abnormal psychology midterm 1
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Psychopathology
The interconnection of behaviors, thoughts, emotions, and physiology that create abnormal psychology.
Western European Values
Independence, individual rights, logic, productivity, happiness, secularization, and scientific support
Abnormality
There is no clear definition of what is abnormal, however there are some clear aspects of abnormality: subjective distress, maladaptiveness, violation of social norms, irrationality or unpredictability, and dangerousness. However, no individual element is sufficient to define and determine abnormality and what is considered deviant changes as society changes.
Subjective Distress
Psychological suffering because of something.
Maladaptiveness
Impairment in important area(s) of life (ex. work, school, or relationships).
Violation of Social Norms
Acting outside of cultural standards.
Irrationality or Unpredictability
Unexpected responses to stressors (context dependent).
Dangerousness
Danger to self or others.
DSM-5
A standardized manual used in the USA and Canada to classify psychological disorders.
ICD-10
A standardized manual used globally to classify psychological disorders.
Psychological Disorder (DSM-5)
A cycle: biological, psychological or development dysfunction/impairment → problems in behaviour, emotion regulation, or cognitive function → distress of disability → …
Prevalence
The number of active cases of a disorder in a population over a specific time, expressed as a percentage.
Classification (pros)
Structure information to communicate in research and clinical settings, organize meaningfully, facilitate research, define what counts as abnormal, and put words to a similar lived experience.
Classification (cons)
Social implications and stigma.
Lifetime Prevalence of DSM-5 Disorders
46%
Research Design
The structure of a study that determines the quality of information gathered about psychological disorders.
Good Research Design
Uses methods that distinguish between what is observable, hypothetical, or inferred. These include cases studies, directed observation, self-report, implicit behaviour, and psychophysiological variables.
Observational Research
A method that studies phenomena as they are, determining correlation but not causation.
Experimental Research
A method that manipulates one variable to observe its effect on another, allowing for causation determination.
Single-Case Experimental Designs
Used to make causal inferences in individual cases and often follow a ABAB structure.
Inherent Error in Many Research Designs
Only use “perfect” participants, not normal people.
Historical Views
The evolution of treatments for mental illness, including unethical practices and the influence of cultural perspectives.
Observation vs Interpretation
While good observation is timeless the interpretation of causes of behaviour is subject to bias and always interpreted within the dominant paradigm.
Demonology
Bad spirits swell within a person and control their mind a body, causing them to exhibit abnormal behaviour.
Demonology Treatments
Ostracism (social exclusion), exorcisms, and trepanning (drilling a hole in the skull).
Somatogenic Theory
The belief that physical problems are the root of psychological issues, leading to specific treatments.
Somatogenic Treatments
Quiet lifestyle, vegetarian diet, exercise, celibacy, and bleeding.
Psychogenic Theory
The belief that psychological malfunctions cause mental illness, leading to various therapeutic approaches.
Psychogenic Treatments
Varied based on disorder. Inadequate moral development would be treated with moral treatment. Getting stuck in a psychosexual developmental phase would be treated with psychodynamic psychotherapy. Reinforced problem behaviour would be treated by creating a token economy.
Paradigm
A viewpoint or set of assumptions about understanding and treating psychological disorders.
First Nations Paradigm
Many indigenous groups in Canada use the mental wellness circles as the major way in which they understand, study, and treat psychological disorders.
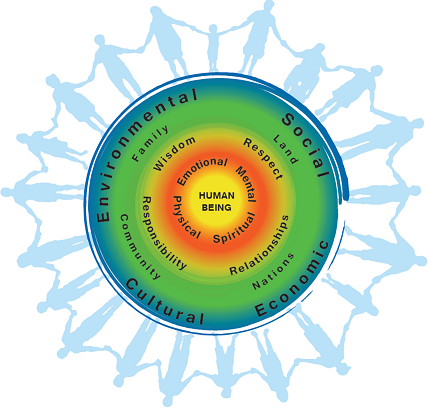
First Nations Approach to Treatment
Approach mental wellness as a continuum and the foundations of treatment are often cultural and traditional healing. Emphasizes providing services that are appropriate to the person’s needs and integrating traditional (nation-based) and western treatment approaches.
