Recording jaw relationships and using articulators
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is jaw relationship?
is the 3D spatial relationship between the upper and lower jaws or teeth in a patient
What 2 components does a jaw relationship typically have?
both vertical and horizontal components
What is the important joint that allows the mandible/jaw to move?
temporo-mandibular joint
Describe the 2 mandibular movements?
mandibular movements can be vertical - like a door opening and closing around a hinge
mandibular movements can also be horizontal - moving forwards and backwards and side to side (protrusion and lateral excursion)
Movements of the jaw are known as?
dynamic movements
Dynamic occlusion is what?
If the teeth are in contact this is known as dynamic occlusion
What 4 structures work together to limit how much the mandible can move?
TMJ
facial muscles
ligaments
teeth
What are border moevements?
the name given to the outer limits of mandibular movements in every possible direction
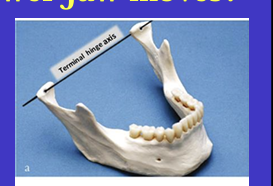
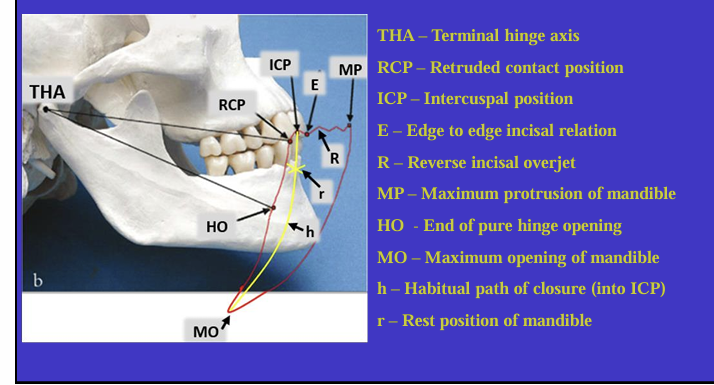
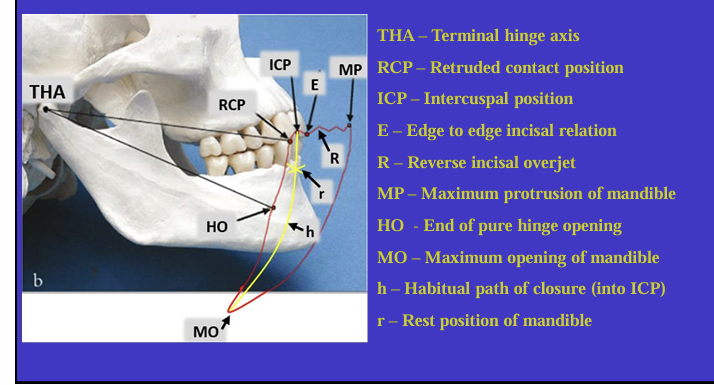
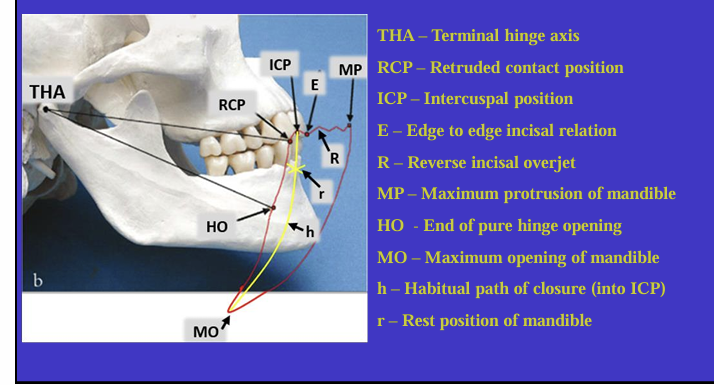
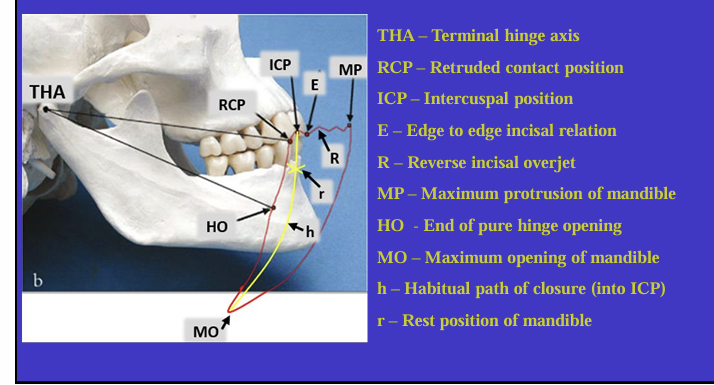
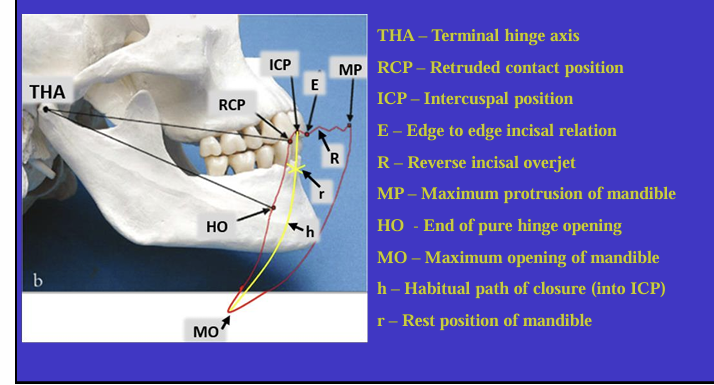
What is this image showing?
