South, East, and Southeast Asia & Early European and Colonial Americas
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
50. Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well and Jacob Wrestling with the Angel, from Genesis
Form;
-tempera, gold, and silver on purple vellum (animal skin)
-illuminated manuscript (pictures with words)
-continuous narrative
Content:
- stories from Genesis
-Jacob wrestles an angel at night
-Rebecca quenches thirst of camels and camel driver
-letters black now bc silver oxidized
-Greek writings> Byzantine
Function:
-tell stories
Context:
-Early Byzantine Empire 6th century CE

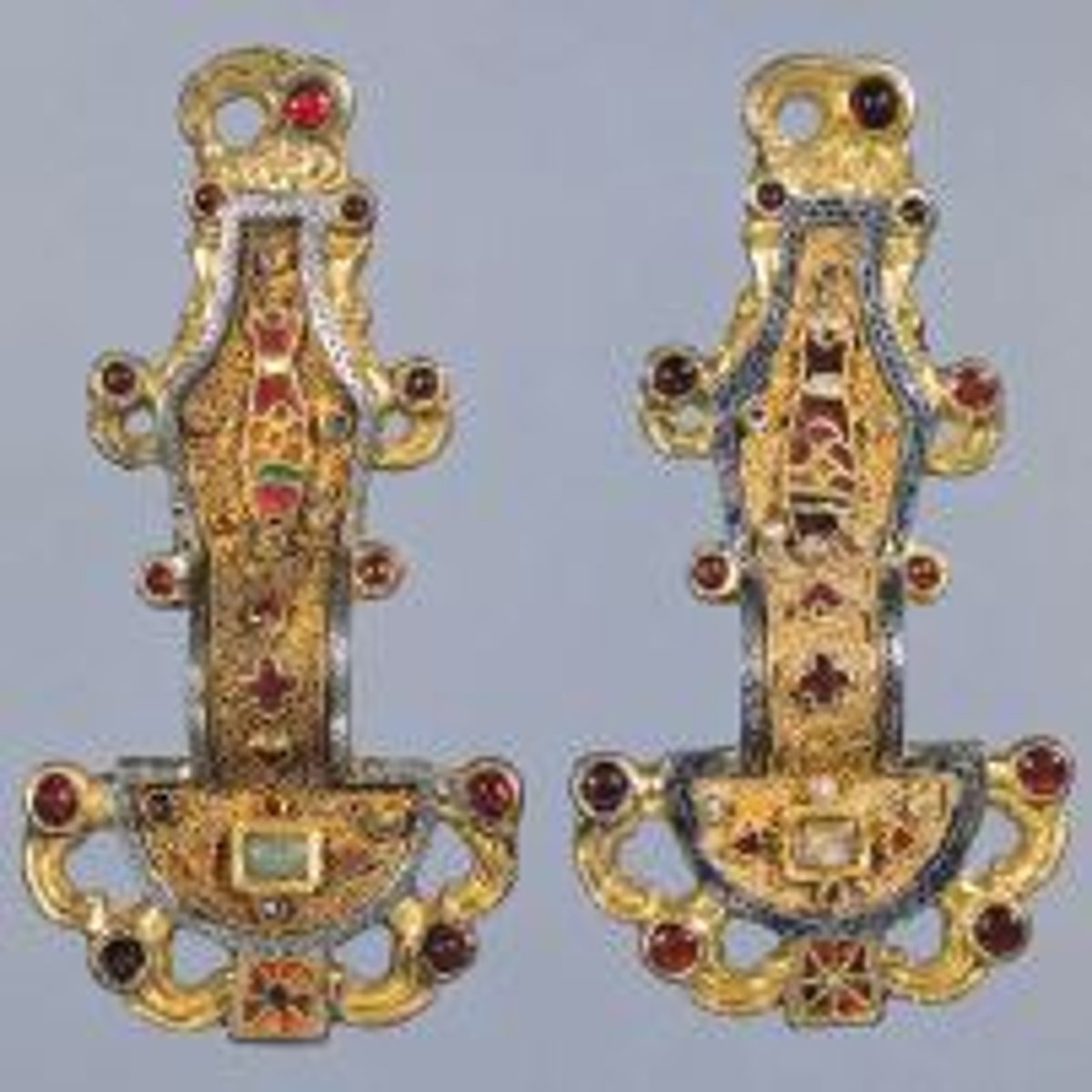
53. Merovingian looped fibulae
Form:
-interlacing (zoomorphic)
-bowed
-filigree 2-4"
-silver gilt (thin layer of gold)
Content:
-animals (fish represents Christ and eagle represents St. John)
Function:
-clip for holding fabric
-clasp that hold fabric to the shoulder
Context:
-mid 6th century CE
-Frankish kingdom
-found in tomb of rich woman

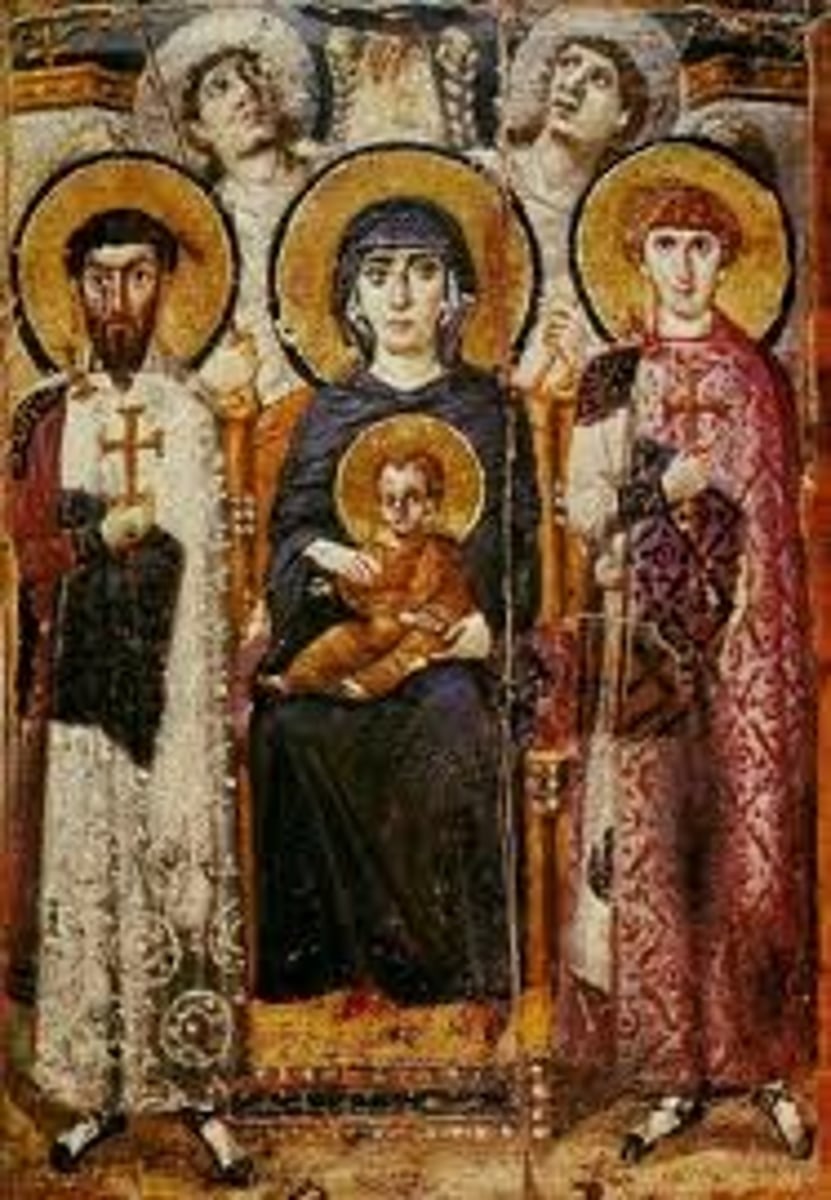
54. Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George
Form:
-encaustic (wax base paint) on wood
-spacial recession but compressed space
Content:
-angels looking towards heaven
-Mary looking over viewers while the warrior saints look directly at viewer
-light falling on Virgin
-depicts Mary and Jesus in a different realm than others
Function:
-portray Mary and Christ protected by saints and hand of God
Context:
-6th-7th century
-Early Byzantine

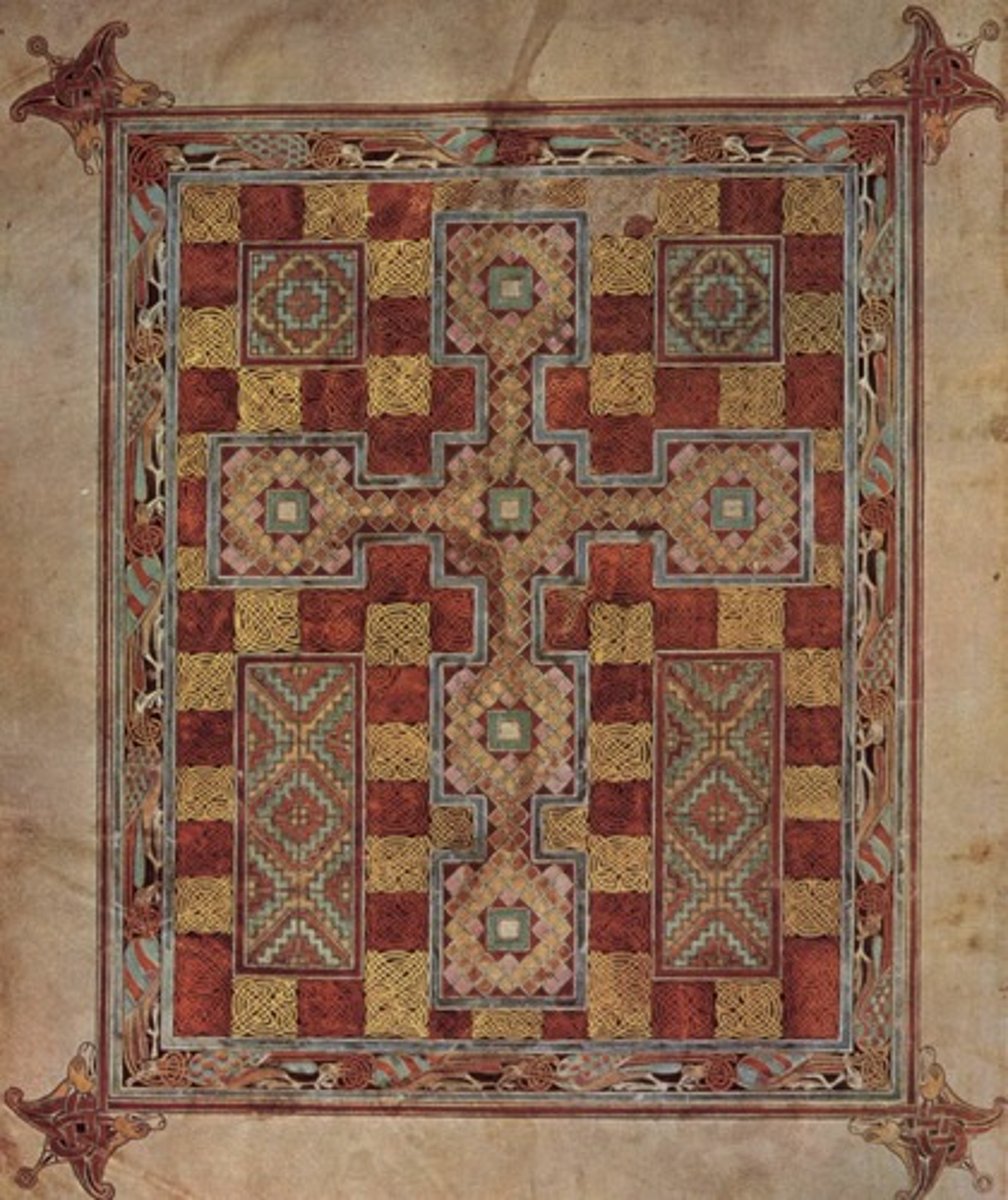
55. Lindsfarne Gospels
Form:
-illuminated manuscript
Content:
-cross carpet page: cross forms out of chaos, creates illusion of 3D in which viewer can lose themselves in contemplation
-portrait page (luke): holds quill/looks prepared to write, gold halo (divinity), ox above his head, robe with purple and streaks of red
-incipit page (Luke): it "begins", animal life, spiral forms, swirling vortexes
Function:
-earliest known translation of the Bible
Context:
-created by monks

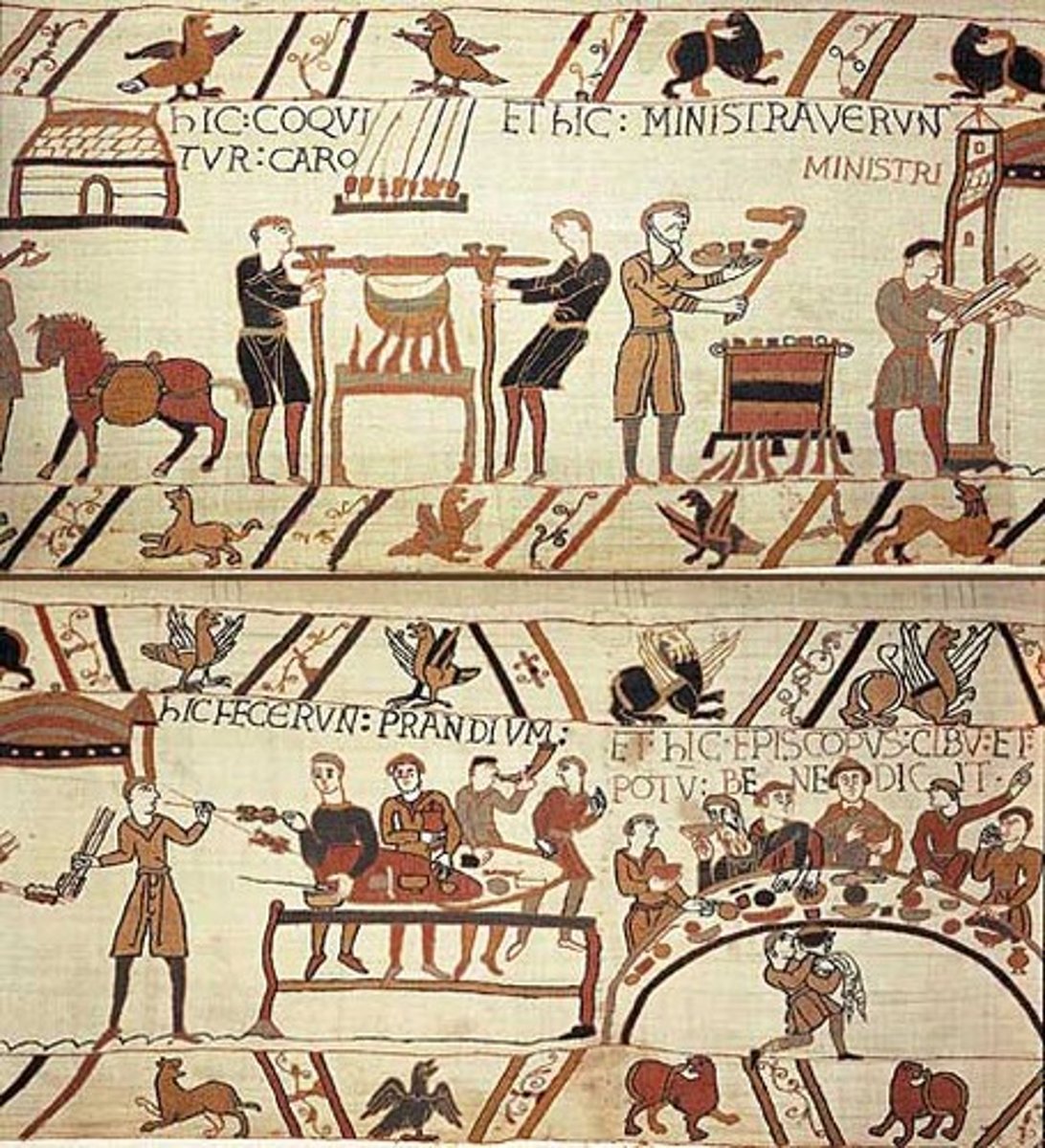
59. Bayeux Tapestry
Form:
-embroidery on linen
-Romanesque (English or Norman)
-2/3 of a football field in length
-continuous narrative
Content:
-a great epic
-2 main scenes
-story of William's conquest of England in the battle of Hastings
-Haley's Comet
Function:
-show Norman conquest
Context:
-Cantebury, NW France
-commissioned by Bishop Odo
-1066-80 CE (11th century)

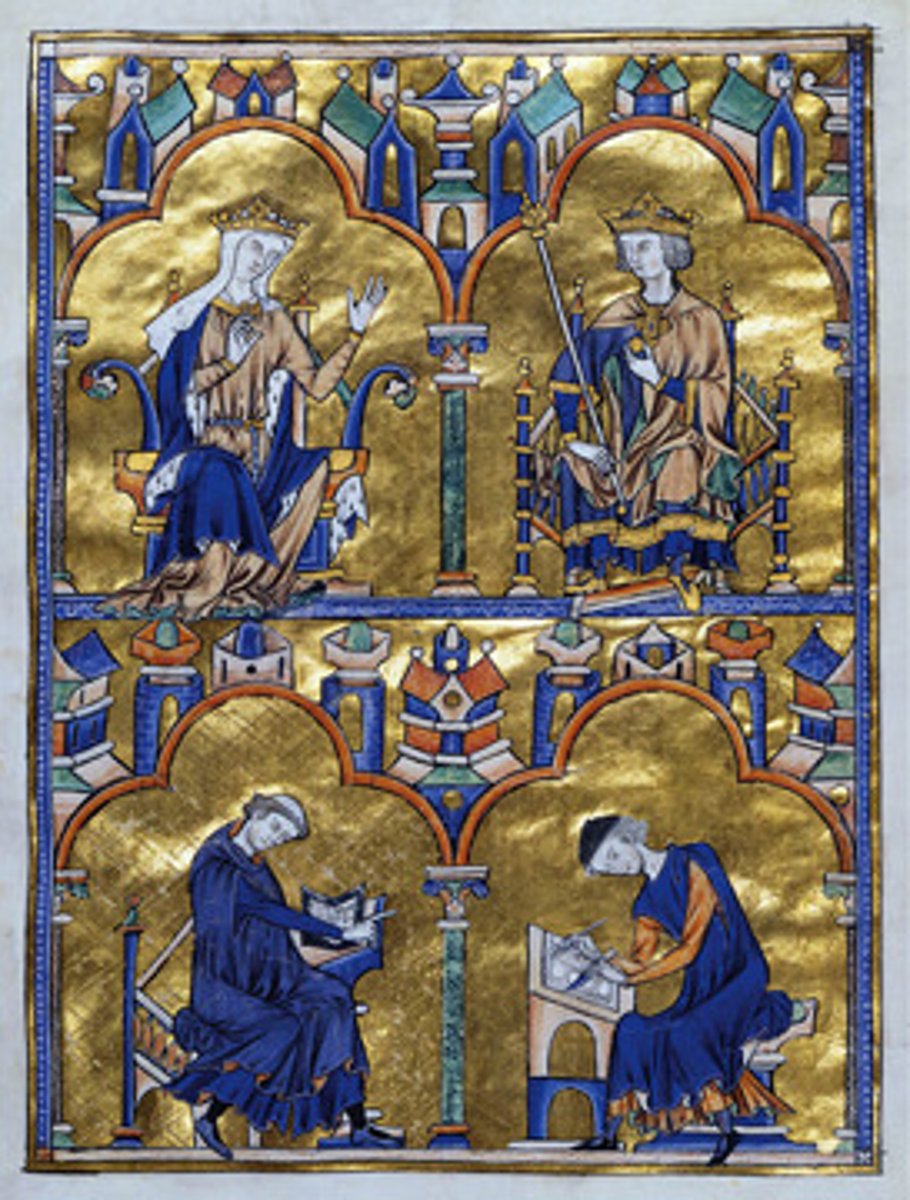
61. Bible Moralisees
Form:
-dedication page
-Gothic
-gold leaf, tempera, ink on vellum
-illuminated manuscript
Content:
-King Louis IX
-Blanche of Castile
-passages from Old and New Testament
Function:
-made for Frnech royals' home (King Louis IV)
-create a moral through visionary readings
Context:
-Paris, France 1225-45 CE (center of learning and bookmaking)

