2ry Hemostasis
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Prekallikrein and High molecular weight kininogen (HMWK) are aka _
Fletcher factor
contact activation cofactor, Fitzgerald, Flaujeac Williams factor
factor I is aka
fibrinogen (Ia = fibrin)
factor II is aka
prothrombin → (IIa = thrombin)
factor III is aka
tissue factor (TF)
factor IV is aka
Ca2+
factor V is aka
proaccelerin, labile factor, accelerator (Ac-) globulin
factor VI (Va) is aka
accelerin
factor VII is aka
proconvertin, serum prothrombin conversion accelerator (SPCA), cothromboplastin
factor VIII is aka
antihemophiliac factor A, antihemophilic globulin (AHG)
*hemophilia A = defic of f-VIII
factor IX is aka
Christmas factor, antihemophiliac B, plasma thromboplastin componenet (PTC)
*Hemophilia B = defic in f-IX
get Hemophilia B for Christmas if Bad Boy
factor X is aka
Stuart-Prower factor
factor XI is aka
plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA)
factor XII is aka
Hageman factor
(rhymes w/Asian for XII defic, no bleeding, inc risk thrombosis)
factor XIII is aka
protransglutaminase, fibrin stabilizing factor (FSF), fibrinoligase
extrinsic factors are
VII, III (TF)
intrinsic factors are
XII, XI, IX, VIII
common factors are
X, V, II, I
contact factors are (do not require Ca2+)
XII, XI, prekallikrein, HMWK
coag testing specimen requires
WB:anticoag must be 9:1
anticoag = 3.2% sodium citrate, loosely binds Ca2+
need plt count of <10,000/mm3
stable at RT for 4 hr
Hct>55% → must adjust
no grossly hemolyzed samples
lipemic or icteric → ACL top read at 671 nm to eliminate interference
prothrombin time (PT)
measures extrinsic & common pw
uses: thromboplastin (TF) + calcium + phospholipid
what value is used to monitor Coumadin/Warfarin therapy?
PT/INR
correction factor assigned to PT rgt/equipment system, based on WHO standard
patients INR = (patient PT/PT geo mean)^ISI
ISI: lower, more sensitive the reagent
Coumadin/Warfarin dec ___?
vit K-dependent factors: II, X , IX, VII (2, 7, 9, 10)
also protein C and S production
takes ~3 days for effect
prolonged use of Abx → kill bacteria that produce majority of vit K → same effect
aPTT (PTT, activated partial thromboplastin time)
measures intrinsic & common pw
uses: contact activator (micronized silica) + calcium + phospholipid (cephalin)
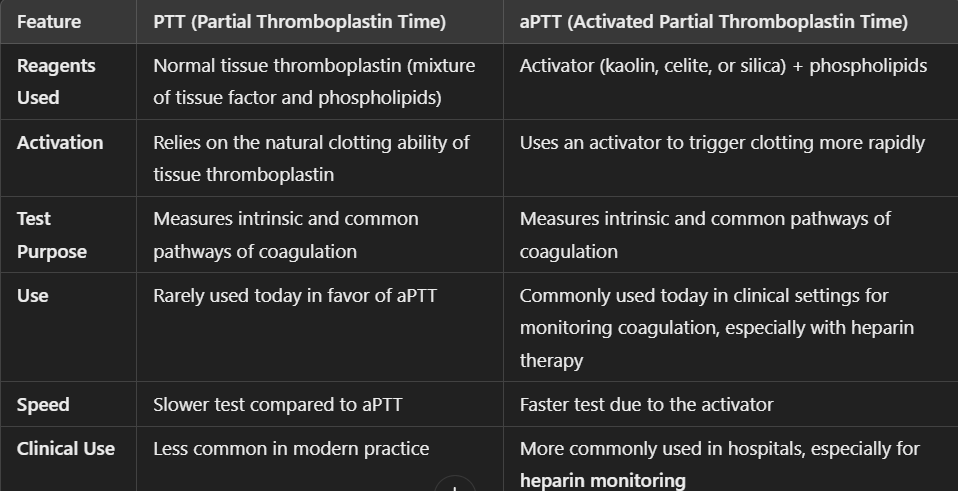
PTT vs aPTT?
