Chem
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Catylist
speads up chemical reaction without getting used up and lowers activation eneryg
reaction rate
The change in concentration of reactants per unit time as a reaction proceeds
rate law
rate = k[A]^x[B]^y
rate expression
mathematical representation relating reaction rate to changes in amount, concentration, or pressure of reactant or product species per unit time
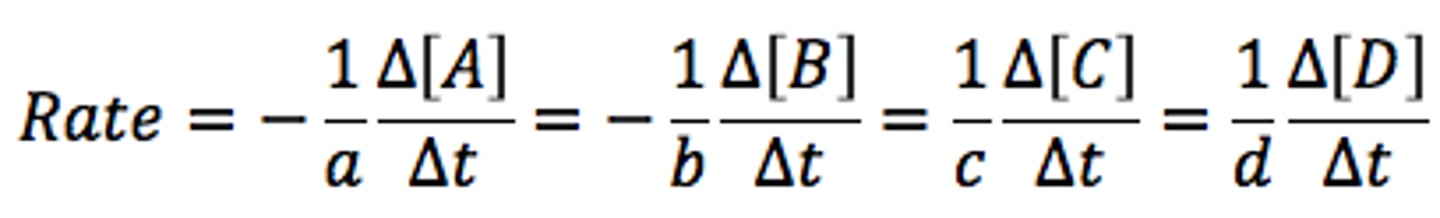
rate constant
K
reaction order
The sum of the exponents in a rate law, where each exponent provides the reaction order with respect to its reactant.
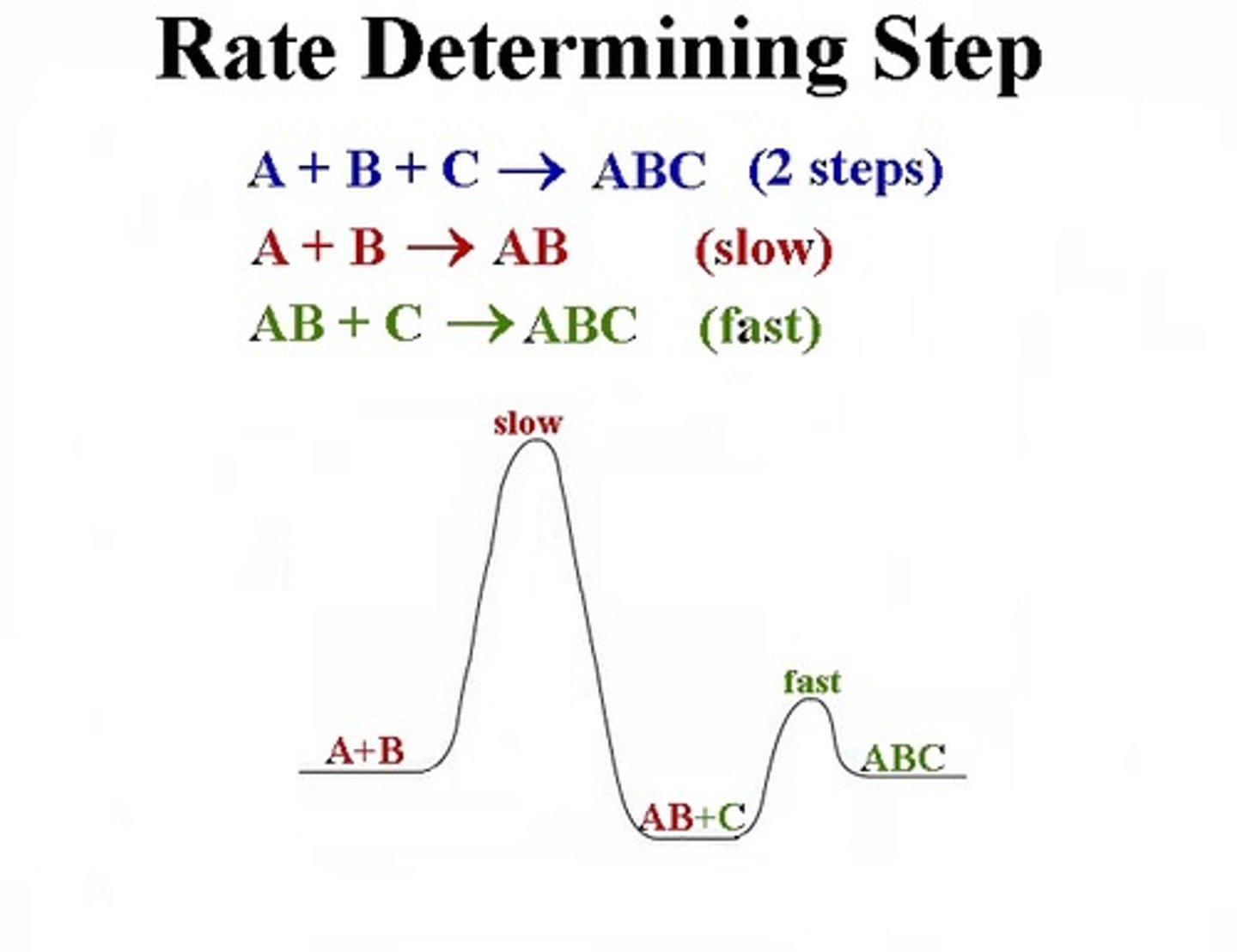
rate limiting step
the slowest step in a pathway
overall order of reaction
The sum of the powers to which the concentration terms are raised in the rate equation