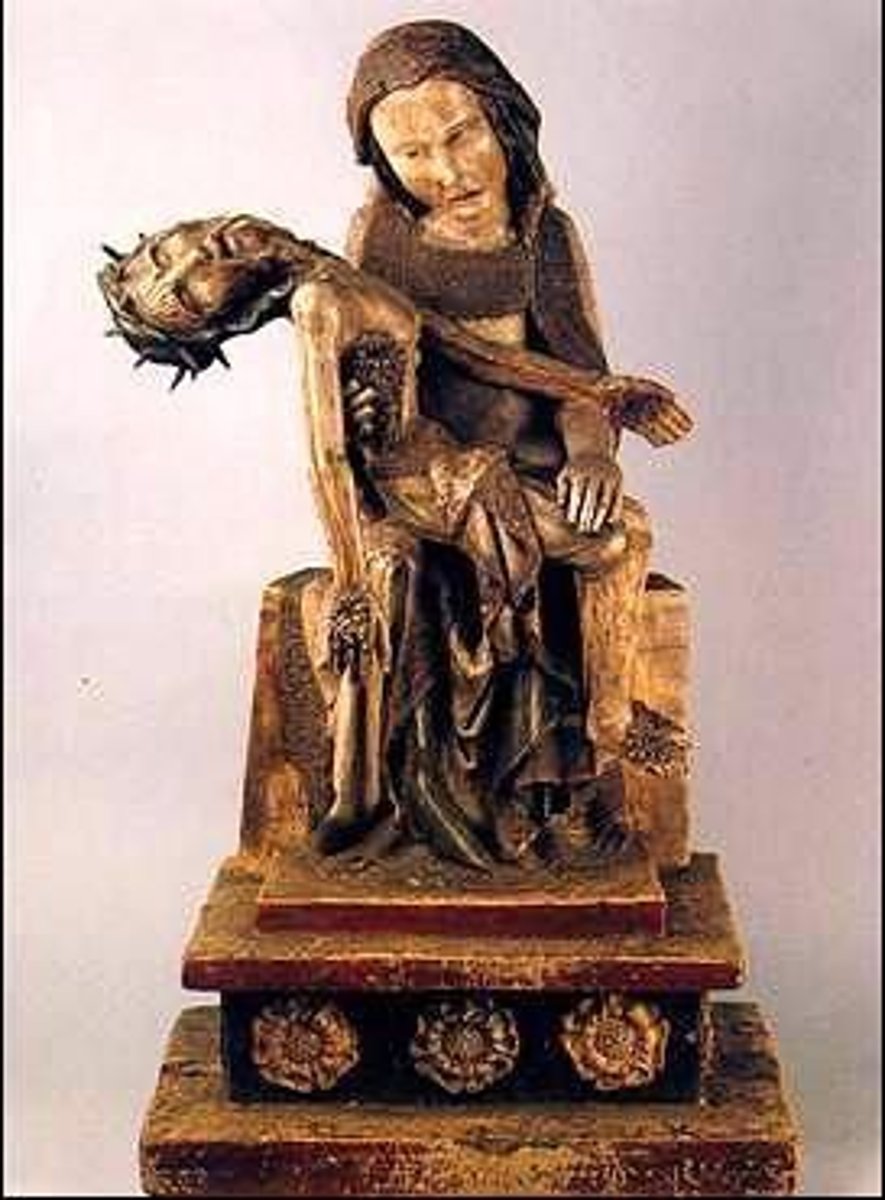
62. Rottgen Pieta
Form:
-painted wood
-Medieval/Gothic and realistic
Content:
-Mary holding her dead son after Cruxifiction
-Mary is pained and anguished
Functions:
-versperbils (German devotional)
-feel the pain she feels
-intended to be used in contemplation and prayer
-devotional image
-shows them closer to the humanity side
Context:
-Bonn, Germany 1300
-German Gothic

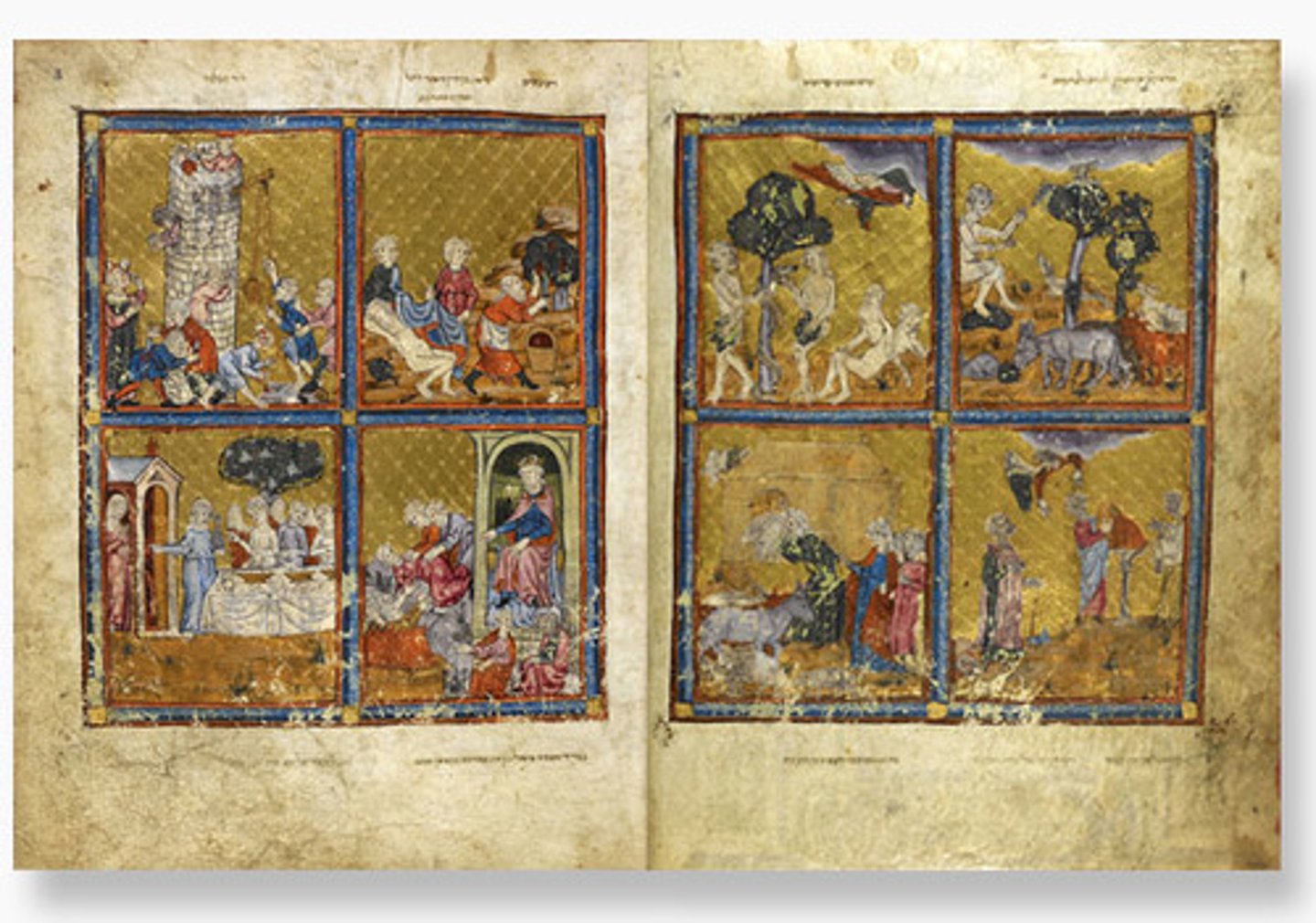
64. Gold Haggadah
Form:
-illuminated manuscript
-pigments and gold leaf on vellum (animal)
Content:
-Left: plagues of Egypt
-Middle: scenes of liberation (Israelites leave)
-Right: Passover
Function:
-book used by a wealthy Jewish family to tell the story of Passover around the sedar table each year
Context:
-Late Medieval Spain 1320 CE
-similar to Christian Gothic manuscripts

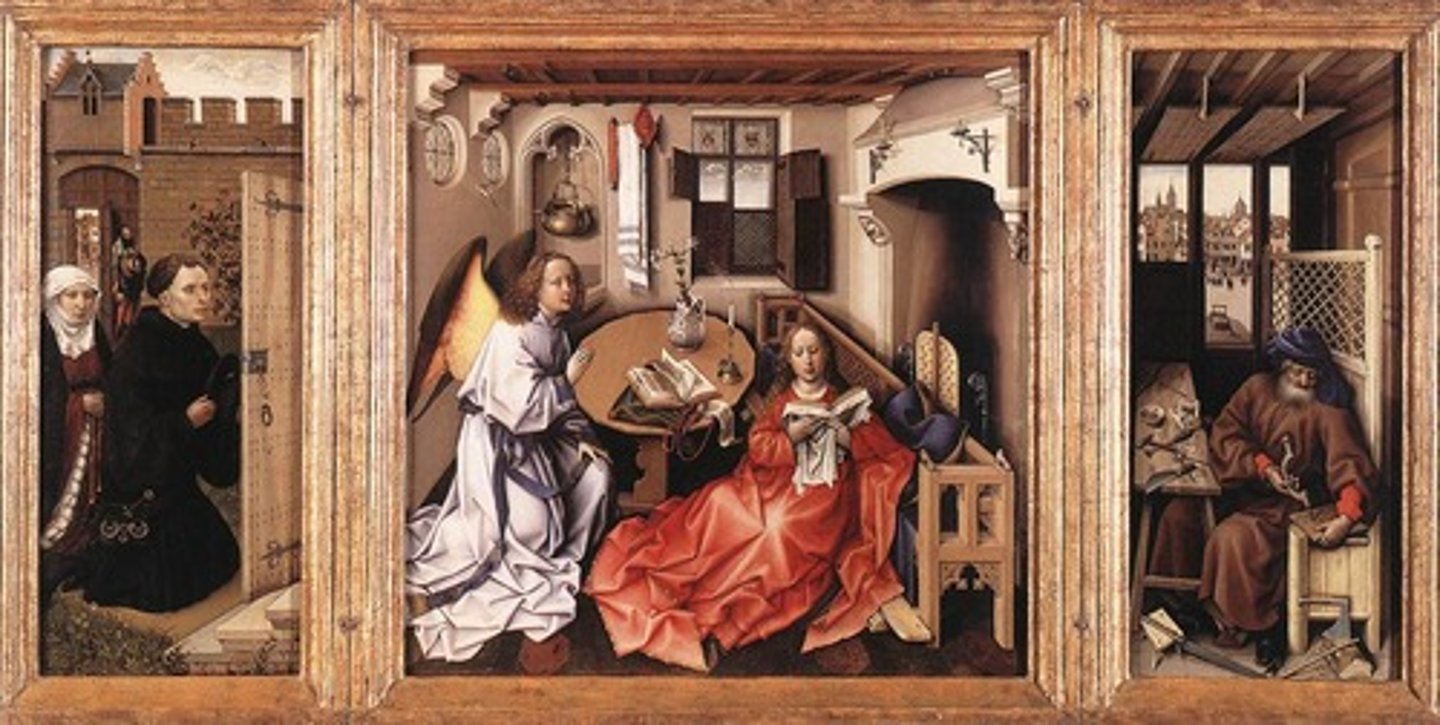
66. Annunciation Triptych
Form:
-triptych
-altar piece (portable)
-renaissance
-Flemish (oil paint, glowing, vivid color)
-hyper reality/hyper clarity
-closed during the week, open during mass
Content:
-scene of the Anunciation
-Holy Spirit and Jesus coming through window
-couple asking for divine intervention
-Joseph on right making mouse traps
-Mary laying down on pew
-image of Chris coming from the window going to Mary's womb
Function:
-private devotional place
Context:
-workshop of Robert Campin (master of flemalle)
1427-32 CE (15th century)
-Flemish Renaissance

68. The Arnolfini Portrait
Form:
-oil on wood
-Renaissance
Content:
-betrothal (engagement)
-dog represents wealth and fidelity
-barefeet- something sacred taking place
-Patron saint of domesticity (St. Margaret
-Vaneyck signature and reflection in mirror
-witnesses of the marriage shown in the mirror
Function:
-shows status, wealth, power
Context:
-artist: Van Eyck
-1434 CE (15th century)
-Flanders

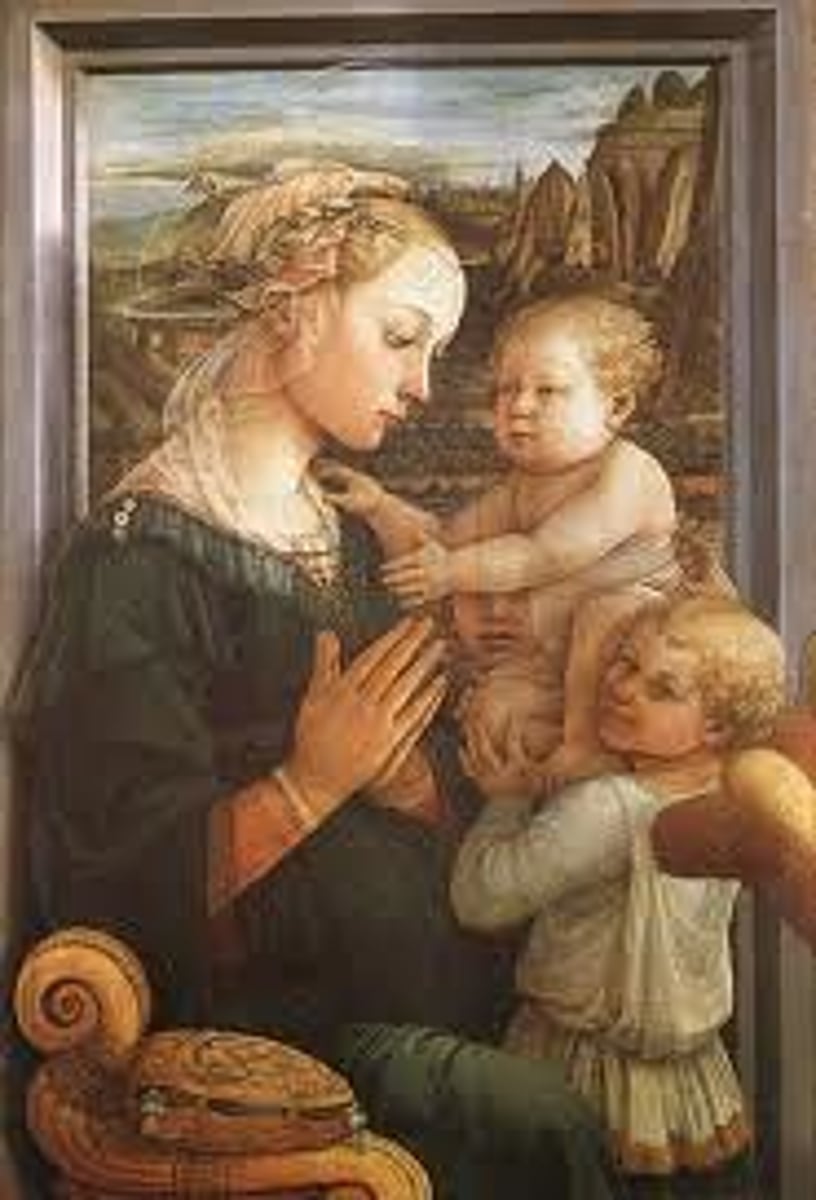
71. Madonna and Child with Two Angels
Form:
-tempera on wood
-3D figures
-sense of space
-elegant lines/curves
-humanism
Content:
-all humanized (mischievous look)
-Mary's halo slowing going away (divinity fading)
-Mary youthful/beautiful
-landscape through window (Flemish background)
-pearls (symbol of immaculate conception
Function:
-relate more to viewers by making humanistic images
-connect us to Mary and Jesus
Context:
-artist: Fra Filippo Lippi (monk of Carmelite order) teacher of Botticelli
-1465 CE
Early Renaissance Italy

