KIN 101 FINAL EXAM FLASHCARDS
1/230
Earn XP
Description and Tags
human physiology chapter 14-20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
231 Terms
what is the endocardium?
inner
layer of endothelial cells
what is myocardium?
middle
cardiac muscle
what is the epicardium?
outer
external membrane
what ist he pericardium and what does it have?
membranous sac that encases and protects the heart
fused with diaphragm
within the sac is pericardial fluid that lubricates and allows heart/myocardium to operate in a friction free environment
what is an echocardiogram?
provides information on size, shape of the heart; pumping strength and location of any damage
compare the thickness of ventricular walls on the left and right side
right ventricle is thin. is a low pressure pump
left ventricle is thick. stronger and holds more blood, a high pressure pump to go everywhere
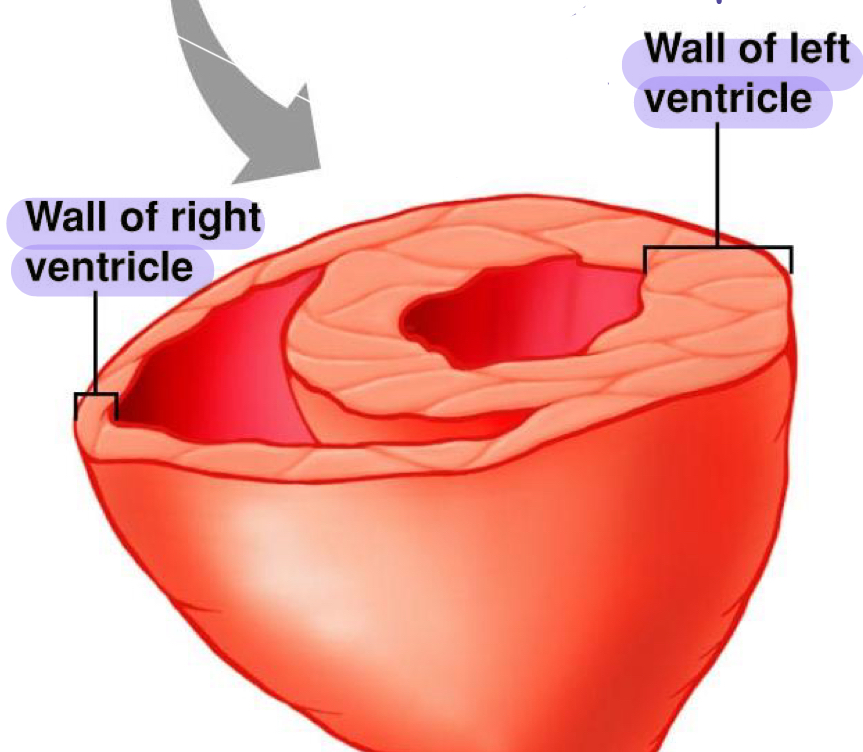
what is the mitral valve?
another name for the bicuspid valve on the left side of the heart
what happens to valves during ventricular contraction?
oxygenated blood flows out of the aortic valve and deoxygenated blood flows out of pulmonary valve
AV valves (right and left) remain closed to prevent blood flow backward to the atria
ventricles and muscles are contracted and tense
what are semilunar valves?
they open and close in response to pressure diffeences
what happens to valves during ventricular relaxation?
oxygenated blood flows into the mitral/bicuspid valve and deoxygenated blood flows into tricuspid valves
semilunar valves prevent blood that what entered the arteries from flowing back into ventricles during ventricular relaxation
ventricles and muscles, they are relaxed and filling with blood
what is coronary circulation
movement of blood through veins and arteries that supply blood to the myocardium (heart muscle)
left coronary artery supplies blood to left side of heart
right coronary artery - supplies blood mainly to right side but assists left with some parts.
what does the systemic circulation include?
arteries: carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the tissues
veins: carry deoxygenated blood back to the right atrium
what does the pulmonary circulation include?
blood vessels that go from right ventricle to the lungs - pulmonary arteries
blood vessels that go from lungs to left atrium - pulmonary veins
what is Ohm’s Law?
flow = change of pressure / resistance
what is the physiological equation for measuring pressure and blood flow
Q = MAP/TPR
Q: cardiac output - heart function
MAP: mean arterial pressure - blood pressure
TPR: total peripheral resistance - blood vessels and diameter
what is cardiac output?
beats/min (heart rate, bpm) x mL(blood)/beat (stroke volume) = mL/min
heart rate x stroke volume
amount of blood leaving the ventricles every minute
L and R ventricle are usually matched
what is MAP (mean arterial pressure)?
outward pressure exerted on walls of blood vessels
what is total peripheral resistance?