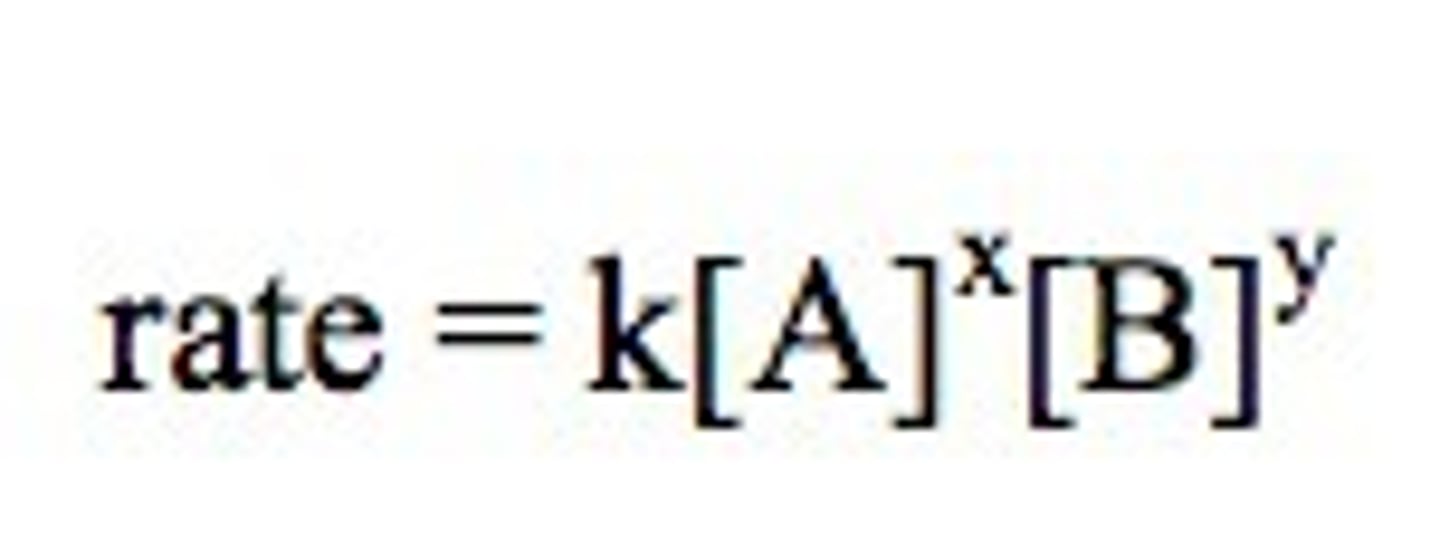
integrated rate law
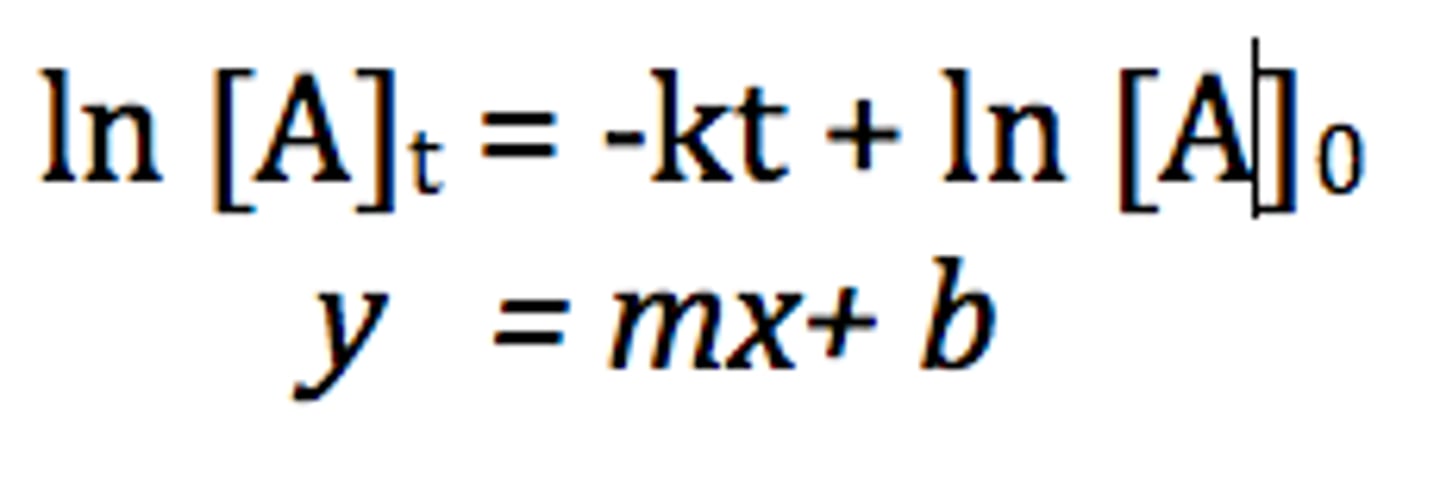
half life
The time required for one half of the atoms of a radioisotope to emit radiation an decay products
intermediate
between two states
collision theory
states that atoms, ions, and molecules must collide in order to react

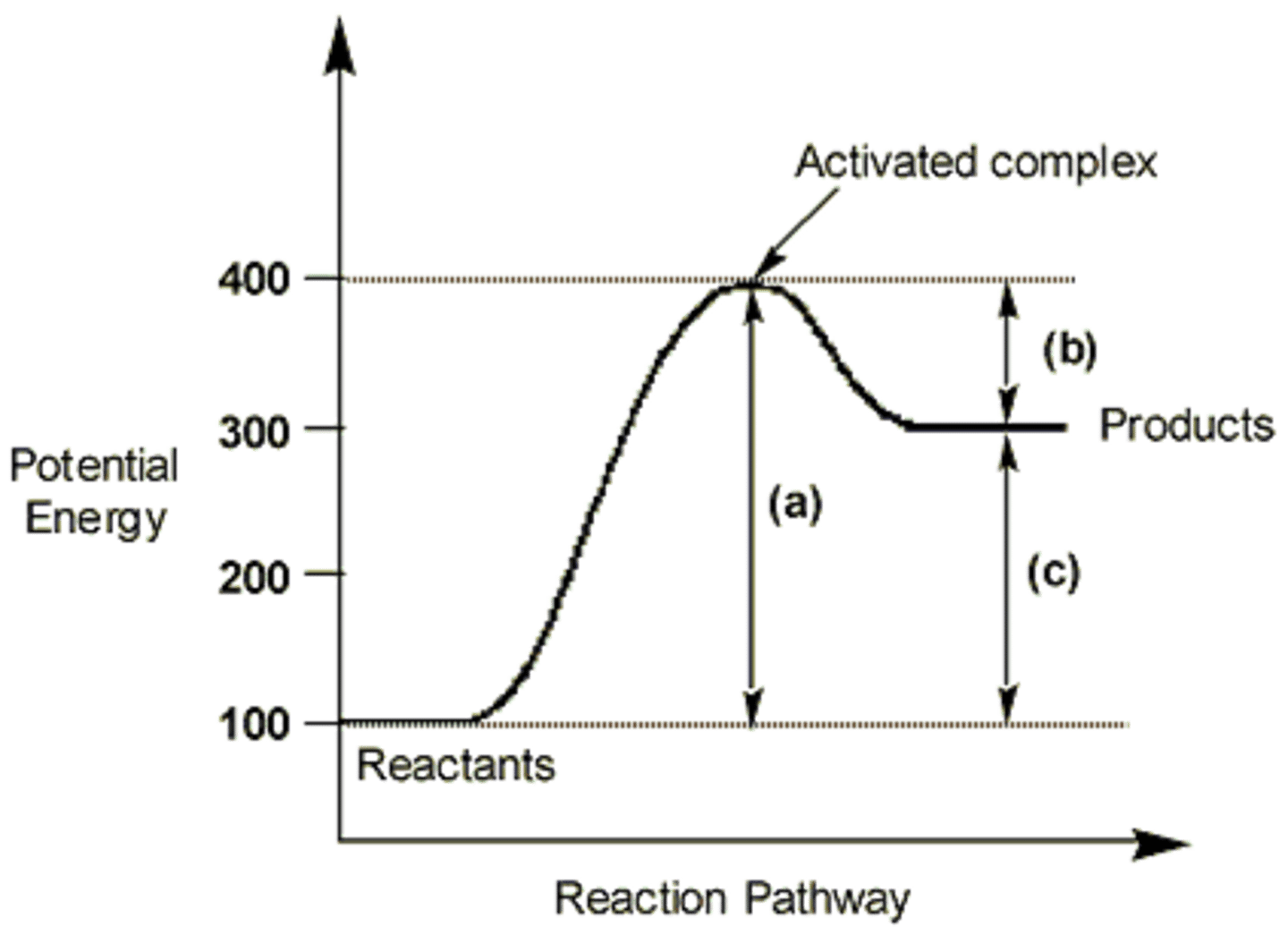
