Unit 1: Introduction to BM
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms

1.1 What is a business?
Business
The organization of human, physical and financial resources to produce goods or services that meet customer needs while adding value
The aim of a business
To satisfy the needs and desires of their customers by selling a good or providing a service
Factors of Production
Resources used in the production process
Land
The natural resources used in the production of a product
E x : Good, water, physical land, fish, metal ores, minerals
Capital
The money and equipment used to produce the product, including non-natural resources
E x : Tools, equipment, machinery, vehicles, buildings
Labour
Physical human effort and psychological intellect used in the production process, hence the employees themselves.
Enterprise
An individual with the necessary skills and ability to take risks in organizing the previous three to generate profitable output
Transformation (adding value)
The process of creating a product that is worth more than the costs of the inputs used
Value added is measured as the difference between the costs of the inputs and the price of the final output
Outputs
Goods
Tangible physical items capable of being stored
Services
Intangible items that cannot be stored and are given to customers when needed
By-products
Combined (Good + Service)
Primary Sector
Businesses in the first stage of production involved in extraction, harvesting, and conversion of natural resources
Relatively low value added in this sector
E x : Fishing, forestry, mining
Secondary Sector
Businesses involved in the processing of raw materials into finished and usable products or inputs for other businesses
E x : Car making, construction, breweries, aerospace, engineering
Tertiary sector
Businesses that focus on providing a service to consumers and other businesses
– High value is added in this section
EX: Banking, insurance, security, catering, education, healthcare, retail, transportation, news media, law, leisure, tourism, entertainment
Quaternary sector
Businesses involved in the creation or sharing of knowledge or information
High value is added
Entrepreneur
Someone who takes the financial risk of starting and managing a new business in return for a profit. They are usually self-employed.
Challenges for starting up a business AO2
Lack of experience in all the different areas of a business:
Poor marketing
Poor hiring
Lack of cash flow
Poor pricing
Difficulties raising money to set up and expand
Businesses are at a high risk in their early stages
Entrepreneurs may have to use their own funds, which can be limited
Can restrict the options when developing and launching the product
Difficulties in building brand awareness
New products must compete with well-established brands
Difficult to attract the attention of intermediaries (e.g. retailers) and customers
New products may not get shelf space as they are risky
Lack of market power
Customers may feel they have the power to delay payments
Suppliers may be worried about getting paid, may insist on early or advance payments
Legal problems, e.g. copyright and patent problems
External influences
Opportunities for starting up a business
Social change
EX: An ageing population brings forth the opportunity to start up businesses taking care of the elderly
Technological change
EX: An increased demand for EVs may inspire startups in the automotive industry
Economic change
EX: Growth in an economy can lead to more consumer spending
Creates new markets & opportunities for new businesses
Environmental change
EX: Growing concern regarding the environment can inspire startups linked to sustainability
Political change
Ex: A decision to join a trading union with another country
Start-ups in tourism or export
Legal change
Ex: Fewer regulations → reduced costs of selling up a business
Ethical change
Ex: Growing interest in the values of a brand
Opportunities to start up businesses with a strong ethical stance

1.2 Types of business entities
Nationalization
Occurs when a government takes ownership of a business from the private sector into the public sector.
Privatization
Occurs when a government transfers ownership of a business from the public sector to the private sector.
Public sector business
A business organization which is owned and controlled by the government.
These organizations may have strategic importance to the country (e.g. defence).
They may provide essential services which the government wants to ensure everyone has access to (e.g. energy).
They may provide merit goods, which are goods or services that private individuals undertake and thus do not consume enough of.
Private sector businesses
Organizations that are owned and controlled by individuals rather than the government.
These businesses are either run to make a profit or have profit and social objectives as dual purposes.
