Social Lectures 7-8 Influence, Attitudes, and Persuasions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
social influence
refers to the many ways people affect one another
Involves changes in attitudes and behavior resulting from comments/actions/presence of others
conformity
compliance
obediance
Social learning theory
Many animals, including humans, can learn by watching others (MIRROR NEURONS)
• Chameleon effect: Unconscious mimicry of the nonverbal mannerisms of an interaction partner.
Chartrand & Bargh (1999): Chameleon effect study
informational influence (conformity)
Other people provide information
leads to internalization (private acceptance)
normative influence (conformity)
We feel pressure to fit in.
• Leads only to ONLY public compliance (we know that maybe alone we do not agree)
Such as with the Asch study (no internalization)—-people did maintain privately they know the answer is wrong but publicly they said something else
when do ppl conform?
group size
unanimity
anonymity
status and expertise
group size
3-4 people for greatest conformity.
• Milgram’s “looking up at nothing” study
1 person looking up, 40% of passers-by conformed
2-3 people looking up, 60-65% conformed
4 people looking up, 80% conformed
unanimity
refers to a situation where everyone in a group agrees—there is complete agreement among group members.
Even 1 dissenter, conformity decreases.
Asch studies: When 1 person dissented, conformity dropped to 5%
In Asch's study, participants conformed to a clearly wrong answer more often when the rest of the group gave the same wrong answer (unanimity).
But when even one other person broke from the group, participants were less likely to conform.
anonymity
means that a person’s identity is hidden—others don’t know who they are or what they did.
Responding in front of group members makes conformity more likely.
Examples:
In online forums, people may say things they’d never say face-to-face (less self-censorship).
In psychological studies, participants may give more truthful answers when responses are anonymous.
status and expertise
If group members are high status or experts, more conformity.
conforming (gender and culture)
Culture
Interdependent cultures - More susceptible to information and normative social influence
Gender
Women conform more in stereotypically male domains • Men conform more in stereotypically female domains
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Cognitive dissonance theory (Festinger): People dislike inconsistency among their beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors.
• Common inconsistency: “I’m X kind of person” but “I do/did Y thing”
• Especially strong when identity is threatened
Ways to reduce dissonance:
• Change something (belief, attitude, or behavior)
• Downplay the importance of something
• Add something that resolves inconsistency
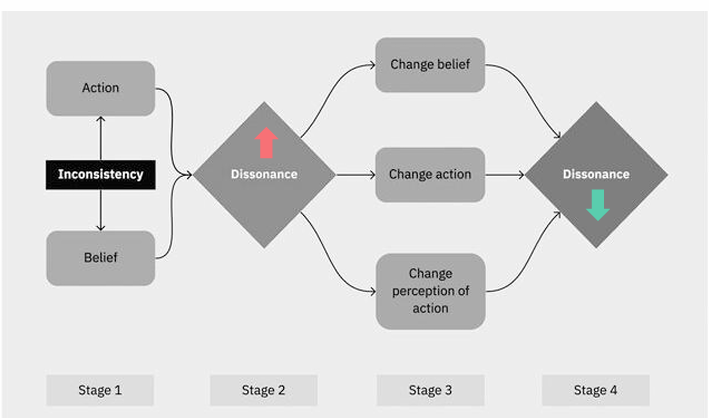
Cognitive dissonance part 2
Insufficient justification: Dissonance arises following a behavior that is unjustifiably inconsistent with beliefs or attitudes.
• Resolve by bringing the attitude in line with the behavior.
