Cell communication - C&M
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
intercellular
between cells
intracellular
inside cells
signaling cells
these cells release chemical signals called ligands
ligands
these interact with protein receptors in target cells:
these & receptors SPECIFICALLY bind to each other
aka signaling molecules
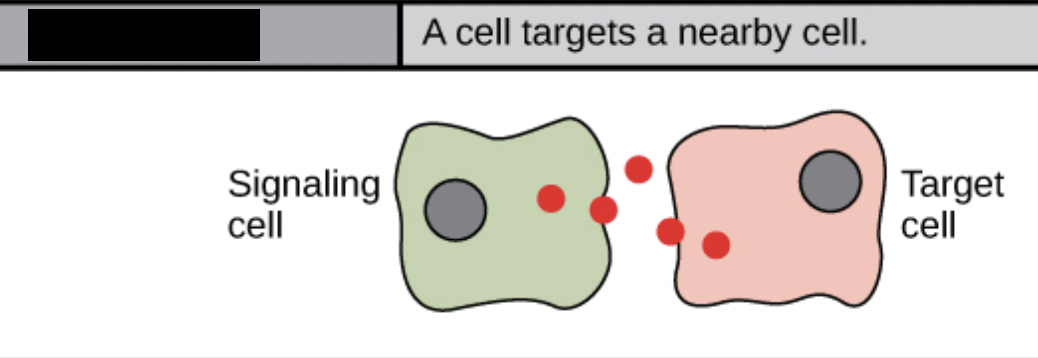
paracrine
move by diffusion through extracellular matrix
synaptic signals & neurotransmitters
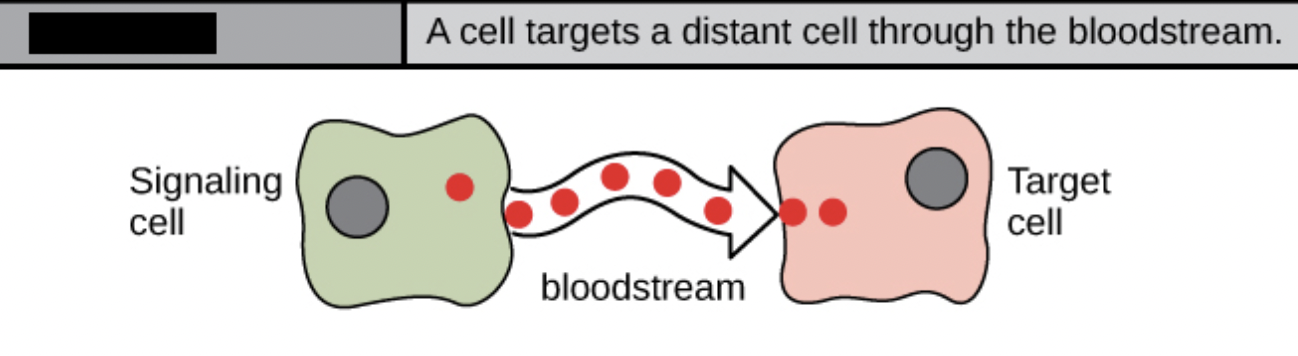
endocrine
signals from distant cells; typically produce a slower response w/ a long-lasting effect
hormones
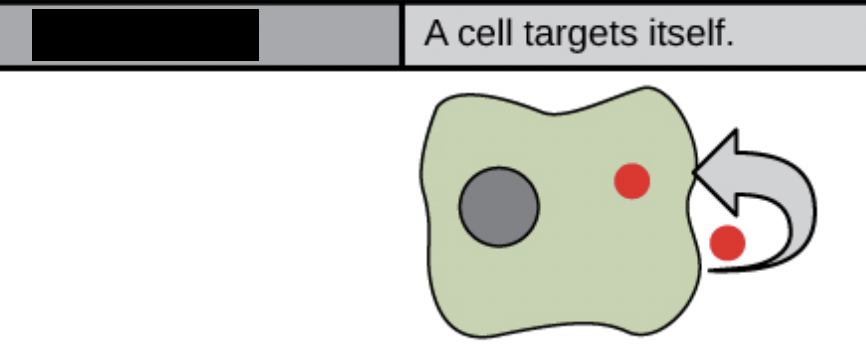
autocrine
a cell secretes a signal molecule that binds to receptors on its OWN SURFACE, leading to changes within that same cell
cancer cells
cell death signaling
developing embryonic cells