Shows an imaginary hinge axis (an imaginary line goes through the heads of both condyles) where the mandible opens and closes around this ‘hinge’ initially
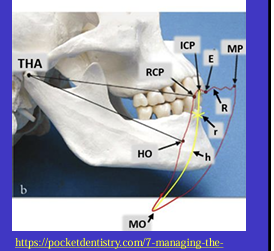
What is this image showing and what is the red shape called?
Tracing the border movements that the mandible makes in space as it moves in the sagittal plane - ‘sagittal border movements of the mandible’
red shape is the Posselt’s envelope or Posselt’s diagram
(incisal edge of one of the lower incisors)
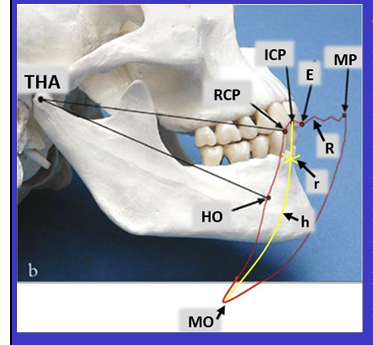
Label the different movements
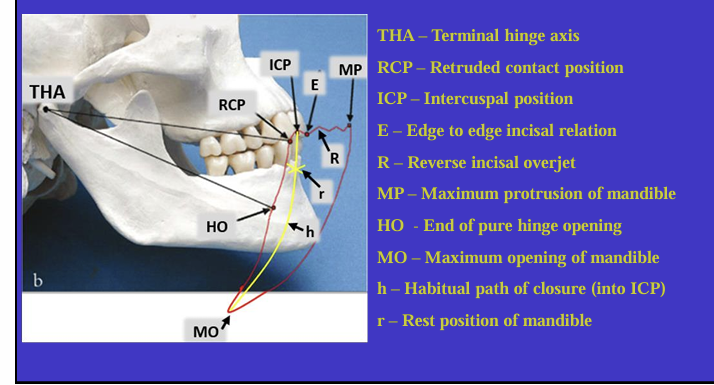
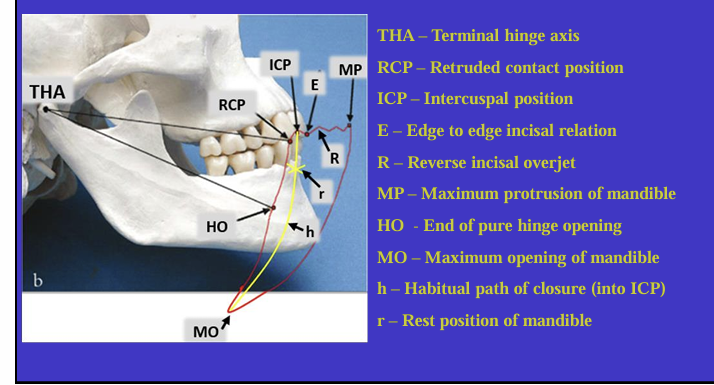
What is the ICP?
it can also be known as?
