2) Atoms elements and compounds
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Define Proton/atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Define Mass/nucleon number
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
Define isotopes
Different atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Define ionic bond
A strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Describe the giant lattice structure of ionic compounds
A regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions.
Define metallic bonding
The electrostatic attraction between positive ions in a giant metallic lattice and a 'sea' of delocalised electrons.
What are elements
Elements are pure substances made of only one type of atom.
What are compounds
Compounds are made of two or more elements chemically combined. They cannot be separated by physical methods.
What are mixtures
Mixtures are a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined, and can be separated by physical methods.
Atomic structure in an atom
An atom contains a central nucleus, consisting of the subatomic particles protons, neutrons and electrons.
Relative mass and charge of protons
Relative mass: 1
Charge: 1+
Relative mass and charge of neutrons
Relative mass: 1
Charge: 0 (neutral)
Relative mass and charge of electrons
Relative mass: 1/1840
Charge: 1-
Electronic configuration facts
- Group VIII noble gases have a full outer shell.
- The number of outer shell electrons is equal to the group number in groups I to VII
- The number of occupied electron shells is equal to the period number.
Describe properties of isotopes
Isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons and therefore the same electronic configuration.
How do you calculate relative atomic mass
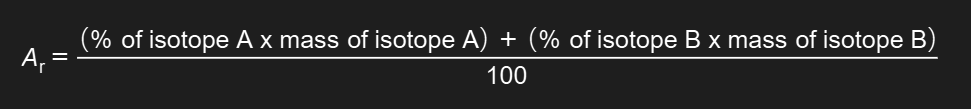
What is an ion
An ion is an electrically charged atom formed by the loss or gain of electrons.
What are cations
Positive ions (cations) are formed when an atom loses electrons, meaning they have more protons than electrons.
What are anions
Negative ions (anions) are formed when an atom gains electron, meaning they have more electrons than protons.
Describe the formation of ionic compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when metal and non-metal atoms react.
Metal atoms lose outer electrons to form a positive ion. Electrons are gained by the non-metal to form a negative ion. The positive and negative ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
All ionic compounds have no overall charge.
Properties of ionic compounds
1) High melting and boiling points: They have giant structures, and strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions, so a lot of energy is needed to overcome the forces. The greater the charge on the ions, the higher the points.
2) Poor conductors in solid state: The ions are in fixed positions in the lattice, so they are unable to move and carry a charge.
3) Good conductors in molten or aqueous state: When the ionic compound is molten or in water, the ions can move and carry a charge.
What is a covalent bond
A covalent bond is formed when a pair of electrons is shared between two atoms, leading to noble gas electronic configurations.
Covalent bond types
Single covalent bond: 1 pair shared (2 electrons total)
Double covalent bond: 2 pairs shared (4 electrons total)
Triple covalent bond: 3 pairs shared (6 electrons total)
Properties of covalent compounds
1) Low melting and boiling points: Small molecules have covalent bonds between atoms, but weak intermolecular between molecules, so less energy is needed to overcome them. The larger the molecules, the higher the melting points as intermolecular forces also increase.
2) Poor electrical conductivity: There are no free ions or electrons to carry a charge. Most covalent solid covalent compounds are insulators.
Describe the giant covalent structure of graphite
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms, leaving one free electron per carbon which becomes delocalised. This forms layers of hexagons of carbon. The covalent bonds between atoms in layers are very strong, but the layers are held together by weak intermolecular forces.
Properties of graphtie
1) Conducts electricity: As each atom has one free electron, the electrons are delocalised and can move through the structure and layers, so they can carry a charge. This is why graphite is used as electrodes in electrolysis.
2) Slippery: As graphite is arranged in layers, they can slide over each other, which allows it to be used in penciles and as a lubricant.
Describe the giant covalent structure of diamond
Each carbon atom is bonded with four other carbons, forming a tetrahedron and do free and delocalised electrons. All covalent bonds are identical and very strong. There are no layers or weak intermolecular forces.
Properties of diamond
1) Hard and dense: As diamond has strong covalent bonds between each atom, it is very strong and hard. This hardness allows it to be used in cutting tools.
Describe the giant covalent structure of Silicon (IV) oxide, SiO2
Each oxygen atom forms single covalent bonds with 2 silicon atoms. Each silicon atom forms single covalent bonds with 4 oxygen atoms. A tetrahedron is formed, similar to diamond.
What are the similarities in properties between diamond and Silicon (IV) oxide, SiO2
1) No intermolecular forces, so it is hard and strong.
2) High boiling point
Properties of metals
1) High melting and boiling points: There are strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the negative delocalised electrons within the lattice structure, so a lot of energy is needed to overcome them.
2) Good conductors of electricity: This is because delocalised electrons are free to move and carry a charge through the whole structure.
3) Malleable: The atoms are arranged in layers which can slide over each other when force is applied, so they can be hammered into shape.
4) Ductile: As the atoms are arranged in layers that can slide over each other, they can be pulled into wires.