Biology a level ocr a cell structure
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Prokaryotic cells
Extremely small (less than 2 um diameter)
DNA is circular
No nucleus (DNA is free in the cytoplasm)
Cell wall is made of a polysaccharide but not cellulose or chitin
Few organelles and no membrane bound organelles eg.mitochondria
Flagella made of the protein flagellin, arranged in a helix
Small ribosomes
Example: E. Coli bacteria
Eukaryotic cells
Larger cells (about 10-199 um diameter)
DNA is linear
Nucleus present (DNA inside)
No cell wall in animals, cellulose cell wall in plants, or chitin in fungi
Many organelles
Flagella made if microtubule proteins
Larger ribosomes
Example: human liver cell
Animal cell (11)
Plasma membrane
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Lysosomes
Ribosome
Nuclear envelope
Golgi apparatus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondrion
Plant cell (14)
All the same organelles as animal cells par lysosomes and plus a few extra:
Cell wall with plasmodesmata
Vacuole
Chloroplasts
Description of Plasma membrane
DESCRIPTION:
The membrane found on the surface of animal cells and inside the cell wall of plant cells and prokaryotic cells. It's made mainly of lipids and proteins.
Function of Plasma membrane
FUNCTION:
Regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. Also has receptor molecules of which allow it to respond to chemicals like hormones
What are Plasma membranes made of?
It's made mainly of lipids and proteins.
description of Cell wall
DESCRIPTION:
Rigid structure that surrounds plant cells, it's is made mainly of the carbohydrate cellulose
function of cell wall
FUNCTION:
Supports plant cells
what are cell walls made of?
made mainly of the carbohydrate cellulose
description of Nucleus
DESCRIPTION:
Large organelle surrounded by a nuclear envelope (double membrane) which contains many pores.
The nucleus contains chromatin (which is made from DNA and proteins) and the nucleolus
