Art and Archeology
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture Slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Importance of pottery
durable, survives most conditions
dateable
used by many groups of people
demonstrates lifeways
can be sourced through chemical petrography
importance of coins
often have dates, people, and events
inscriptions of people and events
regions of greece
Argolis/Argolid
Laconia
Attica → Athens
Thessaly
Maceondia
Greek islands
Crete, Rhodes, Dodecanese, Cyclades
Epistemology
How do we know what we know? How is archaeological knowledge created? How can we evaluate the quality of our knowledge?
Methods of archaeology
not just excavation, often less invasive methodssuch as survey, remote sensing, and analysis of artifacts.
Who did the first classical excavation?
Heinrich Schliemann
What are some methods for identifying sites?
Oral tradition, textual accounts, local memory
walkover survey
LiDAR, satellite imagery
LiDAR
Light Detection and Ranging, a remote sensing method that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create high-resolution maps of the Earth's surface.
Magnetometry
A geophysical surveying technique that measures variations in the Earth's magnetic field to identify archaeological features and structures.
Issues with underwater archaeology
no stratigraphy possible, poor preservation
Key Archaeological features of Pre-Palatial Crete
handmade pottery (Vasiliki Ware), limited trade, first built tombs, development of hierarchy
Palatial Minoan Culture
2000-1500BCE
Primarily on Crete
de-centralized population
palaces (shared storage, religious ceremonies, political activities)
Palatial minoan writing system
Linear A
Palace at Knossos
Mediterranean Bronze Age
3000-1000BCE
Hittites, Minoans, Mycenaean
Minoan power structure
Thalassocracy. Gives Minoans control of the sea, not land. Settlements in port cities
Cycladic Islands
Above Crete
Cycladic Art
3000-1100 BCE
Folded arm figurines
Frying pan pottery
Akrotiri
Minoan Pompeii, located on the island of Santorini
Key features of Akrotiri
Houses, streets, paintings, pottery
Akrotiri frescoes (Minoan)
Blue monkeys, boxing, plant harvesting, horror vacui
Tholos tomb
tombs found in Minoan Crete. They were round, used for storing bones
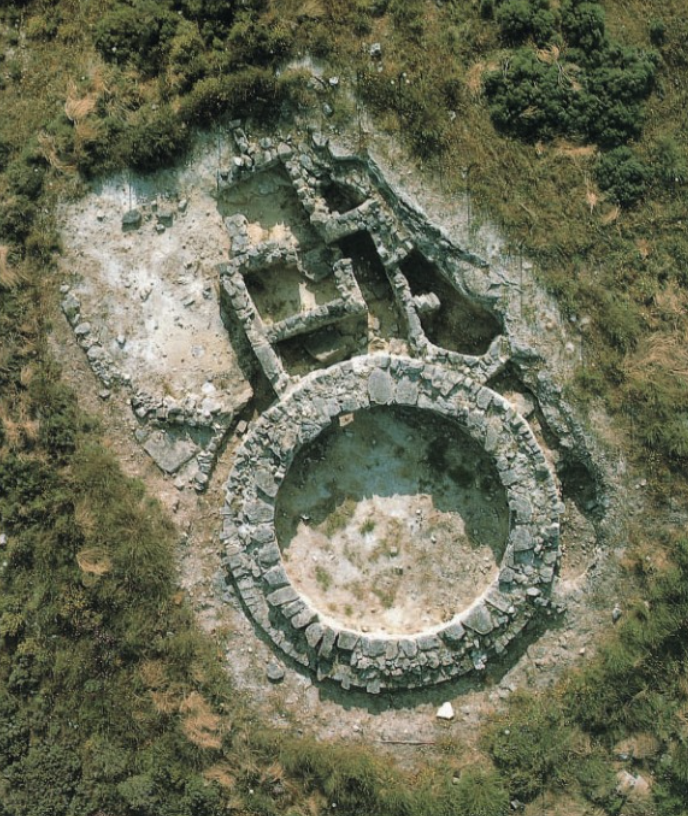

