Mol Bio Final Sp2025
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Which of the following statements regarding topoisomerases is true?
A. Type I topoisomerases use ATP to promote DNA underwinding
B. Type I topoisomerases increase negative supercoiling
C. Type II topoisomerases cut one DNA strand
D. Only eukaryotic cells use topoisomerases to regulate DNA supercoiling
E. All of the above statements are false
E. All of the above statements are false
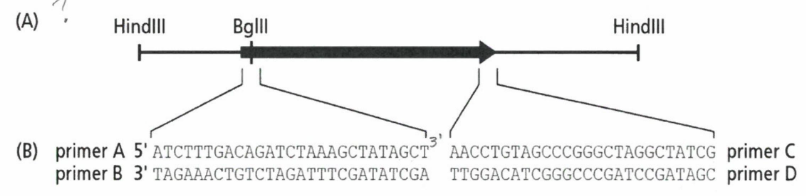
The image below shows different restriction sites in and around a protein-encoding gene. The arrow indicated the position and orientation of the gene in the DNA. In part (B) of the figure, the positions and sequences of four different primers are provided. The orientation of the primer sequences is also indicated. Which primer of primers can be used to amplify the gene?
Primer A and D
Primers A and C
Primer A and B
Primer A alone
Primer A and D
A eukaryotic cell has initiated expression of the Bevo gene in response to a change in the environment. Which of the following processes occurred at the Bevo gene to initiate expression?
A. A histone acetyltransferase increased the positive change of lysine amino acids within histones located at the Bevo gene.
B. A histone deacetylase increased the positive charge of lysine amino acids with histones located at the Bevo gene.
C. A histone deacetylase the positive charge of lysine amino acids within histones located at the bevo gene.
D. A histone acetyltransferase decreased the positive charge of lysine amino acids within histones located at the Bevo gene.
D. A histone acetyltransferase decreased the positive charge of lysine amino acids within histones located at the Bevo gene.
During DNA renaturation, two DNA strands will ________.
A. break the covalent bonds that hold the nucleotides together while maintaining the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together
B. break the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together with no effect on the covalent bonds that hold the nucleotides together
C. re-form a double helix if the two strands are identical in sequence and orientation
D. re-form a double helix if the two strands have complementary sequences
E. will undergo DNA underwinding
D. re-form a double helix if the two strands have complementary sequences
Alpha helices and beta sheets in proteins are formed by ______?
A. topoisomerases
B. electrostatic interactions
C. hydrophobic interactions
D. Hydrogen bonds
E. disulfide bonds
D. Hydrogen bonds
In breast tumors the presence of multiple copies of the HER2 gene is correlated with a more aggressive cancer. Which if the following methods would allow the most accurate comparison of different cancer cells to determine which have more copies of the HER2 gene?
A. PCR with primers that contain restriction sites
B. RT-PCR
C. Quantitative PCR
D. PCR with conventional primers
E. All of these choices are correct.
C. Quantitative PCR
When turns are removed from a closed-circular DNA, the DNA may become _______.
A. underwound and supercoiling will occur.
B. overwould and supercoiling will occur.
C. underwound or overwound, depending on the sequence of the DNA
D. underwound, but this form is unstable and typically reverts to the relaxed state.
E. overwould, but this form is unstable and typically reverts to the the relaxed state.
A. underwound and supercoiling will occur.
Which of the following can evolve?
A. populations
B. individuals
C. genes
D. DNA
E. all of the above
A. populations
A scientist has discovered a yeast strain in which half the H2A molecules have their tails deleted. Which one of the following would you expect to be affected by this DNA mutation, and why?
A. The structure of individual nucleosomes, because histone tails are vital to the core octamer structure that DNA wraps around
B. DNA compaction and gene expression would be affected because histone tails are important for nucleosome-nucleosome interactions and gene regulation.
C. Only DNA compaction would be affected by histone tails because histone tails are important for nucleosome-nucleosome interactions
D. Only gene expression would be affected because H2A histone variants regulate DNA compaction.
B. DNA compaction and gene expression would be affected because histone tails are important for nucleosome-nucleosome interactions and gene regulation.
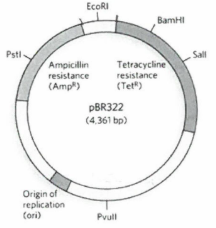
A student clones a segment of DNA into the pBR322 plasmid using an EcoRI restriction enzyme. Which of the following statements accurately describes the media on which the student could expect growth of E. coli containing the recombinant plasmid?