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
activated complex(transition state)
Arrhenius equation
k=Ae^(-Ea/RT)
frequency factor
the number of times that the reactants approach the activation barrier per unit time
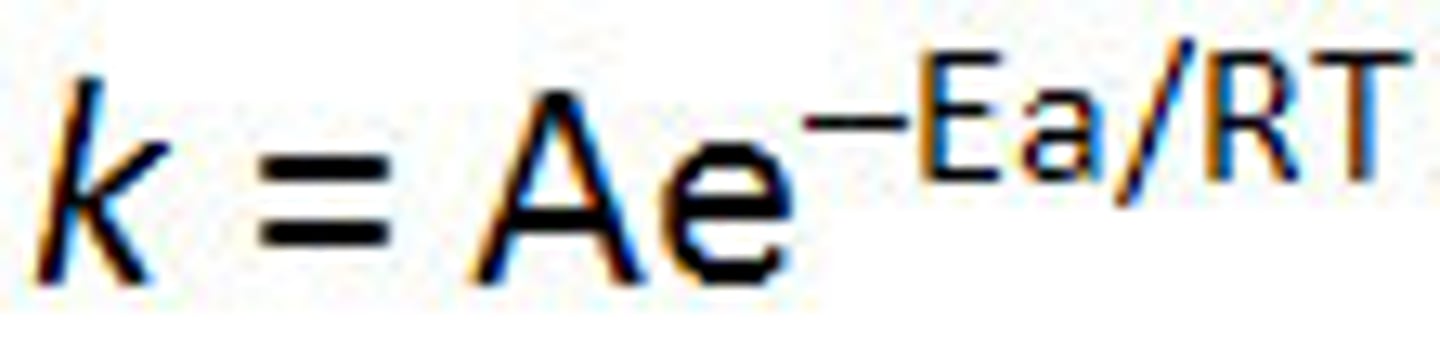
elementary reaction
reactants are converted to products in a single step
homogenous catalyst
