Chemistry: Topic 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
What are all substances made of?
Atoms
What is an atom?
The smallest part of an element that can exist
What are atoms of each element represented by?
A chemical symbol
e.g. What does O represent?
An atom of oxygen
e.g What does Na represent?
Sodium
How many different elements are there?
Around 100
What are elements shown on?
The periodic table
What are compounds formed from?
Elements by chemical reactions
Chemical reactions always involve what?
The formation of one or more new substances
What do chemical reactions often involve?
A detectable energy change
What do compounds contain?
Two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions
How can compounds be represented?
By formulae using the symbols of the atoms from which they were formed
How can compounds be separated into elements?
Only by chemical reactions
How can chemical reactions be represented?
By word equations or equations using symbols and formulae
What does a mixture consist of?
Two or more elements or compounds not chemically combined together
What are the chemical properties of each substance in the mixture like?
Unchanged
How can mixtures be separated? (5)
By physical processes such as:
Filtration
Crystallisation
Simple distillation
Fractional distillation
Chromatography
What do these physical processes not involve?
Chemical reactions - meaning no new substances are made
What might experimental evidence lead to?
A scientific model being changed or replaced
Before the discovery of the atom, what were atoms thought to be?
Tiny spheres that could not be divided (billiard ball theory)
What did the discovery of the electron lead to?
The plum pudding model of the atom
Whose model was the plum pudding model?
JJ Thompson
What did the plum pudding model suggest?
That the atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it
Whose model was the first nuclear model?
Rutherford
What did the results from the alpha particle scattering experiment lead to?
The conclusion that the mass of an atom was concentrated at the centre (nucleus)
That the nucleus was charged
Describe the alpha particle scattering experiment
A beam of alpha particles was aimed at very thin gold foil and their passage through was detected
Some of the alpha particles emerged from the foil at different angles, and some even came straight back
The positively charged alpha particles were being repelled and deflected by a small concentration of positive charge in the atom (nucleus)
What happened due to this?
This nuclear model replaced the plum pudding model
Who adapted the nuclear model?
Niels Bohr
How did Niels Bohr adapt the nuclear model?
By suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances
What agreed with his experimental observations
Bohr’s theoretical calculations
What idea did later experiments lead to?
The idea that the positive charge of any nucleus could be subdivided into a whole number of smaller particles, each particle having the same amount of positive charge
What name was given to these particles?
Proton
What did the experimental work of James Chadwick provide the evidence to show?
The existence of neutrons within the nucleus
How long after was this after the nucleus became an accepted scientific idea?
About 20 years
What is the relative electrical charge of a proton?
+1
What is the relative electrical charge of a neutron?
0
What is the relative electrical charge of an electron?
-1
In an atom, what is the number of electrons equal to?
The number of protons in the nucleus
What is the electrical charge of an atom?
0
What is the atomic number of an element?
The number of protons in an atom of an element
What do all atoms of a particular element have the same number of?
Protons
How do atoms of different elements compare to this?
They have different numbers of protons
What is the radius of an atom?
Around 0.1 nm (1×10-10m)
What is the radius of a nucleus?
Less an 1/10,000 of that of the atom (around 1×10-14m)
Where is almost all of the mass of an atom?
In the nucleus
What is the relative mass of a proton?
1
What is the relative mass of a neutron?
1
What is the relative mass of an electron?
very small
What is the mass number of an atom?
The sum of the protons and neutrons
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons, but the same number of protons
What is the relative atomic mass of an element?
An average value that takes account of the abundance of the isotopes of the element
Relative atomic mass equation
(Isotope 1 mass x abundance) + (Isotope 2 mass x abundance)
abundance as a decimal
How else can relative atomic mass be written?
RAM or Ar
What is relative atomic mass compared to?
The mass of one atom of Carbon-12
What do the electrons in an atom occupy?
The lowest available energy levels (innermost available shells)
What is the electronic structure of an atom in numbers?
2, 8, 8 etc.
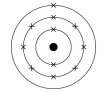
What does this diagram show?