A. Nutrient agar with no antibiotics
B. Nutrient agar with ampicillin
C. Nutrient agar with tetracycline
D. Nutrient agar with ampicillin and tetracycline
E. Both A and B are correct
F. All the above are correct
F. All of the above are correct
_______ can be used to replace canonical histones with histone variants
Chromatin remodeling complex
ATP is commonly referred to as the energy currency of the cell. It has a _____ covalently attached to a nitrogenous base and phosphate.
ribose
________ is used to visualize all proteins in a gel after SDS-PAGE
coomassie stain
When performing a _______, the probe hybridizes to single-stranded RNA.
northern blot
This lab technique can be used to detect a specific DNA mutation using intact cells.
FISH
______ is always observed at telomeres and centromeres because these chromosomal regions do not have protein-encoding genes.
Heterochromatin
Which of the following statements regarding telomerase function is false?
A. Any telomerase extended by telomerase is made double-stranded by lagging strand synthesis.
B. Only one stand of the telomere sequence is elongated by telomerase after DNA replication
C. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase
D. Telomerase carries a DNA template complementary to repeat units of the telomere sequence
E. Telomerase can produce phosphodiester bonds between DNA nucleotides.
D. Telomerase carries a DNA template complementary to repeat units of the telomere sequence
Which of the following DNA lesions would be corrected by base excision repair?
A. Guanine-benzo[a]pyrene-guanine base-pairing with adenine.
B. Pyrimidine dimers
C. Cytosine base-pairing with adenine because of a mistake during DNA replication
D. Double-strand DNA break by radiation
E. Depurination
E. Depurination
Which of the following statements regarding RNA polymerase II is true?
A. It requires a subunit to convert to holoenzyme and bind directly to the promoter sequence.
B. It can transcribe mRNA and rRNA
C. It is phosphorylated by a kinase before it binds to general transcription factors
D. It is bound to a transcription factor before it binds to the promoter
E. It requires a primer to initiate transcription
D. It is bound to a transcription factor before it binds to the promoter
A loss-of-function mutation in the exonuclease domain of DNA polymerase III would most likely result in _______.
A. incorporation of ribonucleotides
B. an increase in the number of mutations in the newly synthesized DNA strand
C. a decrease in the rate of polymerization
D. hydrogen bonds being formed in the sugar-phosphate backbone
E. RNA primers in replicated DNA because they are not being removed
B. an increase in the number of mutations in the newly synthesized DNA strand
Base substitutions within the protein-encoding sequence of a gene do not cause_____.
A. nonsense mutations
B. silent mutations
C. missense mutations
D. frameshift mutations
E. mutations associated with disease
D. frameshift mutations
During the first reaction in RNA splicing, the 2’ OH end of the branch point is used to break a phosphodiester bond between _____.
A. G of an intron and U of an intron at 3’ splice site
B. G of an exon and G of an intron at 5’ splice site
C. G of an intron and G of an exon at 3’ splice site
D. G of an intron and U of an intron at 5’ splice site
B. G of an exon and G of an intron at 5’ splice site
Which of the following statements regarding transcription only applies to prokaryotic cells and does not apply to eukaryotic cells?
A. The transcriptional start site is designated at +1
B. A region of the promoter about 10 nucleotides upstream of +1 contains AT-rich base pairs.
C. A region of the promoter about 30 nucleotides upstream of +1 contains AT-rich base pairs.
D. Important consensus sequences are frequently found downstream of +1
E. All of the above statements apply to eukarytotic cells.
B. A region of the promoter about 10 nucleotides upstream of +1 contains AT-rich base pairs.
Which of the following occurs after a eukaryotic mRNA is exported from the nucleus?
A. exosome binds to mRNA
B. mRNA is polyadenylated at its 3’ end
C. RNA splicing
D. Guanylyltransferase catalyzes a 5’, 5’ triphosphate bond
E. cap-binding complex binds to mRNA
A. exosome binds to mRNA
When does the sigma factor dissociate from the RNA polymerase?