Types of private sector businesses
Profit-based businesses
For-profit social enterprise
Non-profit social enterprise
Types of profit-based businesses
Unincorporated
Sole trader
Partnership
Incorporated
Privately-held companies
Publicly-held companies
Shareholder
Persons or organizations that own a part of a company. Each share represents a part ownership of the business
Limited liability
Investors can only lose the money they have invested in a business in case of bankruptcy the investors’ personal possessions are safe, limiting their risk.
Unlimited liability
Occurs when an individual or group of individuals is personally responsible for all the actions of their business. If the business has financial problems, investors could lose their personal assets
Dividend
Money that is paid out of profits to shareholders. They are a reward to the owners of a business
Social enterprises
Businesses that set out to solve a social or environmental problem
Types of social enterprises
For profit social enterprise
Non-profit social enterprise
For-profit social enterprise/private sector social enterprise
Business that makes revenue and profits but also has a social and/or environmental objectives as part of its business model
A private sector social enterprise is a type of for-profit social enterprise.
Features of a for-profit social enterprise
Private sector business - Independent of state or government control
More than half its income earned through trading (business activities)
At least half of its profits are reinvested/donated towards their mission
Are transparent in the way they operate and the impact they have
Types of for-profit social enterprises
Private sector social enterprise
Cooperative
Advantages of Social Enterprises
Can generate profit while also contributing to society
Self-sustaining
Don’t need to depend on donations or taxpayer money
Employees may be more motivated as they feel they are working towards a greater purpose
Differentiation from competitors (?)
Since the business’s operations have a unique aspect of social goals which sets the business apart from competitors in the eyes of consumers
Disadvantages of Social Enterprises
Funding (??)
Mainly contribute to the social cause through earning profits from trading
If the business is not profitable enough, it may not be able to contribute enough to the social cause.
Investors may receive lower returns
Due to the social aspect within distributing profit.
Greenwashing
There may be a risk that the business may not be genuinely contributing to social/environmental goals.
Challenges with staying true to the business’s social aims as it grows.
Cooperative
type of for-profit social enterprise that is owned and run by and for its members, who each have the power of one vote.
Types of cooperatives:
Employee cooperative
Owned by employees
Producer cooperative
Community cooperative
Owned by members of the community
Non-profit social enterprise
Private sector businesses that are not for the purpose of making profit but to benefit society
Types of non-profit social enterprises
NGOs
Charities
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs)
Non-profit social enterprises that promote a particular cause. They generally operate in the private sector.
Funded by:
Donations
Sale of goods services
Government grants
Sole Traders
An individual who owns and controls their business.
They take all the risk
They keep all the profit
They may hire employees
They are unincorporated
They have unlimited liability
E.g., Hairdressers, Restaurants, Plumbers
Advantages of Sole Traders
Can set up the business easily and quickly
Can keep all the profit
Independence – owners can manage themselves
Direct contact with the market demand and can respond quickly
No report of financial statements to the public
More privacy
Quicker decision making
No time taken to sort out disagreements
Disadvantages of Sole Traders
Unlimited liability
losses will have to be paid out of pocket
Limited sources of finance
Banks are unlikely to lend money to sole traders
when they do it will be with high levels of interest
High risk of failure
Due to inability to cover unexpected costs, lack of specialization or expertise in all required areas
All aspects of the business must be handled by the owner
No economies of scale
Not enough room for significant changes in production
Lack of continuity
If sick, no income
Partnership
Two or more people combine to form a business. They may combine their finances, run the business together, as well as share the profit.