Minoan Palace defining feature
large central courtyard
What were large central courtyards in Minoan palaces used for?
multifunctional, staging assemblies, feasts, rituals, and economic activities
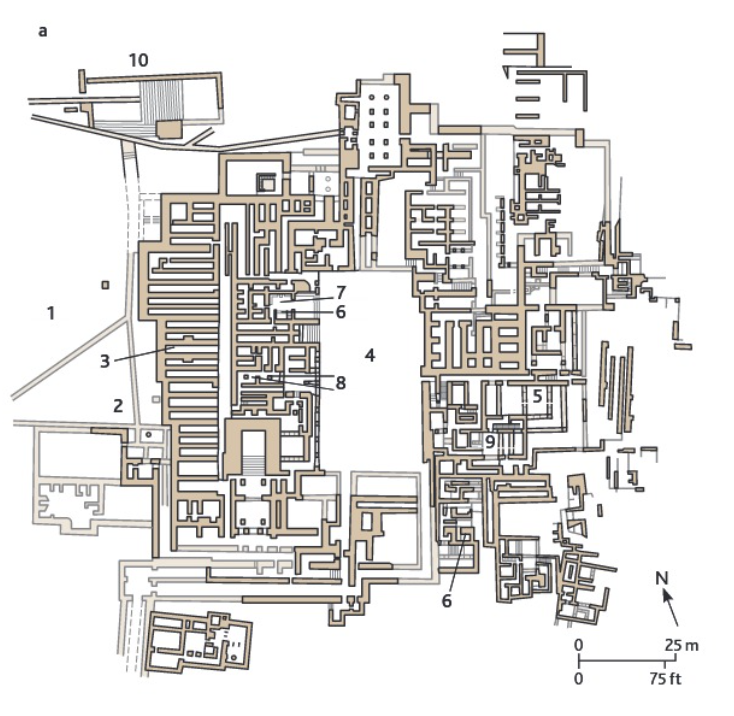
Palace at Knossos (Minoan) Late Minoan
Minoan Hall
a feature of many important buildings that consisted of a chamber with an outer porch opening onto an air shaft. Associated with archives with carved seals. Administrative?
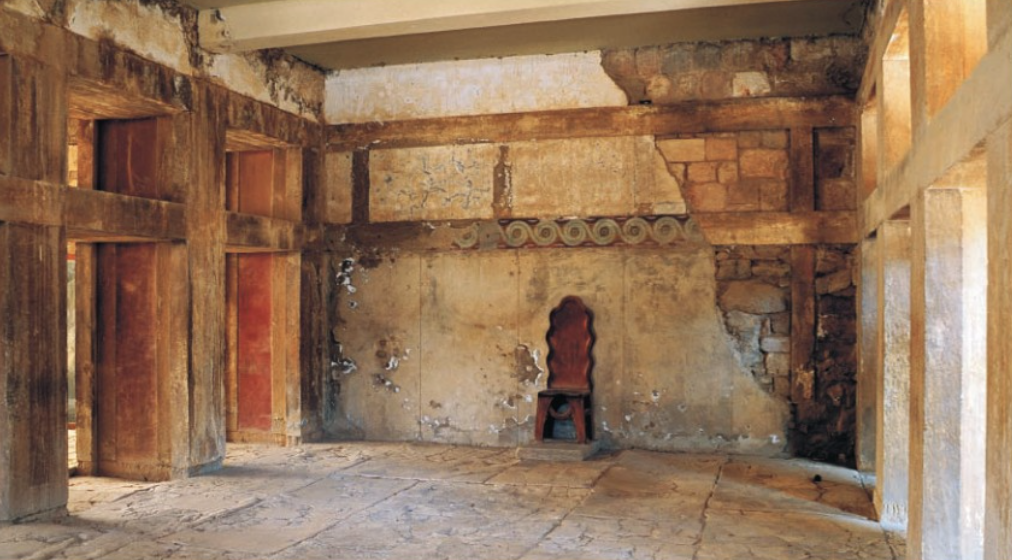

Minoan Hall at Knossos
Lustral basins
resemble time indoor swimming pools, but could not hold water.
Late Bronze Age pottery styles
Floral, Kamares, Marine

Floral style

Kamares style

marine style
OK flashing back forward to Akrotiri
What do frescos in Akrotiri tell us?
Insites about domestic contexts like sport, as well as trade with Egypt and India. They show possible migration of artisans and maybe religious connections with plant harvesting.
What is Minoan art characterized by?
fluidity, interest in the natural environment, and horror vacui
Kolonna
Early Helladic, on the island of Aegina
What is a key difference in Kolonna compared to Minoans?
houses are built against each other vs being free standing
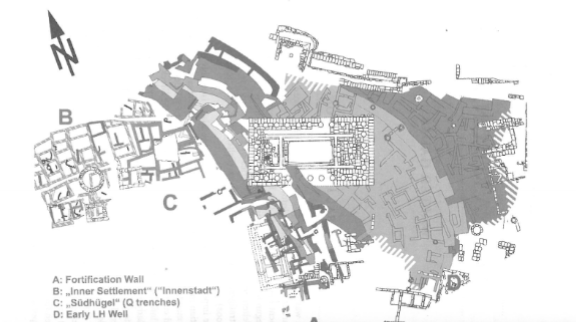
Kolonna
Middle Helladic pottery
Minyan ware
Minyan ware
dark, burnished
Copies of metalwork