the maximum intercuspal position is the position where there is most tooth to tooth contact for that individual’s occlusion
centric occlusion - CO
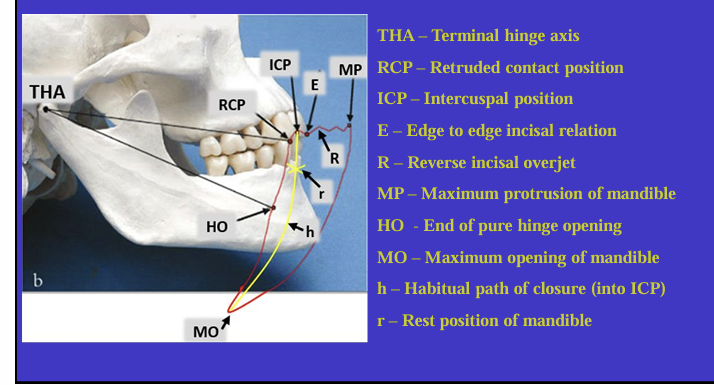
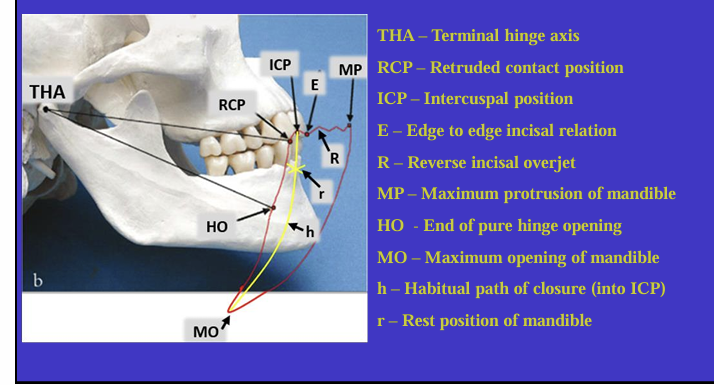
When might the ICP change? (2)
If natural teeth are moved - in orthodontic treatment
teeth change shape - as a result of dental treatment
What is important about the changes in ICP?
most people can adapt to small changes in their ICP
but if large changes are made during restorative treatment then you need to test changes first to make sure the patient can cope
What are other names for the RCP? (4)
other names for the retruded contact position:
centric relation (CR)
hinge axis position (HAP)
terminal hinge relation
ligamentous position
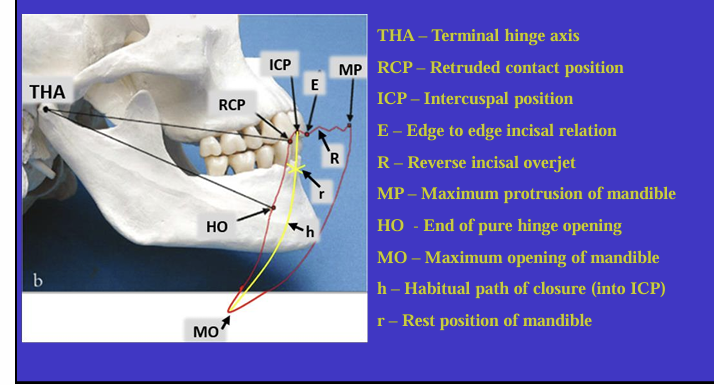
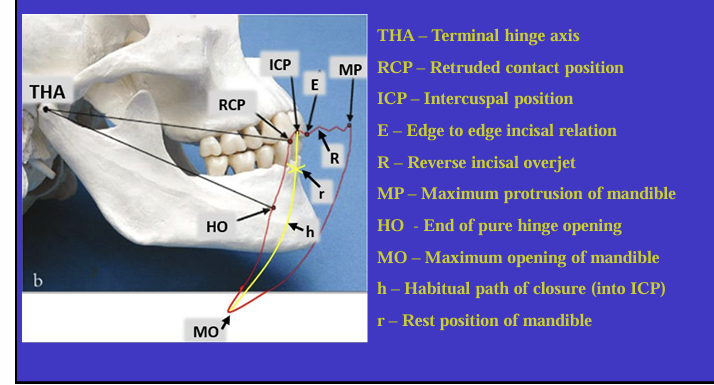
What is the definition of Retruded contact position?
A bilateral unstrained position of the mandible in which the condylar disc assembly is in the most anterior superior position within the glenoid fossa
in this position the initial 20 mm of the incisal opening is a pure ‘hinge’ movement around the hinge axis
if natural teeth are present, the RCP is the point of initial tooth contact as the jaw closes around the hinge axis
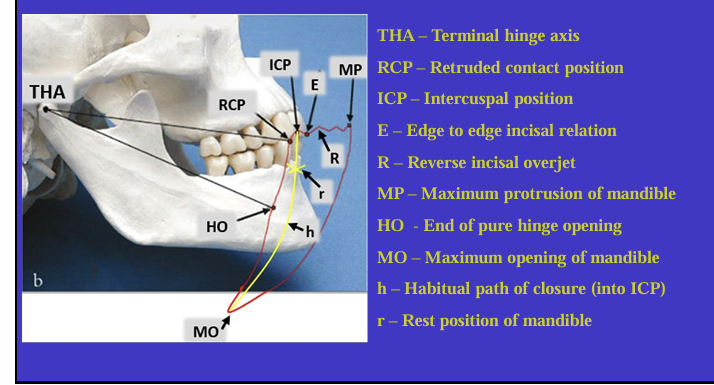
What is the relationship between the ICP and RCP?