A. At the termination of transcription
B. After promoter clearance
C. Immediately after promoter binding
D. Immediately before promoter binding
E. Not until the RNA polymerase is phosphorylated
B. After promoter clearance
In RNA editing, adenosine is ______ which alters ______ between codons and anticodons.
A. deaminated to uracil; covalent bonds
B. deaminated to uracil; hydrogen bonding
C. deaminated to inosine; hydrogen bonding
D. deaminated to inosine; covalent bonds
C. deaminated to inosine; hydrogen bonding
______ can break phosphodiester bonds between ribonucleotides and create phosphodiester bonds between deoxyribonucleotides at the same time.
DNA polymerase I
The _______ is a consensus sequence because it is recognized by protein called rho.
Terminator
At the end of transcription, a(n) ________ cuts an RNA strand so adenines can be added to the 3’ end
endonuclease
________ synthesizes the highest number of RNA strands in eukaryotic cells.
RNA polymerase III
When template slippage occurs, an insertion loop can be created which is removed by ______.
mismatch repair/endonuclease
_______ is responsible for binding to multiple consensus sequences within eukaryotic promoters.
TFIID/ general transcription factor
Which of the following statements about regulatory transcription factors is false?
A. They do not typically disrupt the hydrogen bonds that hold the double helix together.
B. They form non-covalent interactions with DNA
C. Their DNA-binding domains usually bind in the major groove of the DNA helix.
D. They interact with the sugar-phosphate backbone to determine where to bind in the genome.
E. All of the above statements are true.
D. They interact with the sugar-phosphate backbone to determine where to bind in the genome.

How many amino acids would be included in the polypeptide encoded by the following mRNA:
A. 15
B. 13
C. 8
D. 7
E. 6
E. 6
In eukaryotic cells, which of the following describes a location where regulatory transcriptions do not bind to influence gene expression?
A. The 3’UTR on mRNA after transcription
B. Regulatory sequences near the promoters of multiple genes
C. 1,000 bases upstream from the transcriptional start site
D. 1,000 bases downstream from the transcriptional start site
E. Both A and B are correct
A. The 3’UTR on mRNA after transcription
What is attached to the small subunit of the ribosome before it binds to mRNA?
A. IF-2-GTP and IF-3
B. IF-3 and initiator tRNA
C. IF-1 and IF-2-GTP
D. IF-3 and IF-1
E. Initiator tRNA and IF-1
D. IF-3 and IF-1
Which of the following is not true of the LacO region of the lac operon?
A. It is a regulatory sequence that regulates expression of the operon
B. It is used to produce a diffusible product that can regulate expression of the operon
C. It is bound by the Lac repressor when lactose is unavailable
D. Mutations within LacO can lead to constitutive expression of the operon.
B. It is used to produce a diffusible product that can regulate expression of the operon
Optimal activation of transcription of the GAL genes in yeast requires the function of two proteins: Gal4p and Gal11p. Elimination of either protein decreases activation of the GAL promoters. However, inactivation of Gal11p has the additional and dramatic effect of cell lethality. Why might elimination of Gal11p have a greater effect than elimination of Gal4p?
A. The structure of Gal4p accommodates mutations better than Gal11p; a small mutation in Gal11p will inactivate it completely.
B. Gal4p functions as an activator for the GAL genes; Gal11p functions as a repressor for the GAL genes.
C. Gal4p is a critical regulatory transcription factor for GAL genes Gal11p is a critical component of the mediator complex.
D. Gal4p regulates expression of the GAL genes; Gal11p regulates GAL genes and the expression of Gal4p.
C. Gal4p is a critical regulatory transcription factor for GAL genes Gal11p is a critical component of the mediator complex.
Which of the following statements regarding eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis is true?
A. RNA polymerase III makes rRNA and mRNA for the small ribosomal subunit.
B. Critical steps of ribosome biogenesis occur in the nucleolus, nucleus, and cytoplasm
C. One ribosomal protein in an operon is used to regulate expression of other ribosomal proteins.
D. Ribosomal proteins are translated in the nucleolus after being transcribed in the nucleus.
E. The 45S ribosomal gene is tandemly repeated on one chromosome to provide RNA pol
B. Critical steps of ribosome biogenesis occur in the nucleolus, nucleus, and cytoplasm
Epigenetic modifications occur at both DNA and histones. Which of the following describes an accurate similarity or difference between these two types of modifications?