Deed of partnership includes
How much start-up capital each partner puts in
How the profit is distributed
How much each partner will be paid
How a partner may leave
Advantages of Partnership
Easy to set up, only a deed of partnership is required
Better financial strength than a sole trader
Start-up capital combined
Two people would share the loss
Division of Labour
Each owner specializes in what they are good at
No report of financial statements to the public
More privacy
Disadvantages of Partnership
Unlimited liability
Prolonged decision making process frequent disagreements or conflicts
Due to joint legal and financial accountability
Lade of continuity
Incorporation
The process of the company and its owner(s) becoming separate legal identities — the company itself can own assets, incur debts, enter into contracts, be sued, or sue others independent of its owner(s)
The company has limited liability
If the company goes bankrupt, owners can only lose their initial investment in the company
The company is owned by shareholders
Shareholders are entitled to dividends and voting at the Annual General Meeting
A board of directors (elected by the shareholders) will run the company
Continuity ownership is passed on through the transferring of shares
Privately-Held Company
Limited-liability companies whose shares cannot be sold on the open market
Shares can only be sold with the agreement of other shareholders
Mostly small to medium-sized company
Common legal forms:
Ltd.(UK)
inc.(US)
GmbH(Germany)
Advantages of Private Held Companies
Easier to raise finance
Banks are more likely to lend money to a company than an unincorporated business
Limited liability
Continuity
Economies of scale possible as the rate of production can be higher—move room for change in production method
Division of labour
As the company is not only managed by owners—higher productivity
Tax benefit
Corporate tax is lower than tax on an unincorporated business
Disclosure of information
Disadvantages of Private Held Companies
Bureaucracy
Lots of paperwork
Compliance costs
Must hire accountants, lawyers and auditors
Loss of control
Shareholders have a say in how the entrepreneur runs their business
Limited Funding
Shares cannot be sold to the general public
Disclosure of information
Registered companies have to submit audited financial statements
Publicly-Held Companies
A publicly-held company sells a percentage of its shares to the public.
ITis incorporated
Limited liability
Owned by shareholders
Shares can be bought freely on the stock market
Shares are quoted on the stock exchange
Anyone can buy or sell shares easily
Ownership is often split across many people who are often not linked to the company
Common legal forms
Ltd or PLC (UK)
Inc. or Corp (US)
AG (Germany)
Advantages of Publicly-Held Companies
Limited Liability
Can raise large amount of capital
The company issues new shares when they do the IPO
New shareholders, BUT
Easy for shareholders to trade shares
Makes shares more attractive
Specialization
Company can hire specialist managers in each department
Disadvantages of Publicly-Held Companies
Lacks privacy
The business must provide financial statements to the public.
Costly legal requirements
Short-termism of shareholders
Since shareholders are less personally acquainted with the company, their main objectives will most likely be to earn profits and dividends

1.3 Business Objectives
Mission statement
A statement that outlines the overall purpose of a business and what it is trying to accomplish. It is usually specific and realistic.
It is normally unchanged over time
Includes
Core purpose (why it exists)
identity (who they are)
Focus (what they do)
Often includes a reference to
who its customers are
the way it does business
Vision statement
A statement that outlines the goals and dreams of the business in the future. It is usually an inspiring, broad and aspirational declaration.
Not necessarily realistic
Advantages of Vision and Mission Statements
Gives direction and guides
Long-term planning
Decision-making
Behaviour
Brand image is
Solidified
Consistent
... For the customers of the business
Because these statements can be used in promotional materials
Motivates employees
Satisfies the need for self-actualization in Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
A motivating factor (responsibility/work itself) in Herzberg’s motivation theory
Allows external stakeholders to know more about the business and what it aims to be.
Possibly easier to convince stakeholders of decisions if they are more aligned with the businesses' aims to begin with.
Disadvantages of Vision and Mission Statements
Can be too vague and general
Either statement can be this
Can lead to the business losing a sense of direction.
Strategic and tactical objectives [AO3]
Objective
Clearly defined and measurable targets of an organization used to achieve its overall goals. They are given a specific timescale.
Types of business objectives in the private sector
Growth
Revenue
Profit
Market share
Assets
Profit
Involves maximizing the difference between revenue and costs
Protecting shareholders' value
Shareholders generally want higher share prices and dividend payments
Survival
To continue trade over a defined period of time
Key objective during:
Start-up period
Recession or intense competition
Times of crisis
Cash flow
Essential to be able to pay debts on time
Important for businesses which have a long cash cycle
Cash cycle is time that elapses between cash outflow and cash inflow
Diversification
A business aims to produce an increased range of unrelated goods and/or services.