about 97% of the population will have a slide from the initial tooth contact in the RCP to the maximum contacts in the ICP
so in 3% of the population, RCP=ICP
the slide = 1.25 mm ± 1mm
the slide is always forwards but may have a lateral component
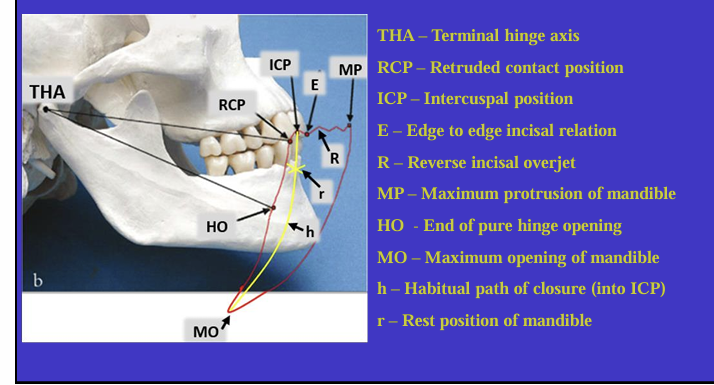
What is the habitual path of closure into the ICP ?
is it a pure hinge movement?
this is the normal path the mandible takes when the patient normally closes their mouth
it is rarely a pure hinge movement as the heads of the condyles are not usually in their most anterioir superior position in the glenoid fossa
the habitual closure is governed by what and what is the importance of this?
The habitual closure is governed by a programme in the brain known as the ENGRAM - this sends a message to the muscles of mastication to avoid any deflective contacts on closing and to find the best fit for the teeth in ICP
this is why changes in the ICP need time to adjust to, as engram needs to be re-programmed
What is an inter-occlusal record and what type of position is this?
You can record a dentate patient’s jaw relationship by asking them to bite on a layer of soft material between the upper and lower teeth and letting it set
static position
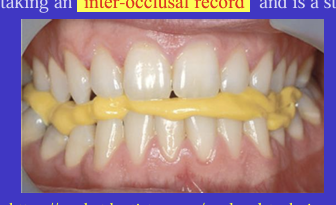
What can the inter-occlusal record be used for?
can be used to accurately position the occlusal surfaces of the upper and lower casts together on an articulator
In a dentate patient, is taking an inter-occlusal record always necessary?
if there are enough good contacts in the ICP there may not be a need to take an inter-occlusal record
in fact, it may actually deflect the casts from their correct position so sometimes we avoid taking one
“Sometimes you can hand articulate the casts in front of the patient so that it matches what you are seeing in the patient’s mouth, and draw on with a pencil on the buccal surface from the upper and lower teeth and line these up when articulating when the patient is no longer there”
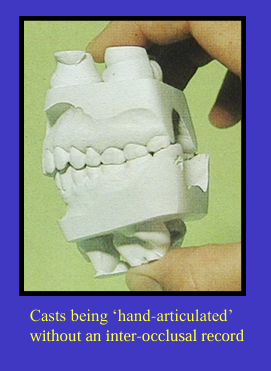
Why may articulating casts in the RCP and not the ICP be useful?
it can allow you to see the slide from the RCP to ICP when mounted on an articulator in the RCP
which may be useful when planning restorations on teeth
How may taking an inter-occlusal in the RCP be different and what wax is used?