total resistance of all blood vessels that are most impacted by arterioles
what is resistance?
the radius of the blood vessels determines resistance and is physiologically regulated
what is vasodilation in term of resistance
radius increase
resistance decreases
blood flow increases
pressure increases
what is vasoconstriction in term of resistance
radius decreases
resistance increases
blood flow decreases
pressure increases
what is the flow and resistance relationship and what is the forumla?
resistance opposes flow
resistance increases, flow decreases and vice versa
flow = 1/R
what are the 3 things that resistance depends on?
length of the tube (L)
radius of the tube ( R)
viscosity (n) of the fluid
R increases as L and n increases and r decreases
explain the MAP equation? (not blood flow one)
MAP = Q x R
MAP: net driving pressure = p1 - P2
Q: flow due to central factors
R: resistance due to peripheral factors (diameter or r^4)
what are desmoses
strong proteins that surrounds sarcomeres and bind neighbouring sarcomeres
allows force to be transferred
gap junctions
provide electrical connection
electrical signals are transmitted via these protein pores
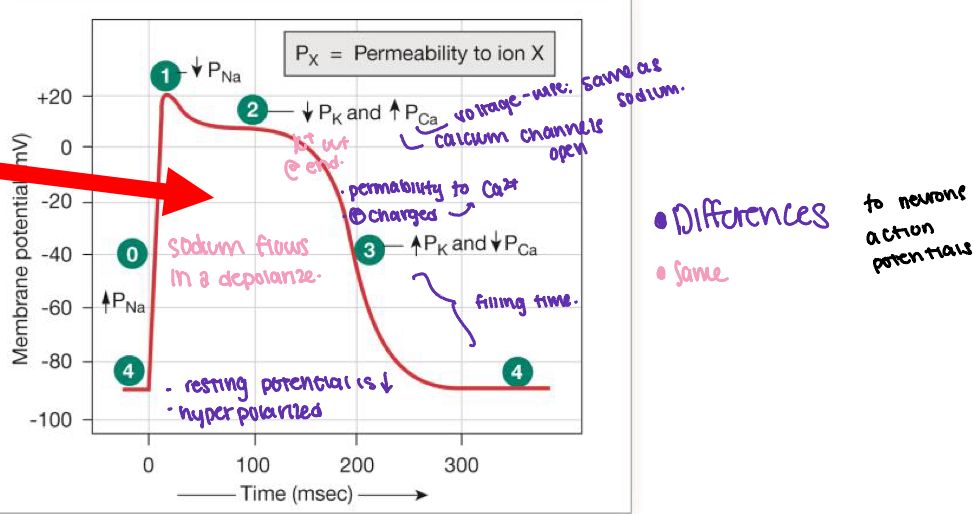
what is the action potential of a cardiac contractile cell?
sodium channels open
sodium channels close
calcium channels open and then fast potassium channels close
calcium channels close and then slow potassium channels open
resting potential starts.
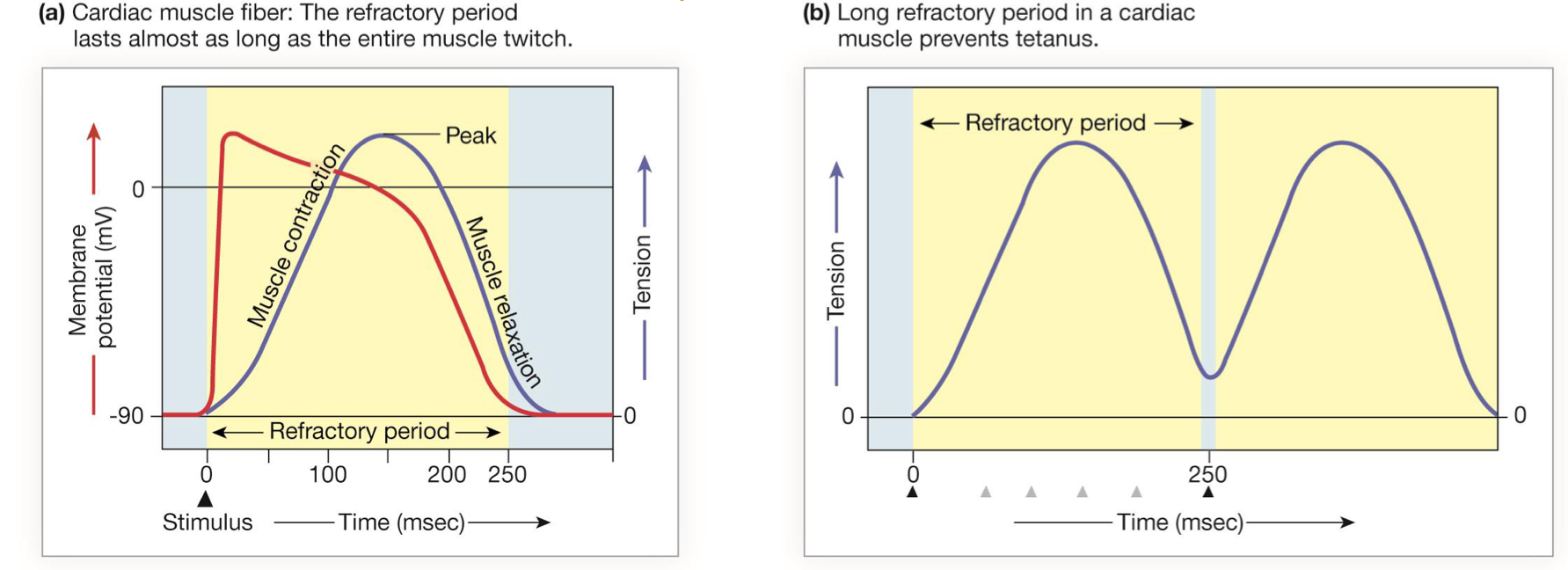
explain the refractory periods and summation in cardiac muscle
theres forced generation in heart muscle and thats proportional to number of active crossbridges
dependent on how much calcium is bound to troponin
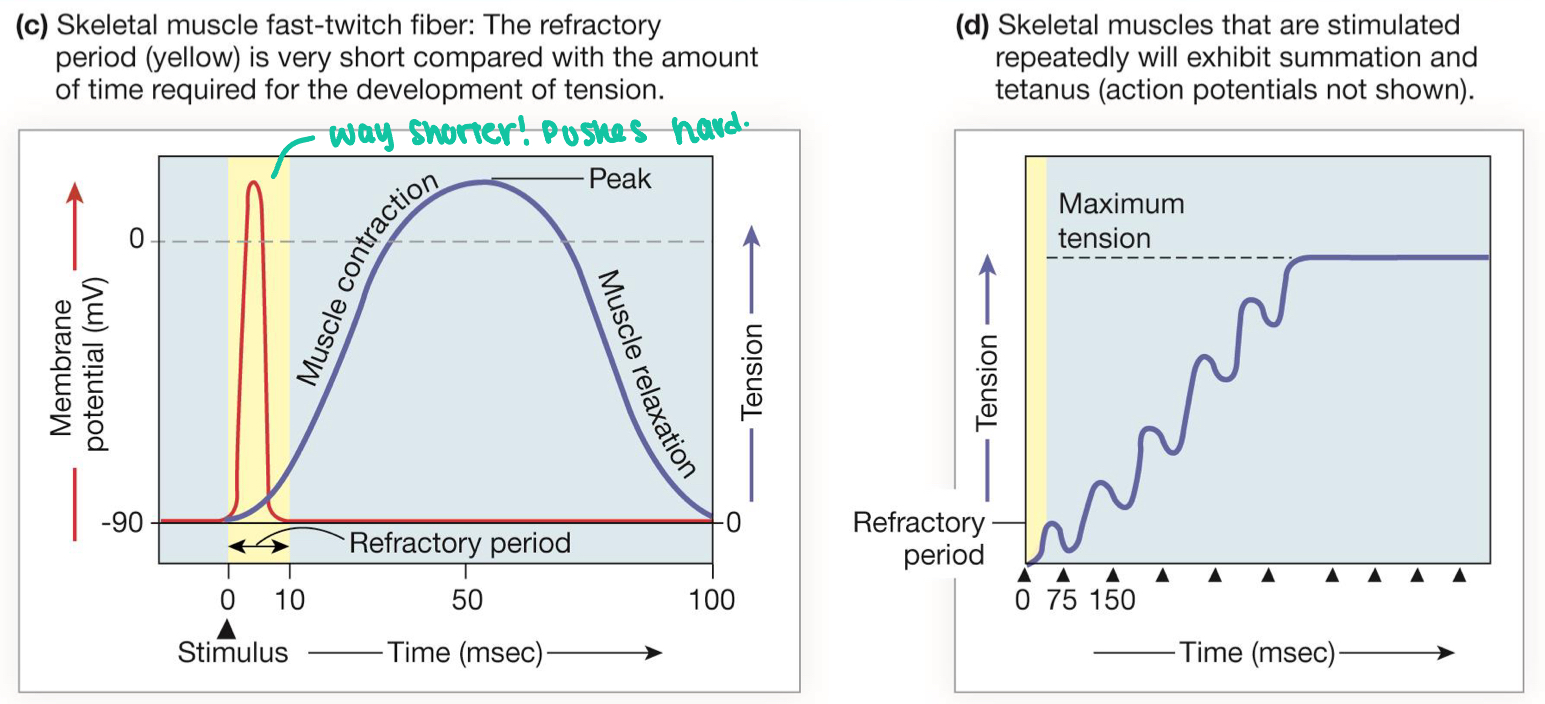
explain the refractory periods and summation in skeletal muscle
forced generating in this muscle is proportional to number and frequency of stimulation
tetanus and fused tetanus build tension
summation determines level of tension
explain the excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle
action potential enters from adjacent cell
voltage gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the cell.