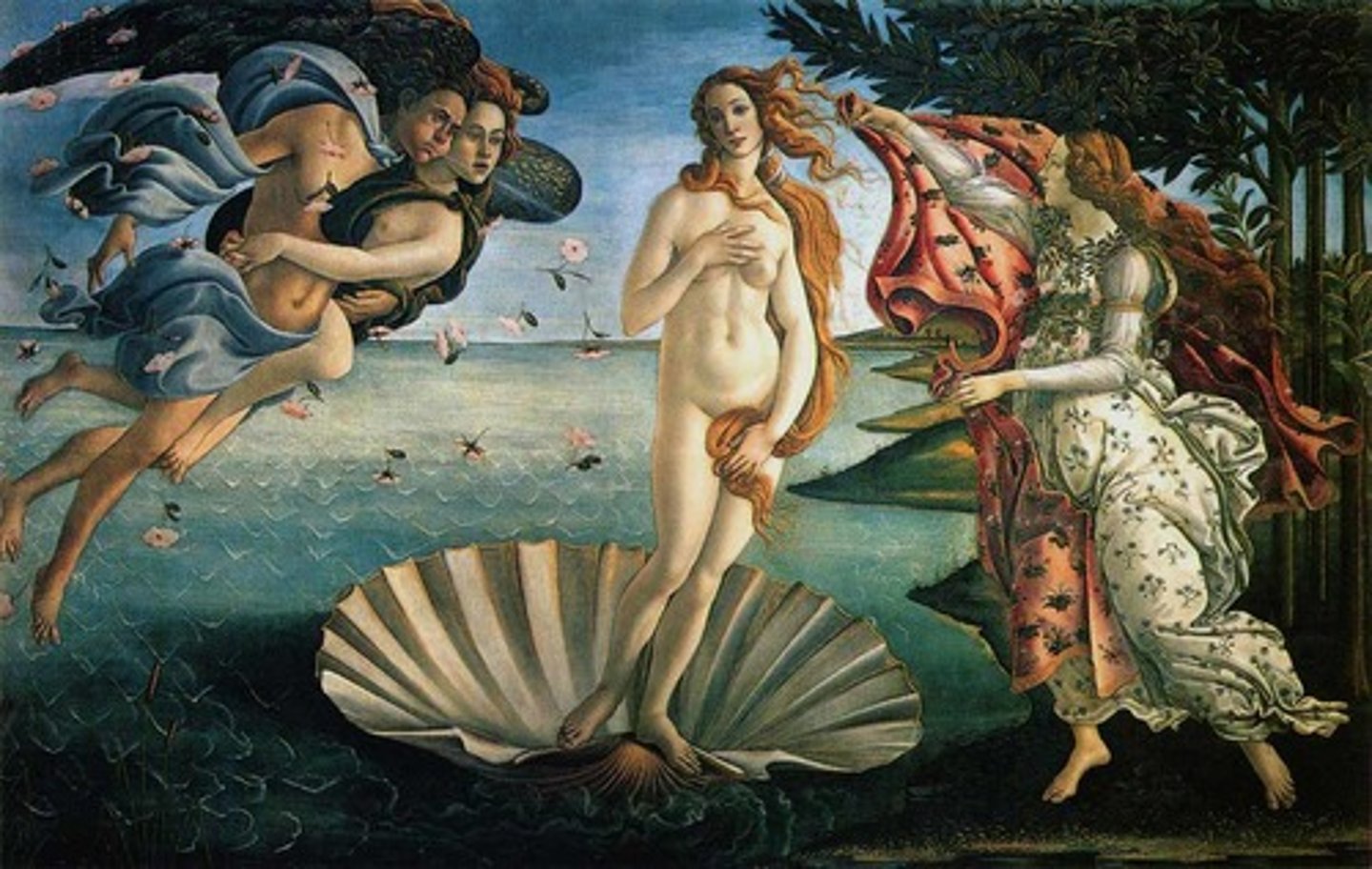
72. Birth of Venus
Form:
-tempera on cancas
-curvy body (flexibility)
-neoplatonic love (classical and Christian)
-sense of pattern and beauty
Content:
-Venus standing on seashell
-born by the sea fullgrown
-couple intertwines; pushing Venus to land
-someone on shore ready to receive Venus with cloth
-floating figures
-Earthly and celestial love
Function:
-probably wedding gift
Context:
-artist: Sandro Botticelli
1484-86 CE
-Medici commission
-Venus is goddess of love
-Early Renaisasnce

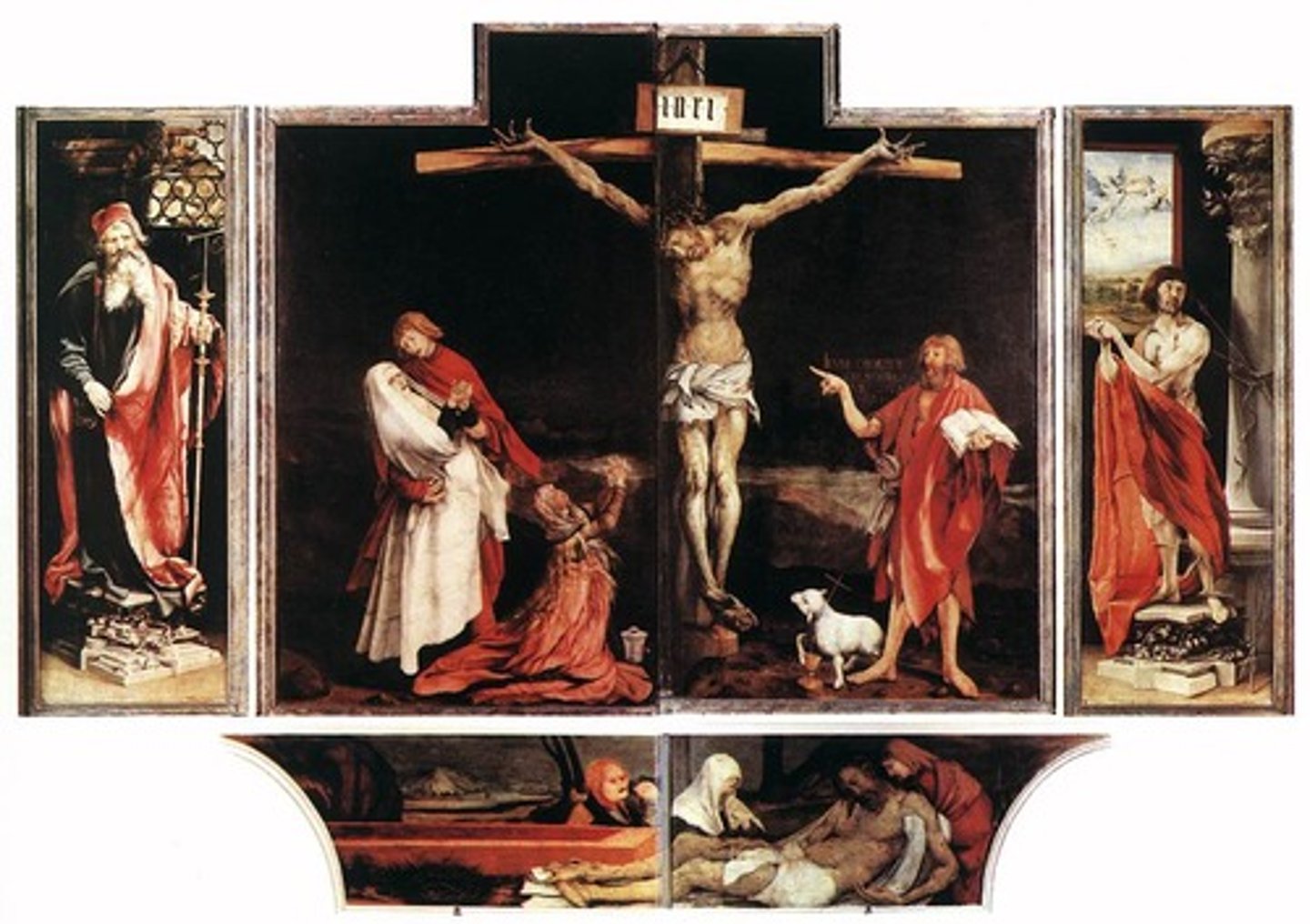
77. Isenheim Altarpiece
Form: oil on wood, diptych (two panels/wings)
Content:
-predella: base of the altarpiece
-1st panel: shows Jesus suffering on the cross symbolizing the suffering of the patients
-2nd panel: shows Jesus resurrection
-3rd panel: statue of St. Anthony who was patron saint of the hospital
Function:
- made for a hospital to relate their suffering to Jesus' suffering in order to make them feel better
Context:
- no longer in situ
- Boarder of France and Germany
-Made by Matthias Grunewalkd in 1512-1516 CE
79. Allegory of Law and Grace
Form:
-woodcut, letterpress
-Protestant
-German text
Content:
-written in people's voice
-left: being chased by death (shows 10 commandments)
-right-washes over with Holy Spirit (can only be saved by God's grace
Function:
-propaganda during Reformation
-debates between Catholics and Luthers on how to get to heaven
Context:
-artist: Lucas Cranach the Elder (High Renaissance North 1530 CE)
-German; worked with Martin Luther

86. Henri IV Recieves Portrait of Marie de 'Medici
Form:
-oil on canvas
-floating figures
-part of a cycle
-shows an event in her life
-Catholic Baroque
Content:
-Henry IV present the picture of Marie that confirmed his religious identity; married a Catholic queen
-marries her so he can have a son and recreate him in a Catholic way
-Jupiter and Juno gives blessing to them
Function:
-"early harmony"
-part of a tribute to her life
-show that their marriage was official bc portrait
-shows political power, sophistication, and stability
Context:
-Peter Paul Rubens (Flemish painter)
-from Marie de' Medici cycle displayed in the Louvre
-1621-25 CE Flemish Baroque

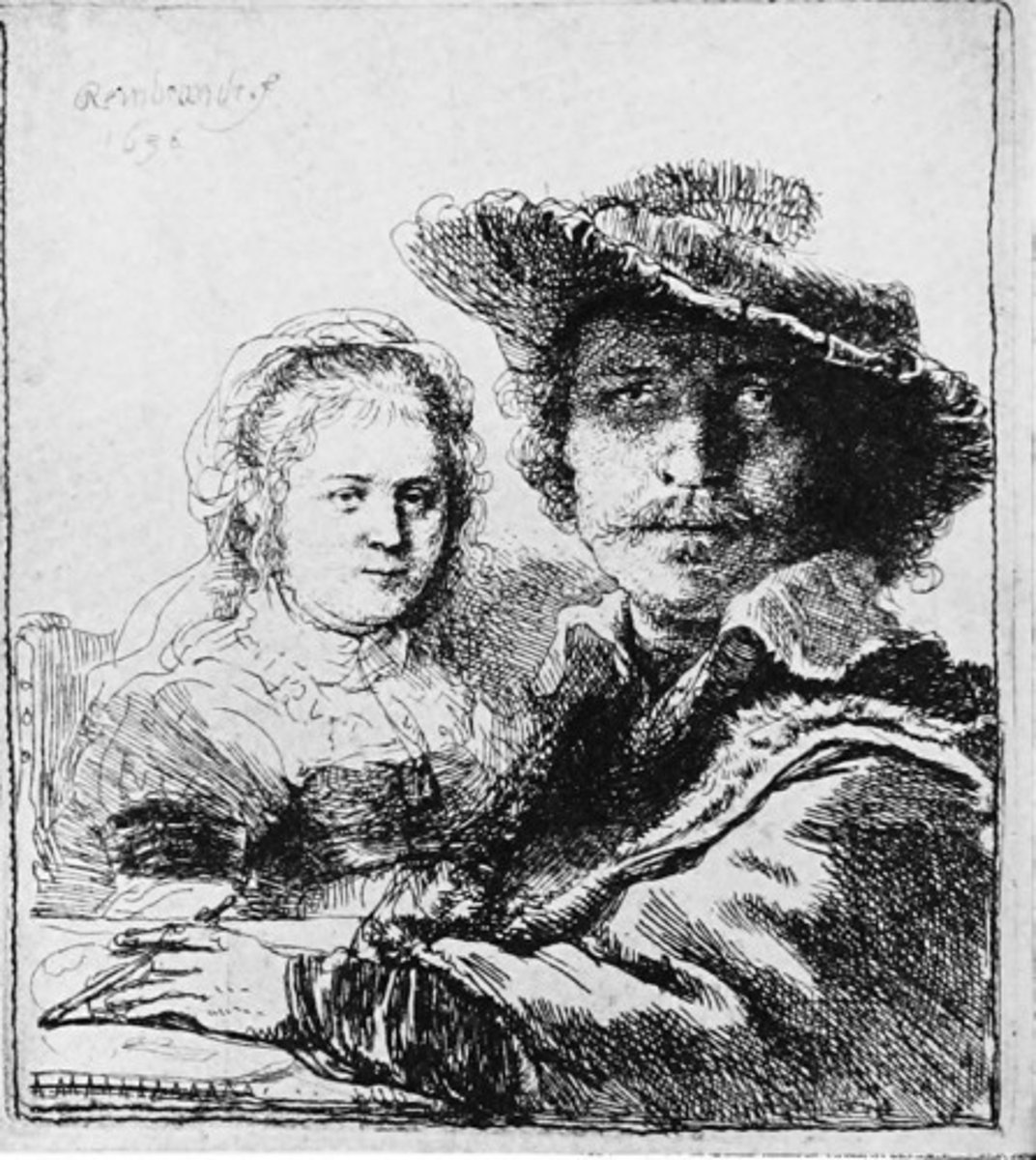
87. Self Portrait with Saskia
Form:
-Dutch Baroque
-difference in emphasis on the figures
-exists in 3 different states
-rich tonal quality
-abrupt spatial construction
-etching (exposing metal)
-genre: private movement between husband and wife
-small scale
Content:
-Rembrandt and wife in historical clothing
-wife, Saskia died at the age of 30 (only piece he did of her)
-Rembrandt drawing his drawing
-exploring who he is
Function:
-self portrait/marriage portrait
-role playing
Context:
-Rembrandt 1636
-he is mostly a portrait maker
-Dutch, Amsterdam
-Dutch Baroque

96. Fruit and Insects
Form:
-still life
-Baroque
-oil on wood
-colors, detailed
Content:
-insects, fruit
-wheat and grapes= Jesus?
-bringing different compositions together
Function:
-harvest in autumn
-microscopic organisms: used microscope to study these organisms
Context:
-artist: Rachel Ruysch (Dutch arist; last famous still painter)
-Florence, Italy 1711 CE (18th century)
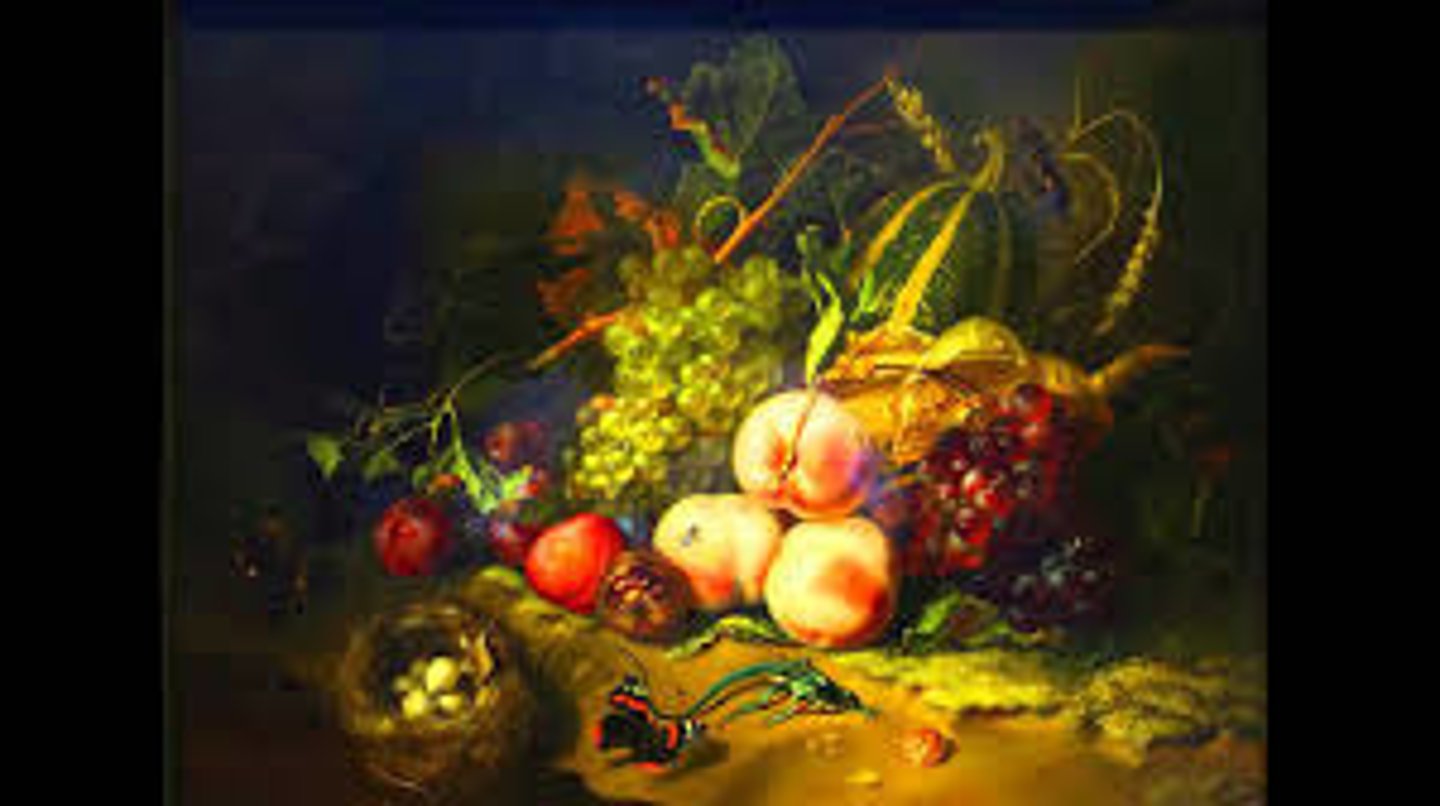

181. Petra, Jordan: Treasury and Great Temple
Form:
-cut rock
-treasury carved into a cliff
-red sandstone walls
-lower platform paved with hexagonal stones
Content:
-complex water system
-temple on platform like apadana and built on hillside
-buried dead in tombs cut out of sandstone cliffs
Function:
- city of powerful nomadic Arabic tradespeople (Nabataeans)
-important commercial center
-connected silk road and other trade routes
Context:
-found in 1812
-probably made around 400-100 CE
-ancient city in Jordan
-influence of Greek and Roman
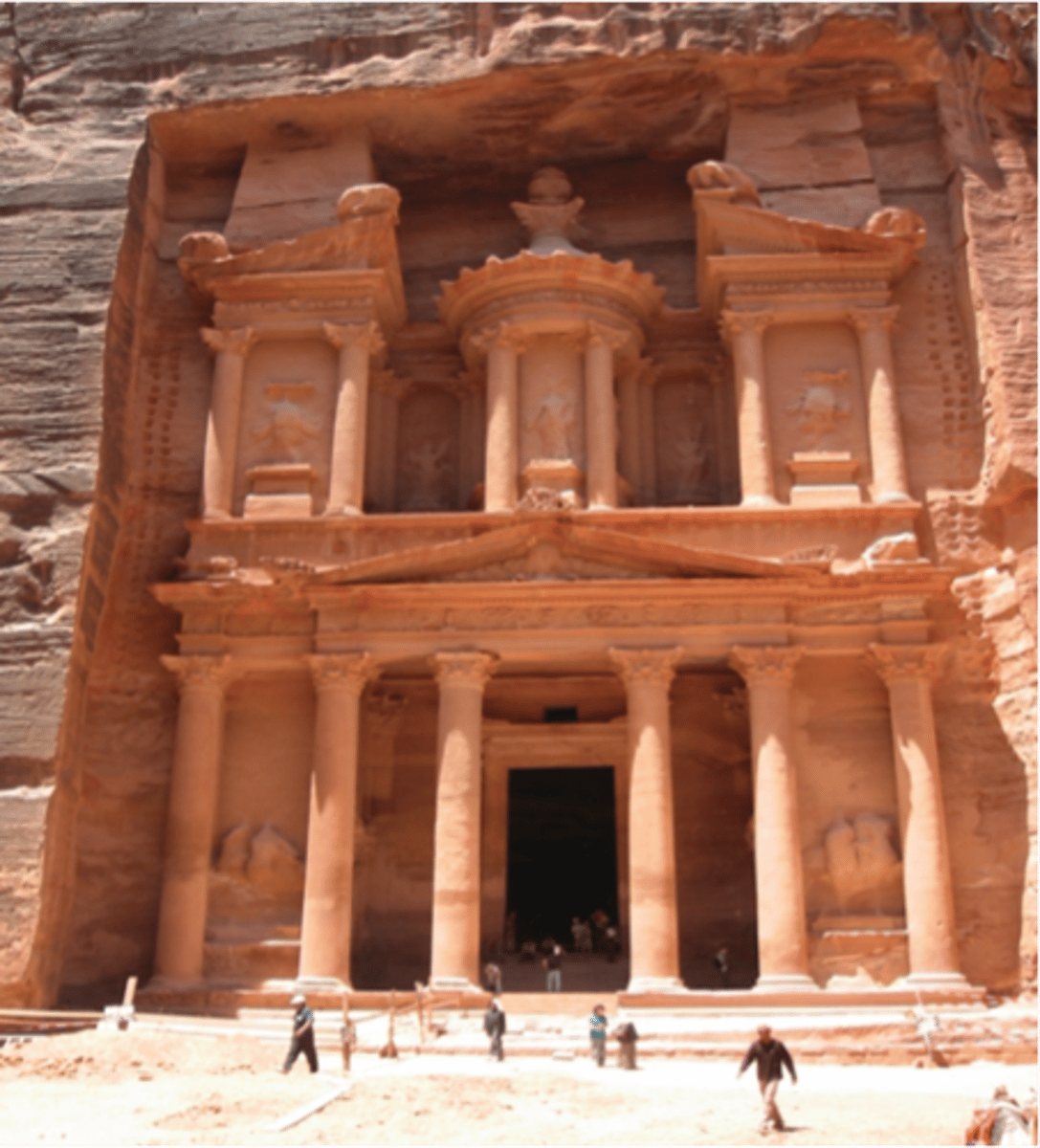