mechanical vs optical clot detection
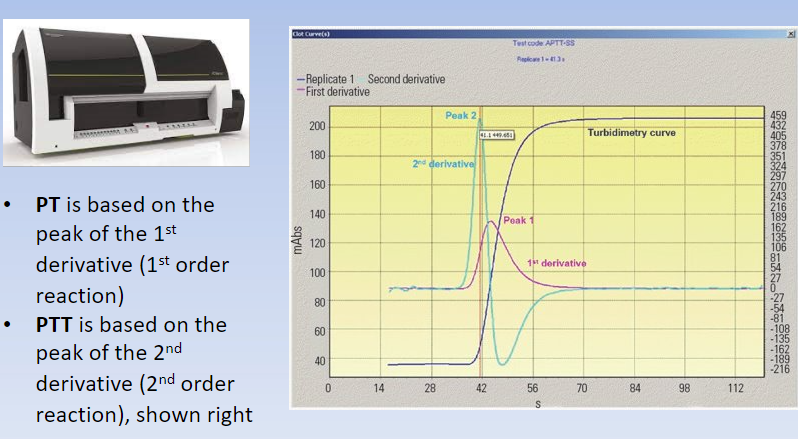
basis of PT, PTT, fibrinogen assays
mechanical: measures based on resistance to mvmt (viscoelasticity)
optical: light transmission through a sample
heparin
what is it?
how does it work
types?
anticoagulant that enhances antithrombin III (ATIII) → ATIII inhibits Xa → inhibits IIa (AT3=8 → 2+8=10)
neutralizes activated serine proteases: XII, XI, IX, X, II (12, 11, 9, 10, 2)
immediately acting
types:
unfractionated: oligos chains of varying lengths
low molecular weight (Lovenox): more predictable response, shorter chains, less bleeding
can’t monitor w aPTT
normal vs abnormal clot curves
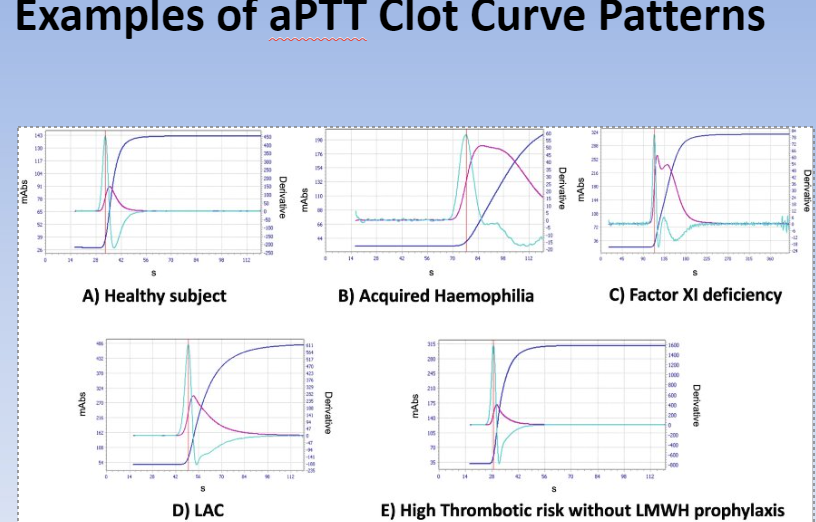
clot curves
which peak = PT?
which peak = PTT?
1st order rxn = 1st derivative = PT
2nd order rxn = 2nd derivative = PTT
chromogenic heparin assay
CHA measures heparin inhibiting factor Xa
requires pt’s own AT3
low heparin activity: less color change bc heparin concentration is low → less Xa inhibited
high heparin activity: more color change → more Xa inhibited
why would PT/aPTT be prolonged? 3 categories:
anticoag therapy
Hep/Warf or new anticoag (Rivoraxiban, etc)
inhibitors
Heparin
Lupus inhibitor (anti-phospholipid Ab against rgt phospholipid)
factor inhibitor (Ab against a factor)
factor deficiency
acquired: usually liver dz, vit K defic, or Warf
congenital: usually single factor (m/c = VIII, IX vWF)
how to differentiate an inhibitor from a factor deficiency?