in RCP in dentate patients, there will be gaps between some opposing teeth, so you use a special type of wax called ‘beauty wax’ - this wax is good at filling those gaps and holding the shape well and also recording the occlusal relationship in RCP
compare beauty wax and pink sheet wax at RT
very rigid and brittle at RT compared to pink sheet wax which will bend easily at room RT
a record taken in the pink could distort without you noticing before it reaches the lab whereas beauty wax will fracture if damaged
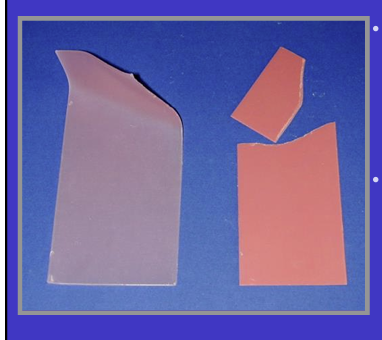
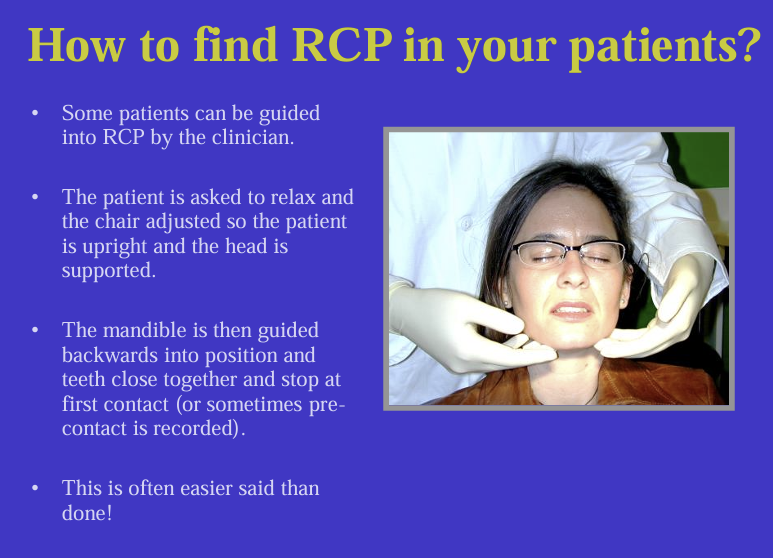
How do you find your patients RCP?
Some patients can be guided into RCP by the clinician.
The patient is asked to relax and the chair adjusted so the patient is upright and the head is supported.
The mandible is then guided backwards into position and teeth close together and stop at first contact (or sometimes pre contact is recorded).
pre-contact record eliminates problem when patient closes in RCP but then autonomically slides back to ICP without realising
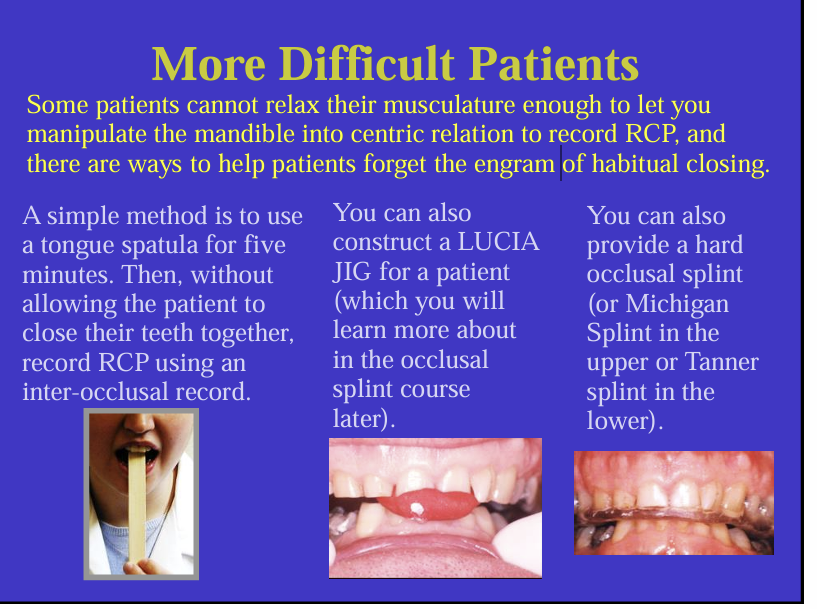
What are 3 methods to help patients in to the RCP position if it is difficult?
Make the patient forget the engram of habitual closing
tongue spatula
LUCIA jig
Michigan or Tanner splint - wear for a while - used when you want a very accurate RCP
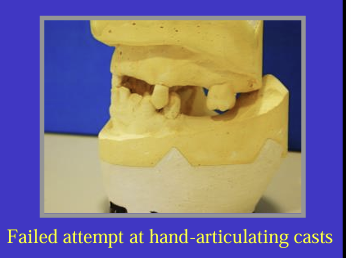
What are two problems faced when trying the get the jaw relationship in partially dentate patients?