a catalyst that is in the same phase as all the reactants and products in a reaction system

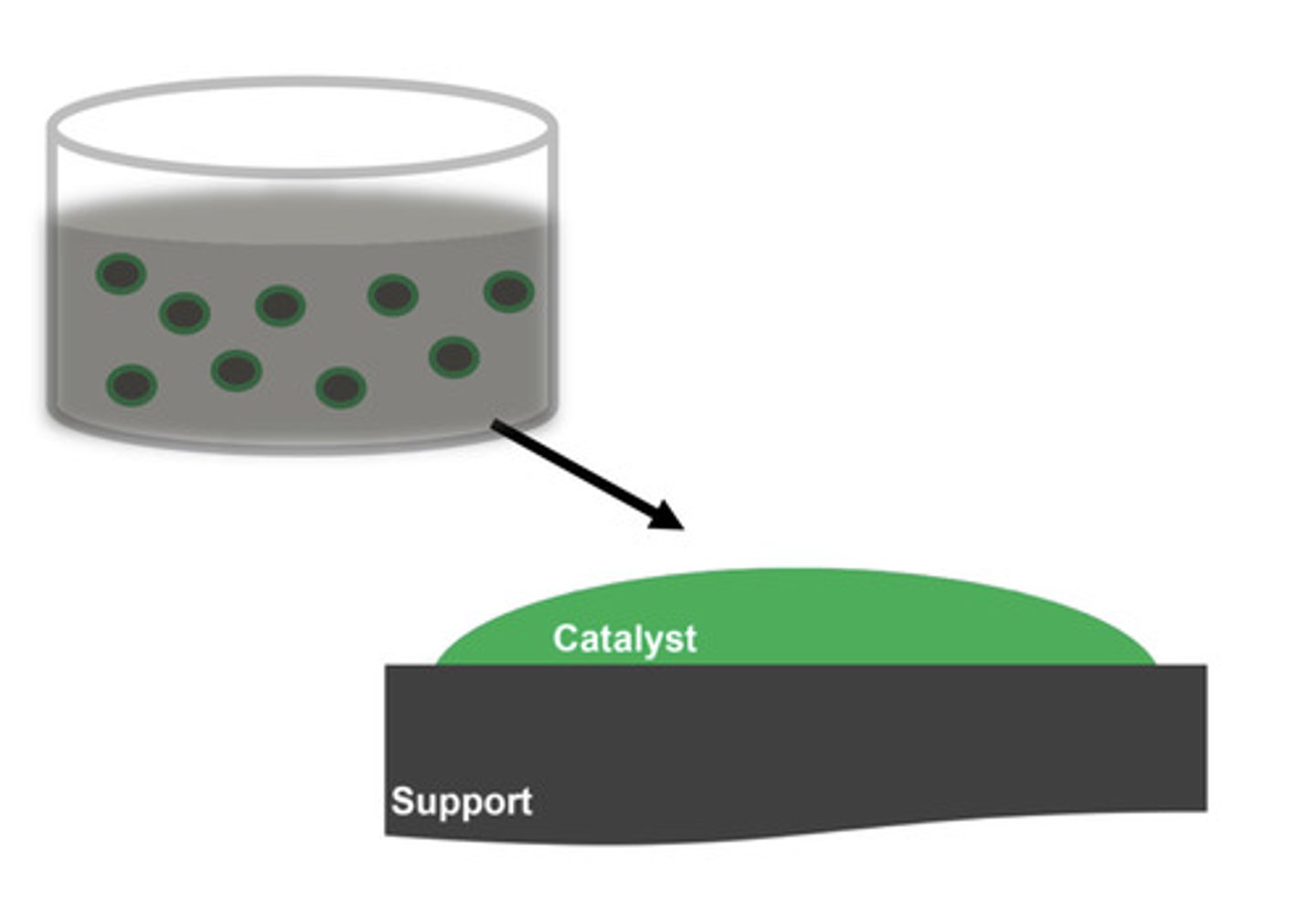
Heterogenous catalyst definition
A catalyst in a different state to the reactants
chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, the state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, so that the relative concentrations of the reactants and products do not change with time.

