fibers
Centromere
Chromosome region joining sister chromatids
Made of cohesin
Kinetochore
Attachment point for spindle fibers on centromere
Spindle Fibers
Microtubule attaching to kinetochore to pull sister chromatids away
Chromatid
Duplicated chromosome DNA
Only classified as such when joined by cohesin
Density-dependent inhibition
Cells stop growing if one layer has been produced on container surface
Anchorage dependence
Cells must attach to something to divide