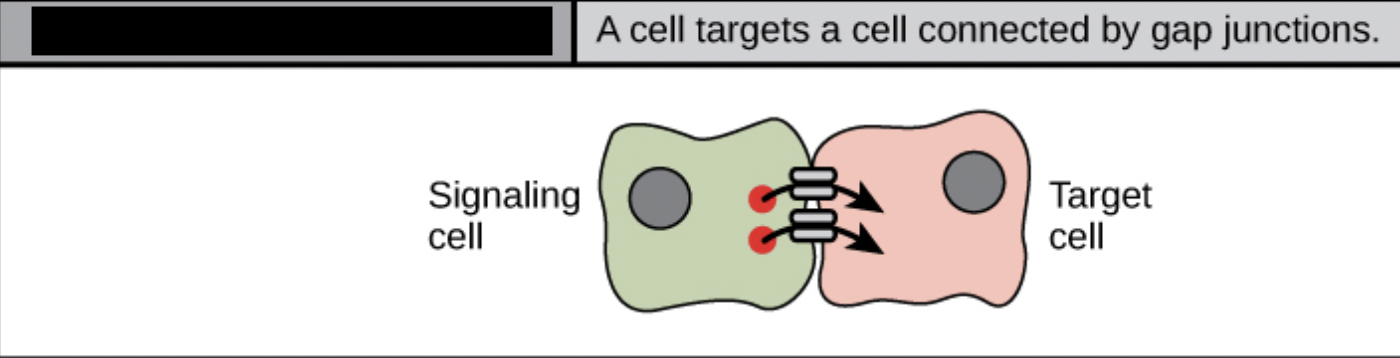
direct signaling across gap junctions
this involves intracellular mediators that allow small signaling molecules to move b/t cells
plasmodesmata — entire plant is a signaling network; only small molecules/ions can cross the gap
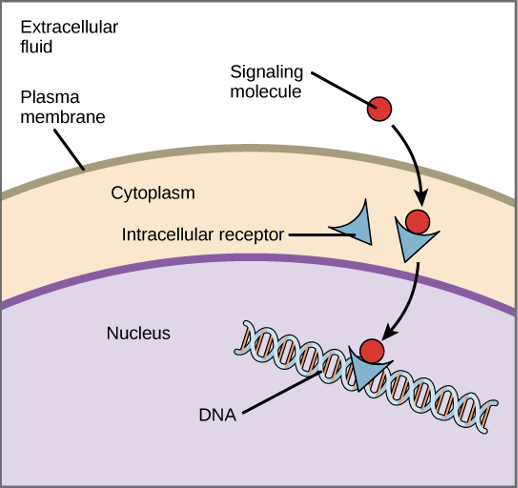
internal receptors
hydrophobic signaling molecules diffuse across the PM & interact w/ intracellular receptors:
many are transcription factors that interact w/ DNA in the nucleus (regulate gene expression)
cell-surface receptors
ion channel-linked
G-protein-linked
enzyme-linked
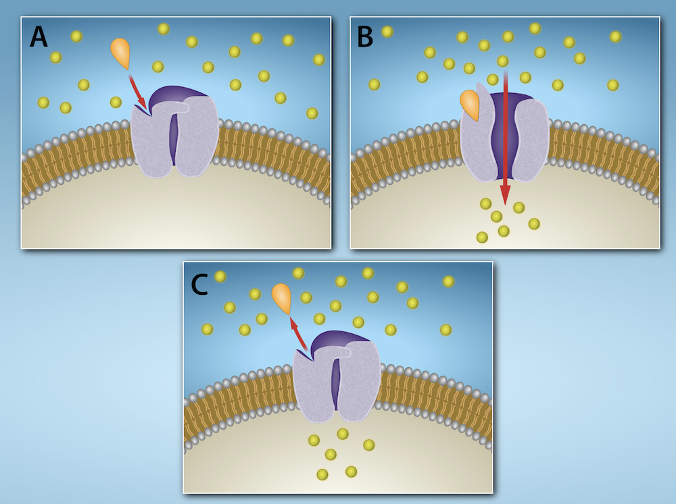
ion channel-linked receptor
gated ion channels form a pore through the PM that opens when the signaling molecules binds
ions flow into/out of cell:
this flow changes the electrical charge difference across the PM
