COMP607 - Week 7 Digital Forensics and Cybersecurity: Incident Response & Investigation
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What is e-Crime?
E-crime refers to all offenses where information and communications technology is used as a tool, target, or storage device in the commission of an offense.
What are the main categories of the information security workforce?
The information security workforce is divided into managerial personnel and technical personnel.
What is the role of a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)?
The CISO is responsible for assessing, managing, and implementing security, reporting directly to the Chief Information Officer (CIO).
What does a Security Manager do?
A Security Manager supervises technicians and security staff, resolves issues identified by technicians, and works on tasks identified by the CISO.
What are the responsibilities of a Security Administrator?
A Security Administrator manages daily operations, analyzes and designs security solutions, and identifies users' needs.
What is the primary function of a Security Technician?
A Security Technician provides technical support, configures security hardware, implements security software, and troubleshoots problems.
What is digital forensics?
Digital forensics is the application of science to the identification, collection, examination, and analysis of data, preserving the integrity of the information.
What was the first practical application of digital forensics?
The first practical application was in 1986, used to capture hacker Markus Hess.
What types of crimes can digital forensics investigate?
Digital forensics can investigate cyberbullying, copyright infringement, cybercrimes involving illegal items, cyberwarfare, and cyberterrorism.
What are the branches of digital forensics?
The branches include computer forensics, mobile device forensics, network forensics, and forensic data analysis.
What does computer forensics focus on?
Computer forensics focuses on explaining the current state of digital artifacts, such as computers, hard drives, and electronic documents.
What does mobile device forensics involve?
Mobile device forensics involves the investigation and recovery of digital evidence from mobile devices, including phone records and GPS location.

What is the purpose of network forensics?
Network forensics is used to monitor computer network traffic, usually intercepted at the packet level.
What is the goal of forensic data analysis?
Forensic data analysis aims to discover and analyze patterns of fraudulent crimes, typically financial crimes.
What is the significance of maintaining a strict chain of custody in digital forensics?
Maintaining a strict chain of custody is crucial to ensure the integrity of the evidence collected during a digital forensic investigation.
What types of offenses does e-crime include?
E-crime includes traditional offenses like drug trading and fraud, as well as new activities like computer attacks and software piracy.
What is the role of information security?
Information security focuses on protecting electronic information from cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
What are some common data-hiding techniques?
Common data-hiding techniques may include encryption, steganography, and the use of hidden files.
What is the purpose of tools used in digital forensics?
Tools in digital forensics are used to validate data and ensure accurate analysis during investigations.
What is the impact of information technology on traditional crimes?
Information technology has influenced traditional crimes by enabling new forms of offenses, such as identity theft and organized crime.
What is the importance of analyzing data in a digital forensic investigation?
Analyzing data is essential to uncover evidence, understand the nature of the crime, and reconstruct events related to the incident.
What is the primary focus of network forensics?
To monitor computer network traffic, usually intercepted at the packet level.
What is the aim of forensic data analysis?
To discover and analyze patterns of fraudulent crimes, usually financial crimes.
What is the first step in digital forensics procedures when responding to an incident?
Secure the crime scene.
Why is it important to secure the crime scene immediately?
To prevent digital evidence from being overwritten, contaminated, or destroyed.
What actions should be taken by individuals in the vicinity of a digital incident?
Perform damage control, contact the incident response team, and secure the electronic equipment.
What should the incident response team document at the crime scene?
The physical surroundings of the device, using video and photographs to capture the state before any evidence is touched.
What is the purpose of labeling cables connected to a device during an investigation?
To document the hardware components and their connections.
What is the second step in digital forensics procedures?
Preserve the evidence.
How can evidence preservation help in legal contexts?
It ensures that important proof is not corrupted or destroyed, aiding in nonrepudiation.
What is e-discovery in digital forensics?
The process of identifying, collecting, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) for investigations or lawsuits.

What is the importance of documenting the chain of custody?
To ensure that evidence is always under strict control and not corrupted by unauthorized persons.
What does the chain of custody documentation include?
Serial numbers of systems, who handled the systems, and how the evidence was transported.
What is the fourth step in digital forensics procedures?
Examine the evidence.
What is meant by 'order of volatility' in digital forensics?
The principle of preserving the most fragile data first during an examination.
What are the first two levels of data considered most volatile?
Cache memory and CPU data.
What is a mirror image backup in digital forensics?
A backup that captures the swap file or pagefile containing data moved from RAM to the hard drive.
What is firmware in the context of digital forensics?
Software that is embedded in hardware, which can be targeted by threat actors.
What is 'slack' in digital forensics?
Hidden data that can be found in unused portions of storage blocks.
What types of slack are commonly used in Windows computers?
RAM slack and file slack.
What is RAM slack?
Data that is padded in the remaining cluster space of a file being saved, containing information from RAM.
What role do IP monitors play in digital forensics?
They provide insight into incidents by collecting and analyzing IP network traffic.
What is metadata?
Data that describes other data, useful for analyzing file, web, mobile, and email information.
Why are security logs important in incident investigations?
They reveal the type of attack directed at the network and how it bypassed security defenses.
What is the purpose of a vulnerability scan?
To identify potential security weaknesses in a system.
What is the function of a SIEM dashboard?
To provide real-time security monitoring and management of security information.
