m2 bipharmaceutics consideration in product design
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
drug and drug product characteristics
drug release and dissolution is determine by _ characteristics
drug
permeation acoress GI linings is determined by - characteristics
drug and physiologic (biologic)
disposition during GI transit are both affected by the _ and the - characteristics
rate-limiting step
slowest step in kinetic process
troches, chewable tablets, sustained release, prolonged or repeat action
exemptiom in USP disintegration test (solid oral dosage form)
Complete disintegration
the state in which any residue of the tablet, except fragments of insoluble coating, remaining on the screen of the test apparatus in the soft mass have no palpably firm core
-
dissolution
the process by which a solid drug substance becomes dissolved in a solvent
dynamic property
measure how fast drug dissolves, formulation sensitive
solubility
the mass of solute that dissolves in a specific mass or volume of solvent at a guven temperature
static property
does not change with time, independent of formulation
dynamic
property of dissolution
static
property of solubility
dissolution test
may be used to predict bioavailability (test)
dissolution test
test required for all US-FDA approved solid oral drug products
Noyes and Whitney equation
describes the overall rate of drug dissolutiom
aqueous environment
The in vitro dissolution system stimulated the in vivo process in terms of:
environment:
same GIT temp
The in vitro dissolution system stimulated the in vivo process in terms of:
temperature:
held at specific rom
The in vitro dissolution system stimulated the in vivo process in terms of:
agitation:
basket
dissolution apparatus type I
paddle
dissolution apparatus type II
reciprocating cylinder
dissolution apparatus type III
flow through cell
dissolution apparatus type IV
Paddle over disk
dissolution apparatus type V
revolving cylinder
dissolution apparatus type VI
reciprocating holder
dissolution apparatus type VII
biopharmaceutics
to adjust the delivery of drug from the product in such a manner as to provide optimal therapeutic activity and safety for the patient
polymorphism
the ability of a drug to exist in various crystal forms may change the solubility of the drug. Also, the stability of each form is important, because polymorphic may convert from one form to another
alkaline buffer
What to add to improve solubility of aspirin
stability-ph profile
a plot of the reaction rate constant for drug degradation vs pH
acidic medium (stomach)
eythromycin, in _ medium decompose rapidly, but is relatively stable in neutral or alkalone ph
enteric-coated
erythromycin tablets are _-coated to protect against acid degradation in the stomach
erythromycin estolate and erythromycin ethylsuccinate (suspensions both)
erythromycin that has better stability (less water soluble)
inversely
particle size and surface area are _ related
directly
dissolution rate is _ proportional to the surface area
micronized
agriseolfulvin, nitrofurantoin and many other steroids having poor absorption are milled to _ form
increased surface area enhance water penetration , thus _ increase disssolution
disintegration
adding this will ensure rapid disintegration and release of drug
surface-active agengs
increases wetting as well as solubility
hydrophobic
excessive particle size reudction does not always increase dissolution rate (in case of _ drugs)
polymorphism
refer to the arrangement of a drug substance in various crystal forms of polymorph
anhydrous
no water of hydration (polymorph)
solvates
(polymorph) contain a solvent or water
desolvad
(polymorph) solvates - solvent remove
solubility
density
hardness
compression characteristic
different polymorphs similar chemical structure but diffrent physical properties:
B-polymorph
the concentration or chloramphenicol in the body depends on the _ in the suspension
B-polymorph
form of cholamphenicol which is more soluble and better absorbed
diamond to graphite
some polymorph are metastable and may convert to a more stable form over time example:
anhydrous
this form of ampicillin dissolves faster and is more rapidly absorbed that the hydrated form
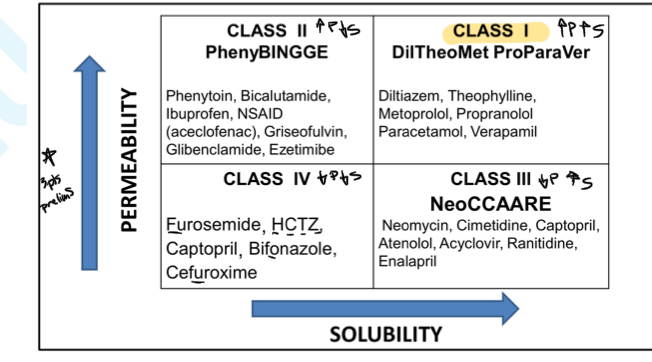
partition coefficient
ratio of the solubility of the drug, at equilibrium, in nonaqueous solvents to that in an aqueous solvent
partition coefficient
measure of the relative affinity of a drug for ttwo immiscible solvents
pKa of the weak acid/base
pH of the solutiom
extent of ionization depends on
more
protonated form is _ lipophilic than the unprotonated, so can cross membrane more rapidly
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
describes the relation between the ionized and nonionized forms of a drug
ph = pka
ph __ pka
lower
for weak acids, if ph is _ than the pKa, it is relatively unionized and more lipid soluble(well absorbed from the stomach)
higher
for weakacids, if ph is _ than the pKA, it is relatively ionzed and more soluble
higher
for weakacids, if ph is _ than the pKA, imcreases gastric solubility with decreasing pH
higher
for weak base, if ph is _ than the pKA, it is relatively unionized and more lipid soluble
salt form
this form is preferred if water solubility is desired
slower dissolution
slower bioavailability
longer duration of action
certain salts are designed to provide;
Sodium ascorbate
other salts are selected for
greater stability
less local irritation at the absorption site
__ preferred over ascorbic acid to avoid irritation
less systemic toxicity
tartaric acid (2), citric acid (1), sodium bicarbonate (3.4)
parts of effervescent granules
more
K and Na salts are _ soluble than cation salts (Ca, Mg)
more soluble : Penicillin Na
less soluble : MgSo4, Al(OH)3
more and less soluble salts for weak acids
more soluble : hcl, sulfate, citrate, gluconate salts (lidocaine hcl, atropine so4)
less soluble : estolate, napsylate, stearate salts
more and less water soluble salts for weak bases
chirality
ability of a drug to exist as optically active stereoisomers or enantiomers
S(+); R(-)
Metachloline _ is 250x more potent than _ enantiomers
S (+)
Ibuprofen (_) is pharmacologically active
S(-); R(+)
Carvedilol (_) is a potent beta-receptor blocker than (_) enantiomer
+; -
Ketamine (_) is more potent and less toxic than _ enantiomer
racemic mixture
most chiral drugs
D and L
an equal mixture of __ enantiomers is optically inactive
complex
a species formed by reverisble or irreversible association of two or more interacting molecules or ions
complex
drugs + (clay, protein, or zimc) is an example of
chelate
complexes that typically involve a ring-structure formed by the interaction between a partial ring of atoms and a metal central atom
iron
entral atom of hemoglobinc
cobalt
central atom of cyanocobalamin
insoluble
chelation leads to __ complex
less
tetracycline + calcium = __ water soluble
more
Theophylline + ethylenediamine (aminophylline) = _ water soluble
increase
cyclodextrins + drug = _ water solubility
drug-protein
_ complexes do not cross membranes easily
insoluble = mask bitter taste of caffeine
caffeine + gentrisic acid =
dissociate
drug complex must _ to free drug for absorption and excretion