This objective may be set in order to spread risk across different markets & products.
Business objectives in the public sector
Ethical objectives
E.g. helping the community or environment
Development of relatively poor regions
Help raise standards of living in less affluent areas
Financial objectives
To cover operating costs
So they do not drain government funds
Providing a service to the community
Serve all of the country’s population
E.g. Operating bus services in places where few people live
Strategy
A long-term plan that involves a considerable commitment of resources.
Tactics
Short-term plans that implement a strategy
Strategic Objectives
Refers to aims and goals of a business that are long-term. These are a result of short-term tactics
E.g.
Become a market leader
Buy a competitor
Achieve a stock market valuation of $1Bn
Tactical objectives
Aims and goals of a business that are short-to medium-term
and often only include parts of the business. These are put in place to implement strategic objectives.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) [AO3]
Corporate social responsibility
An approach under which businesses consider the interests of all groups in society and multiple stakeholders groups as a central part of their decision-making
This approach is used by traditional businesses to include social responsibilities into their business objectives
Advantages of CSR
Enhanced brand image
Recognition as socially responsible builds trust in consumers.
Differentiation from competitors
Being a socially responsible company distinguishes a company from a normal shareholder-focused business in the market
Employee retention & motivation
Maslow: Self-Actualization needs
Herzberg: Motivating factors - Responsibility, work itself
Attracts more investors
Investors may be interested in not only financial returns but also positive societal or environmental impact
Disadvantages of CSR
Increased costs overall
There are compliance costs involved with social responsibility and implementing ethical objectives
Increased publicity for unethical behaviour
Since the company has been established as socially responsible, consumers may see through it
As a strategy to get more revenue
Lower profit in the short-term (?)
Triple Bottom Line
Refers to when businesses have social and environmental objectives alongside profit.
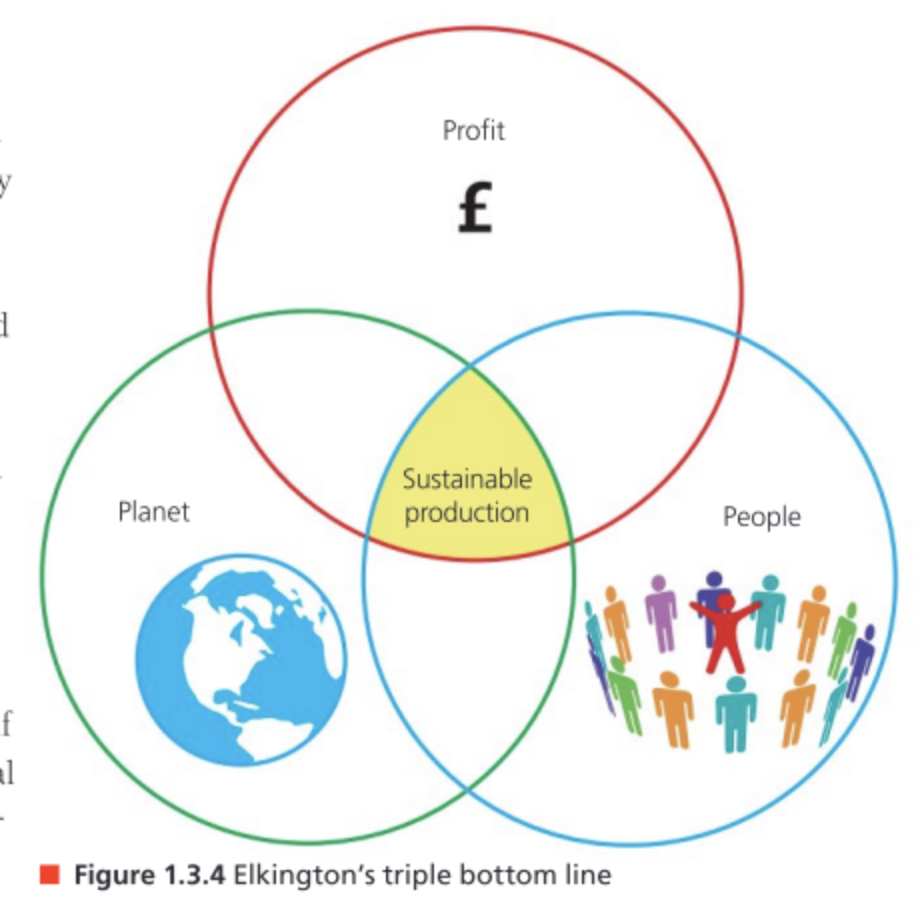
Implementation of Triple-Bottom Line
Marketing-focused
The business claims sustainable practices though often with limited measurable evidence
In order to create a positive brand image
Could be potentially greenwashing