triggers a cellular response
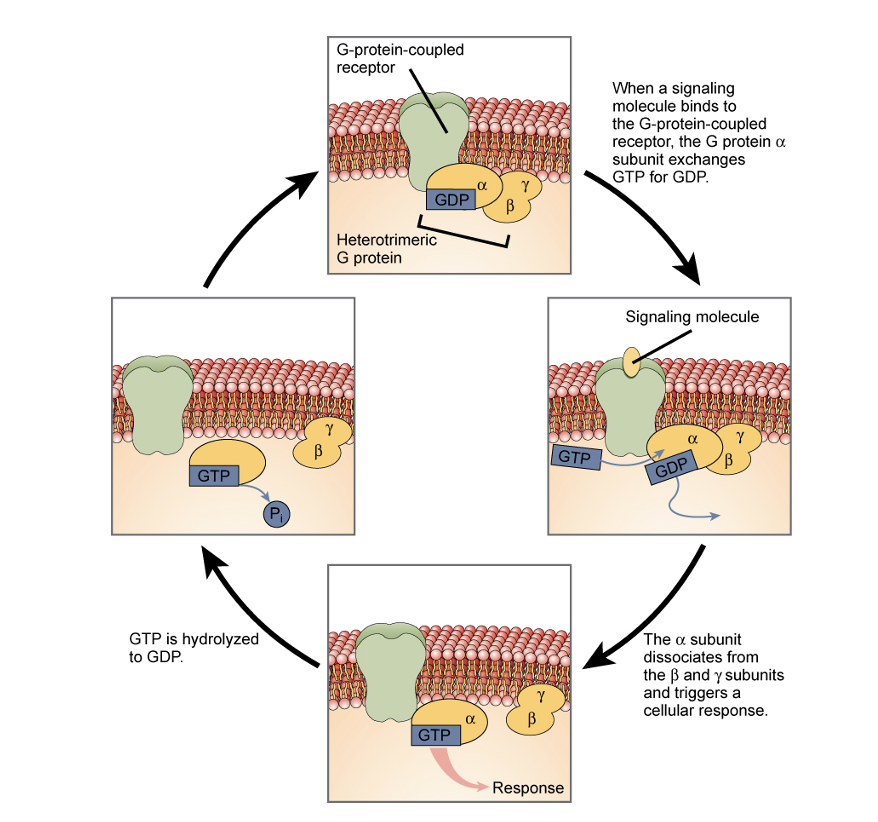
G-protein-linked receptor
a ligand binds & activates G-proteins, causing a signaling cascade
ex. Vibrio cholera
produces a toxin that modifies these receptors in the intestines
leads to severe diarrhea, dehydration, & death
enzyme-linked receptors
a ligand binds & causes intracellular signaling cascades through enzymes
ex. growth factors/mutations
lead to growth abnormalities like dwarfism or cancers
small hydrophobic ligands
steroid hormones have similar chem. structs. to cholesterol
can diffuse directly across the PM where they interact w/ internal receptors
water soluble ligands
these typically bind to cell-surface receptors
gas ligands
one example is nitric oxide:
affected by nitroglycerin (treatment for heart disease) & Viagra
signal transduction
ligand binds to a receptor