A. Both types of modifications use transcriptional gene regulation
B. Both types of modifications use acetylation to regulate gene expression
C. DNA methylation is typically used to activate gene expression, histone methylation can activate or repress gene expression.
D. Epigenetic modifications to DNA change the DNA sequence, modifications to histones do not change the DNA sequence
E. Modifications to DNA are hertitble, modifications to histones are not heritable
A. Both types of modifications use transcriptional gene regulation
Polyglycine is translated from the repeating sequence 5’ GGU-GGC-GGA 3’. If only one tRNA is needed to make polyglycine, which of the following anticodon sequences would be used for translation?
A. 5’ ACC 3’
B. 5’ CCA 3’
C. 5’ GCC 3’
D. 5’ CCG 3’
E. 5’ CCI 3’
F. 5’ ICC 3’
F. 5’ICC 3’
A researcher isolates a mutant variant of the bacterial translation factor EF-Tu. The mutation allows proper folding of the protein and binding of GTP but does not allow GTP hydrolysis. What is the first step in translation that is blocked by this mutant protein?
A. Formation of peptide bond between amino acids
B. mRNA cannot bind to small subunit
C. Binding of initiator tRNA to P site
D. Movement of ribosome along the mRNA to allow binding of a new EF-Tu-tRNA in A site
E. Release of initiation factors
A. Formation of peptide bond between amino acids
The _________ describes a location in the ribosome that only contains aminoacyl tRNAs.
A site
Transcription factors use a _______ to bind to a specific DNA sequence and another transcription factor.
helix-loop-helix
A _______ is critical for adding chemical modifications to a ribosomal RNA.
snoRNA
When LacZ is active and lactose is present in a cell, _____ is produced and binds to a regulatory protein.
Allolactose or Effector
Mediator is a _______ that connects Gal4p to the transcriptional machinery at the promoter.
Coactivator
After DNA replication, some chromatin remodeling complexes have ______ that are critical for identifying modifications to lysine residues that promote gene activation.
Bromodomain
______ synthesizes ribosomal RNA in the nucleolus
RNA Polymerase I
A scientist at a biotech company has decided to create a strain of bluebonnets that will glow under UV light using the GFP gene from jellyfish. Which of the following steps would be performed last in this process?
A. Infect plant cells with transformed bacteria
B. Use restriction enzymes to cut T-DNA vector
C. Transform recombinant vector with GFP gene into bacterial cells
D. Select for bacterial cells that have been recombinant plasmid using selectable marker.
A. Infect plant cells with transformed bacteria
Which of the following statements describes the role of the gRNA in the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system?
A. The gRNA is required to pair the Cas9 with its intended target site in RNA and activate the nuclease domains for cleavage.
B. The gRNA is required to pair the Cas9 with its intended target site in DNA and activates the nuclease domains for cleavage.
C. The gRNA is required to pair the Cas9 with its intended target site in DNA and then cleave one or both nuclease domains.
D. The gRNA is required to cleave both nuclease domains so it will then bind the intended target site in DNA
E. The gRNA sequence is used to determine if nonhomologous end joining or homologous recombination will finish the gene editing.
B. The gRNA is required to pair the Cas9 with its intended target site in DNA and activates the nuclease domains for cleavage.
Which of the following statements does not describe a similarity between ddNTPs and reversible terminators?
A. They are both detected in a gel using a laser
B. They are both added to a growing DNA strand by a DNA polymerase
C. They both use various fluorescent dyes to sequence DNA
D. Both can be used to sequence the human genome
E. They are both nucleotides that have a pentose sugar, three phosphates, and a base
A. They are both detected in a gel using a laser
Which of the following statements most accurately describes genomic imprinting?
A, DNA methylation patterns in a genome are maintained during DNA replication
B. Some genes are regulated by DNA methylation at promoters, and some genes are regulated by DNA methylation at enhancers.
C. Gene expression can be altered by epimutations which can cause disease
D. One copy of a gene is preferentially silenced by an epigenetic mechanism
E. DNA methylation is erased which allows genes that should be silenced to be expressed.
D. One copy of a gene is preferentially silenced by an epigenetic mechanism
Which of the following statements regarding epigenetic reprogramming in humans is true?