182. Buddha
Form:
-cut rock with plaster and polychrome paint
- carved into niches on the side of a cliff
Content:
-staircase that ascended up to the Buddha's shoulder for travelers
-mutras: hand gestures
-hair in bun and big ears
Function:
-was the largest Buddha sculpture in the world until it was blown up in 2001 by Taliban
-travelers were Buddhists who offered gifts of thanks or prayers to the statue
Context:
-Bamiyan, Afghanistan- Gandaran 400-800 CE
-located on crossroads of the Silk Road
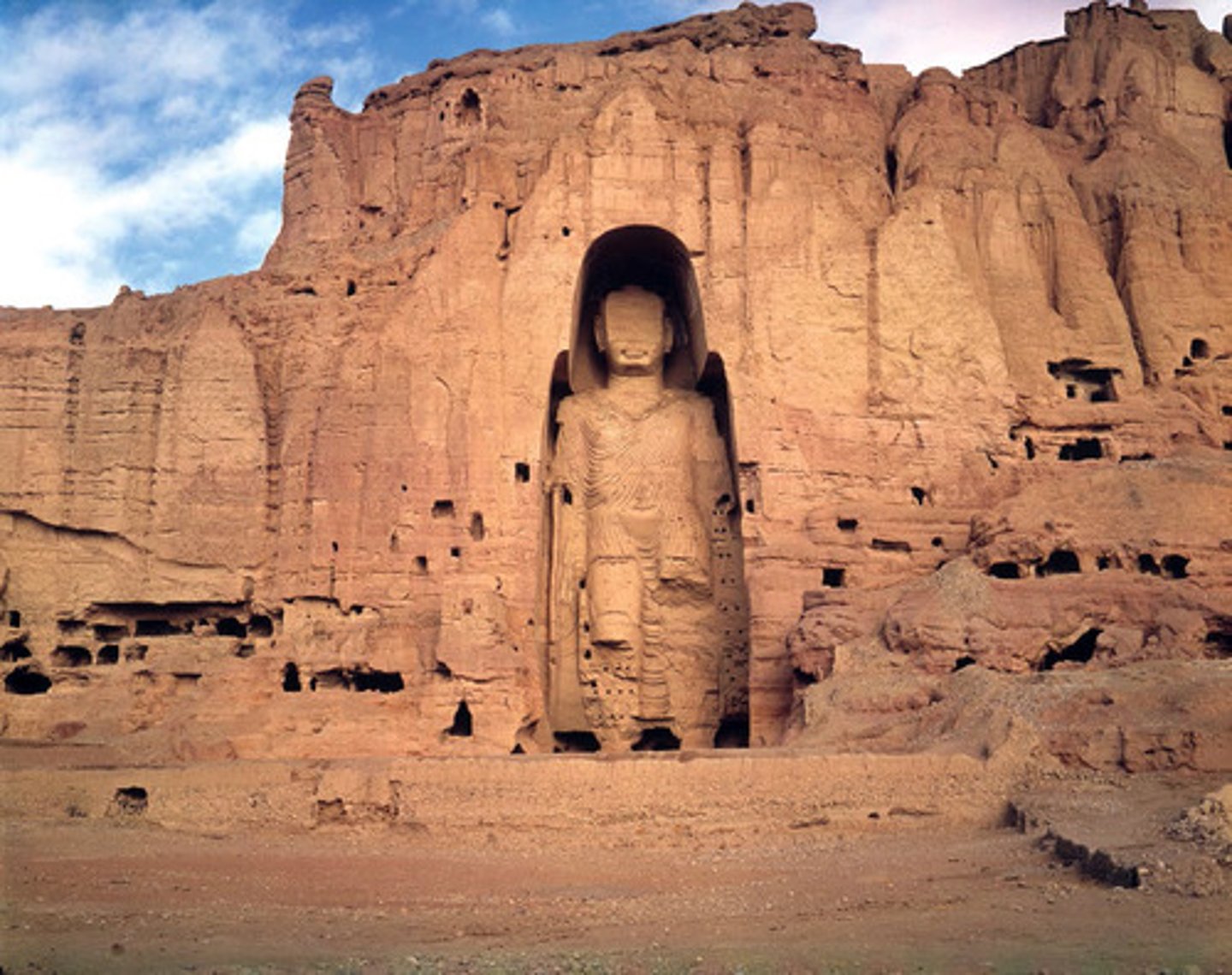

183. The Kaaba
Form:
-calligraphy on cloth covering the cube (kisna)
-corner points on the cardinal points
-granite with silk curtain
-set in a mosque
Content:
-kaaba in middle of Mecca
-kaaba filled with pagon god statues and the Black Stone
Function:
-holds relics of Muhammad
-walking meditation in counter-clockwise motion
-place of pilgrimage-hajj (one of the 5 pillars)
Context:
- Mecca, Saudi Arabia
-pre-Islamic monument
-631-632 CE
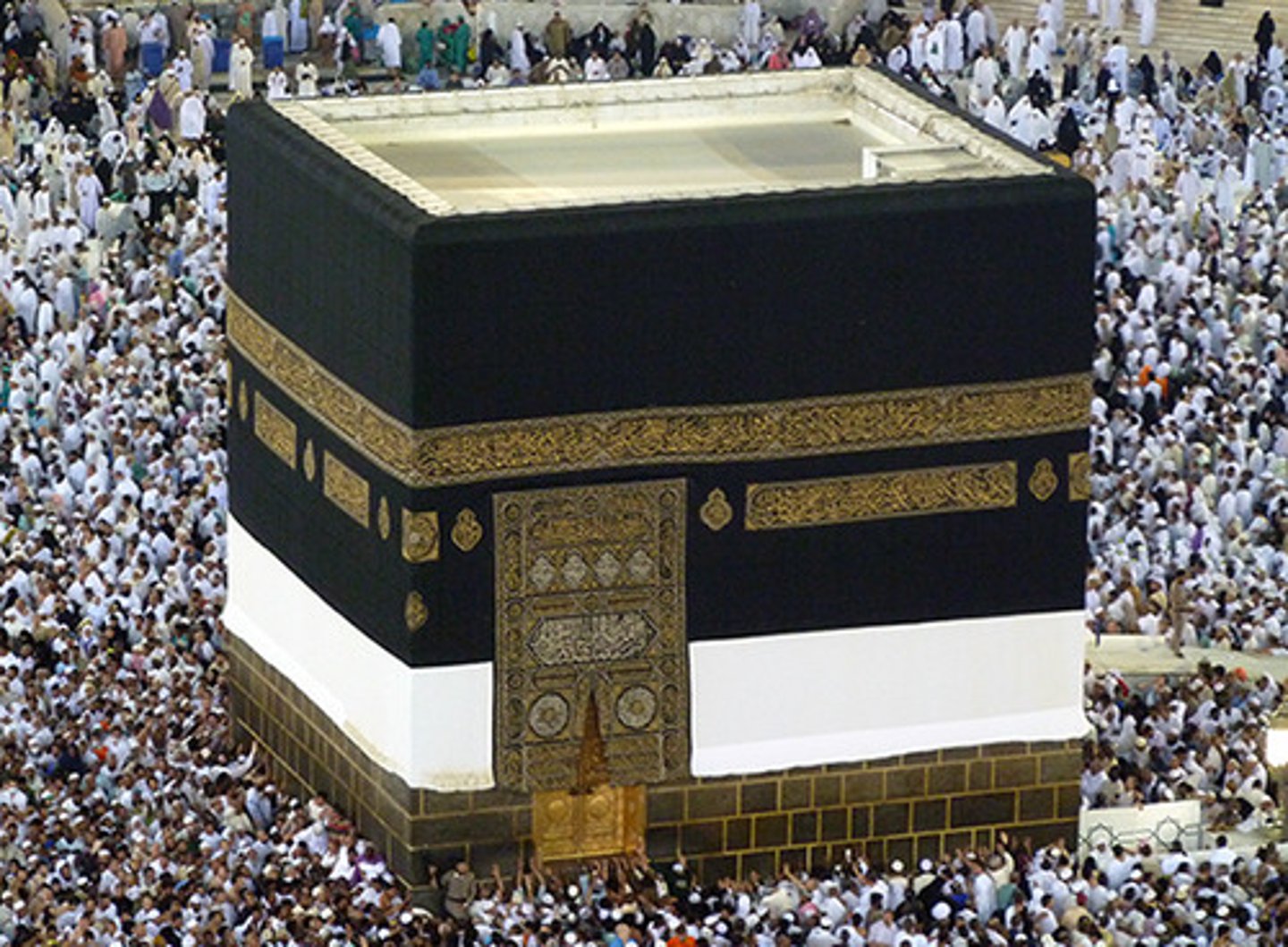

184. Jowo Rinpoche
Form:
-gilt metals with semiprecious stones, pearls, and paint
Content:
-various offerings, candles
Function:
-sacred image of Tibet
-idea is that you don't have to meditate or site a mantra; just seeing this will be a religious experience itself
-pilgrimage site
-believed to have ability to grant wishes
Context:
-enshrined in the Jokhang Temple
-Llasa, Tibet- Yarlung Dynasty
-brought to Tibet in 641 CE
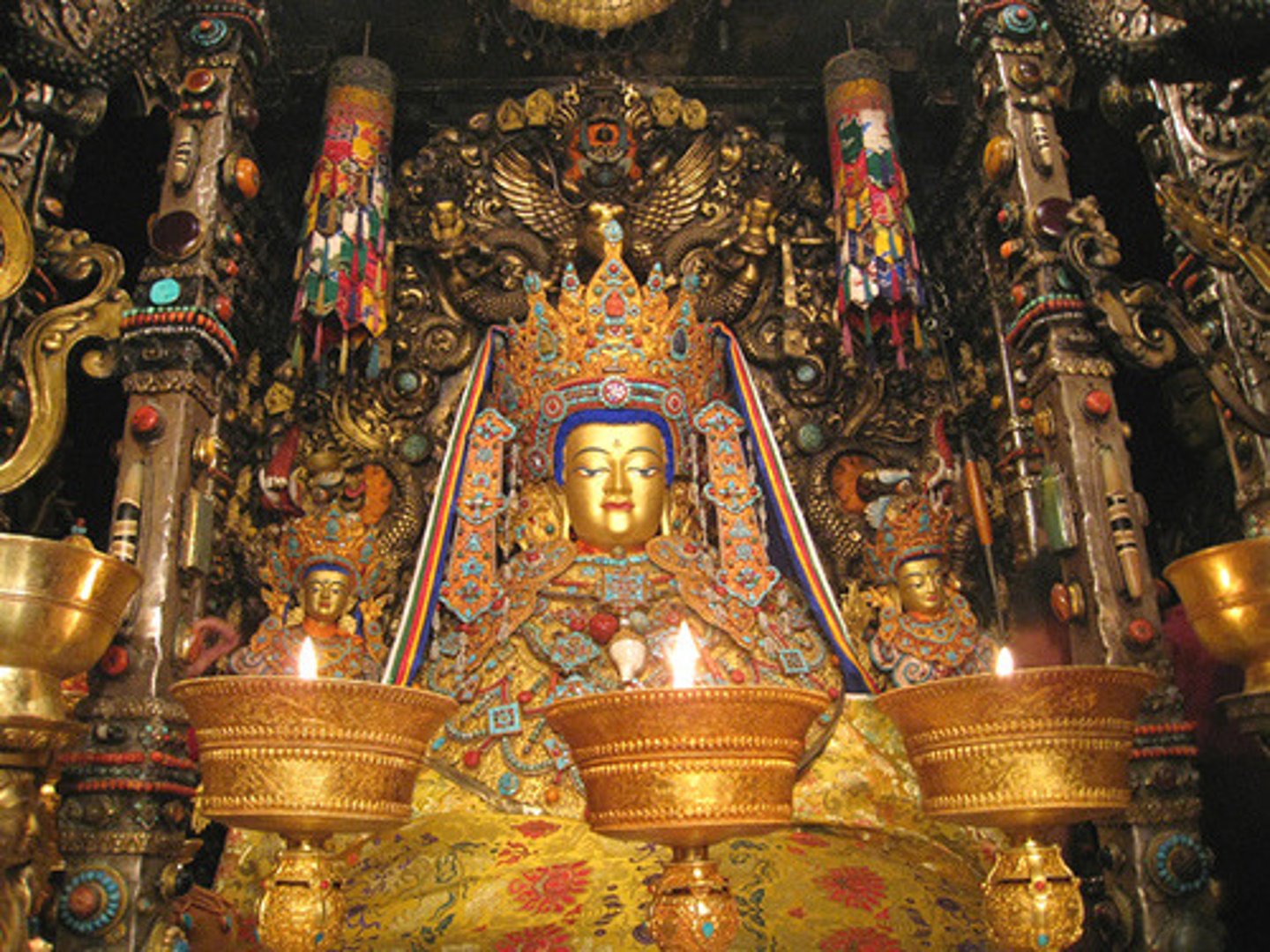

185. Dome of the Rock
Form:
-octagonal centralized plan
-arcades, colonades
-heavily decorated on outside
-stone masonry decorated
-wooden roof and cermaic tile
-bronze dome
Content;
-building surrounding a rock
-mosaic contains no human or animal figures
Function:
-building over rock
Context:
-Jerusalem, Palestine 691-692 CE
-Umayyad- islamic
-rock is where Abraham prepared to sacrifice his son
-Mohammed's night journey
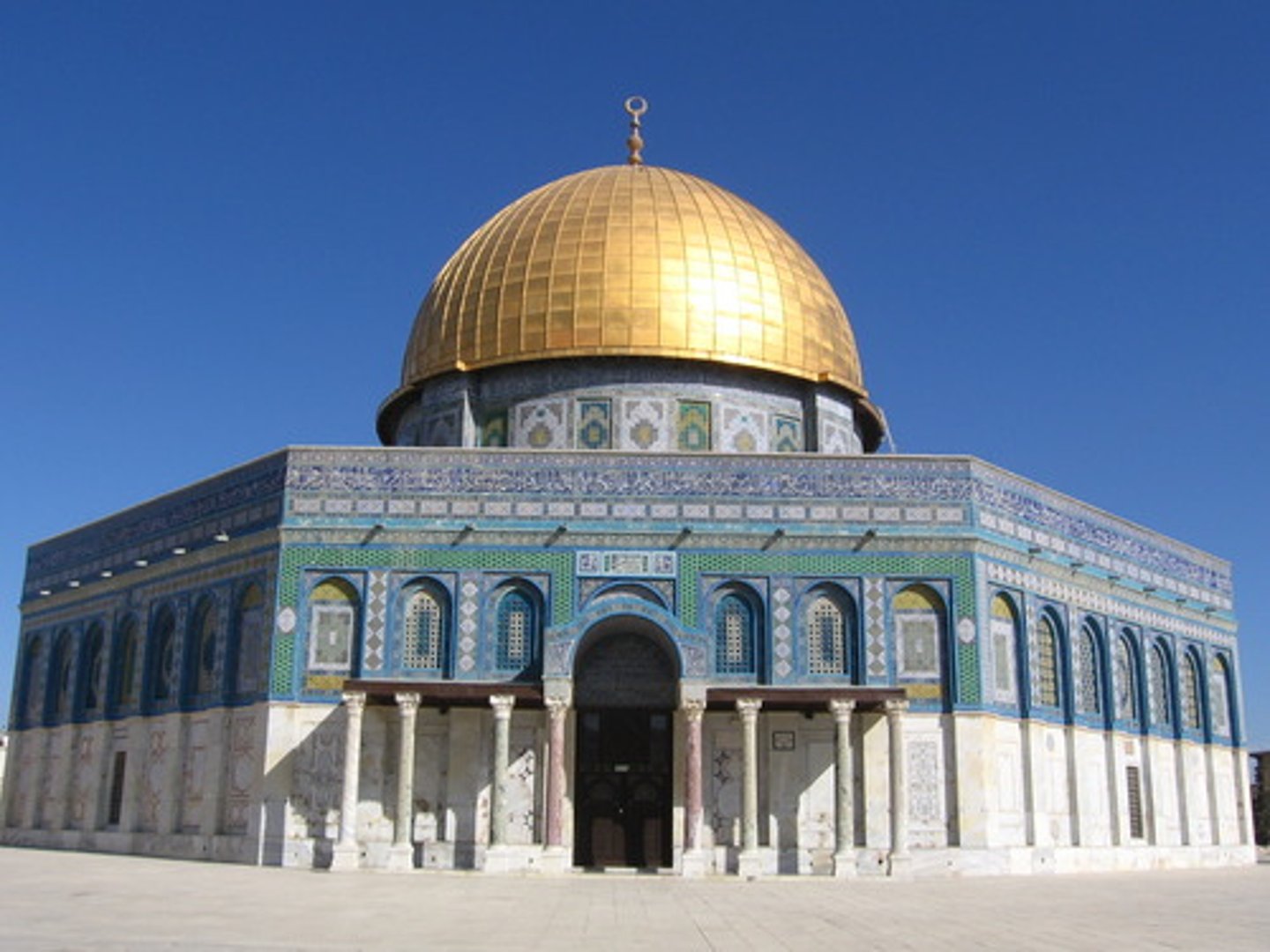