Ca2+ induces Ca2+ release from S through RyR
local release causes Ca2+ spark
summed Ca2+ sparks create a Ca2+ signal.
Ca2+ binds to troponin to initiate contract then relaxation occurs when Ca2+ unbinds from troponin
calcium is put back into SR
calcium is exchanged with sodium and sodium gradient is maintained with SPPs
how is cardiac muscle contraction graded?
the contraction force is generated proportionally to the number of active crossbridges
how much calcium is bound to troponin
sarcomere length affects force of contraction
what are the action potentials in cardiac autorhythmic cells?
If channels open
Some calcium channels open then If channels close, then more calcium channels open. calcium increases (depolarization)
at the peak, calcium channels close and pottasium channels open
potassium channels close. potassium decreases (repolarization)
If channels open up again
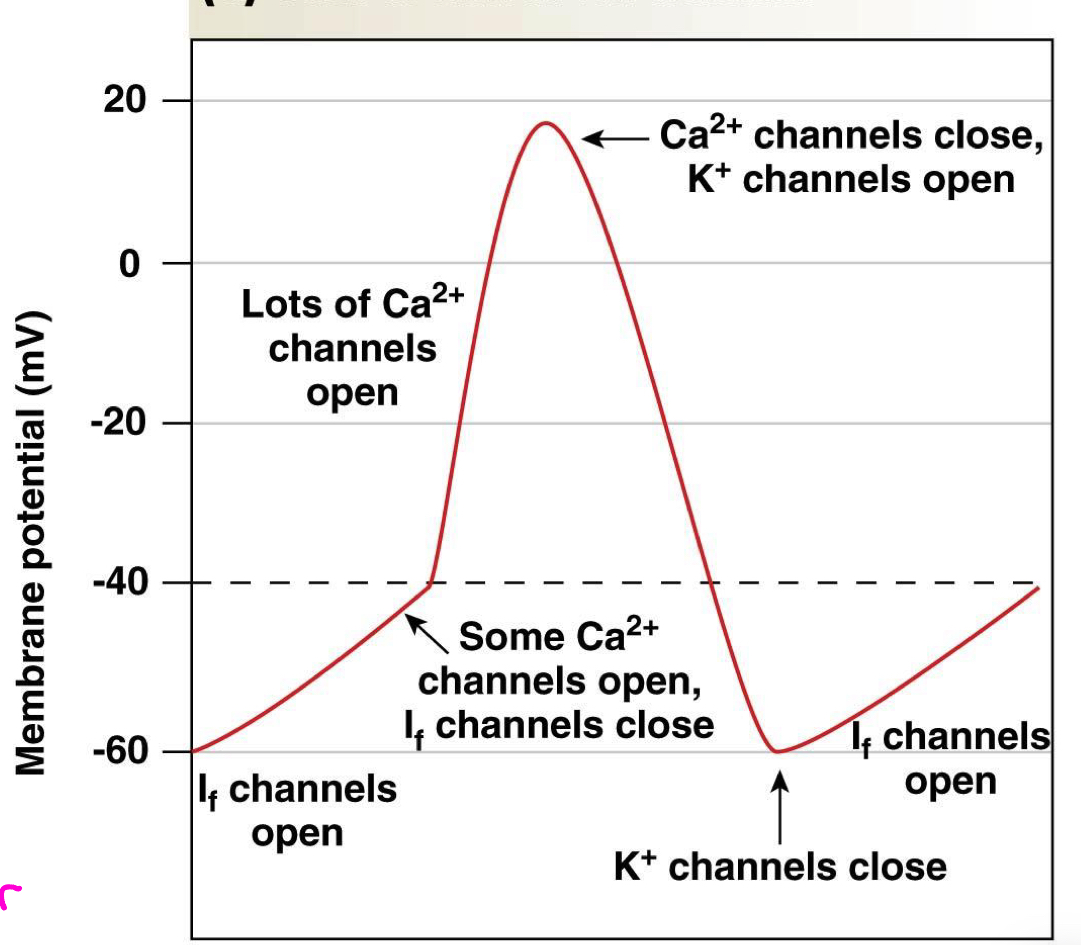
what are If channels?