equilibrium constant
K
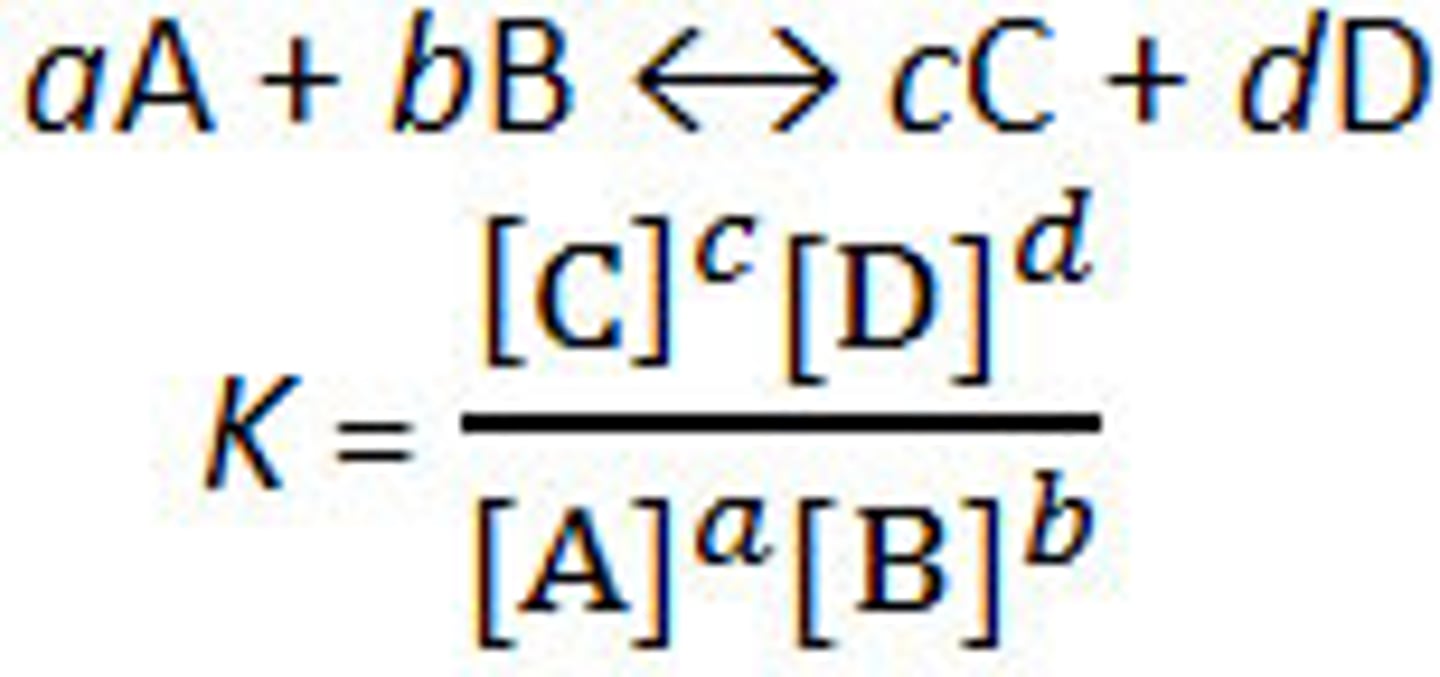
Kc
equilibrium constant
Kp
equilibrium constant for gas-phase reactions based on partial pressures of reactants and products
Homogenous equilibrium
all the reactants and products are in the same physical state
reaction quotient
Ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentrations of the reactants at any point during the reaction aside from equilibrium, where each reactant and product in the expression is raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient. Commonly denoted by Q.