A. Only non-imprinted genes are altered during epigenetic reprogramming
B. During protection of egg cells, DNA methylation at all ICRs is erased and they stay erased throughout gametogenesis
C. Epigenetic reprogramming is genome-wide during gametogenesis
D. DNA methylation at ICRs is altered during preimplantation development
E. All of the above statements are false
C. Epigenetic reprogramming is genome-wide during gametogenesis
Which of the following describes the role of HOTAIR when it is used to regulate gene expression?
A. It increases the amount of DNA methylation at regulatory sequences by recruiting a DNA methyltransferase to a specific genome location.
B. It binds to mRNA and promotes RNA degradation
C. It increases H3K27 methylation and decreases H3K4 methylation to alter chromosome structure at target genes by recruiting histone modifying enzymes to a specific genomic location.
D. It decreases H3K27 methylation and increases H3K4 methylation to alter chromosome structure at target genes by recruiting histone modifying enzymes to a specific genomic location.
E. It increases H3K9 methylation and increases H3K4 methylation to alter chromosome structure at target genes by recruiting histone modifying enzymes to a specific genomic location.
C. It increases H3K27 methylation and decreases H3K4 methylation to alter chromosome structure at target genes by recruiting histone modifying enzymes to a specific genomic location.
Which of the following statements regarding the H19/Igf2 cluster is true?
A. DNA methylation at the H19/Igf2 cluster is only observed on the maternal chromosome.
B. During preimplantation development, DNA methylation is erased on both chromosomes.
C. During production of sperm cells, DNA methylation is established on both chromosomes after erasure.
D. During production of egg cells, DNA methylation is erased on both chromosomes and established on the paternal chromosome after erasure.
C. During production of sperm cells, DNA methylation is established on both chromosomes after erasure.
The CRISPR Cas system uses Cas proteins and non-coding RNAs. Which of the following descriptions of the different components of the CRISPR Cas system is true?
A. tracrRNA can make direct contact with DNA and RNA
B. Cas9 degrades viral DNA and packages sections of viral DNA into bacterial chromosome
C. crRNA can identify viral DNA with a fully or partially complementary sequence, similar to miRNA
D. Cas1 nuclease is only active when bound to RNA
E. All of the above statements are false
E. All of the above statements are false
Which of the following is a similarity between crRNA and miRNA?
A. they are both observed in prokaryotic cells
B. They both bind to mRNA
C. They are both used to regulate the expression of prokaryotic genes
D. They are both transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
E. None of the above are similarities between crRNA and miRNA
E. None of the above are similarities between crRNA and miRNA
Which of the following best explains the mechanism by which Xist contributes to X-inactivation?
A. The Xist gene encodes a histone-modifying enzyme that add repressive histone modifications to one X-chromosome
B. Xist is transcribed from the active X chromosome and recruits RNA polymerases to maintain active expression
C. Xist binds directly to DNA methyltransferases to activate both chromosomes during early development.
D. Xist is a non-coding RNA that promotes heterochromatin on one X chromosome in female cells.
E. Xist is a microRNA that promotes degradation of mRNAs from X-linked genes for dosage compensation.
D. Xist is a non-coding RNA that promotes heterochromatin on one X chromosome in female cells.
The creation of the ______ allowed computers to assemble millions of short DNA sequences into a genomic sequence.
Reference sequence or NGS
A(n) ________ can change gene expression without changing the DNA sequence.
Epimutation
Genetic testing can sometimes detect a(n) _______ which describes a mutation that could be pathogenic or benign.
VUS
Discovery of a ______ helped create a shuttle vector that could be maintained in bacteria and yeast.
2-micron plasmid
_________ is often performed using blood or saliva to determine the risk that an individual may have for hereditary cancer.
Germline testing
When performing IVF, the use of _________ has to potential to disrupt erasure of ICRs because it coincides with epigenetic reprogramming
Superovulation
_________ is a component of the CRISPR-Cas system that can directly interact with protein and RNA at the same time
tracrRNA
Which of the following statements regarding SDS-PAGE is true?
A. It uses BME to disrupt hydrogen bonds in proteins
B. It uses SDS to disrupt ionic bonds in proteins
C. Proteins are coated with positive charge before being loaded into a gel.
D. Rate of migration is dependent on percentage of polar amino acids
E. It uses SDS to disrupt ionic bonds in proteins
B. It uses SDS to disrupt ionic bonds in proteins
Which of the following statements describes a difference between primers used in PCR and cDNA conversion?