function of nucleus
FUNCTION:
Controls cells activities (by controlling the transcription of DNA)
DNA contains instructions to make proteins.
Pores allow substances (eg. RNA) to move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm,
the nucleolus makes ribosomes.
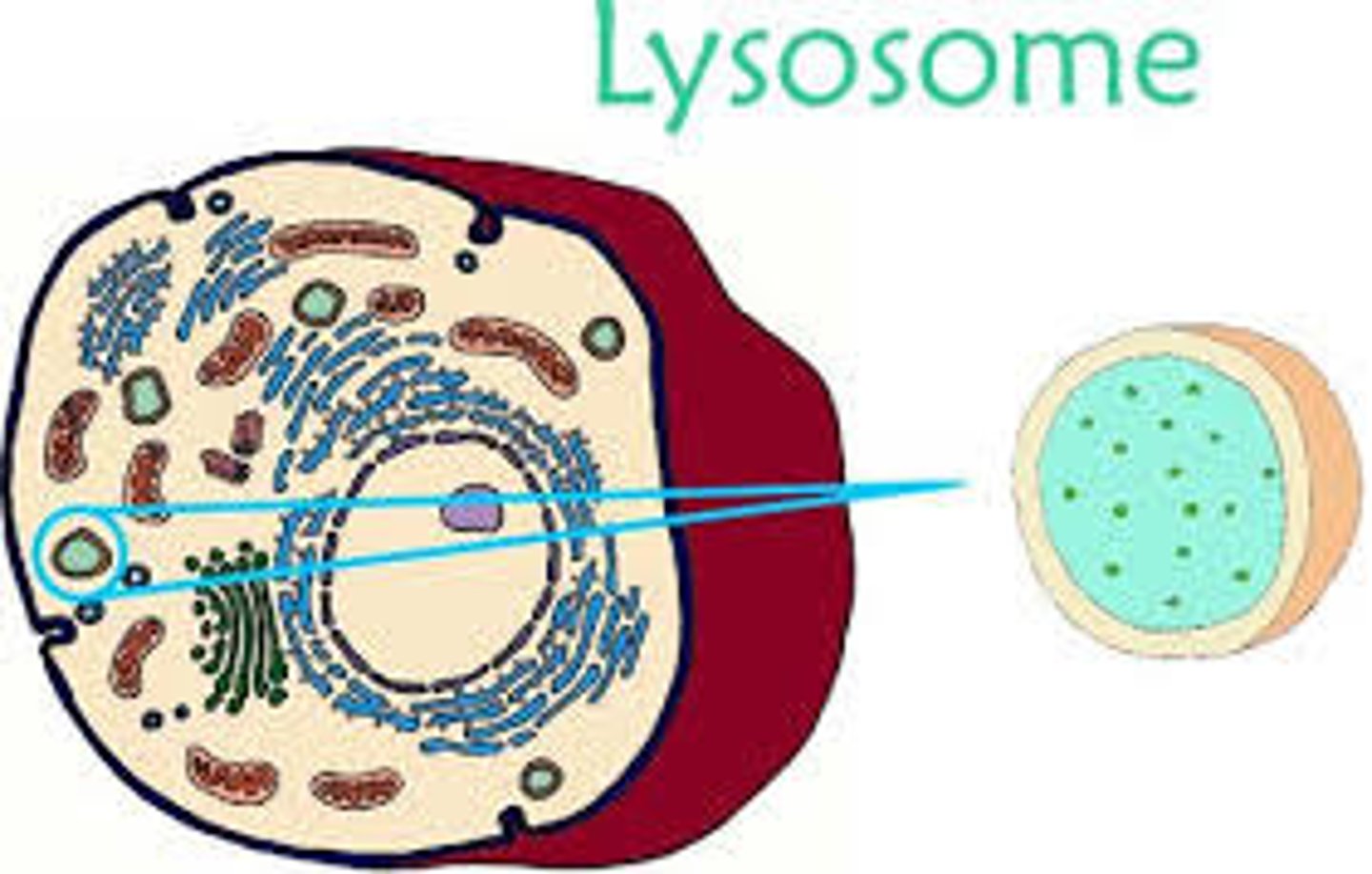
description of Lysosome
DESCRIPTION:
round organelle surrounded by a membrane, with no clear internal structure.
function of Lysosome
FUNCTION:
Contains digestive enzymes.
Kept separate from the cytoplasm by the surrounding membrane,
Can be used to digest invading cells or break down worn out components of the cell.
description of Ribosome
DESCRIPTION:
small organelle that either floats free on cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
made up of proteins and RNA.
It's not surrounded by a membrane.
Function of Ribosome
FUNCTION:
The site where proteins are made.
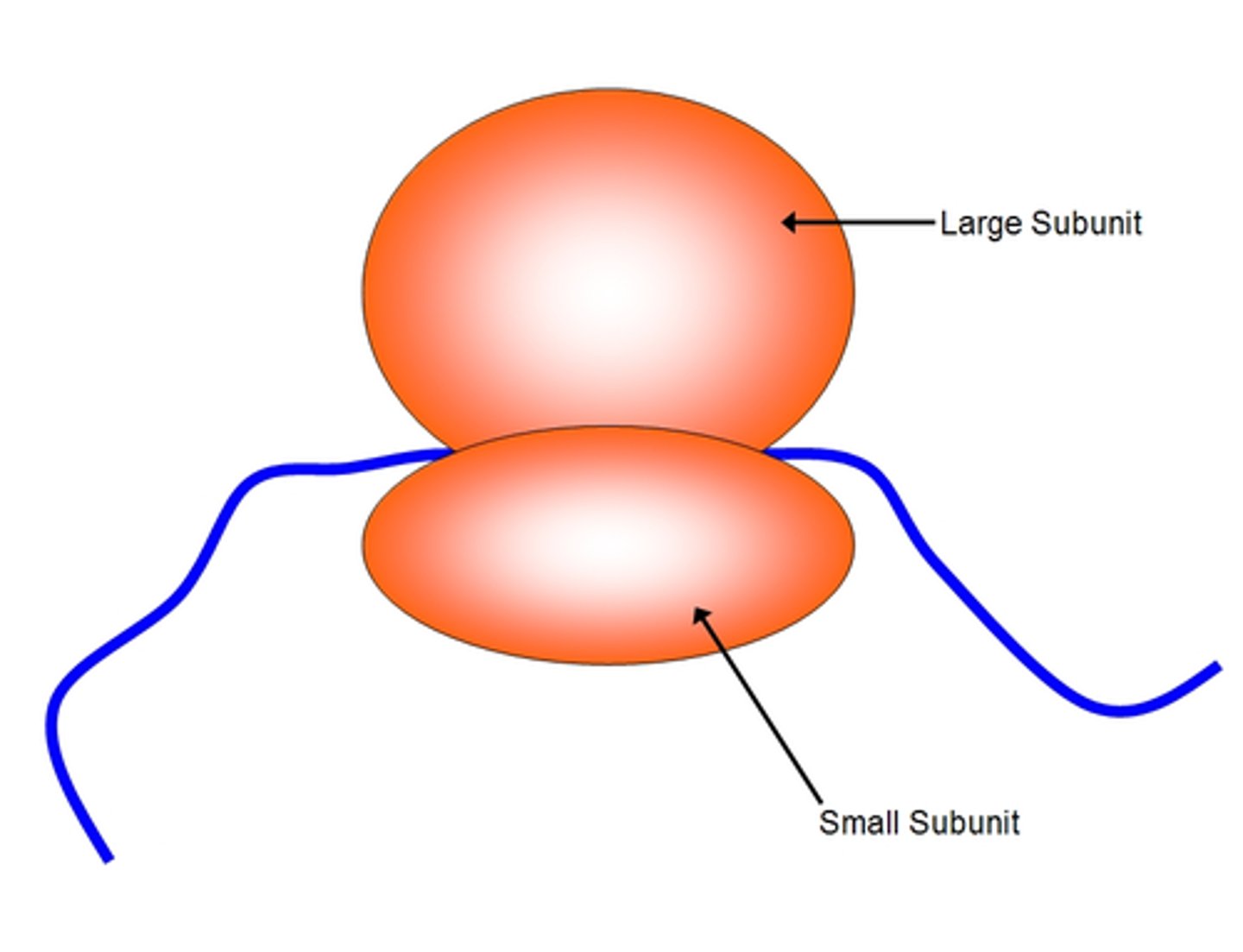
what are ribosomes made of?
made up of proteins and RNA.
description of Rough endoplasmic reticulum
DESCRIPTION:
System of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space.
The surface is covered with ribosomes.
function of Rough endoplasmic reticulum
FUNCTION:
Folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
DESCRIPTION:
Similar to RER but with no ribosomes.
FUNCTION:
Synthesises and processes lipids.
Vesicle
DESCRIPTION:
A small fluid-filled sac in the cytoplasm, surrounded by a membrane
FUNCTION:
Transports substances in and out of the cell (via the plasma membrane) and between organelles.
Some are formed by the Golgi apparatus or the endoplasmic reticulum, while others are formed at the cell surface.
Golgi apparatus
DESCRIPTION:
A group of fluid filled, membrane bounded flattened sacs. Vesicles are often seen at the edges.
FUNCTION:
Processes and packages new lipids. Also makes lysosomes
Mitochondrion
DESCRIPTION:
Usually oval shaped. Have a double membrane- the inner one is folded to form cristae. Inside is the matrix which contains enzymes invoked in respiration.
FUNCTION:
Site if aerobic respiration, where ATP is produced. They're found in large numbers in cells that are very active and require a lot of energy.
Chloroplast
DESCRIPTION:
A small, flattened structure found in plant cells. It's surrounded by a double membrane, and also has membranes inside called thylakoids membranes. These membranes are stacked up in some parts of the chloroplast to form grana. Grana are linked together to form lamellae-thin flat pieces of thylakoids membrane.
FUNCTION:
The site where photosynthesis takes place. Some parts of photosynthesis happen in the grana and other parts happen in the stroma (a thick fluid found in chloroplasts)
Centriole
DESCRIPTION:
Small, hollow cylinders made of microtubules (tiny protein cylinders). Found in animal cells but only some plant cells.
FUNCTION:
Involved in the separation if chromosomes during cell division
Cilia
DESCRIPTION:
Small, hair like structures found on the surface membrane of sine animal cells. In cross-section they have an outer membrane and a ring of nine pairs with protein microtubules inside with two microtubules in the middle.
FUNCTION:
The microtubules allow the cilia to move. This movement is used by the cell to move substances along the cell surface.
Flagellum
DESCRIPTION:
On eukaryotic cells are like cilia but longer. They stick out from the cell surface and are surrounded by the plasma membrane.v.inside they're like cilia too-two microtubules in the centre and nine pairs around the edge.
FUNCTION:
The microtubules contract to make flagellum move. Flagella are used like outboard motors to propel cells forward (eg. when a sperm cell swims)
Protein production
-proteins made at ribosomes
-ribosomes on Rough ER make proteins that are excreted or attached to the cell membrane. The fee ribosomes in the cytoplasm make proteins that stay in the cytoplasm.