The electronic structure of sodium - 2,8,1
Two electrons in the lowest energy level
Eight in the second energy level
One in the third energy level
How are the elements in the periodic table arranged?
In order of atomic (proton) number
What are elements with similar properties arranged in?
Columns/ groups
What is the table called the periodic table?
Similar properties appear at regular intervals
What are the columns of the periodic table called?
Groups
What do elements in the same group of the table have?
The same number of electrons in their outer shell (outer electrons)
This gives the, similar chemical properties
What are rows of the periodic table called?
Periods
What do the periods of the table show?
How many shells the element has
How did scientists attempt to classify the elements at first?
Before the discovery of protons and neutrons
Arranged elements in order of their atomic weights
What were the early periodic tables like?
Incomplete
Some elements were placed in inappropriate groups if the strict order of atomic weights was followed
WHo played a big part in the development of the periodic table?
Demitri Mendeleev
How did Mendeleev overcome some of the problems with the periodic table?
By leaving gaps for elements that he thought had not been discovered
In some places changed the order based on atomic weights
What happened with the elements with properties predicted by Mendeleev?
They were discovered and filled the gaps
What made it possible to explain why the order based on atomic weights was not always correct?
Knowledge of isotopes
What are metals?
Elements that react to form positive ions
What are non-metals?
Elements that do not react to form positive ions
What are the majority of elements?
Metals
Where are metals found on the periodic table?
To the left and towards the bottom of the table
Where are non-metals found on the periodic table?
Towards the right and top of the table
What are the elements in Group 1 of the periodic table known as?
Alkali metals
Why do the elements in Group 1 have characteristic properties?
Because of the single electron in their outer shell
What are group 1 elements like?
soft
low density
What are the trends as you go down the group?
increased reactivity
lower MPs and BPs
higher RAMs
Why is sodium more reactive than lithium?
sodium needs a full outer shell
has to lose 1 electron
the attraction between the nucleus and electron is smaller as they are further away and sodium has more shells
the outer electron is more easily lost, so sodium is more reactive
How do group 1 elements react with non-metals?
They don’t need much energy to lose their one outer electron to form a full outer shell, so readily form 1+ ions
Only ever react to form ionic compounds
These are usually white solids that dissolve in water to form colourless solutions 
How do G1 elements react with water?
react vigorously
produce hydrogen gas and metal hydroxides
Equation for G1 reaction with water
Element + water > element hydroxide + hydrogen
2E + 2H2O > 2E + 2NaOH + H2
What are metal hydroxides?
Compounds that dissolve in water to produce alkaline solutions
How does lithium react with water?
fizzes steadily on surface
gradually disappears
How does sodium react with water?
fizzes rapidly, moves around surface as liquid ball
disappears quickly
How does potassium react with water?
Ignites with sparks and a lilac flame
Disappears very quickly
Why does the reaction with potassium produce a flame?
The reaction releases enough energy to ignite the hydrogen in the water
What do group 1 elements react with oxygen to form?
Metal oxides
How does lithium react with oxygen?
burns strongly
crimson flame
produces a white solid
What does Lithium + Oxygen form?
Lithium Oxide (Li2O)
How does sodium react with oxygen?
strong orange flame
produces a white solid
What does sodium + oxygen form?
Sodium Oxide (Na2O) and Sodium Peroxide (Na2O2)
How does potassium react with oxygen?
large pieces produce a lilac flame
smaller ones make a solid immediately
What does Potassium + Oxygen form?
A mixture of Potassium Peroxide (K2O) and Potassium Superoxide (KO2)
Why do G1 elements tarnish in air?
The metal reacts with oxygen in the air to form a dull metal oxide layer
How do G1 elements react with chlorine?
React vigorously when heated in chlorine gas
Form white metal chloride salts
Equation for reaction of G1 elements with chlorine
Element + Chlorine > Element Chloride
2E + Cl2 > 2ECl
How does lithium react with chlorine?
white powder is produced and settles on the sides of the container
How does sodium react with chlorine?
burns with a bright yellow flame
clouds of white powder produced and settle on the sides of the container