leaky channels that are specalized channels found in pacemaker
more active in SA nodes than AV nodes
what is stroke volume (SV) and it’s equation?
amount of blood pumped by one ventricle during a single contraction
units = ml/beat
EDV (end diastolic volume) - ESV (end systolic volume)
compare and contrast end diastolic volume and end systolic volume
EDV is the volume of blood in a ventricle just at the end of a diastole (hearts relaxation phase)
max amount of blood in ventricle jutst before a contraction
ESV is the volume of blood left in a ventricle at the end of a systole, hearts contraction phase
amount of blood remaining after ventricle has ejected blood → aorta or pulmonary aretery
what are the two divisions of Q (cardiac output)
heart rate (bpm)
stroke volume (mL/beat)
EDV - ESV
what are two ways stroke volume can increase
increase end diastolic volume (more blood in the ventricle to be ejected. preload
increase ejection fraction (more blood in the ventricle IS ejected.) contractility
what is pulse rate?
time between pressure waves in an artery
what is systole, diastole and pulse pressure?
highest pressure in the ventricles and arteries
lowest pressure in the ventricles and arteries
difference between systolic and diastolic pressures (S-D)
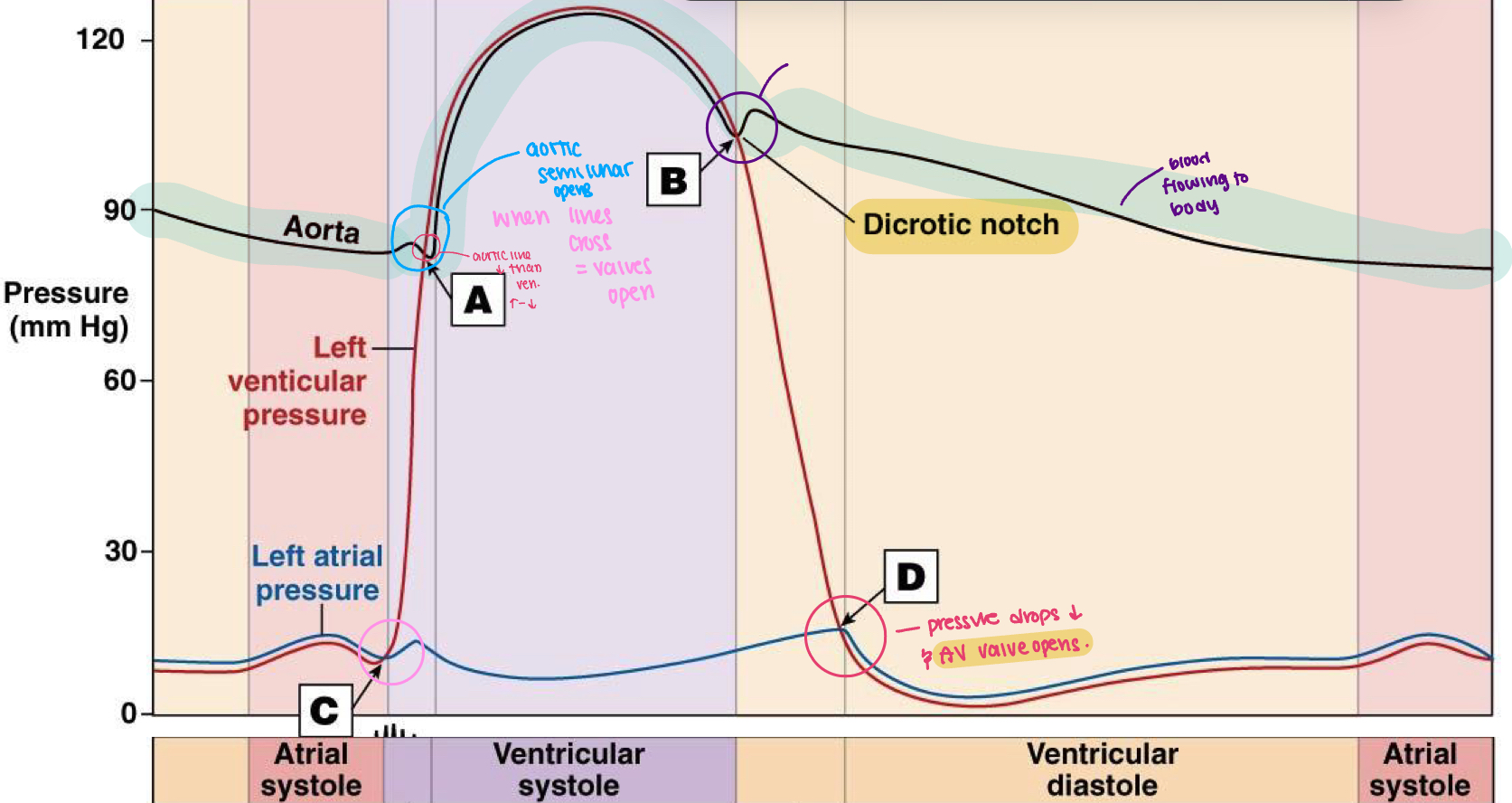
explain the process of atrial diastole
P. Eletrical event. Atrial depolarization happens and the blood is being pushed to the ventricles from atria
atrial contdaction begins in the latter part of the P wave
QRS: mechanical event. blood incoming to ventricle and contract happens (ventricular depolarization)
T: atria is filling with blood and ventricle is squeezing blood out (ventricle repolarization)
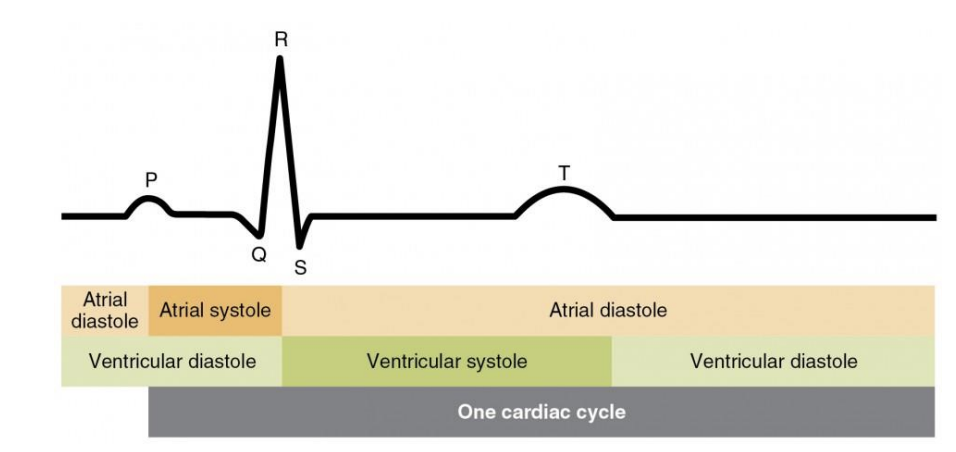
what is heart rate?
time between two R waves and two P waves
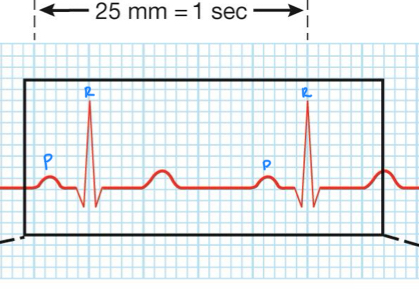
what is the main function of the P wave, Q wave and R wave.
depolarizes SA node then the atria
SA node depolarizes and then the bundle of branches located in the septum