-new proteins produced at the rough ER are folded and processed (eg.sugar chains are added) in the rough ER
-then they're transported to the Golgi apparatus in vesicles
-at the Golgi apparatus the proteins undergo further processing (eg.sugar chains are trimmed and more are added)
-the proteins enter more vesicles to be transported around the cell eg.glycoproteins (found in mucus) move to the cell surface and are secreted.
Cytoskeleton
DESCRIPTION:
Network of protein threads. In eukaryotic cells the protein threads are arranged as microfilaments (small solid strands) and microtubules (tiny protein cylinders)
FUNCTION:
1) the microfilaments and microtubules support the cells organelles keeping them in position
2) strengthen the cell and maintain its shape
3) responsible for movement of materials within the cell. Eg. The movement of chromosomes when they separate during cell division depends on contraction in microtubules in the spindle.
4) the proteins of the cytoskeleton can also cause the cell to move. Eg.the movement if cilia and flagella is caused by the cytoskeletal protein filaments that run through them. So in the case if single cells that have a flagellum (eg.sperm cells) the cytoskeleton propels the whole cell
Magnification
How much bugger the image is than the specimen
Magnification = image size
-----------
Object size
Resolution
How detailed the mirage iss how well a microscope distinguishes between two points that are close together.
Light microscopes
-use light
-have a lower resolution than electron microscopes- max.resolution of about 0.2 micrometers. Usually used to look at whole cells or tissues.
-max.useful magnification of a light microscope is about x1500
Laser scanning confocal microscope
-Uses laser beams to scan the specimen, which is usually tagged with the fluorescent dye.
-the laser causes the dye to fluoresce. This light is then focused through a pinhole on to detector. The detector is hooked up to computer, which generates an image. The image can be 3-D.
-The pinhole means that any out of focus light is blocked, so these microscopes produce a much clearer image and normal light microscope.
-they can be used to look at objects of different depths in thick specimens
Electron microscope
Use electrons instead of light to form an image. They have a higher resolution than light microscopes, so give more detailed images. There are two kinds of electron microscopes.
Transmission electron microscope
use electromagnets to focus on the beam of electrons, which is then transmitted through the specimen. Denser of the specimen absorb more electrons, which makes them look dark on the image you end up with. TEMs are good because they provide high resolution images (so they can be used to look at a range of organelles) but they can only be used on thin specimens.
scanning electron microscope
Scan of beam of electrons across the specimen. This knocks off electrons from the specimen, which are gathered in the cathode ray tube to form an image. The images produced show the surface of the specimen and can be 3-D. But they give lower resolution images and TEMs.
Staining samples for light microscopes
-for the light microscope, this means using some kind of due. Common stains include methylene blue and eosin.
-The stain is taken up by some parts of the object more than others-the contrast mix different part show up.
-Different stains is to make different things show up. For example, eosin is used to stain cell cytoplasms. Methylene blue stains DNA.
-More than one stain can be used once.
Staining samples for electron microscopes
Objects are dipped in a solution of heavy metals (like lead). The metal ions scatter the electrons, again creating contrast-some parts of the object show up darker than others.
Dry mount (preparing a slide)
-Take a thin sample your specimen so light can get through it easily
-use tweezers to pick up your specimen and put it in the middle of the clean the slide.
-Pop a coverslip (a square of tin, transparent plastic or glass) on top.
Wet Mount
-Start by putting a small drop of water onto the slide. Then use tweezers to place the specimen on top of the water drop.
-To put the cover slip on, stand the slip up right on the slide, next to the water droplet. Then carefully tilt and lower it to so that covers the specimen. Try not to get any air bubbles under there- they'll obstruct the view of the specimen.
-once the coverslip is in position, you can add a stain. Put a drop of stain next to one edge of the coverslip. Then put a bit of paper towel next to the opposite edge. The stain will get drawn under the slip, across the specimen.
How to use a light microscope to view a specimen
1) Start by clipping The slide containing the specimen you want to look out onto the stage.
2) Select the lowest power of projective lens (I.e. the one that produces the lowest magnification).
3) Use the coarse adjustment knob to move the objective lens down to just above the slide.
4) Look down the eyepiece (which contains the ocular lens) and adjust the focus with the fine adjustment knob, until you get a clear image of whatever is on the other side.
5) If you need to see the side with greater magnification swap to a higher powered objective lens and refocus