A. cDNA conversion can be performed with one primer, PCR always required two different primers
B. cDNA conversion only uses RNA primers, PCR only uses DNA primers
C. cDNA primers bind to chromosomal DNA, PCR primers binds to bacterial plasmids
D. Primers used in cDNA conversion promote the synthesis of RNA strands, primers used in PCR promotes the synthesis of DNA strands.
A. cDNA conversion can be performed with one primer, PCR always required two different primers
Which of the following steps occurs first when using the FISH technique?
A. Digest DNA with restriction enzymes
B. Cell fixation
C. Look at cells with a fluorescence mircoscope
D. Hybridize probe to target sequence
E. Denature DNA
B. Cell fixation
You purify the genome from an unknown virus. When you heat the nucleic acid, the UV light absorption at 260nm increases. You also determine the uracil is present in the nucleic acid. What nucleic acid is present and what is the likely structure of the nucleic acid at room temperature?
A. Double-stranded RNA
B. Single-stranded RNA
C. Double-stranded DNA
D. Single-stranded DNA
A. Double-stranded RNA
Which of the following statements does not accurately describe an aspect of the central dogma?
A. DNA replication ensures the accurate copying of the DNA sequence
B. The process where ribosomes synthesize proteins based on mRNA sequences
C. The conversion of RNA back into DNA
D. mRNA is translated into a polypeptide chain
E. The synthesis of a protein from a DNA template using transcription
E. The synthesis of a protein from a DNA template using transcription
In prokaryotic transcription, which of the following could be located at position +35?
A. Base in gene sequences that is downstream from the promoter
B. Terminator sequence
C. Regulatory sequence
D. Transcriptional start site
E. Sigma factor binding site
A. Base in gene sequences that is downstream from the promoter
Which of the following enzymes is considered a reverse transcriptase?
A. DNA ligase
B. DNA polymerase
C. Primase
D. Telomerase
E. None of the above
D. Telomerase
DNA and RNA polymerases are similar and different. Which of the following statements if not a similarity?
A. They both covalently link nucleotides to make a nucleic acid
B. They both use primers to initiate synthesis
C. DNA and RNA polymerases can bind and hydrolyze nucleotide triphosphates
D. DNA and RNA polymerase both bind to DNA but at different locations
E. All of the above statements are similarities
B. They both use primers to initiate synthesis
Which of the following DNA repair mechanisms is incorrectly matched to the type of damage that is corrected?
A. Mismatch repair: mismatched bases
B. Nucleotide excision repair: chemically modified bases
C. Base excision repair: errors during DNA replication
D. Nucleotides excision repair: bases on same strand covalently linked together
E. Nonhomologous end joining: DNA damage from radiation exposure
C. Base excision repair: errors during DNA replication
A point mutation that changes one amino acid but does not alter protein activity is called a _______.
A. silent mutation
B. frameshift mutation
C. loss-of-function mutation
D. Missense mutation
E. Nonsense mutation
D. Missense mutation
In which of the following sentences is the word constitutive used correctly, and the statement is true?
A. Repressors hinder transcription in a constitutive manner
B. Effector molecules constitutively regulate the function activators and repressors.
C. Regulated genes in different cell types are often controlled constitutively by activators
D. Activators may promote the formation of the open complex by causing a constitutive change in the promoter.
E. Enzymes involved in the production of tRNAs are expressed at a constitutive level.
E. Enzymes involved in the production of tRNAs are expressed at a constitutive level.
Which of the following is similar to an enhancer in the GAL gene regulatory system?
A. Galactose
B. Gal4p
C. Gal80p
D. Gal3p
E. UAS
E.UAS
Consider a prokaryotic cell that is grown in two different conditions (glucose present/lactose present and glucose absent/lactose present). Which genotype will exhibit low expression of the lac operon in both conditions?
A. Lacl+, LacO+, LacP+, Crp+
B. Lacl-, LacO+, LacP+, Crp+
C. Lacl+, LacO+, LacP-, Crp+
D. Lacl+, LacO+, LacP+, Crp-
D. Lacl+, LacO+, LacP+, Crp-
why is the agouti mouse a good example of how epigenetics can be used to regulate a trait of an organism?