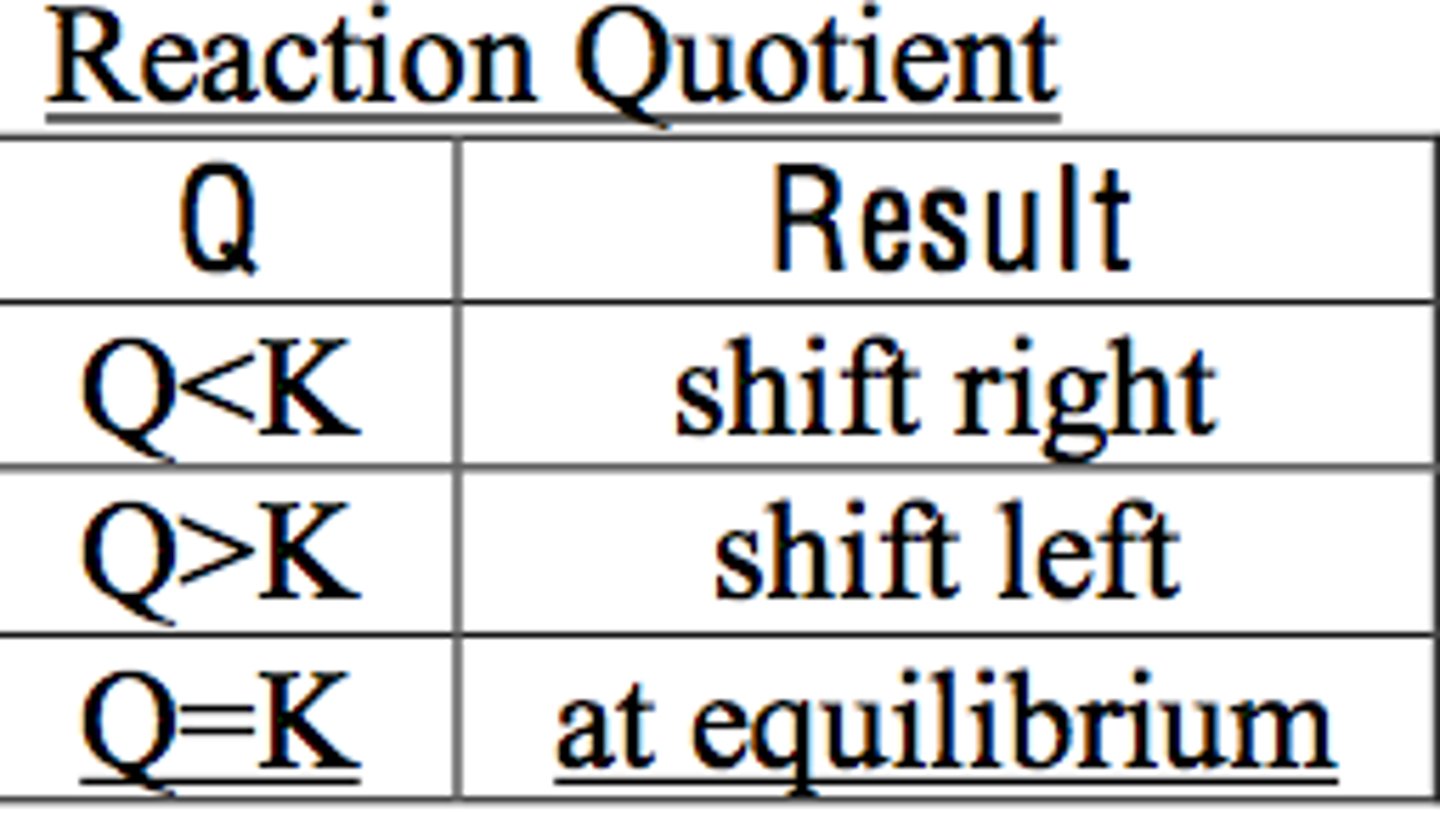
Le Chatelier's Principle
States that if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that relieves the stress.