Two-Eyed Seeing
The integration of traditional and Western treatment approaches for optimal mental health outcomes in Indigenous populations.
Major Western Paradigms
Biological, psychoanalytic, learning/behavioural, cognitive, and humanistic/existential.
Biological Paradigm
The view that mental illness results from dysfunctional biological processes including biochemistry, behavioural genetics, and biological insults.
Temperament
An aspect of personality that is strongly influenced by genes and includes 5 dimensions: openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism.
Norepinephrine (NE)
An excitatory neurotransmitter that causes arousal and prepares the body for action.
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA)
An inhibitory neurotransmitter that regulates behaviour and emotion.
Dopamine (DA)
Has effects that are both excitatory and inhibitory and controls motivation and reward systems.
Serotonin (5-HT)
An inhibitory neurotransmitter that regulates bodily functions including mood, appetite, sleep, and impulse control.
Glutamate (GLU)
An excitatory neurotransmitter that affects learning and memory.
Psychoanalytic Paradigm
Freud's theory that the mind consists of the Id, Ego, and Superego, influencing behavior and mental health.
Id
The most basic structure and controls basic urges for food, warmth, and sex, also known as the pleasure principle.
Ego
The reality principle and is tasked to deal with how we can meet our basic needs in the real world.
Superego
Our conscious that helps us decide what is right and what is wrong.
Defense Mechanisms
Unconscious strategies used to protect the ego from distress.
Repression
The act of burying an event so deep that you believe it never occured.
Denial
Denying that a traumatic event ever occured.
Projection
Projecting your emotions onto another person.
Displacement
Being upset at one thing/person and taking it out on a different thing/person.
Rationalization
The act of attempting to explain why you behaved in a certain way to yourself and others.
Reaction formation
The tendency of emotions to be expressed in a contradictory form (ex. I’m mad at my mom so I’m going to go give her a hug).
Regression
Exhibiting behaviours from when you were younger, often to soothe.
Sublimation
Putting your emotions into a creative output.
Learning/Behavioral Paradigm
The belief that all behavior is learned, with psychological disorders stemming from classical and operant conditioning.
Classical Conditioning
The association of unrelated elements due to repeated pairing.
Operant Conditioning
The idea that behaviour followed by pleasant consequences will increase while behaviour followed by unpleasant consequences will decrease.
Positive reinforcement
When a stimulus is added to reinforce behaviour.
Negative reinforcement
When a stimulus is taken away to reinforce behaviour.
Positive punishment
When a stimulus is added to decrease behaviour.
Negative punishment
When a stimulus is taken away to decrease behaviour.
Mowrer’s Two Factor Theory
The first step in developing psychological disorders is classical conditioning through the form of an emotional response to a neutral stimulus. The second step is operant conditioning which is learned avoidance of the conditioned stimulus.
Cognitive Paradigm
The view that cognitive errors and interpretations lead to psychological disorders.
Schemas
Organized networks of accumulated knowledge that guides our interpretation of events.
Humanistic/Existential Paradigm
The focus on subjective experiences, personal growth, and responsibility in understanding mental health. It emphasizes positive growth, searching for meaning in like, using agency and taking responsibility for your choices and attitude, and living life according to your values.
Social Factors that Influence Psychopathologies
Poverty, especially in development → poor housing, unsafe conditions, and disrupted social ties.
Parental stress → parental depression, family conflict, and harsh parenting.
Minoritized status, often due to discrimination.
Immigration.
Accessibility of services in native languages.
Community knowledge.
Cultural approaches to mental health.
Biopsychosocial Model
A comprehensive approach to understanding mental health that includes biological, psychological, and social factors.
Biopsychosocial Grid
Y-labels are biological, psychological, and social and the x-labels are etiology (cause), presentation, and treatment.
Diathesis-Stress Model
A framework explaining how predispositions and stressors interact to lead to psychological disorders.