signal is transmitted through the cell membrane & into the cytoplasm
continues the signal
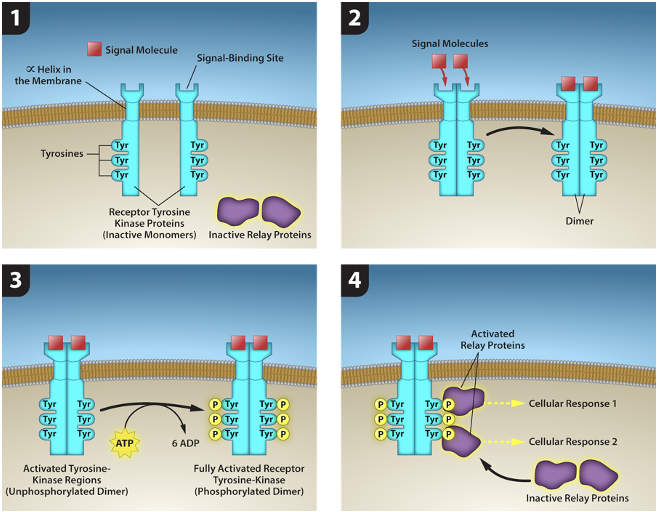
dimerization
2 receptors bind to each other to form a stable complex
signaling pathway
chain of events that happens after a ligand binds to a receptor & include:
2nd messengers
enzymes
activated proteins
signal integration
signals from 2 or more different cell-surface receptors merge to activate the same response in the cell
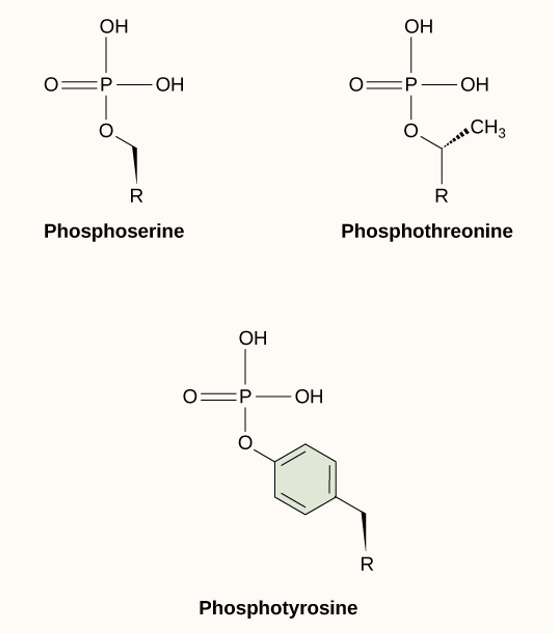
phosphorylation
method of intracellular signaling:
phosphate group is added to residues of serine, threonine, & tyrosine (AAs)
kinase — enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group
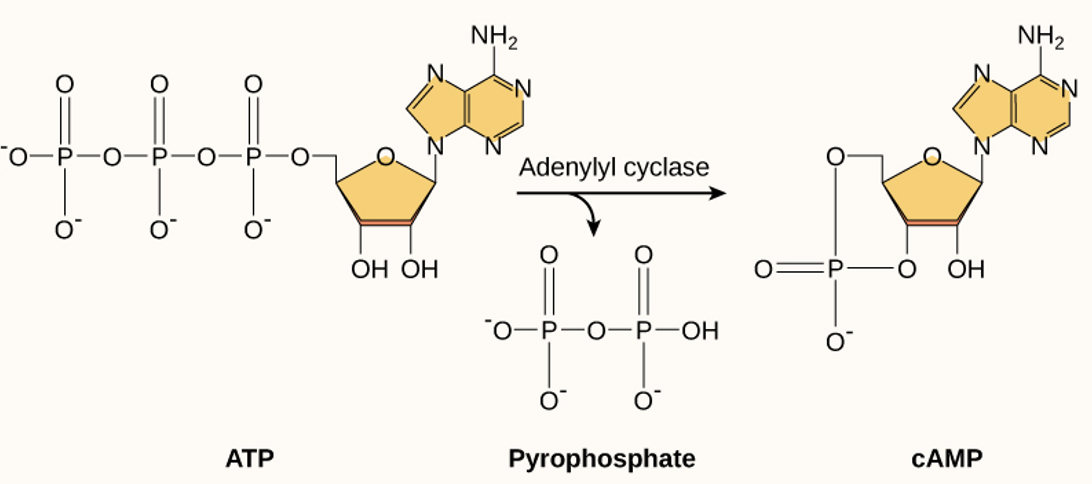
second messengers
small molecules that propagate a signal (after ligand-receptor binding)
