3.4.3 Genetic Diversity can arise as a result of mutation or during mitosis
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is genetic diversty?
a measure of the number of different alleles in genes in a population
What causes genetic diversity (5)?
gene mutations
chromosome mutations
crssoing over
random assortment
random fusion of gametes
Which of the causes of genetic diversity occur in meiosis
crossing over, chromosome mutations and random assortment
What is a gene mutation?
a change in the base sequence of a chromosome
When do gene mutations usually occur?
DNA replication
What happens if a gene mutation occurs in an exon?
the polypeptide coded for may be different and as the tertiary structure is different, may be non-functional
What are neutral mutations?
When the change in amino acid sequence does not affect the function of the protein
What is an allele?
a new base sequence of a gene
Give 3 types of gene mutations?
substitution
deletion
addition
What is a substitution gene mutation?
When one or more bases in the gene are exchanged / subsititued for others. This only affects one triplet and the rest stay the same, changing only one amino acid
Why might some substitution gene mutations not result in a change to the polypeptide chain?
The DNA code is degenerate, so the substituted triplet may code for the same amino acid
What are mutations that don’t result in change called?
Silent mutations
If a triplet is substituted with a stop triplet, what happens to the amino acid?
The chain will be shorter
What is an addition gene mutation?
When one or more bases are added to the base sequence of a gene
What is a deletion gene mutation?
When one or more bases are deleted from the base sequence of a gene
What does an addition or deletion gene mutation result in?
a frame shift. Each triplet following the frame shift is altered with the consequence of an antirely new amino acid code
What effect does a deletion or addition gene mutation usually have?
the protein coded for will likely be non functional
What are mutagenic agents?
Factors that increase the rate of mutation
Give 4 examples of mutagenic agents
High energy raduation
Ionising radiation
Tar in cigarettes
Virusses (HPV)
What ae carcinogens?
Substances which cause mutations in oncogens that causes a cell to become cancerous
What are oncogenes?
genes asssociated with regulation of cell division
How frequently to gene or chromosome mutations take place?
randomly
When do chromosome mutations occur?
meiosis
What happens when 2 gametes fuse?
The diploid number is restored
What is the n number of a zygote?
2n
What is non-disjuntion??
When the homologous chromosomes do not separate in meiosis meaning that a gamete is diploid for one chromosome
Describe a non-disjunct chromosome
Two chromosomes of the same type
If someone had a non-disjunct chromosome and had a child, describe the chromosomes of the child
3 homologous chromosomes of that specific chromosome
What causes down syndrome?
non-disjunction of chromsome 21 (3n)
What is meiosis?
the division of a diploid cell to four haploid daughter cells (gametes)
Where does meiosis occur in humans?
gonads
Describe the meiosis daughter cells
genetically different
haploid
Why are meiosis daughter cells not identical?
crossing over
independent segregation of chromosomes
What happens when two haploid gametes fuse?
the diploid chromosome number is restored
Why is meiosis important?
chromosome numbers are kept constant through the generations
How many divisions are there in meiosis?
2
What occurs in meiosis I?
The homologous chromosomes are separated
What happens in meiosis II?
The sister chromatids are separated
When does crossing over take place?
meiosis I
When does independent segregation of homologous chromosomes occur?
meiosis I
Draw a diagram of meiosis
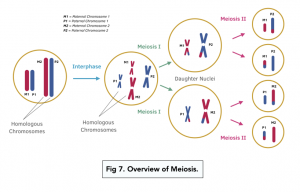
What type of division is meiosis I?
reducing division
How does the n number change during meiosis I?
changes from 2n to n
Describe the chromosomes before meiosis I?
each chromsome consists of 2 sister chromatids
Describe the chromosomes after meiosis I?
each chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids
Describe the chromosomes after meiosis II
each chromosome consists of one sister chromatid
What is crossing over?
When homologous chromosomes pair and come together, wrapping round each other and essentially swapping sections
What do the chromosomes form in crossing over?
bivalent
Describe the process of crossing over?
non sister chromatids wrap around each other
They attatch at points called chiasmata
They break and rejoin, swapping sections of non-sister chromatids
New combinations of alleles
What are the points where the chromosomes rejoin called in crossing over?
chiasmata
What happens as a result of crossing over?
new combinations of alleles in the gametes
Draw a diagram of crossing over?