186. Great Mosque (Masjid-e Jameh)
Form:
-stone, brick. wood. plaster, and glazed blue ceramic
-each entrance corbelled
Content:
-built around a courtyard with 4 arches coming from it
-madrassa- place for Islamic instruction
-iwan: vaulted space that opens on one side to the courtyard)
Function:
-prototype for future iwan-mosques
-connects political, commerical, social, and religous activities within the city
Context:
-Isfahun, Iran- 700 CE
-Islamic, Persian- Timrud and Safavid dynasties
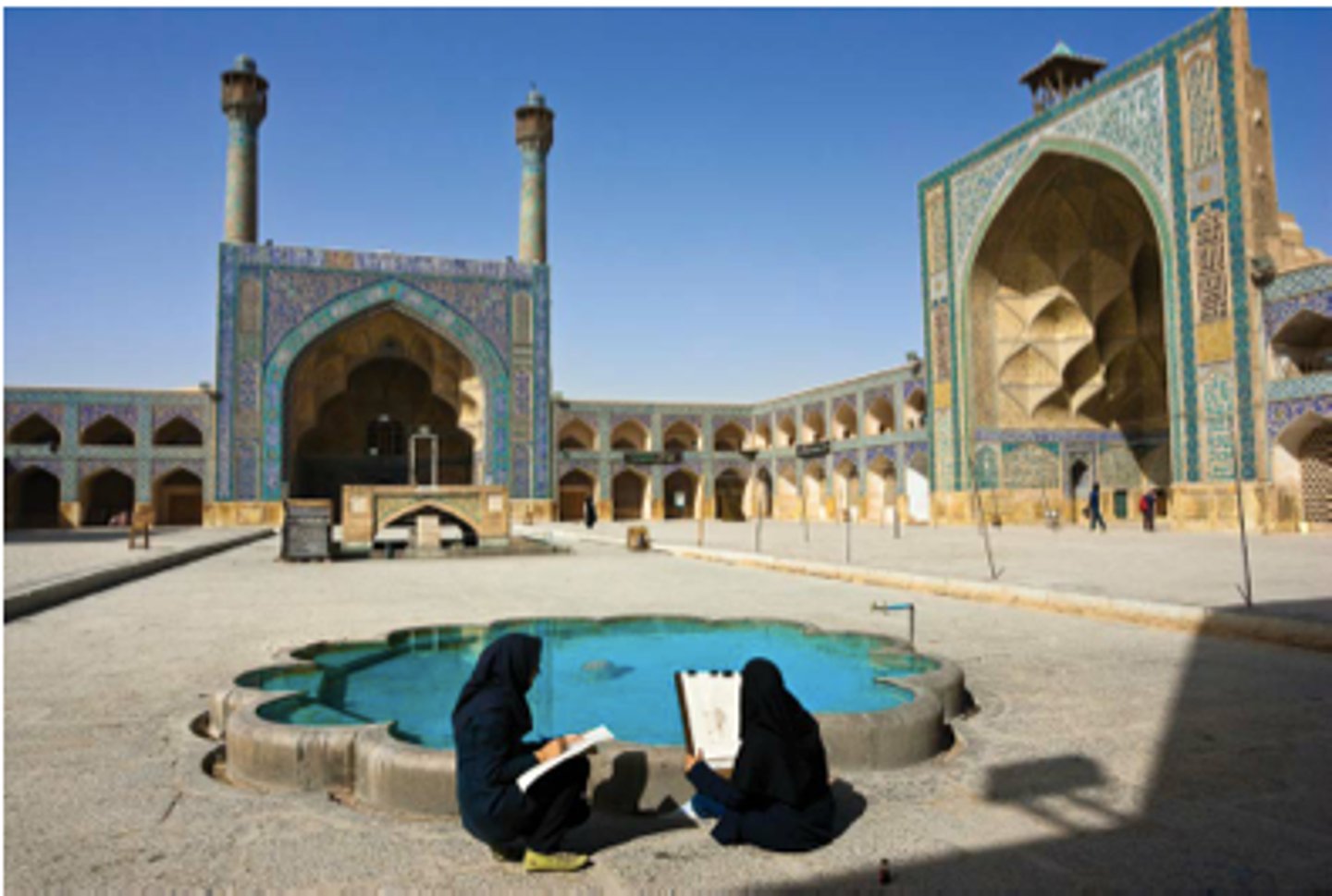

187. Folio from a Qu'ran
Form:
-ink, color, and gold on parchment
-wide page rather than vertical like normal
Content:
-brown Arabic ink read from right to left
-vegetal and geometric motifs because animal and human figures not allowed
Function:
-made for a wealthy patron
-Mus'haf: a codex Qu'ran (bound version)
Context:
-Arab, North Africa, or Near East- Abbasid
-8th-9th century

188. Basin
Form:
-brass inlaid with gold and silver
-very detailed, interconnected
Content:
-battle scenes on interior
-sea animals interconnected designs
-men on horseback
-men hunting
-artist's signature (6 times)
Function:
-orginially: washing hands at ceremonies
-later: used for baptism in the French royal family (St. Louis)
Context:
-Mumluk artists
-1320-40 (14th century)
-Egypt and Syria
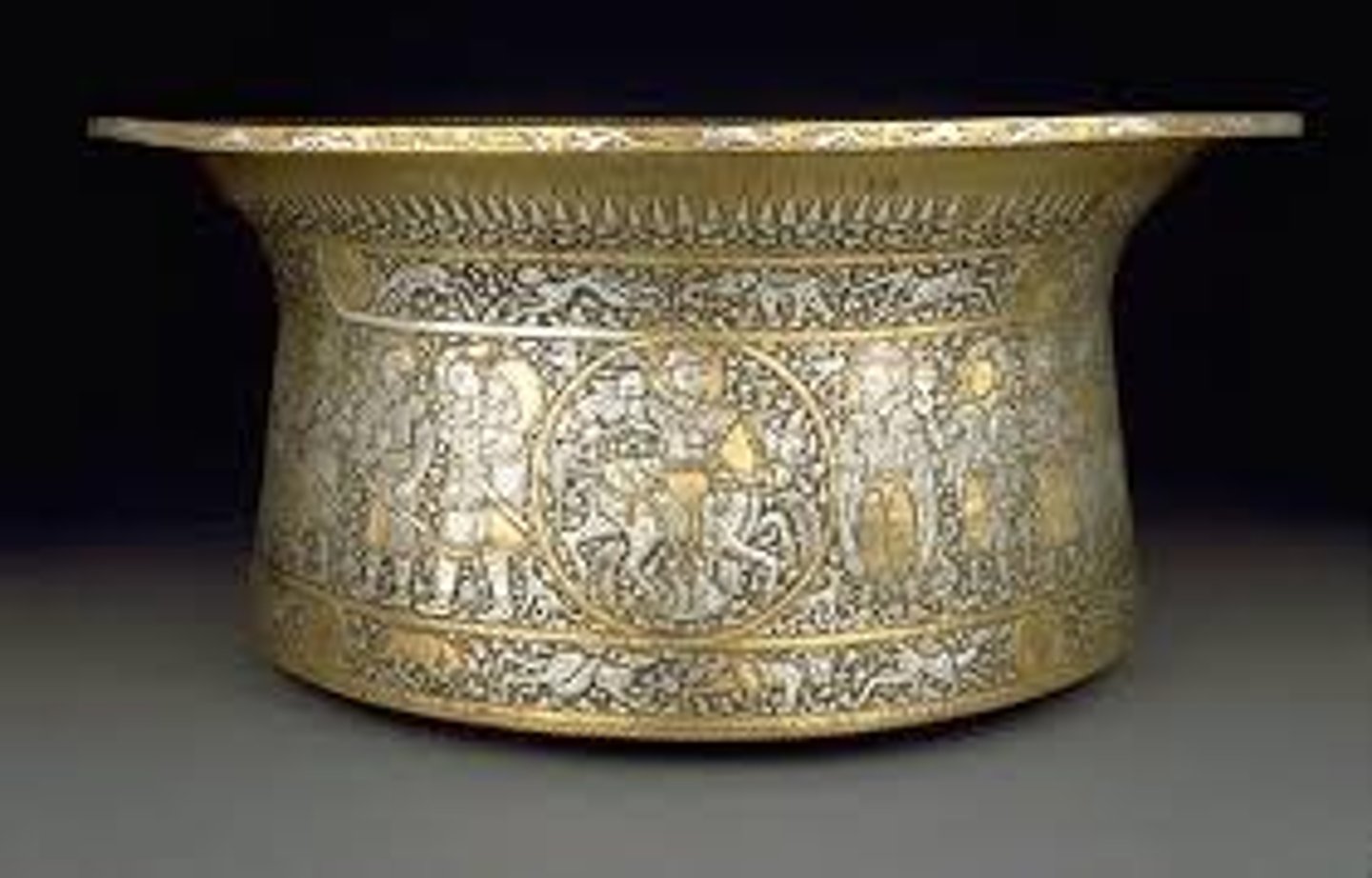

189. Bahram Gur Fights the Karg
Form:
-ink, opaque watercolor, and gold on paper
-shown wearing European clothing but background looks Chinese (combination of cultures)
Content:
-Bahram Gur went on the court of Hind disguised so he could observe the kingdom and its civilians
-king tricks him into showing his true identity and decided to send him away by making him slay a karg (horned wolf)- Barham pierces the wolf with arrows and cuts off his head
-this folio shows Bahram after he has defeated the wolf- confident and relaxed
Function:
-expresses political power attempting to legitimize the Elkhanid's claim to Iranian kingship
-shows the ideal king (crown and halo)
Context:
-folio from the Great II-Khanid
-1330-1340 CE (Islamic/Persian)
-from the Book of Kings
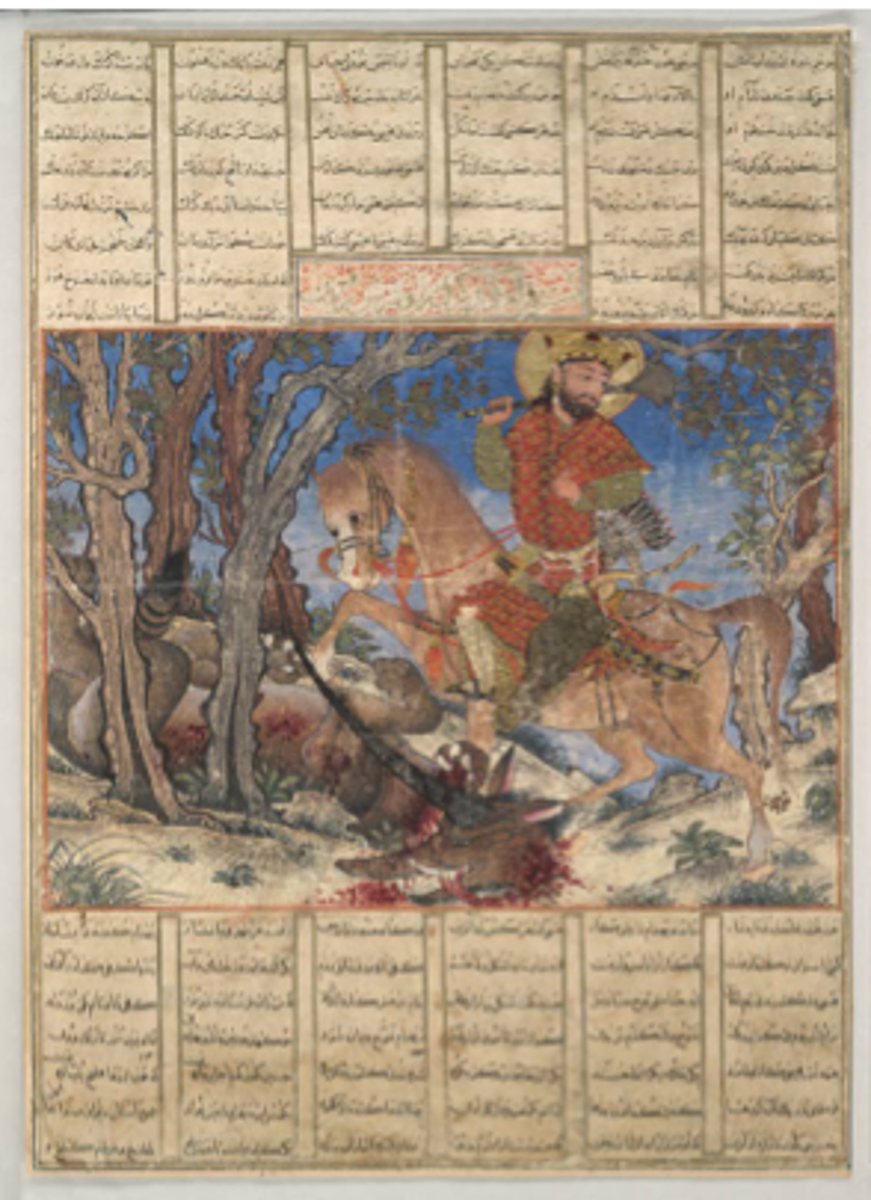

190. The Court of Gayumars
Form:
-ink, opaque watercolor, and gold on paper
-clothing identifies who they are not their faces
-minute scale drawing and detail
Content:
-opening page of the Shahnama
-Gayumar is surrounded by his son and grandson he looks down on the court to address them
Function:
-telling ancient history of Persia
Context:
-folio from Shah Tahmasp's Shahnama
-artist: Sultan Mohammad
-1522-1525 CE
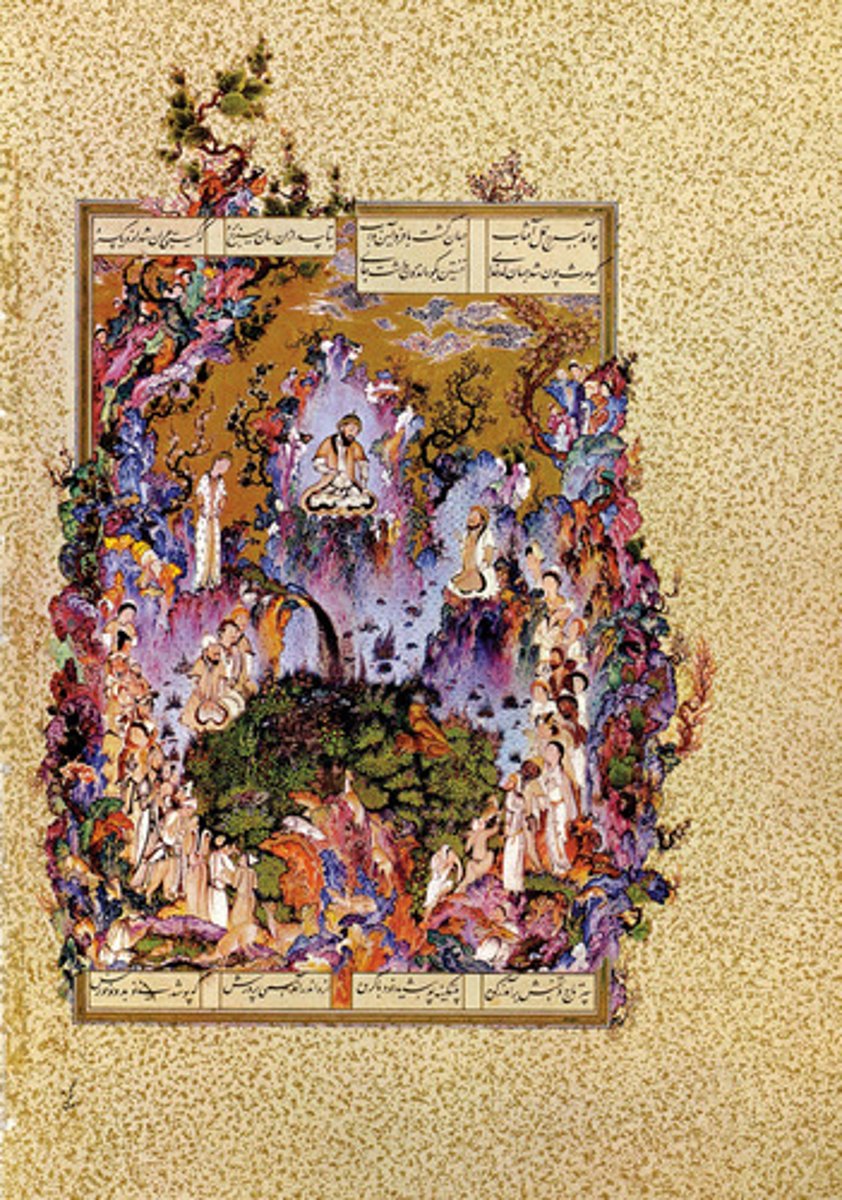

191. the Arbabil Carpet
Form:
-many many details
-silk and wool carpet
-central sunburst medallion creates illusion of a heavenly dome with lamps reflection in a pool of water full of lotus flowers
-slightly symmetrical
Content:
-two different lamps suspended from the ceilings
-one panel with inscription that tells you who made it and when
Function:
-made for the funerary shrine of Safi al-Din Ardabil
-prayer carpet
Context:
-Maqsud of Kashan 1539-40 CE
-one in a pair of carpets

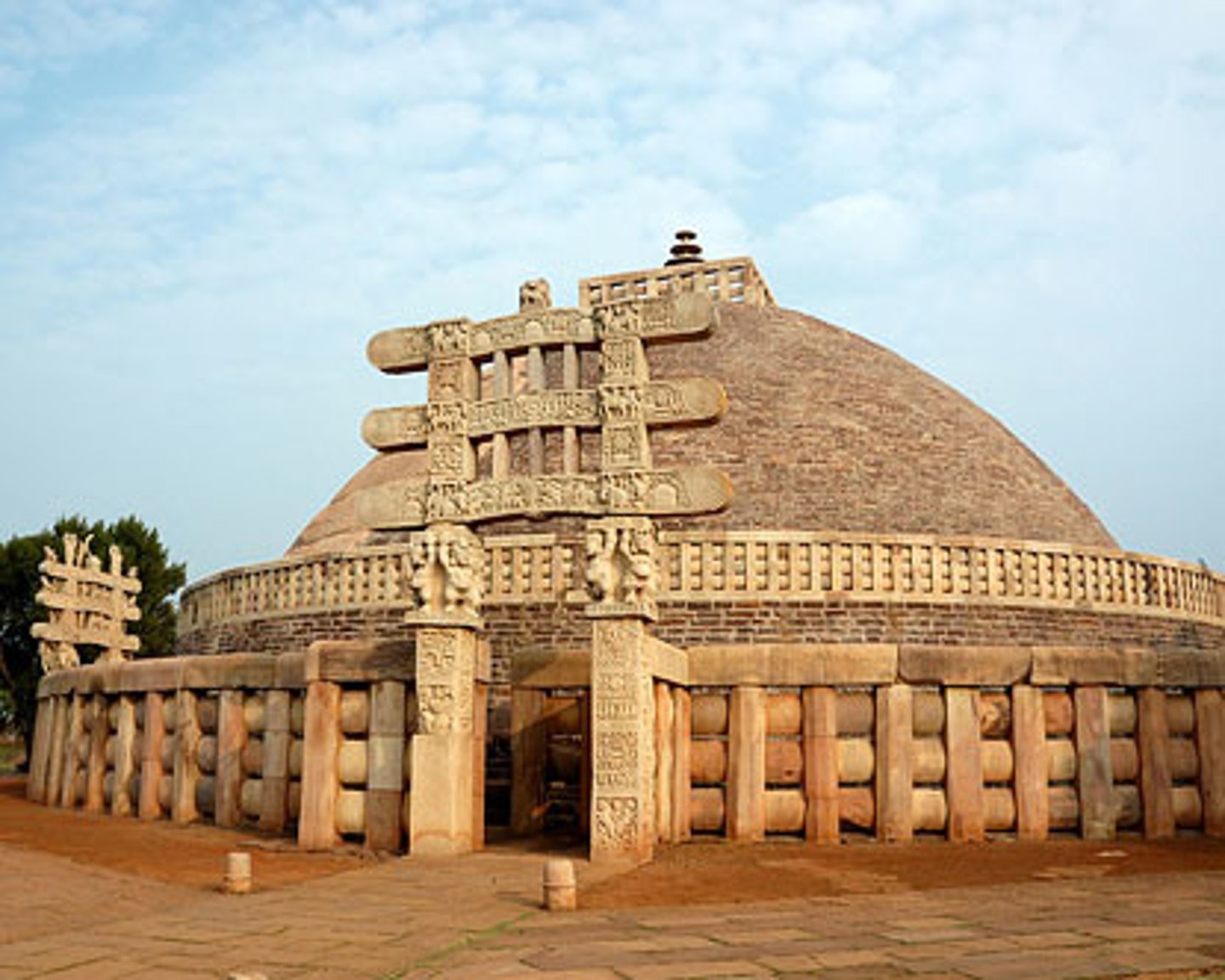
192. Great Stupa at Sanchi
Form:
-mandala plan (map of the cosmos)
-sandstone
Content:
-4 gateways
-hemispherical dome
-yakshis and yakshus- nature goddess/god
Function:
-monastery
-reliquary mound holds Siddhartha's relics
-symbolic representations of the Buddha (footprints, lion, elongated pathway, empty seat)
-no actual pictures of Buddha's face
-show inclusiveness of Buddhism
Context:
-300-100 BCE Madya Pradesh, India
-late Sunga dynasty