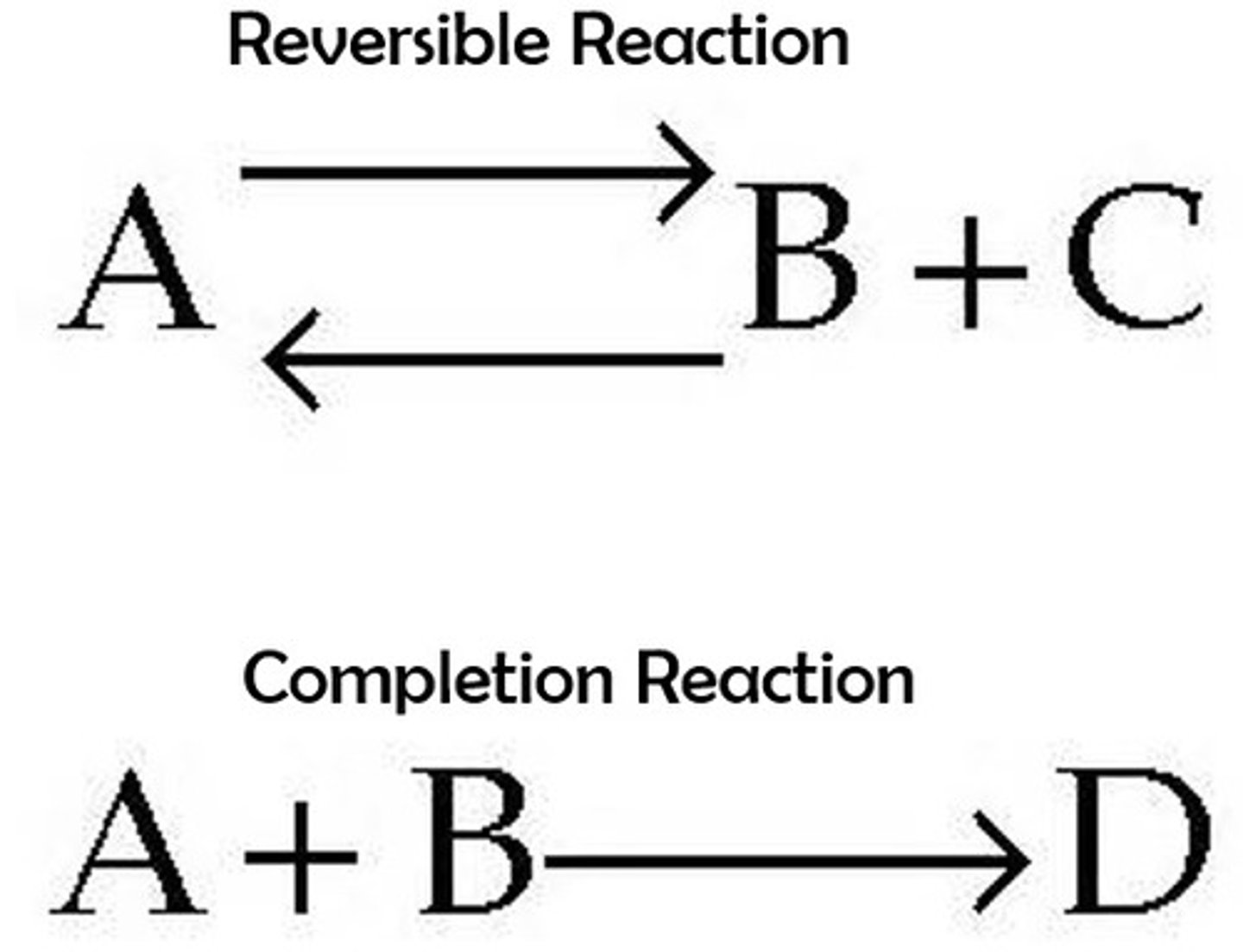
reversible reaction
a chemical reaction in which the products re-form the original reactants