Impact report and societal impact
A business produces an impact report to show evidence of social-and-environment-friendly practices
Becoming a private sector social enterprise
A business with social, environmental, or community goals as its main objective
E.g. B-corps, which certifies companies committed to social impact

1.4: Stakeholders
Stakeholders
An individual or group that is interested in or affected by the decisions made in a business organisation
Internal Stakeholders (list)
Shareholders/owners
Managers
Employees
Rights / wants of Shareholders
Rights
To receive a share of profits
To be kept informed by the management
Wants
Maximize share price
Maximize dividend
Responsibilities of Shareholders
To treat management fairly
Employees
The workers within an organization
Rights/wants of employees
Rights
To be treated fairly (good working conditions
Job security
To be paid fairly
To be kept informed
Wants
High pay
Promotion opportunities
Competitive remuneration packages
Responsibilities of employees
To work effectively
To show up for work on time
Rights/Interests of managers
Rights
To be appropriately rewarded for responsibilities
Duties correspond to level of authority
Interests
Maximize salary
Satisfy shareholders
Maximize profits
Make the business grow/be more efficient
They may want to reinvest profits to grow the business but the shareholders want higher dividends —> Conflict
Responsibilities of managers
To carry out duties to the best of their abilities
To be discreet when handling sensitive business data
External stakeholders (definition)
Refers to individuals or groups outside of the business organization who are interested in or affected by a business
External stakeholders (list)
Customers
Competitors
Suppliers
Government
Pressure groups
Banks
Customers
Refer to a firm’s clients, individuals or organizations who puchase a business’s goods and services
Rights/Interests of customers
Rights
To be able to purchase goods/services at a reasonable price
Receive good quality service/goods in exchange for the price paid
To have a range of choices
No business having an unreasonably high market share so customers don’t have any option but to buy from them
To be supplied on time
Responsibilities of customers
To pay suppliers on time
Competitors
Competitors are businesses which operate in the same industry as a business and contest for the same customers
Wants of competitors
We dont care
Pressure groups
Individuals who come together or organizations which are set up for a common concern. They aim to influence government and public opinion to create social change.