Interactive Diathesis-Stress Model
If someone has no diathesis (predisposition) they will not develop mental illness such as anxiety and depression whereas someone who has high diathesis has a high likelihood of developing them even at low levels of stress.
Additive Diathesis Stress Model
If someone has no diathesis they will still develop certain disorders however they require more stress to develop them then someone with a high level of diathesis.
Protective Factors
Factors that can influence a person’s response to stress and make it less likely that a person will have a bad reaction. The strongest protective factor is resilience.
Resilience
An individual’s ability to successfully adapt to very difficult circumstances
Polygenic
Influenced by multiple genes.
Gene-Environment Interaction
The interplay between genetic predispositions and environmental factors in the development of mental health issues.
Gene-Environment Correlation
The relationship between an individual's genetic makeup and the environment they create or inhabit.
Rats Adoption Experiment
Two female rats, one aggressive and one calm, had babies and the babies were swapped. The nurturing mother, even when raising the aggressive mothers babies, ended up raising gentle rats which was dictated by their maternal environment and not their genes.
Underlying Premise of Western Treatment
The belief that people can change how they interact with the world.
Two Major Division of Western Treatment
Biological and psychological.
Biological Treatments
Treatments including psychopharmacology (medication), ETC, and TMS.
Psychological Treatments
Often psychotherapy including psychodynamic, behavioural, cognitive, cognitive-behavioural, humanistic, and interpersonal.
Evidence-Based Treatments
Treatments that efficacy studies have found to be efficacious, meaning that the treatment works to decrease symptoms and the treatment group performs better than the comparison group.
Not-Evidence-Based Treatments
Treatments that aren’t back by scientific data (yet) and usually rely on personal experiences of success rather than statistical analyses.
Psychopharmacology
The prescription of various medications to treat psychological disorders.
Psychosis Medication
Antipsychotics (DA)
Bipolar Mood Disorders Medication
Lithium (GABA)
Anxiety Medication
Benzodiazepines (GABA)
Depression Medication
SSRIs (5-HT)
Classical Psychoanalysis
Includes practices like free association, dream analysis, transference, and resistance.
Psychoanalytically Oriented Psychotherapy
Focuses on object-relations and attachment styles.
Behavioural Therapy
Founded on the premise that if you modify behaviour, a modification in feelings will follow. Types include exposure therapy, modeling, reinforcement, and behavioural activation. Commonly used to treat anxiety disorders and sometimes depression.
Cognitive Therapy
Founded on the premise that thoughts cause feelings and moods, and those feelings and moods influence behaviour. Examines distorted patterns of thinking and focuses on changing a person’s behaviour by changing their thoughts.
Cognitive-Behavioural Therapy
Incorporates thoughts and behaviours and contributes them both to the maintaining of a disorder. Works well to treat anxiety, mid-moderate depression, conduct disorders and bulimia.
Three Component Model of CBT
Affect (feelings) → behaviours (actions) → cognitions (thoughts)
Humanistic Therapy
Client-centered and often uses motivational interviewing or Gestalt therapy.
Motivational Interviewing
Good for building commitment to treatment and is often used to treat behaviours that are difficult to target with other treatment options (ex. substance abuse or domestic violence.
Interpersonal Therapy
A premise that uses multiple paradigms to address the ways the client relates to others. Uses the therapist-client relationship to work towards clients changing their thoughts and behaviours. Has been successfully used to treat borderline personality disorder and depression.
Minoritized Groups and Treatment
People in minoritized groups tend to be less studies, use fewer mental health services, and have less clinicians who are part of the minoritized group. In-turn, people in minoritized groups often have less access to empirically supported treatment options which has an impact on individual and community mental health.
HPA Axis Activation
Occurs under stress and triggers the release of cortisol.
Extreme or Prolonged Stress
Increases reactivity in the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in more stress in response to stressful fituations.
Decreases the efficacy of the bodies immune system.
Decreases psychological self-efficacy making it harder to resist other stressors.
Causes personality deterioration.
Can cause death.