where there is significant number of teeth missing, it might not be possible to hand-articulate casts with certainty outside of the mouth
also, just taking an inter-occlusal record in the mouth may not be accurate or reliable
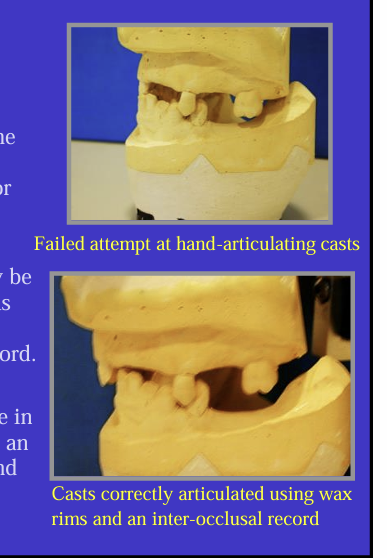
How do you overcome the problem of partially dentate ?
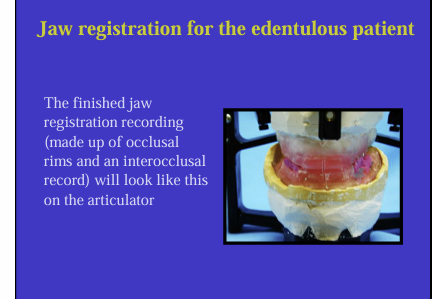
It may be necessary to pre fill those edentulous areas with blocks of wax - called occlusal rims and then take an inter-occlusal record
occlusal rims need to be trimmed to shape in the mouth first and can then be used with an inter-occlusal record to articulate upper and lower casts on an articulator
problems with edentulous patients ?
residual alveolar ridges left
no clear guide to patient’s previous natural tooth position
use occlusal rims and inter-occlusal record to record jaw relationship
there are no natural teeth to record ICP, so jaw relationship is recorded using retruded position - RCP
occlusal rims are constructed on casts and the bases can be made in either wax, self-cure acrylic or heat-cured acrylic - not possible to make heat-cured bases in partially dentate patients
choices of base materials for occlusal rims: wax vs heat cured bases
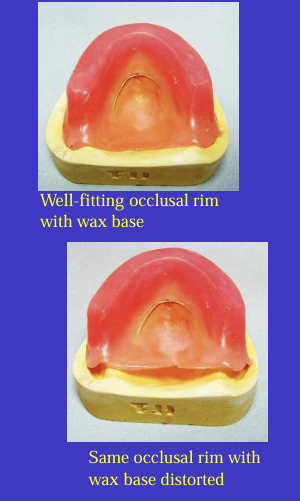
an occlusal rim made in wax (and a wire strengthner) can easily distort -
either the rims don’t seat properly in the mouth or they don’t seat properly on the casts when you try to articulate them
using heat-cured bases is only possible in edentulous arches but ensures no base distortion and also means the rims fit well in the mouth which helps accuracy when recording jaw relationships
jaw registration for the edentulous patient
What is a facebow?
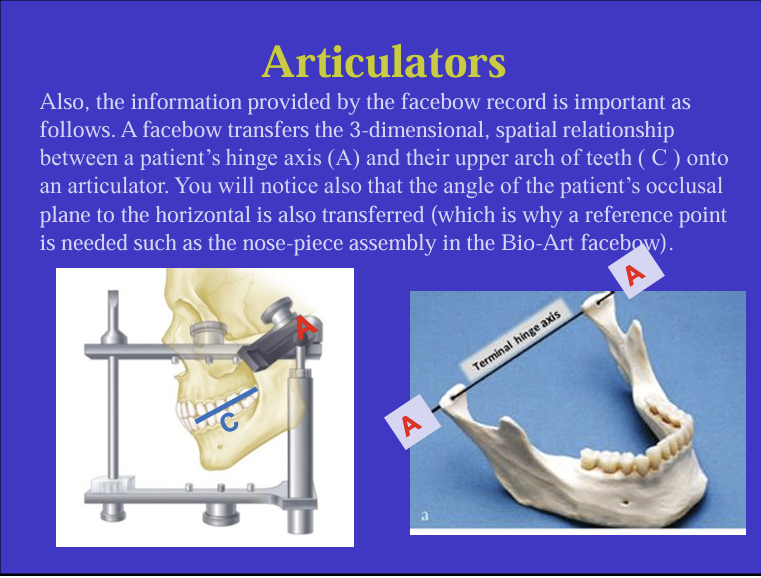
it is a mechanical means of transferring the spatial relationship between the patient’s maxillary teeth and the TMJ or hinge axis onto an articulator
it is what is used to articulate the upper casts on an articulator
What are articulators?