193. Terracotta warriors
Form:
-lifesize painted terra cotta warriors
Content:
-warriors with individual faces but same bodies
Function:
-funerary art
-express imperial power and authority
Context:
-Qin Dynasty in China
-221-209 BCE
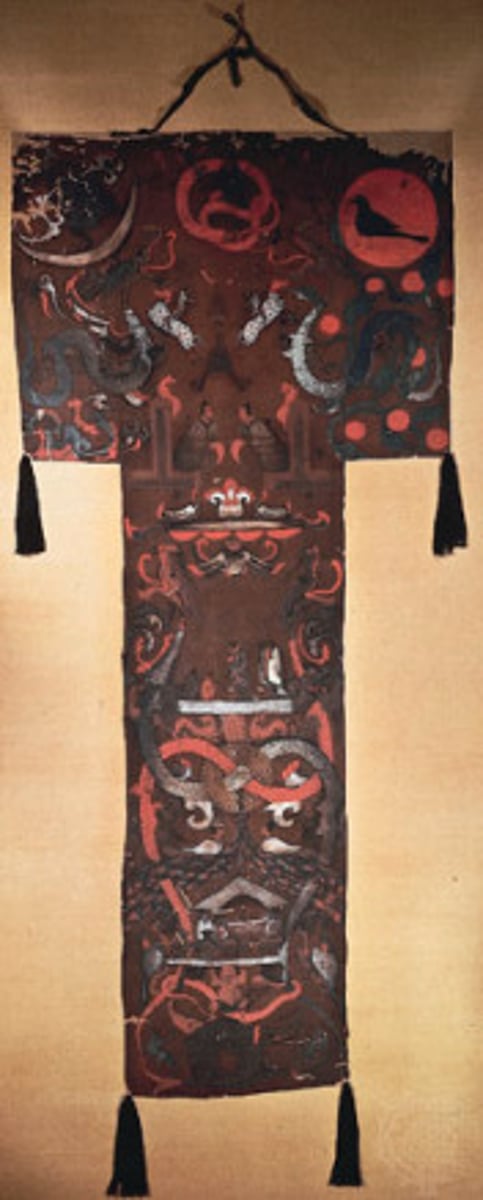
194. Funeral banner of Lady Dai (Xin Zhui)
Form:
-T-shaped painted silk banner
-over 6' long
-set in registers
-depth shown
-naturalistic scenes not just abstract shapes
-bi: disc with a hole that represents the sky
Content:
-registers represent the 3 layers of the universe
-Lady Dai stands on platform with her servants as she is pictured ascending into heaven
-dragons frame the scene on both sides
-sacrificial funerary rituals shown taking place in a mourning hall in the bottom register
Functions:
-put over the tomb
Context:
-Han Dynasty, China- 180 BCE

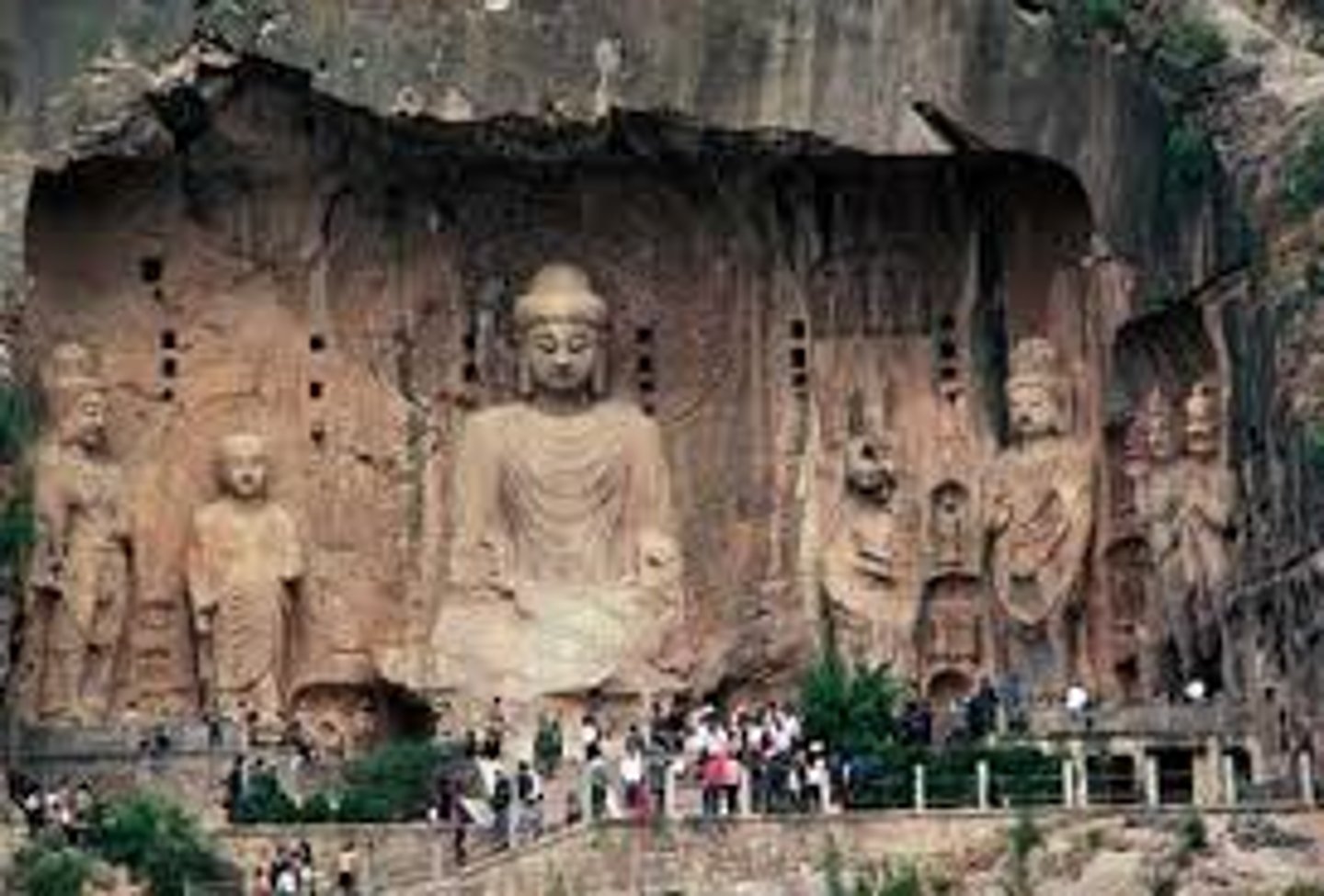
195. Longmen caves (grottoes)
Form:
-limestone
-guardians and vajrapani are more in motion and engaging figures
Content:
-110k Buddhist statues, 60 stupas, 2800 inscriptions carves on steles
-the Vairocana Buddha (representing the celestial Buddha) with bodhisattva, a heavenly king, and a thunderbolt holder on the sides
Function:
-signifies the arrival of Buddhism in China
Context:
- Luoyang, China- Tang Dynasty
- 493-1127 CE

196. Gold and jade crown
Form:
-metal work with gold and jade
Content:
-3 prongs in the back; prongs look like antlers coming out the sides
-jade pieces hanging down- connected by thin wiring
Function:
-queen crown
Context:
-found in tomb of a queen
-Silla Kingdom, Korea
-Three Kingdoms Period
-5th-6th century CE

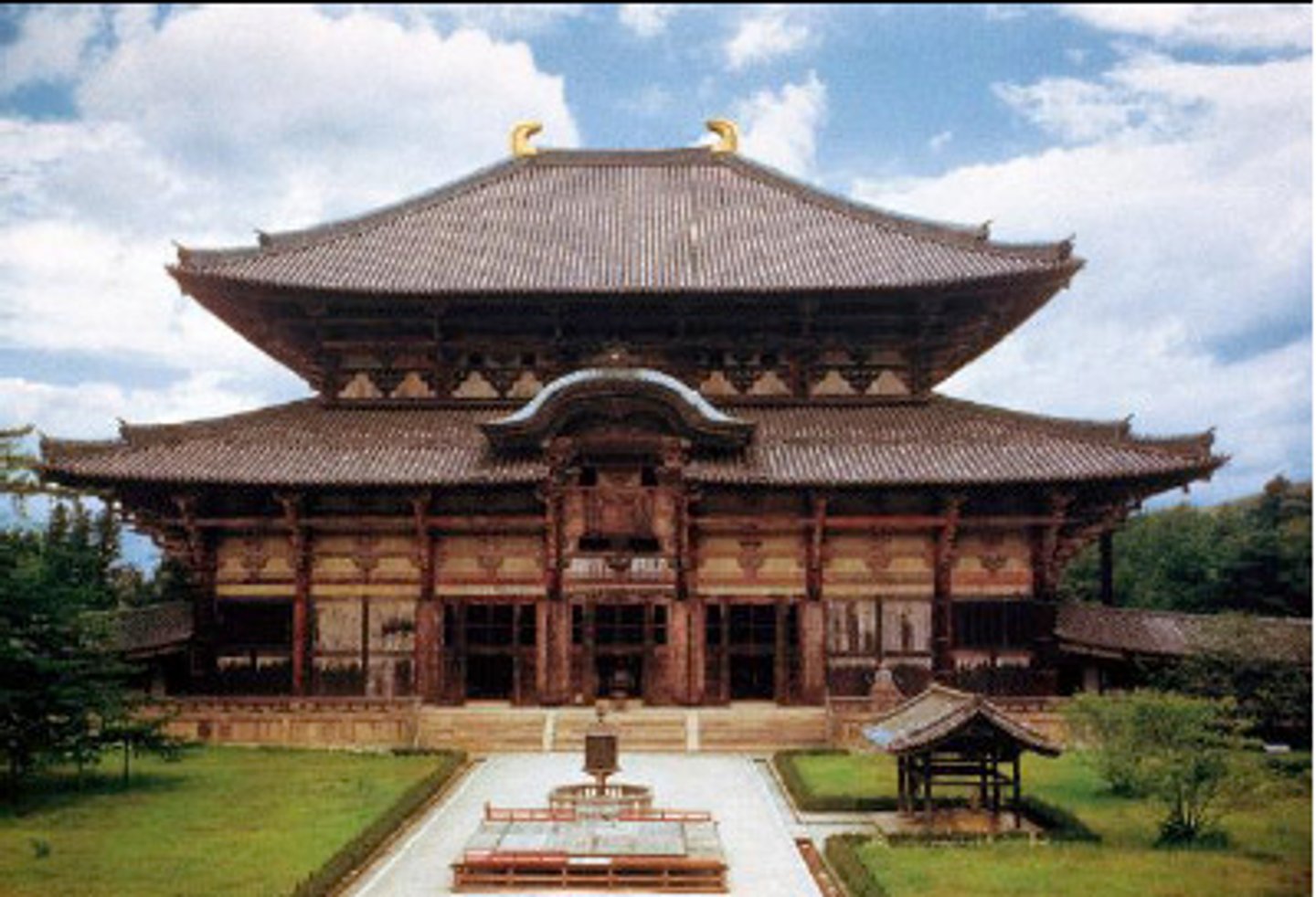
197. Todai-ji
Form:
-bronze and wood (sculpture)
-wood and ceramic roofing (architecture)
-bracketing system to support the roof
-massive pillars
-contrapposto stance of the Nios (powerful, dynamic bodies)
Content:
-50' tall wood statues: Ungyo (open mouth) and Agyo (closed mouth)
-Colossal Buddha image (bronze)
Function:
-Buddhist temple
-meant to meditate with the Buddha statue
-expression of Buddhism and State mixing in Japan
Context:
-743 CE rebuilt 1700 CE
-various artists of Kei school
-commissioned by emperor Shopu
-Nara, Japan 1st imperial capital, end of Silk Road

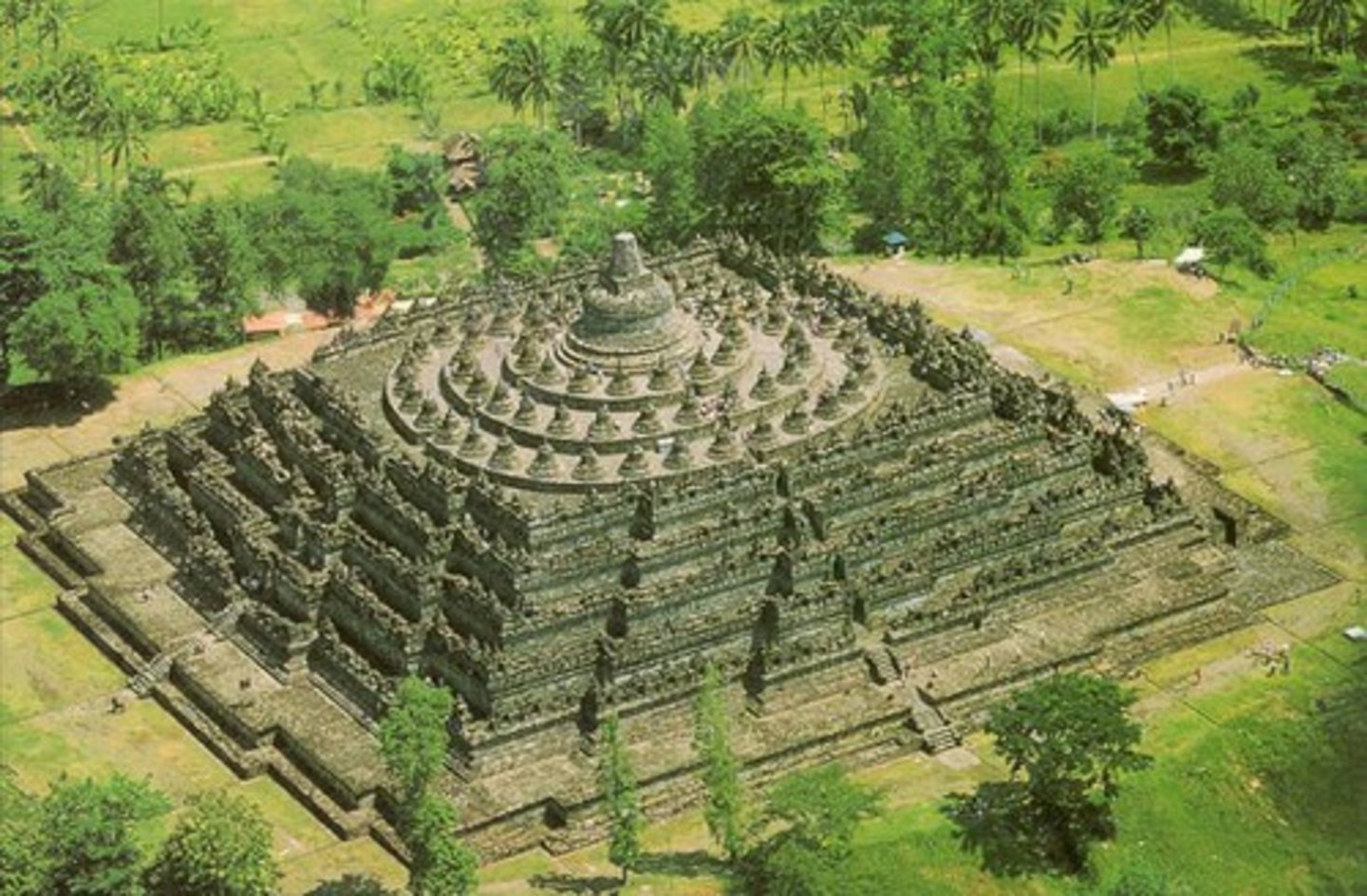
198. Borobudur Temple
Form:
- relief sculptures
- elevates
- clockwise up and around
Content:
-72 stupas, 1460 reliefs, 9 platforms in sets of 3, 504 Buddha statues
-narrate Buddha's teachings
-Jataka tales (Buddha's past lives)
Function:
-built as monument to Buddha
-pilgrimage site/shrine
-narrative guides you
-physical and spiritual journey to higher state of consciousness
Context:
-Buddha- poet, thinker, and architect of this temple
-Saliendra dynasty commissioned this (the leaders of maritime power