A. The agouti mouse has a DNA mutation that produces a unique coat color.
B. The expression of the agouti gene changes when DNA bases in the promoter are modified
C. Eating a high folate diet provides an effector molecule that changes the coat color.
D. The agouti gene is in an operon, so its expression is regulated by environmental conditions.
E. The agouti gene is regulated by post-translational control.
B. The expression of the agouti gene changes when DNA bases in the promoter are modified
Which of the following statements regarding chromodomains and bromodomains is true?
A. Chromodomains can be used to bind acetylated lysines
B. Proteins with chromodomains are involved with exposing promoters of genes.
C. Proteins with bromodomains bind to methylated lysines
D. Bromodomains and chromodomains are important for making epigenetic modifications heritable
D. Bromodomains and chromodomains are important for making epigenetic modifications heritable
Which of the following statements regarding riboswitches if false?
A. They are located within untranslated regions within mRNA
B. They can form secondary structures
C. They are used to regulate gene expression in prokaryotic cells
D. They interact with proteins that are recruited by small non-coding RNAs
E. All of the above statements are true
D. They interact with proteins that are recruited by small non-coding RNAs
Which of the following statements most accurately describes gene therapy?
A. A vector delivers a functional gene to a human cell with a recessive condition.
B. Making target modifications to a gene in chromosomal DNA to treat a disease
C. Selective breeding modifies a gene that increases growth during the early stages of development
D. The Bt toxin is inserted into a plant chromosome to create a plant that will not be eaten by insects
A. A vector delivers a functional gene to a human cell with a recessive condition.
Which component of the prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas system can directly interact with DNA and RNA at the same time?
A. tracrRNA
B. sRNA
C. Cas1
D. Cas2
E. crRNA
??? ed disucssion it
Which of the following statements accurately describes a difference between HOTAIR and Xist?
A. HOTAIR uses post-transcriptional gene regulation and Xist uses transcriptional gene regulation
B. HOTAIR binds to DNA methyltransferases, Xist binds to histone modifying enzymes
C. HOTAIR is a long non-coding RNA, Xist is a microRNA (miRNA)
D. HOTAIR is used by prokaryotic cells, Xist is used by eukaryotic cells
E. HOTAIR regulates about 10 genes, Xist regulates hundreds of genes.
E. HOTAIR regulates about 10 genes, Xist regulates hundreds of genes.
Which of the following statements accurately describes a similarity between miRNA and siRNA in human cells?
A. They are both long non-coding RNAs.
B. They are both used for transcriptional gene regulation
C. They are both encoded from human genes that are transcribed from chromosomal DNA
D. They are both processed by Dicer
E. They both recruit histone-modifying enzymes to specific locations on chromosomal DNA
D. They are both processed by Dicer
What effect will DNA gyrase have on relaxed, covalently closed DNA within cells?
A. Amount of turns in a segment of relaxed DNA with 84bp will increase from 8 to 9.
B. All of the DNA will transition to B-DNA
C. The treated DNA will migrate farther in agarose gel than relaxed DNA
D. The relaxed DNA will migrate farther in an agarose gel than the treated DNA
E. The treated and relaxed DNA will migrate at the same time
C. The treated DNA will migrate farther in agarose gel than relaxed DNA
Consider a double-stranded DNA molecule that has the sequence CCCATTCTA when read from the 5’ to the 3’ end on one strand of DNA. The base at the 5’ end of the complementary strand is ____ and there are a total of _____ base pairs that have 2 hydrogen bonds
A. G;4
B. G; 5
C. T; 4
D. T; 5
D. T; 5
Which of the following statements regarding the FISH technique is false?
A. FISH can be used to identify the presence of mutations on chromosomes
B. Radioactive probes are often used to hybridize to DNA sequences in chromosomes.
C. A microscope is always used with the FISH technique
D. FISH requires a minimum of two probes; one for chromosomes and one for a specific
E. The FISH technique cannot be performed on living cells
B. Radioactive probes are often used to hybridize to DNA sequences in chromosomes.
Which of the following statements regarding genomic imprinting is false?
A. In a human zygote, only one copy of each imprinted gene is expressed
B. An allele for a maternally-expressed imprinted gene will not be expressed if it is inherited from the father
C. For a paternally-expressed imprinted gene, an embryo that inherits a mutant allele from its mother and a wild-type allele from its father will be unaffected.