A device that aims to replicate the patients occlusion and jaw movements
if we position casts correctly on an articulator we can observe static and dynamic relationships between upper and lower casts/teeth outside of the mouth
they vary in complexity, the more complex they are, the more they simulate what happens in the real patient
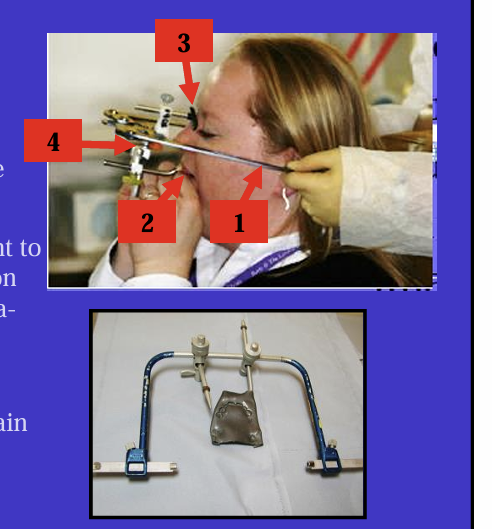
What are the labelled features of the facebows? - all facebows have some features in common:
1 - a bow - fits into the ear canals of the patient
2 - a bite fork to record the maxillary occlusal plane - upper cast
3 - a marker/reference point to help stabilise the position of the facebow (e.g infra-orbital pointer or nose piece assemble)
4- jog which joins the main arm of the bow to the bite fork
each articulator will have its own facebow - can’t mix and match
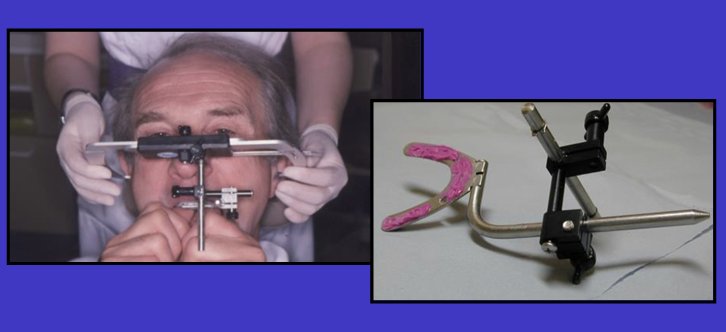
earpieces of the bow are placed how?
the patient is asked to place the earpieces in the their own ears as though they were placing earphones in position so it is comfortable
be aware that a facebow can amplify sound when in position on a patient
What is sent to the laboratory?
only the jig is sent and not the whole bow assembly
will be rinsed and disinfected
What are different types of articulators increasing in complexity?
simple hinge, free-plane articulators, semi-adjustable, fully adjustable articulators

for the greatest accuracy, some dimensions of the articulator and the angles of some of its components should ideally be similar to the patient
what are 2 things ?
the distance between the two condyles and condylar angles which represents the path followed by the head of the condyle in protrusive movements
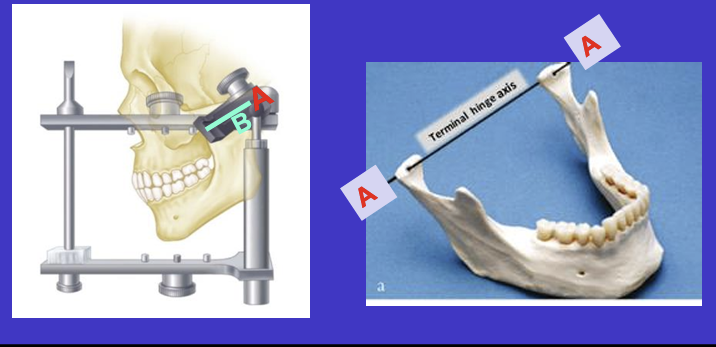
What is also another measurements that is transferred onto the articulator using the facebow?
the angle of the patients occlusal plane to the horizontal
Simple hinge articulators
allow what movements?
