Biology - Unit 2 - Topic 1 - Magnification and Microscopes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is the formula for magnification?
magnification = size of image/size of real object
define the term magnification
the number of times larger an image is compared with the real size of an object
define the term resolution
the ability to distinguish between two separate points
what is the limit of resolution of a light microscope?
½ the wavelength of the radiation used to view the specimen
the shortest wavelength of light is 400nm so the max resolution is 200nmwha
what does a light microscope look like?
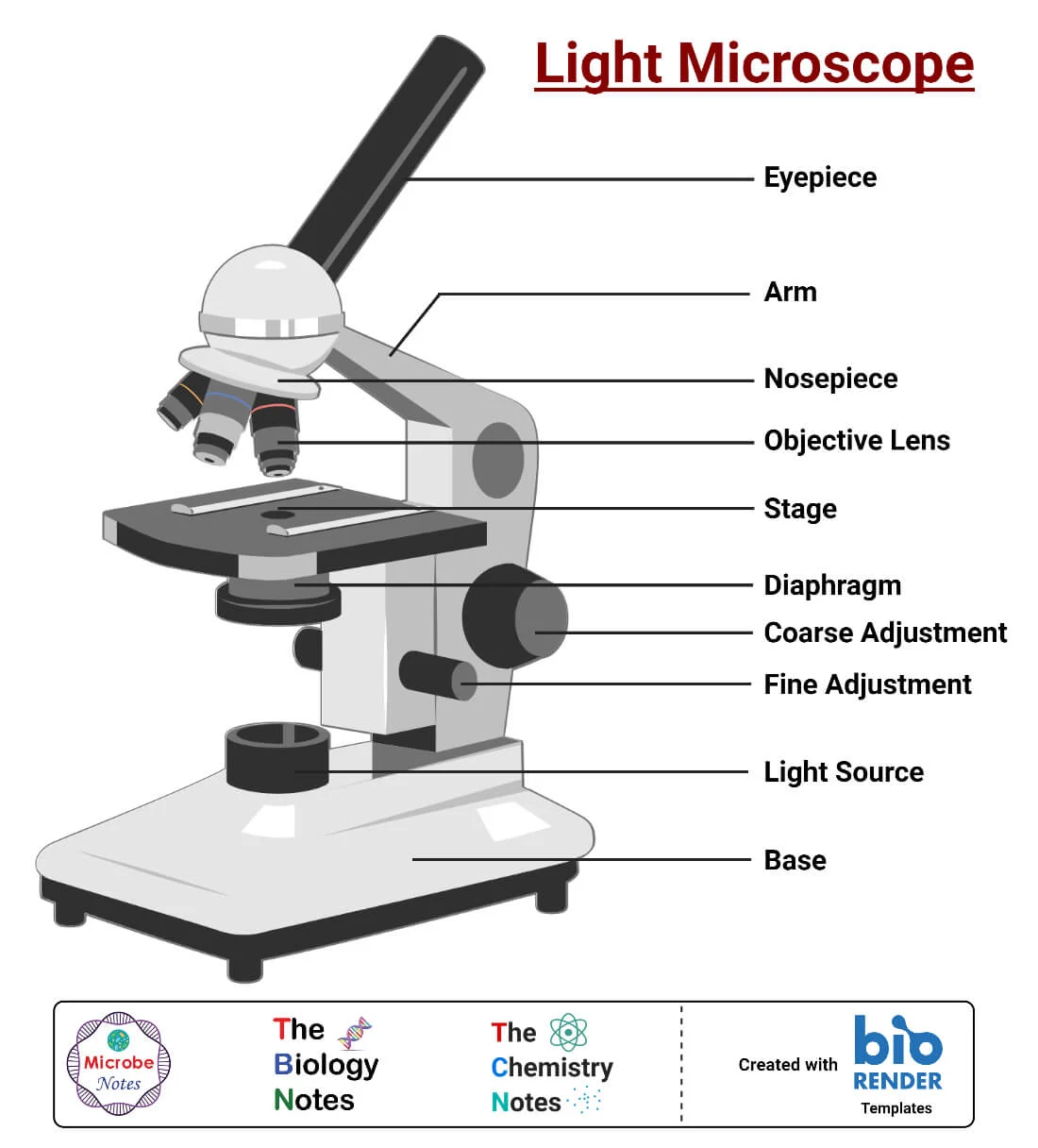
what is the maximum useful magnification of an optical microscope?
x1500
which organelles can you not see using a light microscope?
ribosomes
lysosomes
mitochondria
endoplasmic reticulum
what is the other kind of microscope?
electron microscopes
what are the two types of electron microscope?
transmission electron microscope
scanning electron microscope
what is the maximum resolution of a transmission electron microscope?
0.1nm
what is the maximum resolution of a scanning electron microscope?
20nm
describe how a TEM works
use electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons, which are transmitted through the specimen
denser parts of the specimen absorb more electrons, making them look darker on the resulting image
describe how an SEM works
scan a beam of electrons across a specimen
this knocks off electrons from the specimen
these are gathered in a cathode ray tube to form an image
the resultant images show the surface of the specimen and the 3-D
what are the advantages of TEMs?
gives the highest resolution images so shows small objects
what are the advantages of SEMs?
can be used on thick specimens
produce 3D images
have a relatively high resolution
what are the disadvantages of TEMs?
can only be used on very thin specimens
can only be used on non-living specimens
the specimen must be viewed in a vacuum
images may contain artefacts which can make it difficult to identify organelles
what are the disadvantages of SEMS?
give lower resolution images than TEMs
can only be used on non-living specimens
need to be used in a vacuum
images may contain organelles
describe how to prepare a temporary microscope slide
place a small drop of water on the centre of the slide
use tweezers to place a thin section of your specimen on top of the water drop
add a drop of iodine on top
place a coverslip on top
blot off any excess iodine using filter paper