purkinje fibers depolarize and ensuring coordination contract of the heart muscle
what does a normal electrocardiogram
waves: deflections above/below the baseline
segments: sections of baseline between waves
intervals : combos of waves and segments
what is ejection fraction and the equation
percentage of EDV ejected with a single contraction
as this percentage goes up, you remove more blood from the heart chambers
EF = stroke volume/end diastolic volume x100
what are the two segments of an ECG
P-R: time between end of atrial depolarization and onsent of ventricle depolarization.
S-T: end of ventricular depolarization and onsent of ventricular repolarization
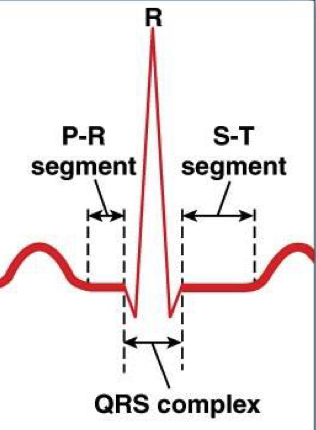
what are the two intervals of an ECG
PR: time between onset of atrial depolarization and ventrical depolarization
QT: onsent of ventricular depolarzation and end of repolarization
compare the parasympathetic and sympathetic control on heart rate (heart rate and beats, neutrotransmiter, ion permability)
decreases heart rate, receives Ach on muscarinic receptors and potassium increases. farther apart heart beats
increases heart rate, norepinephrine receives b1-adrenergic receptors in SA nodes and increases sodium and calcium permeability. closer together heartbeats
what is the parasympathetic system control on the heart (neurotransmitter, ion permeability, polarization effect and heart rate effect)
releases ACh to muscarinic receptors on autorhythmic cells
potassium leaves the cell and calcium comes into the cell
cell hyperpolarizes and lowers depolarization rate
lowers heart rate
what is the sympathetic system control on the heart (neurotransmitter, ion permeability, polarization effect and heart rate effect)
released norepinephrine to b1-receptors on autorhythmic cells
sodium and calcium increase and go into the cell
the rate of depolarization increases
heart rate increases
what are the mechanical events of a cardiac cycle?