199. Angkor, the temple of Angkor Wat, and the city of Angkor Thom
Form:
-Panchayatana plan (one main room with 4 surrounding, on a platform)
-Mandala (cosmic map of the world)
-Enter a grand space
-Corbelled gallery roofing
Content:
-Water surrounding temple
-Angkor Thom: Buddhist part
-Angkor Wat: Hindu part
-Sculptures in rhymic dance poses
-Horror vacui of sculptural reliefs
Function:
-Meant to be a tomb, express the divine power of a leader
-Built complex to show his power and might
Context:
-Hindu and Buddhist parts of a medieval capital of Cambodia
-Cambodia, Hindu, Angkor Dynasty 800-1400 CE
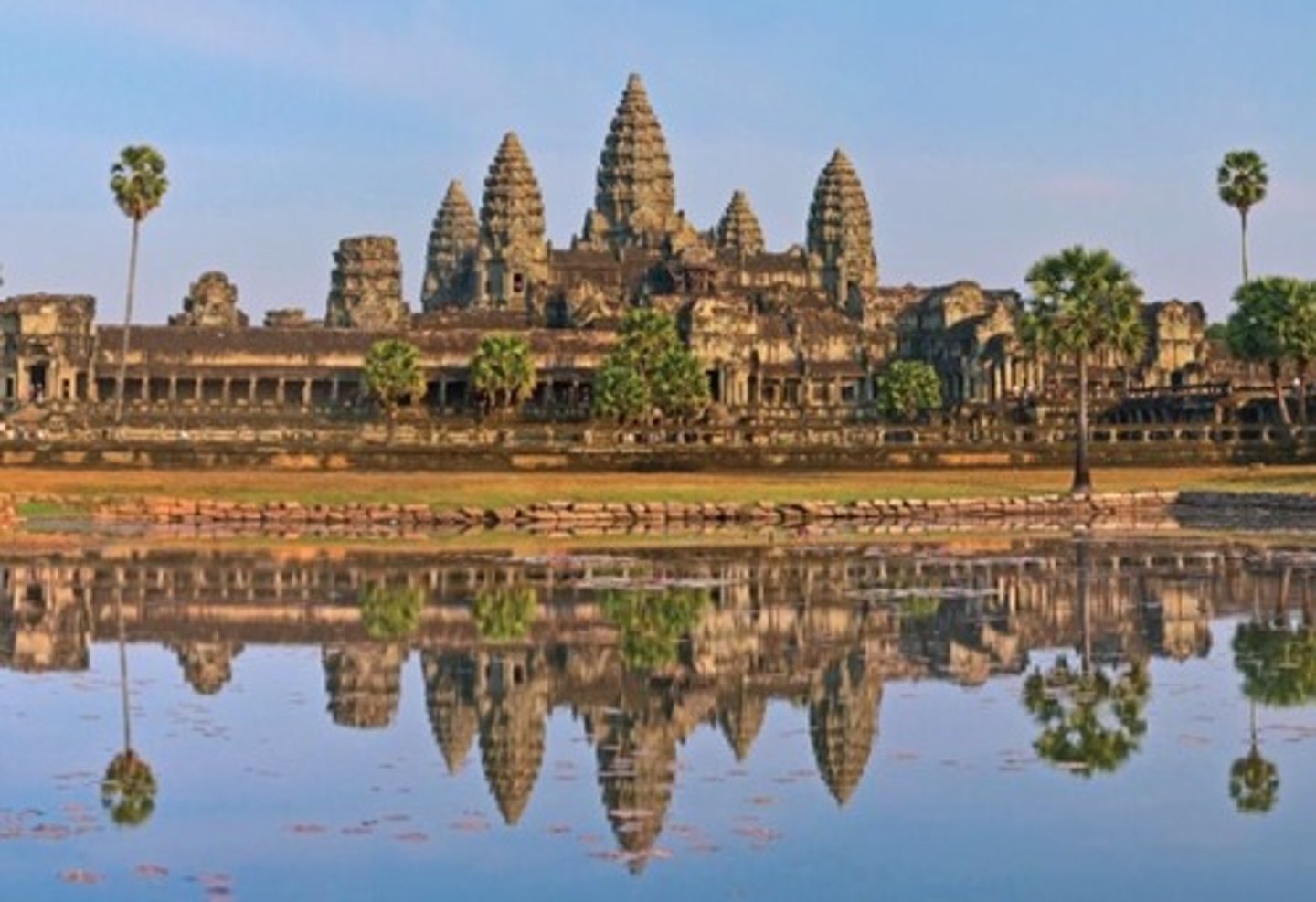

200. Lakshamana Temple
Form:
-Sandstone
-Axial plan
-Panchayatana temple type: Configuration of 5 rooms is the typical setup for Indian temple
-High base/platform
-Deep entrance porch
-Complex horizontal banding crosses the ribs of the tower
Content:
-Series of rooms
-Tallest part of building: marks spot of most important part of building (inner sanctuary that holds the image)
-4 shrines/chapels around main room
-Lion statues (symbols of male figures)
-Murti: embodied image of a divine figure
-Mandapa: hall
-Sensuous couple (controversial figures): shows deeper connection with gods
Function:
-Hindu temple dedicated to Vishnu
-Mandir temple: Space that is the house for gods (in this case, for Vishnu)
-place of worship, the divine endowed in its idealized architectural form
Context:
-Chandella Dynasty 950 CE
-Khajuraho, India (North Central India)
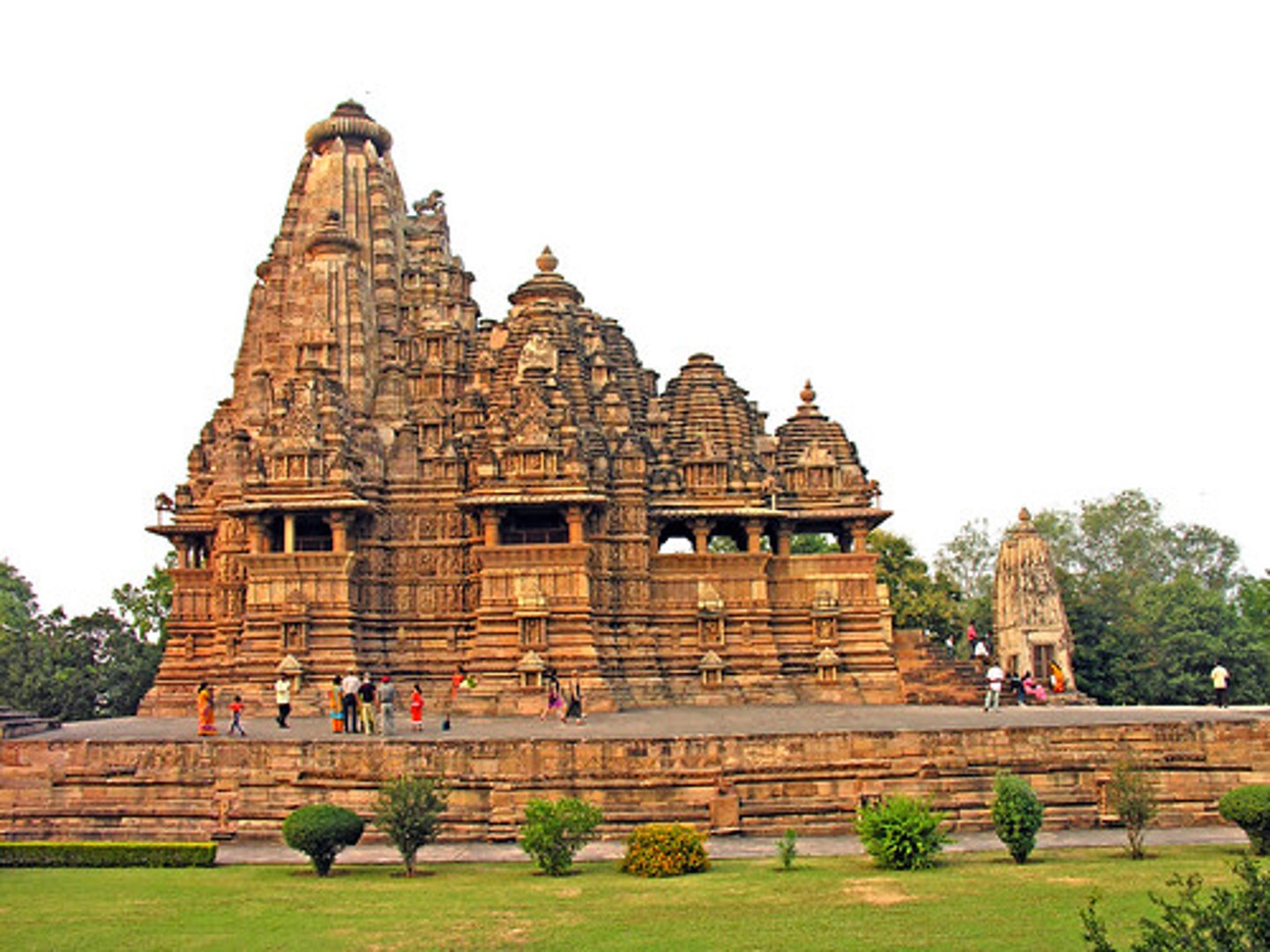

201. Travelers among Mountains and Streams
Form:
-hanging scroll (see all at once)
-ink and colors on silk
-in proper scale
-Neo-Confucianism ideals
Content:
-Chinese landscape (no specific place)
-waterfall, travelers, boulders, trees, mist
Function:
-reverence for rocks and stone because of their "chi" (energy)
-evoke Buddha
-after long period of political disunity
Context:
-artist: Fankuan (scholarly artist)
-Song Dynasty, China
-1000 CE
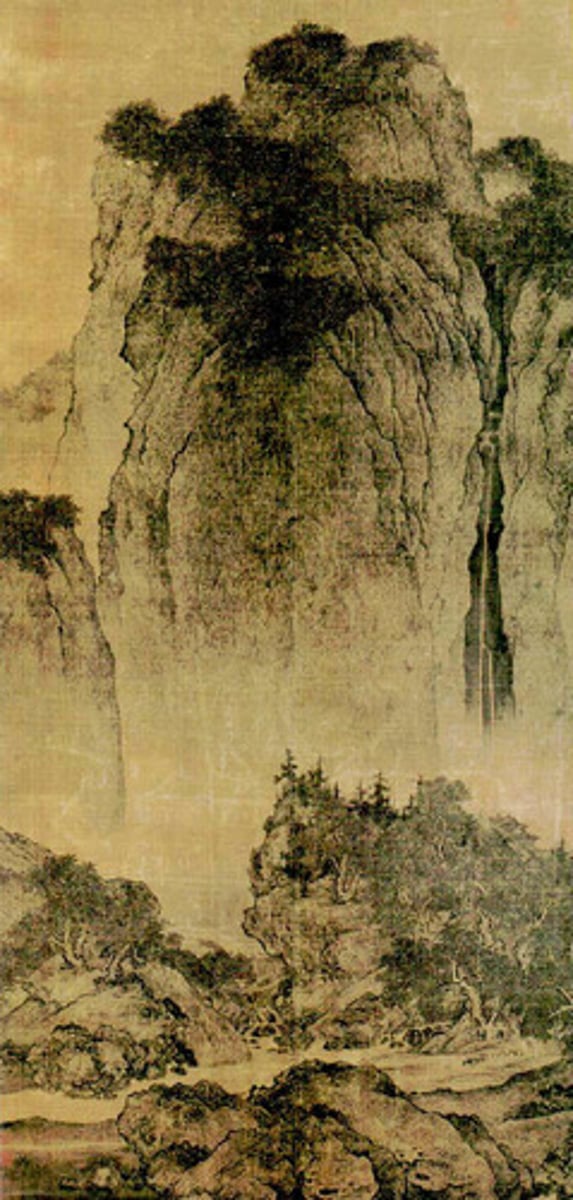

202. Shiva's Lord of Dance
Form:
-cast bronze
-stance signifies refuge for troubled soul
Content:
-Shiva: destroyer god-keeps us from afterlife, but also creator
-flaming circle crushing Apas mara (dwarf)
-Hindu trinity: Brahma (creator), Vishnu (preserver), Shiva (destroyer/transformer)
-Wedas: sacred texts of Hinduism
Function:
-shows the never-ending cycle of life Indians believe in
-immortal symbol that in this physical world there will always be ignorance or things we have to overcome
Context:
-Hindu, India
-Chola Dynasty 1000-1100 CE

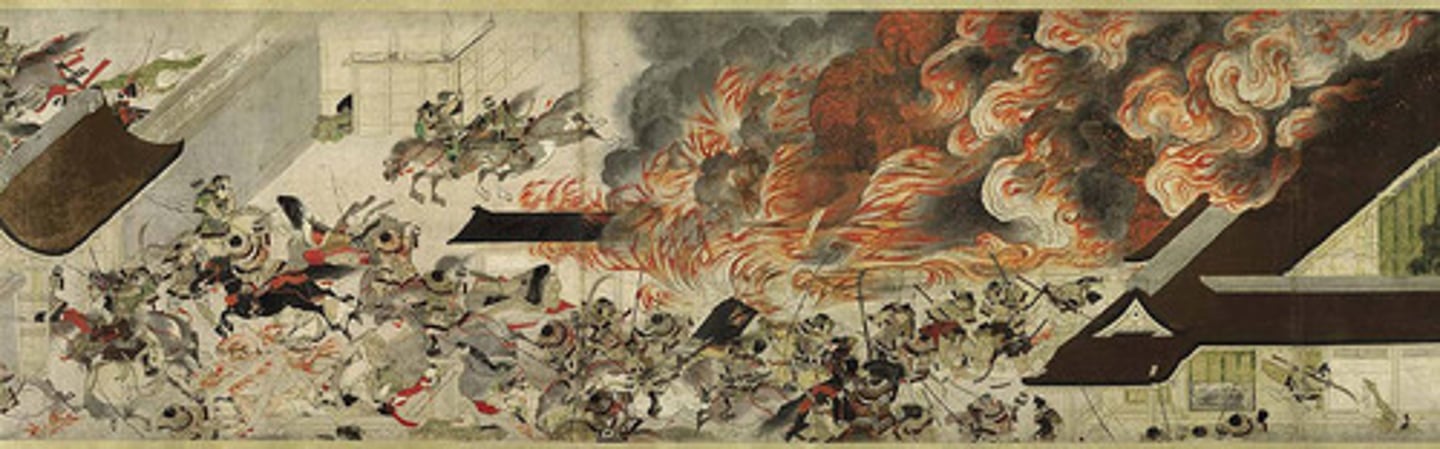
203. Night Attack on the Sanjo Palace
Form:
-combining image and text
-Yamato-e: high vantage points, strong angles, cropping, narrative scroll
-read right to left
-strong angles
-handscroll
-extraordinary detail
Content:
-rival families (Fujiwara and Minamoto) attack the Taira clan and defeat them
-establish shotgun empire
-battle: 1159
-extreme detail of armor, weaponry, war tactics
-struggles between emperor and rising shogons
Function:
-turning point in Japanese history
Context:
-piece made 1250-1300 CE
-Karamkura Period, Japan

204. David Vases
Form:
-Mongolian style
-white porcelain with cobalt blue underglaze from Iran
-2 1/2 feet tall
-text
Content:
-peonies= prominent scrolling flower
-inscription with date, location, temple, patron, and purpose
-phoenix and dragon balanced (symbol of Daoist faith- ying and yang)
-elephant handles
Function:
-made for Daoist temples to honor a military leader who was diefied
-expression of Silk Road
-held flowers beside an altar
Context:
-apart of wealthy man's collection
-1351 CE
-Yuan Dynasty, Mongol Empire
-Beijing, China

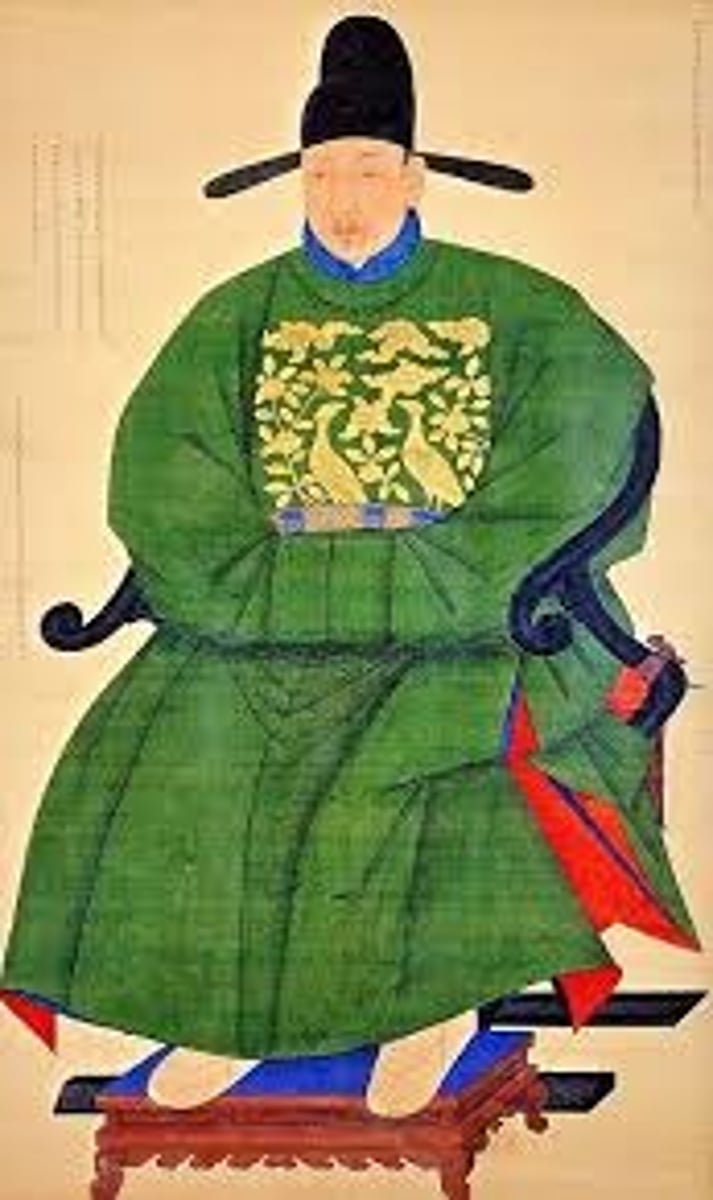
205. Portrait of Sin Sukju
Form:
-crisp and angular lines
-color characterization
-hanging scroll
-ink and color on silk
-possible collaborative pice
Content:
-head slightly turned (1 ear shown)
-rank badge worn on front and back
-peacocks with plants and cloud
-intellectual scholar
-seated in specific chair
Function:
-respect for one's elders and ancestors
-officially honors for his distinguished service @ court and loyalty to the King during hard times
-portrait cherished by descendants
Context:
-Imperial Bureau of Painting, Korea
-1417-1475 CE

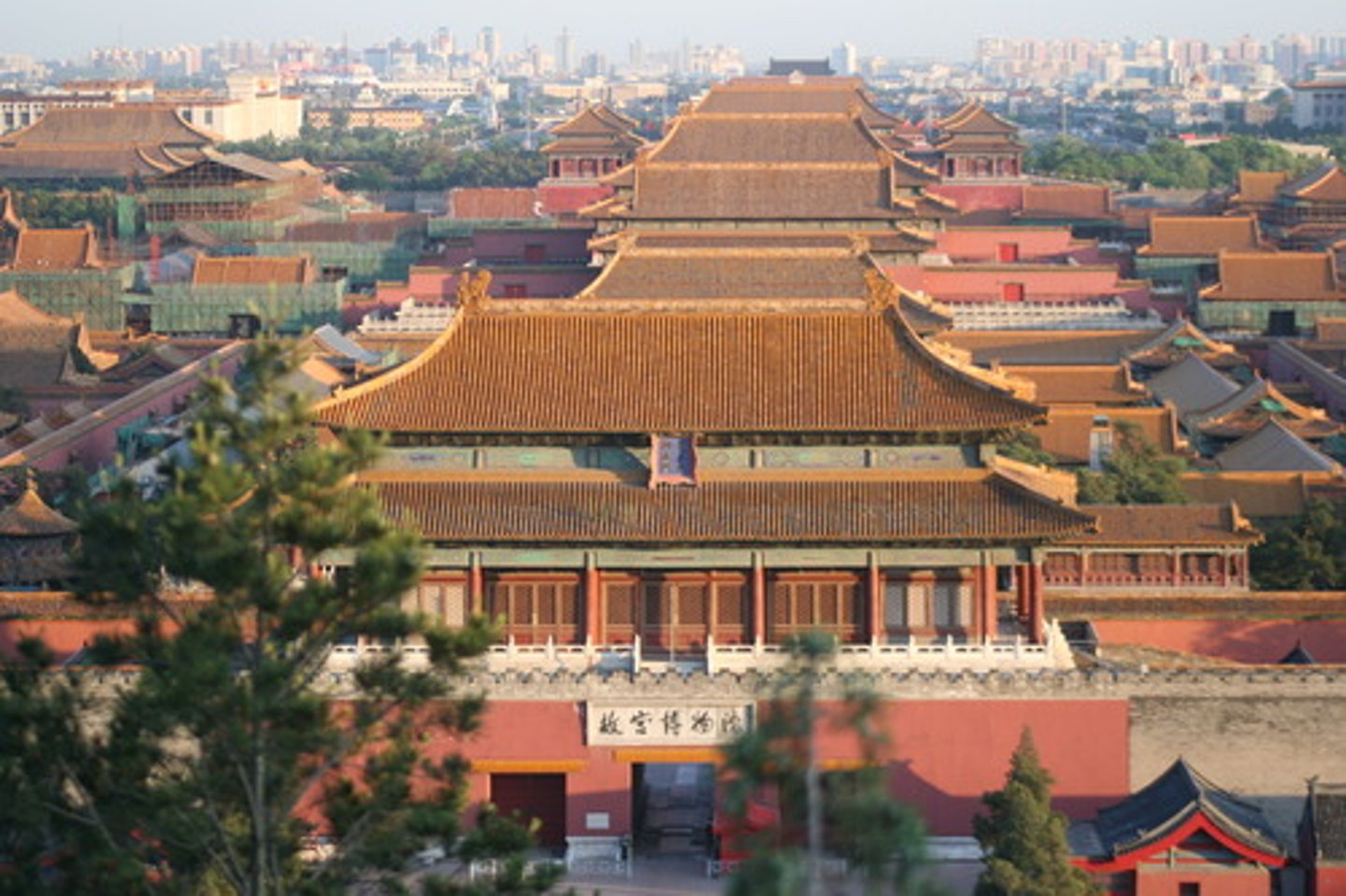
206. Forbidden City
Form:
-Stone masonry, marble, brick, wood, and ceramic tile
-Layout based on Chinese philosophy
-Certain palette to signify (dark red-sun, yellow-earth, blue-heaven)
Content:
-30 ft. tall walls surrounding the city
-Moat around the wall
-Series of bridges
-Front Gate (Mao Zedong's portrait over doorway), Meridian Gate
-Private realm: where the royal family lives (outer and inner court)
Numbers everywhere
-Complex of roughly 100 buildings, 9000 rooms
Function:
-Express that the emperor is the Son of heaven
-Political and ceremonial center for nearly 500 years
-Main building: to discuss the issues of the state
-Importance of numbers spiritually
-Walls provide privacy and protection for the families
Context:
-Largest political complex in the world
-City at center of a city
-Beijing, China, Ming Dynasty 15th century CE-later