cyclic AMP (cAMP) — activate/inactivate proteins in a cell; is terminated when an enzyme converts it to AMP
responses to the signal
gene expression
increase in cellular metabolism
cell growth
apoptosis
cell death; signals are terminated by degradation of ligands or by other signals
embryonic development — cells b/t fingers & toes undergo this
yeast
single-celled
can communicate by releasing a signaling molecule called a mating factor
mating factor binds to cell-surface receptors in nearby cells
stop normal growth cycles & initiate a signaling cascade
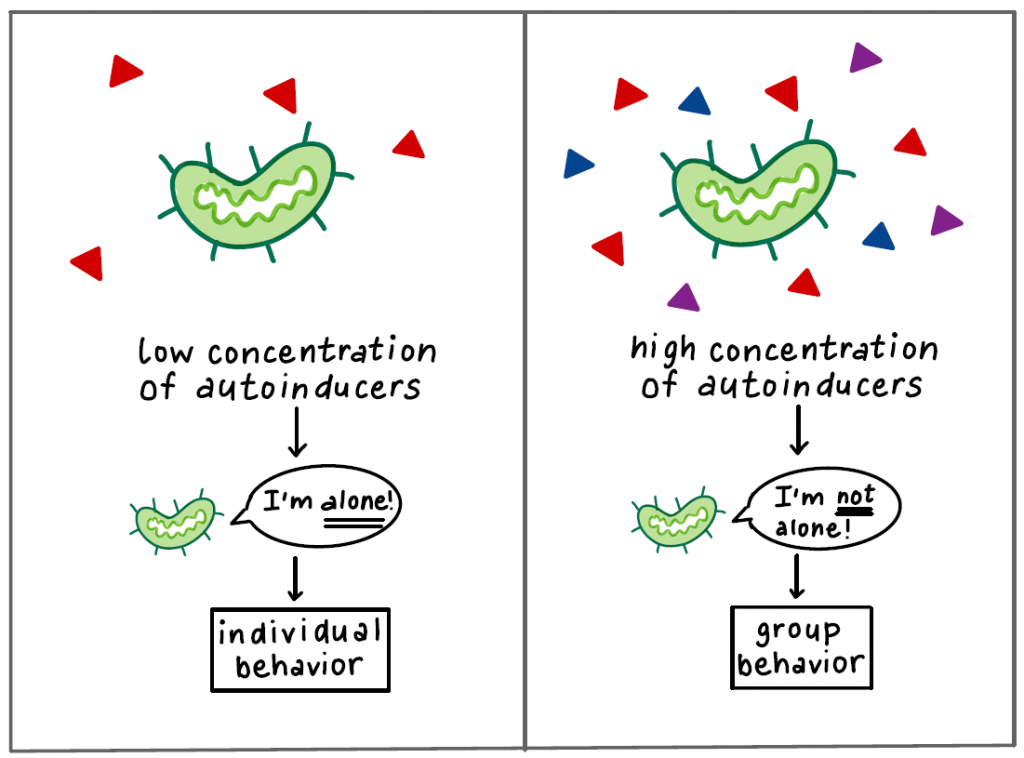
quorum sensing
a chemical language that bacteria use to communicate:
autoinducers are released into the environment
as the bacterial population grows, autoinducers increase
at a certain concentration, the bacteria recognize that they’re part of a community & can coordinate their behavior