late diastole (all chambers are relaxed and ventricles fill passively)
atrial systole (atrial contraction forces a small amount of additional blood into ventricles)
isovolumic ventricular contraction - pushes AV valves closed but doesn’t create enough pressure to open semilunar valves
ventricular ejection - as ventricular pressure rises above pressure in arteries, semilunar valves open and blood is ejected
isovolumic ventricular relaxation - as ventricles relax, pressure drops. blood flows back into cusps of semilunar valves and snaps them closed.
explain the pressure-volume changes during cardiac cycle
A-B: ventricle is filling
B-C: isovolumic contraction. mitral valve closes and aortic valve opens
C-D: ejection of blood into aorta (C volume - D volume = stroke volume)
D-A: isovolumic relaxation
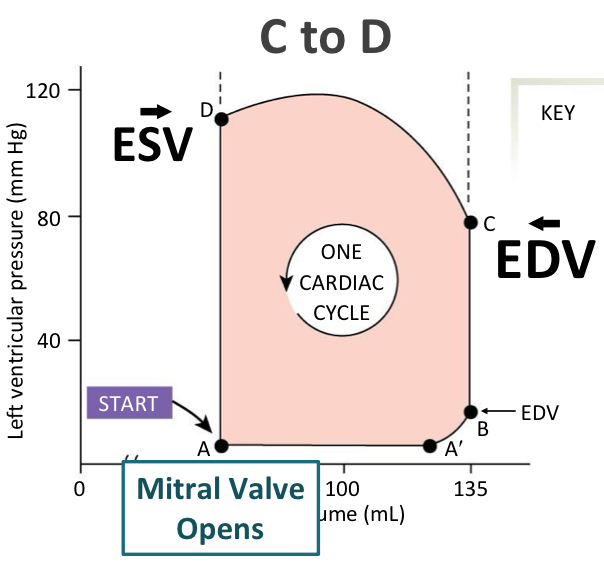
changes in pressure during the cardiac cycle
A: aortic valve opens and blood leaves
B: aortic valve closes and most blood has been ejected out of the heart
C: bicuspid (mitral) valve closes - ventricles are full of blood
D: mitral valve opens
what are the 3 factors that effect stroke volume?
preload - more stretch = more force
contractility
afterload
what are the neurotransmitter and sympathetic activity affects on contractility?
norepinephrine can enhance contractility which is a positive inotropic agent.
increased symapthetic activtity = stronger contractions and higher stroke volume. this is caused by increased epinephrine which can increase cardiac contraction
decreased symapthetic activity = weaker contractions and lower sv
what is contractility?
hearts ability to contract more forcefully
what is frank-starling law of the heart?
stroke volume is proportional to EDV
fill more = empty more
what happens if afterload is increased?
heart must work harder to maintain stroke volume
ventricles increase force contraction, metabolic demands increase (more oxygen and atp)
what is afterload?
a factor that effects stroke volume
combined load of end diastolic volume and arterial resistance during ventricular contraction (ventricular force must be greater than resistance
blood must be pushed through semilunar valves → circulation
what are the sympathetic effects on contractility?
increased sympa activity means increased epinephrine release
increased strength of contraction
increases rate of contraction and relaxation but a lower contraction duration
how can you increase the blood volume in ventricles?
increase venous return
amount of blood that returns to the heart from venous circulation
what are the 3 things venous return is affected by?
skeletal muscle pump
respiratory pump
venous constriction
how does a skeletal muscle pump affect venous return?
contraction of skeletal muscle compresses veins and pushes blood toward the heart
enhanced venous return
how does a respiratory pump affect venous return?
decreased pressure on the inferior vena cava allows more blood to be drawn in from the abdoment
enhanced venous return
how does venous constriction affect venous return?
increased sympathetic activity causes the veins to constrict
decreased volume in the veins
more blood is squeezed out of the veins
what are the 3 components of poiseuille’s law?