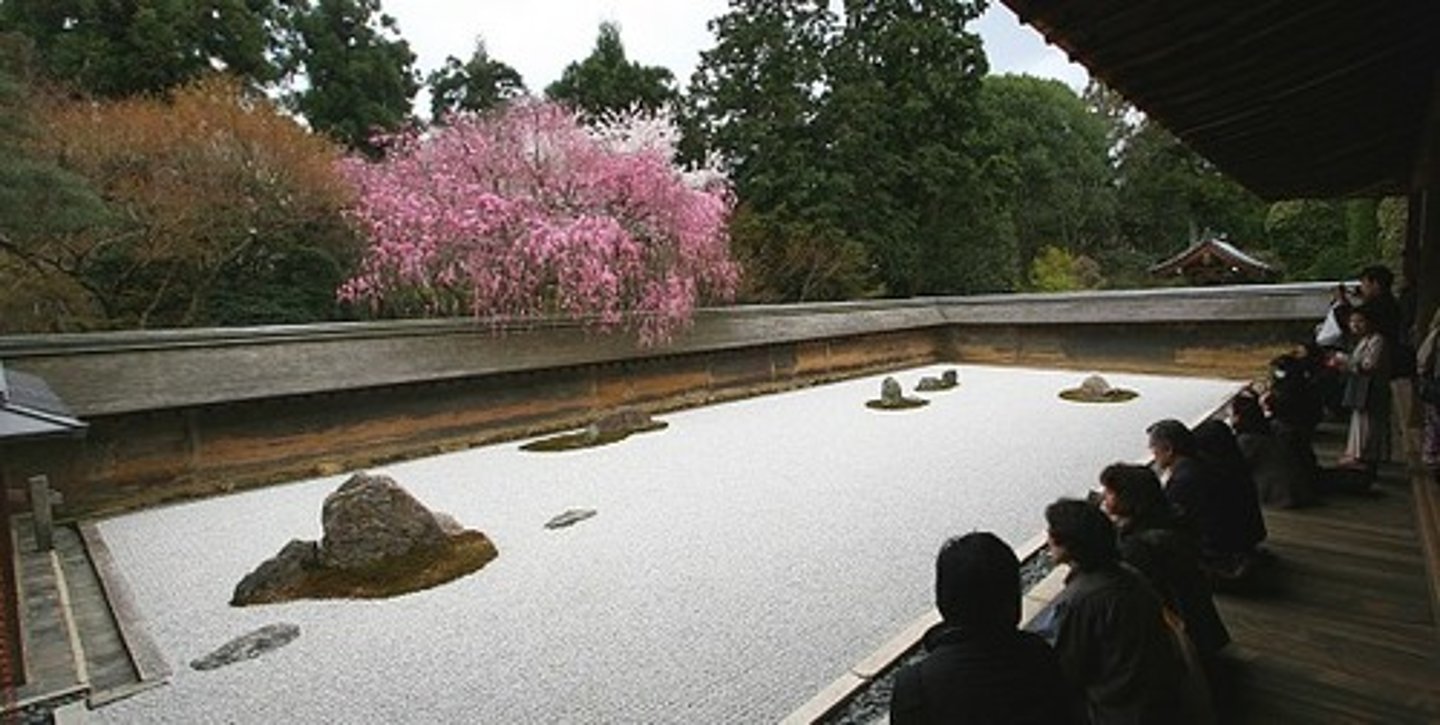
207. Ryoan-ji
Form:
-asymmetrical
-abstract
-gravel=flowing elements
-stones=islands, shore, bridges
Content:
-15 stones
-raked stone garden
-monastery (Zen Buddhist monks)
-mirror pond
Function:
-can only enter garden through your mind (spiritually enter)
-power of emptiness
-each rock is a different visual "pull"
-Zen seated meditation
Context:
-1480 CE, Kyoto, Japan
-Muramachi Period
-Zen Buddhist

208. Jahangir Preferring a Sufi Shaikh to Kings
Form:
-texts, geometry, natural world
-Persian traditions
-proportions play into importance
Content:
-manuscript pages
-Mugal leader sitting on throne
-text describing reign
-children dressed up
-guy at bottom is the court artist
-Suffi: Muslim mystic giving gift to Jahangir
-combo of the sun and moon symbolizing ruler's emperorship and divine truth
Function:
-Mughal painting skill
-cross-cultural nature of Art
-artist puts himself at lowest class
Context:
-artist: Bichitr (Hindu)
-1620 CE
-signed

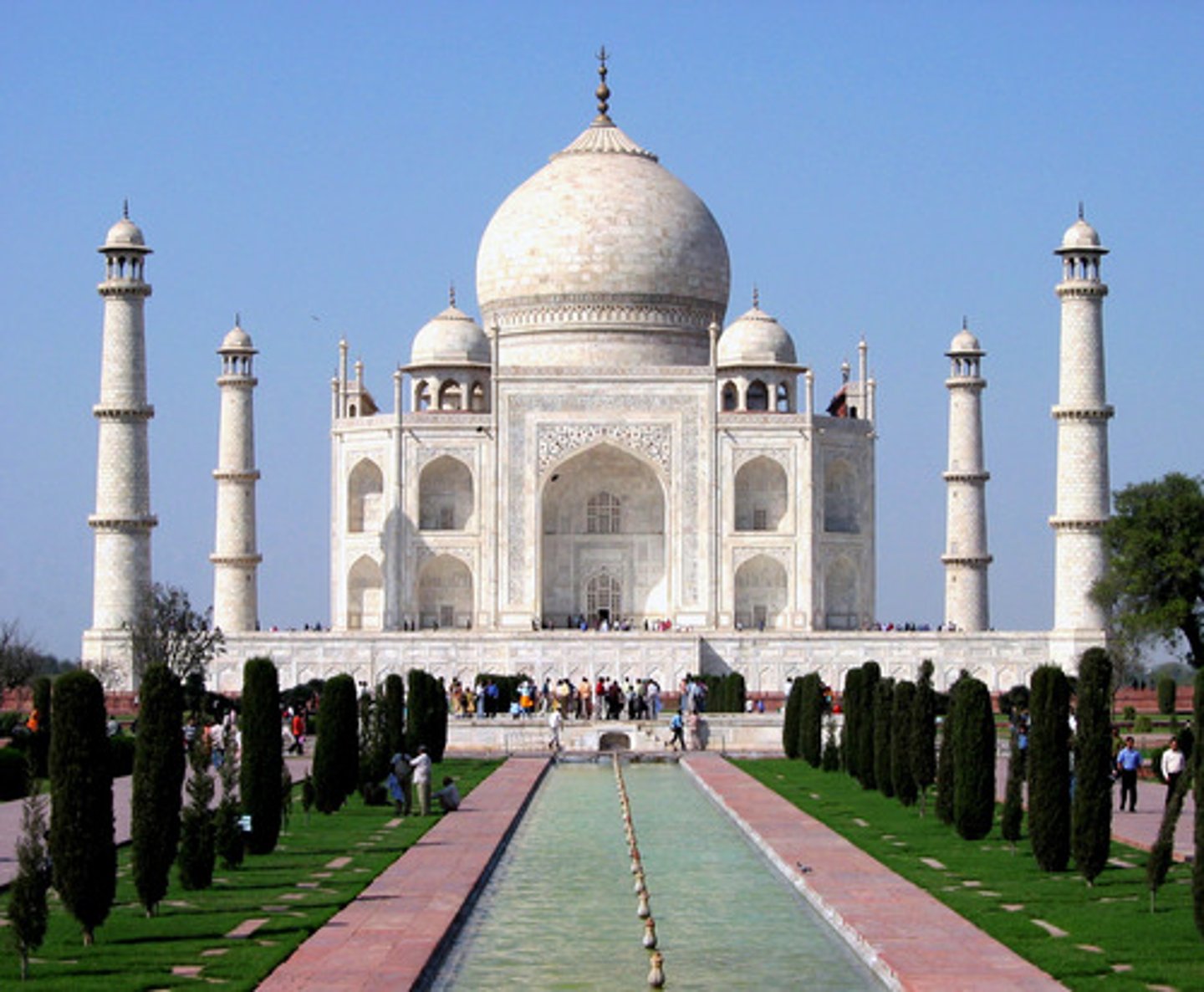
209. Taj Mahal
Form:
-Iwan
-Onion domes
-cross axial plan
-fused aspects of other Islamic traditions
-marble, stone masonry
-stone inlay
-symmetrical harmony
Content:
-charbagh- Persion garden into 4 quadrants representing paradise on Earth
-flowing water throughout
-Arabic text from the Quran
-chartriss
-mosaics
-cenotaphs: inscriptions (symbol of tombs, tombs are actually empty)
-minarets
Function:
-resting place for Shah Jahan's wife, Mumtaz Mahal
-India 1632-53 CE
-architect: Usted Ahmad Lahori
-Mughal Empire

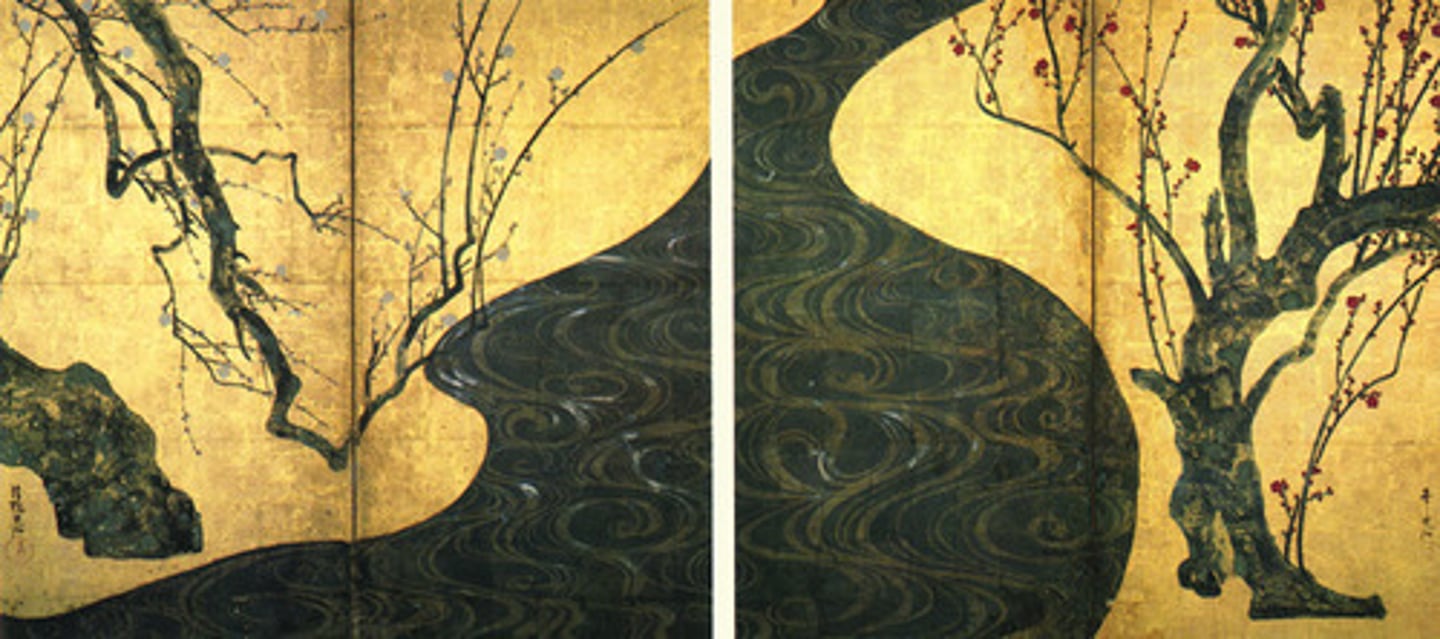
210. White and Red Plum Blossoms
Form:
-ink, watercolor, gold leaf
-swirling illusion of expansion
-byobu: painted screen
-rich colors/gold
Content:
-swirling water
-nature/flowers alongside
-early spring
-two flowering trees
-vantage points
-turns simple landscape theme into dream vision
Function:
-rimpa school painting
-painted screen
Context:
-1710-16 CE Japan
-artist: Ogata Korin
-Edo period

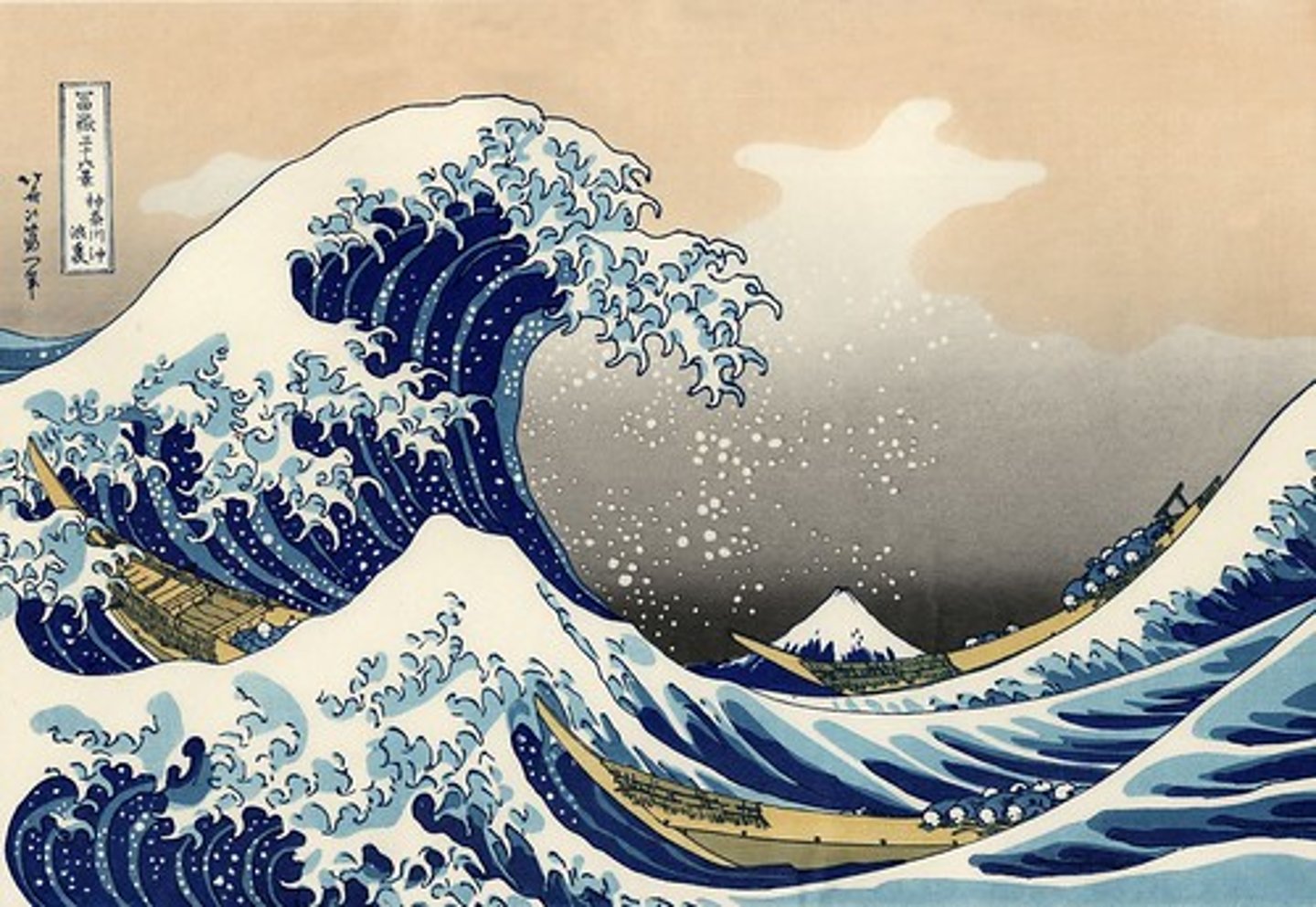
211. Under the Wave off Kanagawa
Form:
-polychrome and woodblock priint made of ink and color on paper
-Ukiyo-e: Japanese woodblock prints made during Edo Period
-part of series of 36 showing Mt. Fuji in each
-genre scene in series/travel
-flat colors, high angles, cropped, large foreground, nature specific
-large foreground
Content:
-text: name of series, artist, censor's seal
-crashing wave (dragon claws)
-Mt. Fuji in background (small in comparison)
Function:
-show moutain and wave's resemblance
-show Dutch influence
-genre scenes in seires'travel of the sacred Mount Fiji
Context:
-artist: Katsushika Hokusai
-1830-33 CE Edo Period

212. Chairman Mao en Route to Anyuan
Form:
-Propaganda
-Portraiture
-Socialist realism (clear, intelligible subject/emotionally moving themes)
Content:
-Mao on way to organize a coal worker/miner strike
-Portrait of Mao (oil paint)
-Telephone poll and water cascades from a dam (modernity)
-Chinese landscape
-Umbrella under his arm
Function:
-Used Chinese landscape to portray that Mao was capable of leading a revolution
-Combatting tradition Chinese art but still not modern
-Mao as a person working for the people
Context:
-based on oil painting by Lui Chunhua
-artist unknown 1969 CE