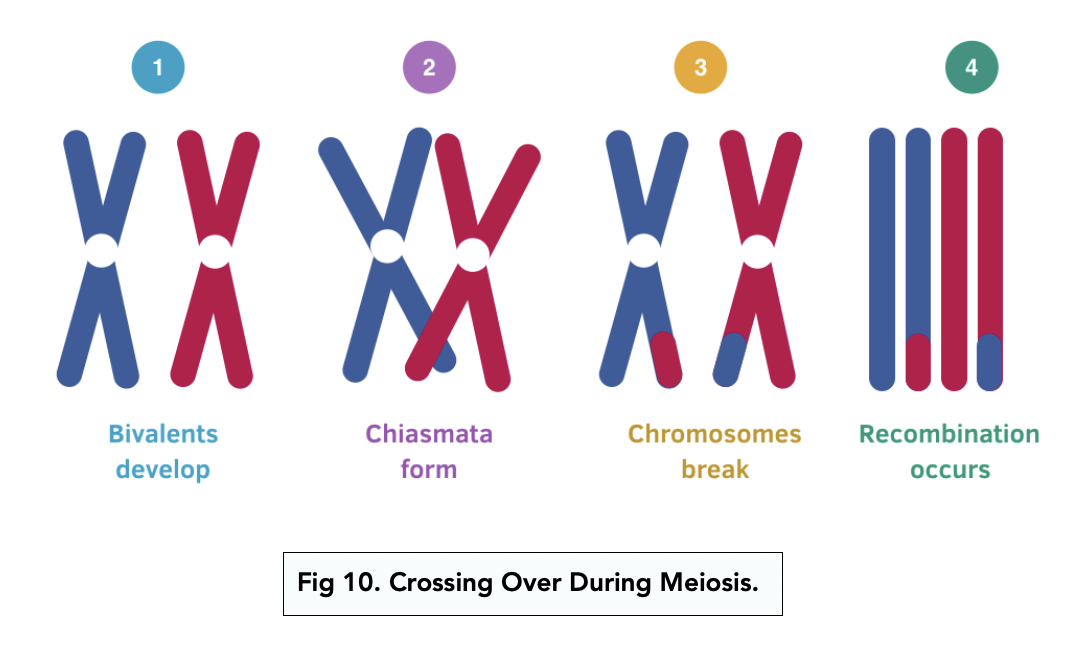
Describe the process of independent segregation of chromosomes
In the first meiotic division the homologous pairs of chromosomes randomly align at the equator, the pair is the separated to opposite poles of the cell
The paternal and maternal homologous chromsomes are separated from each other
They are segrated independently
Draw a diagram of independent segregation
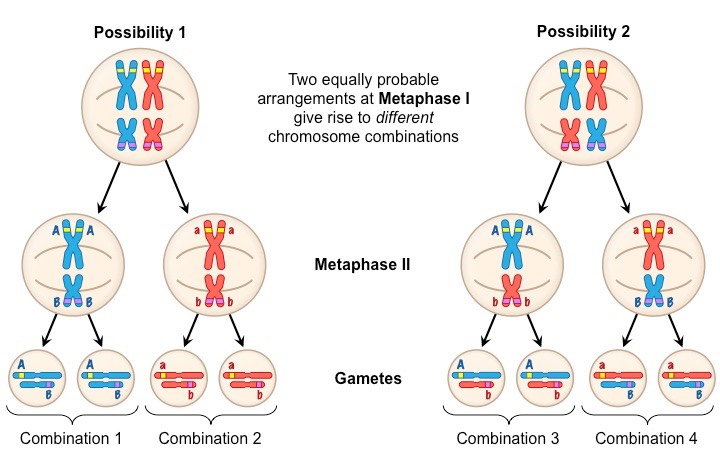
How can you calculate the number of combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes?