PTT or PT inhibitor screen/Mixing Studies (50/50 mix)
mix 1:1 pt plasma & normal pool plasma → incubate 5 min 37C → retest
incubate 2 hr 37C → retest
if return to normal PT/PTT value → pt has factor defic
if still prolonged value → factor specific inhibitor or Lupus anticoagulant or heparin
inhibitors in mixing studies
heparin: thrombin time is v long
Lupus anticoagulant (LA): anti-PL → confirm w/ anti-PL panel: DRVVT (dilute russell viper venom time), hexagonal phase, anti-cardiolipin
factor inhibitor (Ab)
fibrinogen assay
does this measure amount of fibrinogen?
what dz may this test indicate?
pt clotting time is compared to reference curve
= functional assay (does NOT directly measure fibrinogen)
may indicate fibrinogen DO
afibrinogenemia - lack of
hypofibrinogenemia - low fxnal
defic
dysfibrinogenemia - qualitative
thrombin (thrombin = factor IIa) time (TT) vs reptilase time (RT)
TT = time for fibrinogen → fibrin (I → Ia)
pt plasma + dilute thrombin rgt → fibrin clot
SUPER sensitive to heparin (inhibits Xa & IIa)
RT
reptilase sub’d for thrombin (converts I → Ia)
insensitive to heparin, use when heparin is suspected
inc TT and normal RT → heparin present
if inc TT/RT → problem w fibrinogen → eg dysfibrinogenemia
factor VIII:C assay (C = coagulant)
key in dx Hemophilia A (defic in factor VIII) and vWD
measures activity of VIII
make 1:1 dilution w normal pool plasma that has depleted factor VIII
pt clotting time is compared to reference curve
??
factor XIII
is this factor tested in PT/PTT? if not, what test can be used for XIII defic?
XIII stabilizes fibrin clot via covalent bonds b/t fibrin strands
activated by thrombin
XIII defic → unstable blood clots
NOT part of PT/PTT test system
qualitative test: clot stabilizing factor urea clot lysis screen
create clot + 5M urea → incubate 24 h
clot dissolved → <10% factor XIII → 13 defic
stable clot → normal
also indirectly test XIII activity on TEG/ROTEM/Quantra
Hemophilia A
congenital defic of VIIIC (m/c defic)
sex-linked to X chromosome
→ joint bleeds, deep muscle bleeds, intracranial hemorrhage)
recall vWF is the carrier of VIII → vWD type 2N: dec binding → mimics Hemophilia A
also recall common name of VIII
Hemophilia B
congenital defic of factor IX (2nd m/c)
aka Christmas factor; if Bad → get Hem B for gift
sex-linked to X chromosome
→ joint bleed, deep muscle bleeds, intracranial hemorrhage (same as Hem A)
recall common name of factor IX
Hemophilia C
autosomal recessive, defic in factor XI
rare, except in European Jewish subpopn
mostly asympto, but → mild mucus membrane or post-surgery bleeds
defic in factor XII (Hageman factor)
autosomal recessive
rare, but prevalent in Asians
doesn’t bleed, but may have inc thrombosis, since XII is activator for clot lysis system
acquired coag disorders
liver disease
all factors made in liver, except vWF and VIII
vit K defic
majority prod by gut bacteria → Abx, chronically ill, or Warfarin → vit K defic → dec factor II, VII, IX, X
DIC
consumes factors, plt, esp fibrinogen
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
what does it do?
what are the various causes?
consumes coag factors & plts → produces fibrin clot → bleeding and/or thrombosis
due to exposure of TF in underlying tissue layers which occurs via:
bacterial sepsis (triggered by GNR’s LPS)
blood parasites
pregnancy: dead fetus, amniotic fluid emobolus
surgery complications
brain/lung trauma
burns
snake venoms: direct factor activators
DIC is tested via
PT, aPTT
fibrinogen
plt count
FDP (fibrinogen degradation product, 1ry & 2ry fibrinolysis)
D-dimer (2ry fibrinolysis)
IIa (thrombin) acts on which coag cascade factors?
VIII
V
I
XIII
XI
(1, 5, 8, 11, 13)
13-11 = (2)
13=8+5
just remember 1