D. A paternally-expressed imprinted gene is only expressed in the male offspring, not female offspring
E. For many imprinted genes, expression from both chromosomes causes developmental abnormalities
D. A paternally-expressed imprinted gene is only expressed in the male offspring, not female offspring
Which of the following would most likely decrease the transcription of one specific gene in a bacterial cell?
A. A decrease in the amount of sigma factor 70 (s70) in the cell
B. A decrease in the amount of RNA polymerase in the cell
C. A mutation in the terminator sequence of a bacterial gene
D. A mutation 20 bases upstream from the transcriptional start site
E. A mutation 20 bases downstream from the transcriptional start site
D. A mutation 20 bases upstream from the transcriptional start site
Which of the following statements regarding the initiation of eukaryotic transcription is false?
A. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases require specific subunits to recognize different promoters
B. There are different RNA polymerases that recognize different promoters
C. RNA polymerase II can bind to eukaryotic promoters that do not have a TATA box
D. Mediator is only used when eukaryotic transcription; prokaryotic cells do not use this protein complex
E. All of the above statements are true
A. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases require specific subunits to recognize different promoters
Which of the following statements does not accurately describe RNA editing in eukaryotic cells?
A. It can be used to change codons in an mRNA after splicing
B. It can be used to create a different start codon
C. It can be used to create a different stop codon
D. It can be used to create a splicing site
E. It can be used to deaminate adenine to uracil in a mature mRNA
E. It can be used to deaminate adenine to uracil in a mature mRNA
Which of the following statements regarding regulatory transcription factors is true?
A. All cell types express the same regulatory transcription factors
B. They can influence transcription without directly interacting with RNA polymerase
C. Enhancers are silencers are common regulatory transcription factors in eukaryotic cells
D. Regulatory transcription factors always bind to DNA close to the promoter
E. All of the above statements are false
C. Enhancers are silencers are common regulatory transcription factors in eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic pre-mRNAs undergo several modifications such as capping an end of the mature mRNA with a modified base. Which of the following describes a characteristic of this cap?
A. It contains a triphosphate bridge between a modified base and the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA
B. It consists of multiple modified adenines
C. It has a 3’-to-5’ linkage between a modified base and the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA
D. It has a negative charge because of methylation in the modified base
E. It serves as a binding site for exon-junction complexes
A. It contains a triphosphate bridge between a modified base and the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA
Which of the following statements most accurately describes proofreading by a DNA polymerase
A. DNA polymerase uses endonuclease activity to correct errors in the newly synthesized DNA strand
B. Proofreading is accomplished by the 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase
C. Mistakes made by DNA polymerase are removed from the template strand
D. Several bases on the daughter strand are removed by the DNA polymerase
E. Proofreading involves the removal of damaged nucleotides by DNA helicase
A. DNA polymerase uses endonuclease activity to correct errors in the newly synthesized DNA strand
Which of the following can connect unicorporated dNTPs to another nucleotide without a primer?
A. DNA ligase
B. Primase
C. DNA polymerase III
D. Reverse transcriptase
E. Telomerase
B. Primase
Which of the following statements accurately describes snRNAs?
A, They are translated into snRNPs
B. They are important for producing mature mRNA transcripts in bacteria
C. They are removed by the spliceosome during RNA splicing
D. They can bind to specific sequences on an mRNA during transcription
E. They are critical for the addition of a modified guanine base to the 5’ end of a primary transcript
D. They can bind to specific sequences on an mRNA during transcription
Which of the following DNA lesions would be corrected by base excision repair?
A. Guaniune-benzo[a]pyrene-guanine base-pairing with adenine
B. Double-strand DNA break by radiation
C. Cytosine base-pairing with adenine because of a mistake during DNA replication
D. Cytosine deamination
E> Pyrimidine dimers
C. Cytosine base-pairing with adenine because of a mistake during DNA replication
Which of the following is only observed in eukaryotic cells during the initiation stage of translation?
A. Amino acid attached to initiator tRNA is chemically modified
B. Modified base in 5’ cap base pairs with ribosomal RNA in small subunit of ribosome
C. Initiation factor uses GTP hydrolysis to form initiation complex
D. mRNA binds to small ribosomal subunit after initiator tRNA binds to P site
E. Initiation factors are bound to small ribosomal subunit before initiator tRNA binds to P site
E. Initiation factors are bound to small ribosomal subunit before initiator tRNA binds to P site