What does digital forensics aim to recover?
Data from security events and the lessons learned from them.
What is CAINE in digital forensics?
A Linux distribution that offers user-friendly tools for investigative purposes.
What does NetworkMiner do?
Detects operating systems, hostnames, and open ports through packet sniffing.
What is the purpose of ProDiscover?
To image and analyze evidence found on a drive.
What is the function of CryptHunter?
To notify users if active encryption is running on a system.
What are some features of digital forensic workstations?
Configured with multiple gigabit network ports, hot swap bays, and RAID 5 for redundancy.
What information can call detail records provide?
Details about telephone calls, including time, duration, and involved cell towers.
What does GPS data reveal in mobile forensics?
The precise location of a user and their activities at that location.
What is the significance of SMS texts in mobile forensics?
They leave electronic records of communication that can serve as evidence.
What are the primary concerns in cloud forensics?
Ensuring digital evidence is not tampered with and understanding the legal implications.
What is steganalysis?
The art of detecting and decoding hidden data within files.
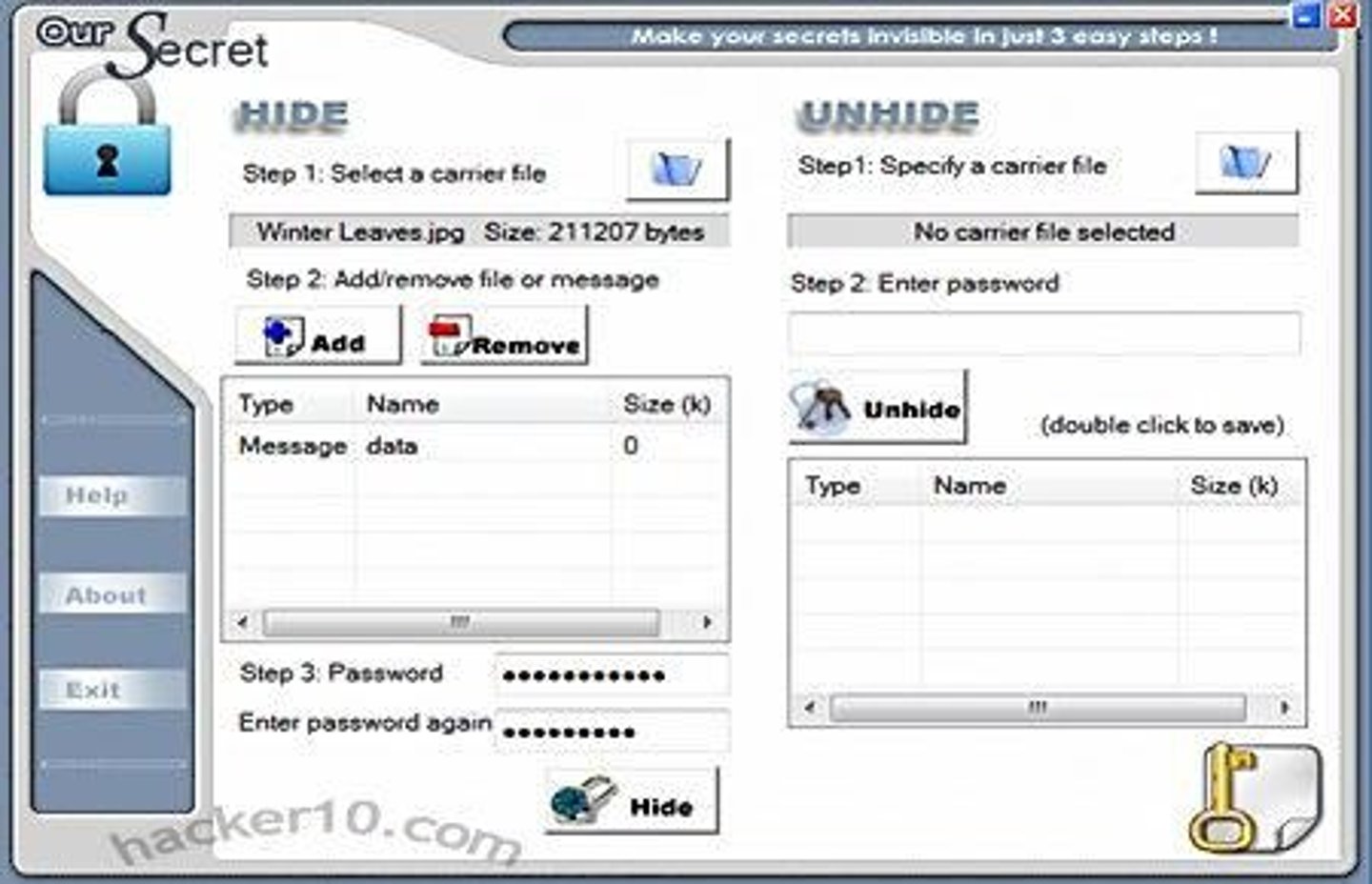
What methods can be used for steganalysis?
Software analysis, disk analysis utilities, and statistical analysis of images or audio.
What challenges exist in recovering watermarked data?
It is very difficult to recover data hidden in pictures, videos, or audio.
How can deleted data be reconstructed?
Even if a disk has been wiped, deleted data can often be recovered.