2^n where n is the number of pairs of chromosomes
Complete the meiosis vs mitosis table:
Mitosis | Meiosis |
Genetically identical daughter cells? | |
How many daughter cells? | |
How many divisions? | |
n number before and after |
Mitosis | Meiosis |
Yes | No |
2 | 4 |
1 | 2 |
2n → 2n | 2n → n |
Draw a human lifecycle with n number
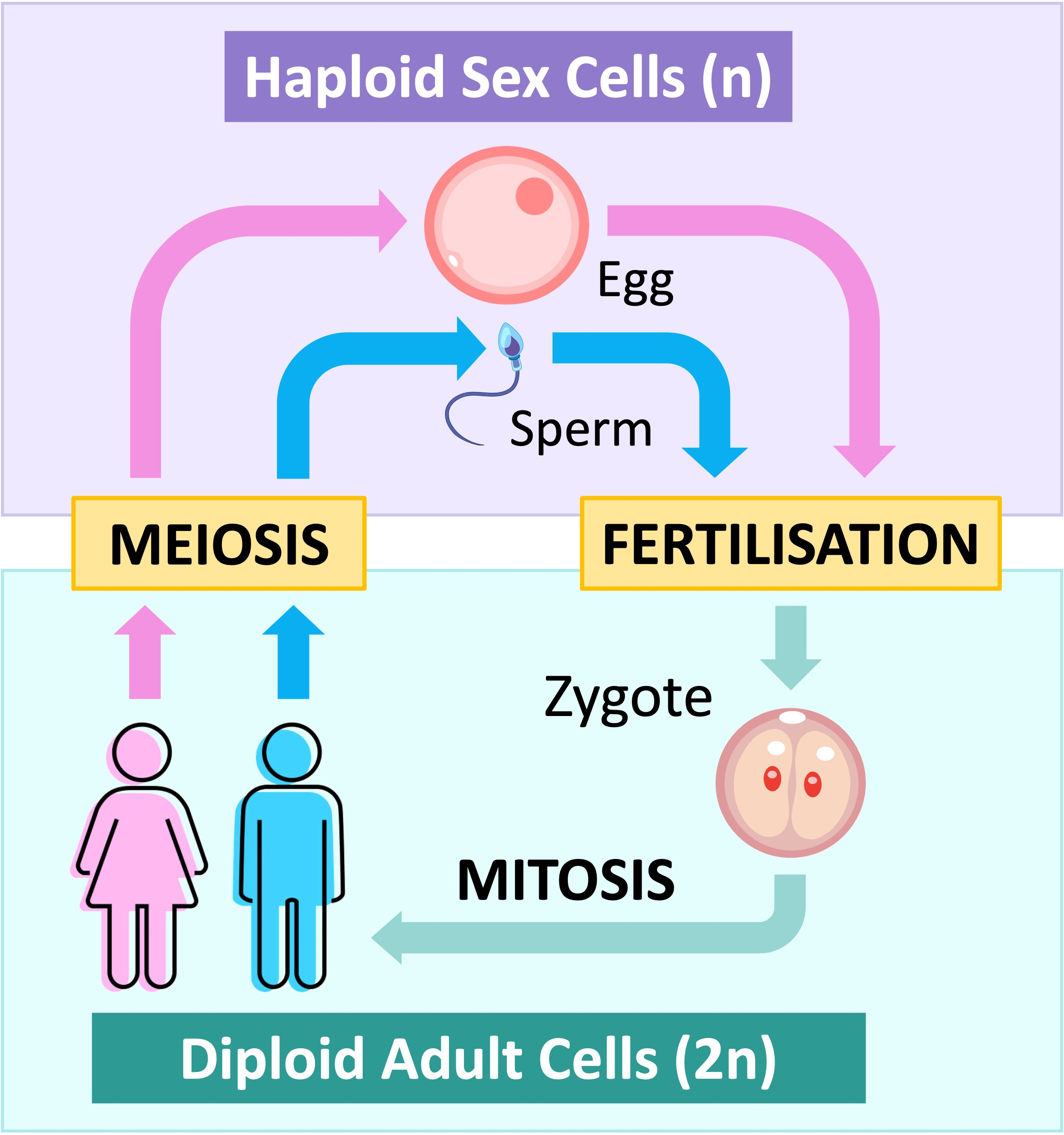
What does 2n represent?
diploid cells
What does n represent?
haploid cells
Draw the moss life cycle
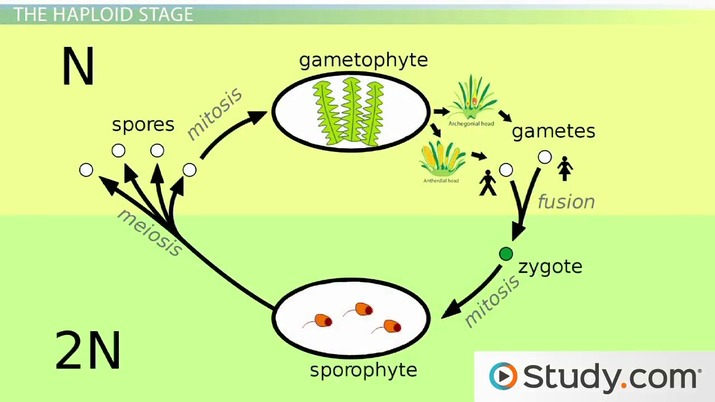
How do you know meiosis has occured in a life cycle?
the n number changes from 2n to n