length (L) of the tube/blood vessel
viscosity (η) or thickness of the blood/fluid
resistance is inversely proportional to blood vessel radius
what are arteries
act as a pressure reservoir
has thick layers of vascular smooth muscles
lots of elastic and fibrous connective tissue
what are arterioles?
a site of variable resistance
controls resistance
it is apart of the microcirculation
less elastic and more muscular
lots of blood can flow through them
what are metarterioles
branches of artierles
partially has smooth muscle
has precapillary sphincters that open and close to direct blood flow into capillaries or venous circulation
what happens as resistance decreases in blood vessels?
total crocss-sectional area increases
radius of individual vessels increase by a factor of 4
which blood vessel has the greatest cross-sectional area?
capillaries
how does the total cross sectional area increase?
they increase as the blood vessels branch
each vessel is small but the combined diameter (where the blood can flow) is greater
where is the velocity of the blood slowest?
where the cross sectional area is the greatest
what is our volume reservoir in the body?
our veins - they can stretch so at rest they hold the majority of the blood volume at rest
redistribution of the blood volumes can occur as cardiac output increases and tissues demand more o2 and nutrients (during events like exercise)
what are venules?
they receive blood from capillaries
has little connective tissue
thin exchange of epithelium
has a convergent pattern of flow
what are veins?
take blood back to the heart
has thin walls of vascular smooth muscle
has 1 way valves to prevent backward flow
closer to the body surface
less elastic tissue
what are capillary beds?
a site of nutrient and gas exchange (needs more during exercise)
can control amount of blood that goes through capillaries which depends on how active the tissue is
what is angiogensis?
development of new blood vessels
necessary for normal development
enhances heart and skeletal muscle blood flow
how do we measure blood pressure outside the body?
MAP = diastolic pressure + 1/3(pulse pressure)
what are the 4 factors that influence mean arterial pressure?
blood volume
cardiac output (how effective the heart pump is)
resistance of the system to blood flow
redistribution of blood between arterial and venous blood vessels
explain how blood volume is a factor of mean arterial pressure.
determined by fluid intake and fluid loss. fluid loss could be passive or regulated at kidneys
increased b.v leads to increased b.p and can either trigger vasodilation, lowering cardiac output, increased urine flow
all can lead to lowering blood pressure to normal
high b.v = high b.p
explain how cardiac output is a factor of mean arterial pressure.
determined by heart rate and stroke volume
explain how resistance of the system to blood flow is a factor of mean arterial pressure.
determined by the diameter of the arterioles
in vasoconstriction, theres more resistance, increased pressure and decreased flow
in vasodilation, lower MAP, lower pressure and increased flow
what is hyperemia?
locally mediated increase in blood flow
active: matches blood flow to increased metabolism (has local control factors. paracrines can cause vasodilation)
reactive: follows a period of decreased blood flow
what is arteriolar resistance?
resistance to blood flow in arterioles
influenced by local and systemic control mechanisms
sympathetic system affects the diameter of the blood vessels. (norepi on alpha and ephi on beta)
what is myogenic autoregulation?
adjusts blood flow
contracts to resist stretching. is automatic
explain how relative distrubution of blood between arteiral and venous blood vessels is a factor of mean arterial pressure.
is determined by diameter of veins
willing to stretch to hold blood at rest
what is plasma composed of?
water (92%), proteins (7%), ions, gases, organic molecules, vitamins (1%)
what are the cellular elements of blood?
red blood cells (RBC): erythrocytes
platelets (cell fragments): from megakaryocyte
white blood cells (WBC): leukocytes
what are the functions of plasma?
transports materials around the body
solvent for cellular elements
what is colloid osmotic pressure
force keeping water within the plasma and preventing it from leaking out of blood vessels
proteins in the plasma (ex: albumin) create this pressure
what are albumins?
major contributor to plasma colloid osmotic pressure
transport FFAs
what do white blood cells include? (LMNOP)
lymphocytes
monocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
what are eosinophils?
produce toxic compounds directed against invading pathogens
what is a neutrophils?
mobile phagocyte that ingests foregin substances and pathogens
what are monocytes?
phagocytes
engulf and digest invaders (bacteria, dead, damaged cells)
what are lymphocytes?
they produce specific immune responses directed against invaders
what are hematocrit?
percentage of total blood volume thats occupied by packaged rbc’s
ratio of rbcs to plasma
in males: 40-54%
females: 37-47%
whats the significance of the hemoglobin value?
reflects oxygen-carrying capacity of rbc’s
males: 14-17. females: 12-16
how long do red blood cells live and why?
120 days
has no nuclues
if fully saturated, how many mL of o2 can 1g of hemoglobin transport?
1.34 mL of O2