• Festinger & Carlsmith (1959): Peg-turning study
Post-decisional dissonance: Finalizing a difficult decision often leads to dissonance.
ex: choosing btwn two job offer—both are desirable to an extent
Effort justification: Reducing dissonance by convincing ourselves that suffering was valuable
ex: hated movie but justify saying popcorn was good
Persuasion
Intentional efforts to change someone’s attitude, usually in hopes of changing their behavior
Central route processing (elaboration likelihood model)
Thinking systematically and evaluating the arguments, effortful processing; System 2
• Must have motivation and ability to focus on arguments
• Good for long-lasting attitude change
Peripheral route processing (elaboration likelihood model)
Influenced by incidental or irrelevant characteristics
• Effective for unmotivated, tired, or distracted audience
• Also useful when arguments are weak
ex: carls junior adds
Yale approach to attitude change
“Who says what to whom?”
Who - Speaker effects
What - Message effects
To Whom - Audience effects
approach tells us when persuasion is more likely to occur

the “who” speaker effects
What makes a speaker more persuasive?
Credibility: A combination of expertise and trustworthiness.
Attractiveness: Often physical attractiveness, but also being likeable, well-dressed, etc.
Certainty: Confidence is persuasive (in themselves).
Similarity: We trust people who are similar
exception:
Sleeper effect (also called source forgetting): Delayed impact of a message that occurs when we remember the message but forget the reason for discounting it (the source)
see gossip abt celeb on magazine and remember it later but not the validity of source—-availability heuristic and persuades to believe gossip about celeb
the “what” message effects
Message Quality/ content of it
Straightforward, clear, and logical
Explicitly refute the other side
Speak against your own self-interest
Vividness: Statistics and facts are often less persuasive than a compelling story.
• Identifiable victim effect
ex: sad pet shelter ads
the “what” message effects pt 2
Fear appeals: Can increase or decrease persuasion
• Reception-yielding model: Be scary enough to be convincing but not so scary that people tune out.
Best way to use fear appeals:
• Moderate amount of fear (not too much, not too little)
• Include a solution
“to whom” audience effects
Age: Younger people are easiest to persuade
• College students are primary targets for cults
Mood: Good mood is generally better, but could also match the message
Resisting Persuasion: How can we resist persuasion?
• Be forewarned
• Be informed
• Make a public commitment to your position
foot in the door (compliance)
Agree to a small request, more likely to comply later with a larger request.
• Freedman & Fraser (1966): Drive carefully study
Researchers asked homeowners to place a large, ugly “Drive Carefully” sign in their yard.
→ Only 17% agreed when asked directly.But if homeowners were first asked to sign a small petition about safe driving...
→ Later, 76% agreed to the large sign!
door in the face (compliance)
Turn down a large request, more likely to comply with a reasonable request.
• Blood donor study:
Donate blood for long-term commitment?
Donate tomorrow? 50% agreed
Donate blood tomorrow? 32% agreed
reciprocity (compliance)
The expectation that people will help those who have helped them
appeal to norms (compliance)
descriptive norms: What are most people ACTUALLY doing?
prescriptive norms: What SHOULD people be doing?
Milgram 1974 (obedience)
Participants were told to give electric shocks to a “learner” for wrong answers, increasing voltage each time.
65% obeyed fully, delivering what they believed was a fatal shock (450 volts).
They obeyed despite visible stress, simply because an authority figure told them to.
Key Point:
People will follow orders—even harmful ones—when instructed by authority.
altering obedience
Characteristics of the authority figure:
Strength: Experimenter replaced by a clerk
20% obeyed
Distance: Experimenter called in by phone
23% obeyed
Characteristics of the situation:
Emotional distance:
Shock by remote, nearly 100% obeyed
Hold hand to shock plate, only 30% obeyed
Someone else flips the switch, 93% obeyed
Institutional authority:
Office in Bridgeport, CT instead of Yale
48% obeyed
Presence of resisters:
Two defiant teachers
10% obeyed
resisting obedience: reactance
A motive to protect one’s sense of freedom arises when freedom feels threatened.
Occurs when we feel someone is trying to limit choices or decisions
A threat to our freedom
Example: If an authority figure insists you must do something, you might refuse—not because you disagree, but because you don’t want to be controlled.