Rights/Interests of pressure groups
Interests
Businesses follow the pressure group’s vision
E.g. Sustainable operations
To live in an area that is free from excessive noise or pollution
To benefit from employment
Responsibilities of pressure groups
To cooperate with the business in its daily activities
Suppliers
Refers to organizations that provide the goods and services for other businesses
Rights/Interests of suppliers
Rights
To be paid on time
To be kept informed about any changes in future orders
Interests
Shorter trade credit durations
Responsibilities of suppliers
To provide products which
Are good quality
Meet specifications requested
Are sent on time
Government
Refers to the ruling authority within a state or nation
Rights/Interests of the government
Rights
The business pays its taxes
The business obeys the law
Interests
The business provides employment to the local community
(Ties in with MNCs and their impact on the host country —> if they don’t provide employment, stakeholder conflict with government)
Responsibilities of the government
To protect business, customers, employees, and the environment
Banks/other lenders
A source of finance for the business who may provide loan capital
Rights/interests of banks/other lenders
Rights
That the business is able to pay back the loan
Interests
To have a good/long-lasting with the business
Responsibilities of banks/other lenders
To not charge excessive interest rates
To not withdraw loans without a reasonable period of notice
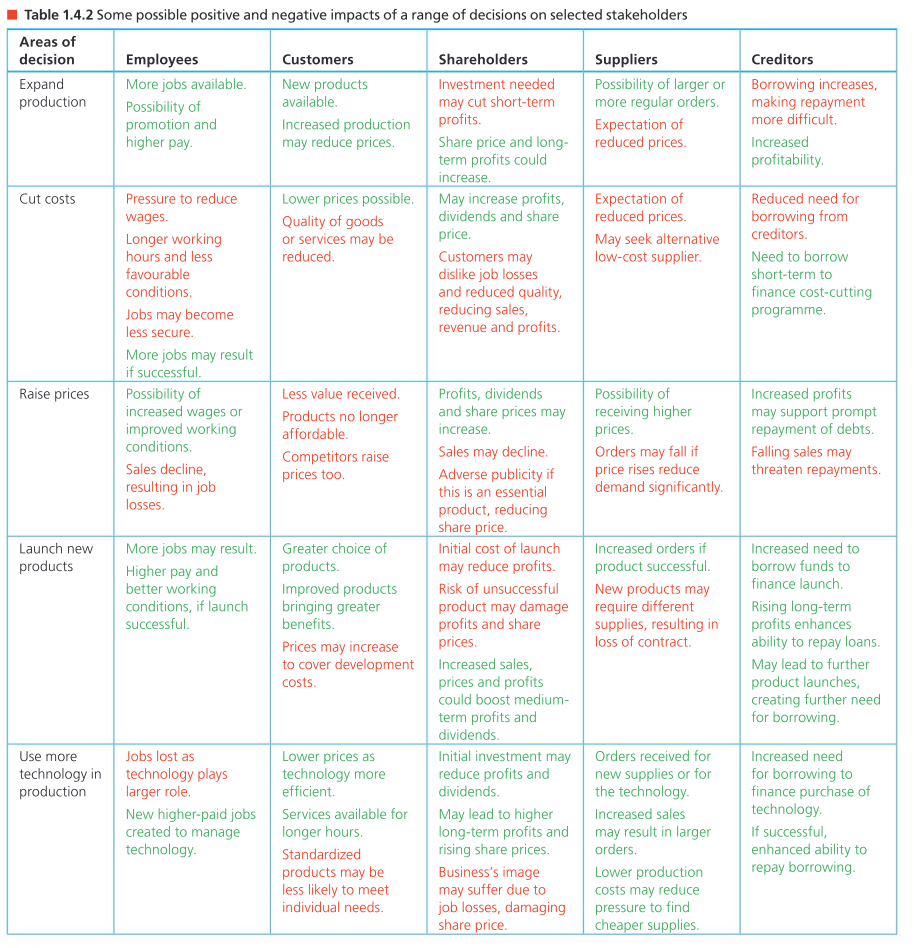
Common types of stakeholder conflicts
Managers vs. consumers
Managers want to raise price of product to gain more profit
Consumers want a reasonable price
Managers vs. Shareholders
Shareholders want high dividend payouts
Managers may want a higher bonus instead
Shareholders vs. pressure groups
Shareholders may not be worried about environmental harm as long as they can maximize their share price and dividends
Pressure groups are concerned about the environment

1.5 Growth and Evolution
How is the size of a business measured
Sales Revenue
Market share → Revenue/market revenue
Value
Profit
No. of employees