What are the problems with simple hinge articulators?
only allow up and down movements and no lateral excursion
the hinge is too near the teeth compared to reality, this affects the mandibular arc of closure and ultimately how the teeth occlude on the cast
there is only one hinge joint whereas there are 2 in the patient
not usually recommended but sometimes ok for very simple dentures
if it is used for more complex work then be aware of their limitation and potential error on your restorations

free plane articulators
better than the simple how?
limitations?
slightly better than the hinge articulator as the condyles are in reasonable position and there are 2 of them
]there is lateral movement - but this is too free and unrealistic
![<ul><li><p>slightly better than the hinge articulator as the condyles are in reasonable position and there are 2 of them</p></li><li><p>]there is lateral movement - but this is too free and unrealistic </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a20a150f-4a6d-466b-b473-8ecda9322c7b.png)
semi adjustable articulators:
have condyles positioned in the correct place and an average value apart from each other
What are two angles on the semi-adjustable articualtors?
condylar and bennet angles

what do the fully adjustable articulators allow for?
complete range of intercondylar distances
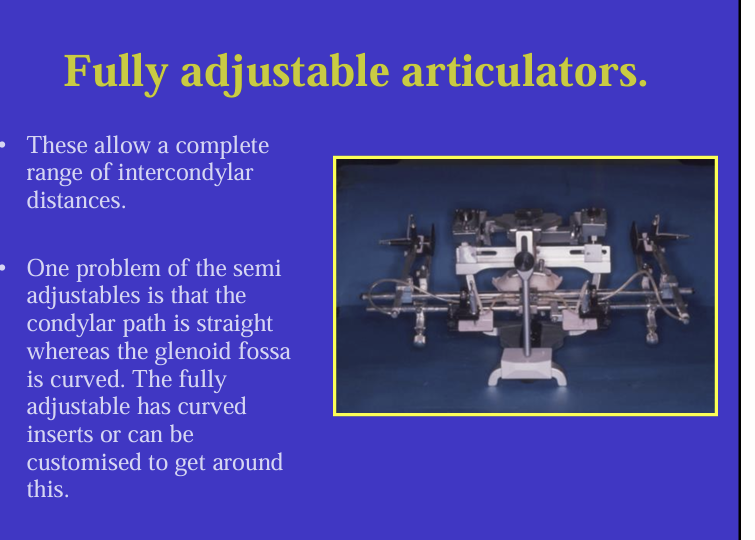
what is the purpose of the pantograph in fully adjustable articulators?
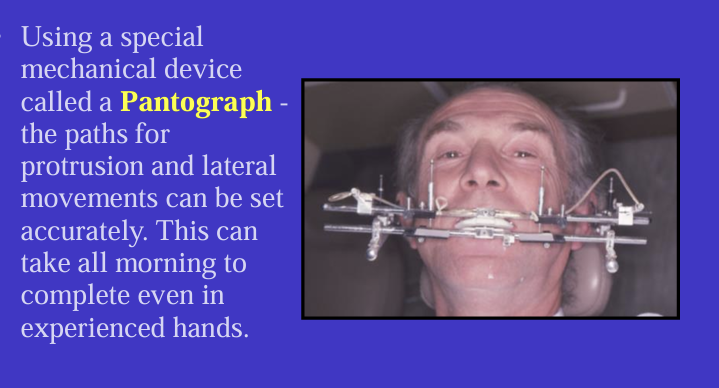
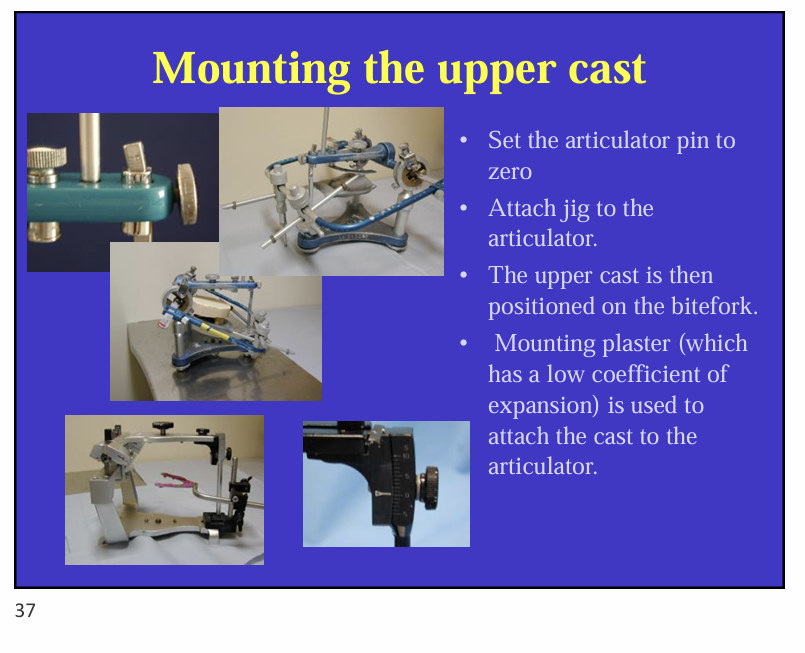
What are steps in mounting an upper cast?