Minyan Ware
Late Helladic
Mycenaean (idfk)
Palace complex has role in religious rituals
Centralized economies (factories for oils, pottery)
Grave circles
Mystery destruction
Key part in Mycenaean palaces
Megaron
Megaron
large rectangular hall with a porch. Ceremonal hall
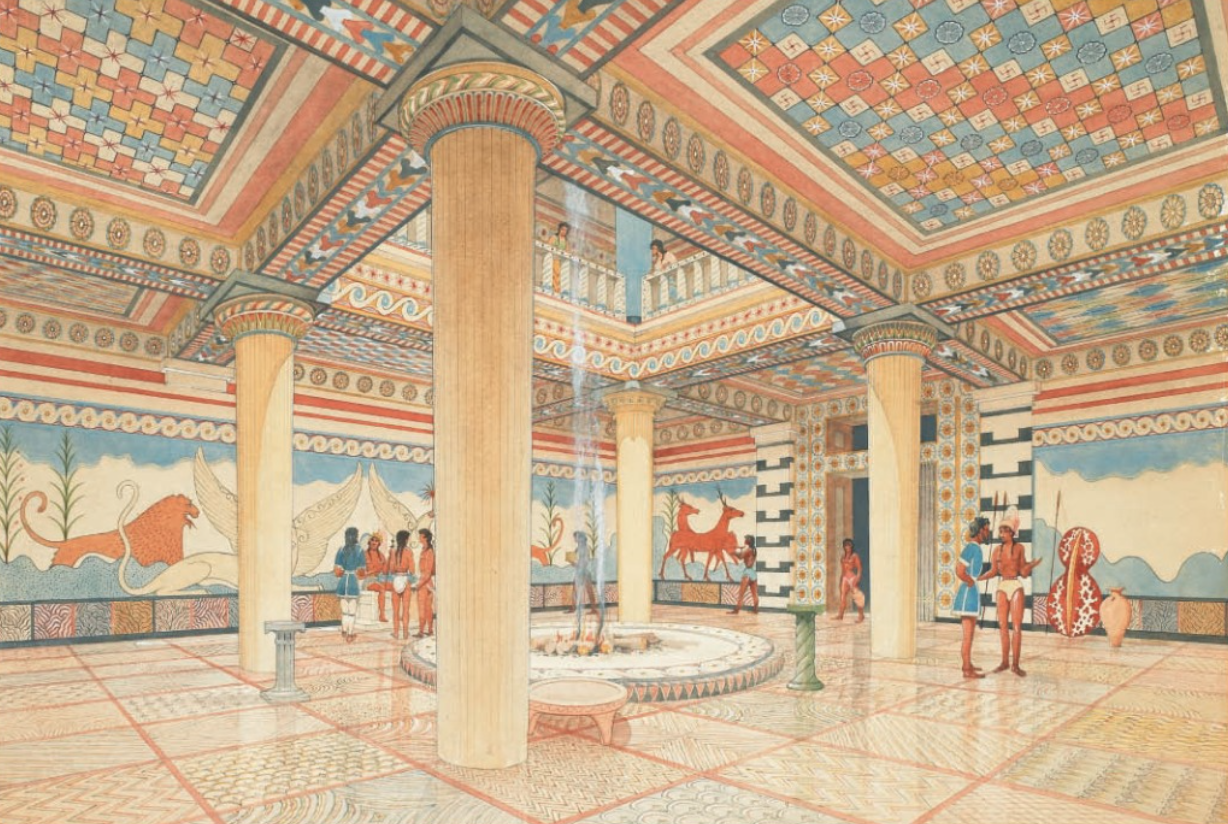

megaron, Pylos
Minoan vs Mycenaean palaces
Mycenaean were not labyrinth-like. They were clearly articulated into concentric rings, each separated by a courtyard. At the core, was the megaron, and from this core additional units could be added.
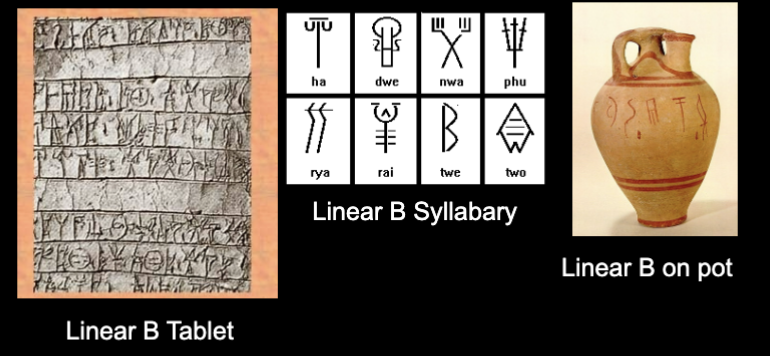
Linear B
Updated linear A.
Mycenaean Walls
some Mycenaean centers invested in fortifications, aka big ass walls, which the Greeks called Cyclopean because they thought cyclopes built them.
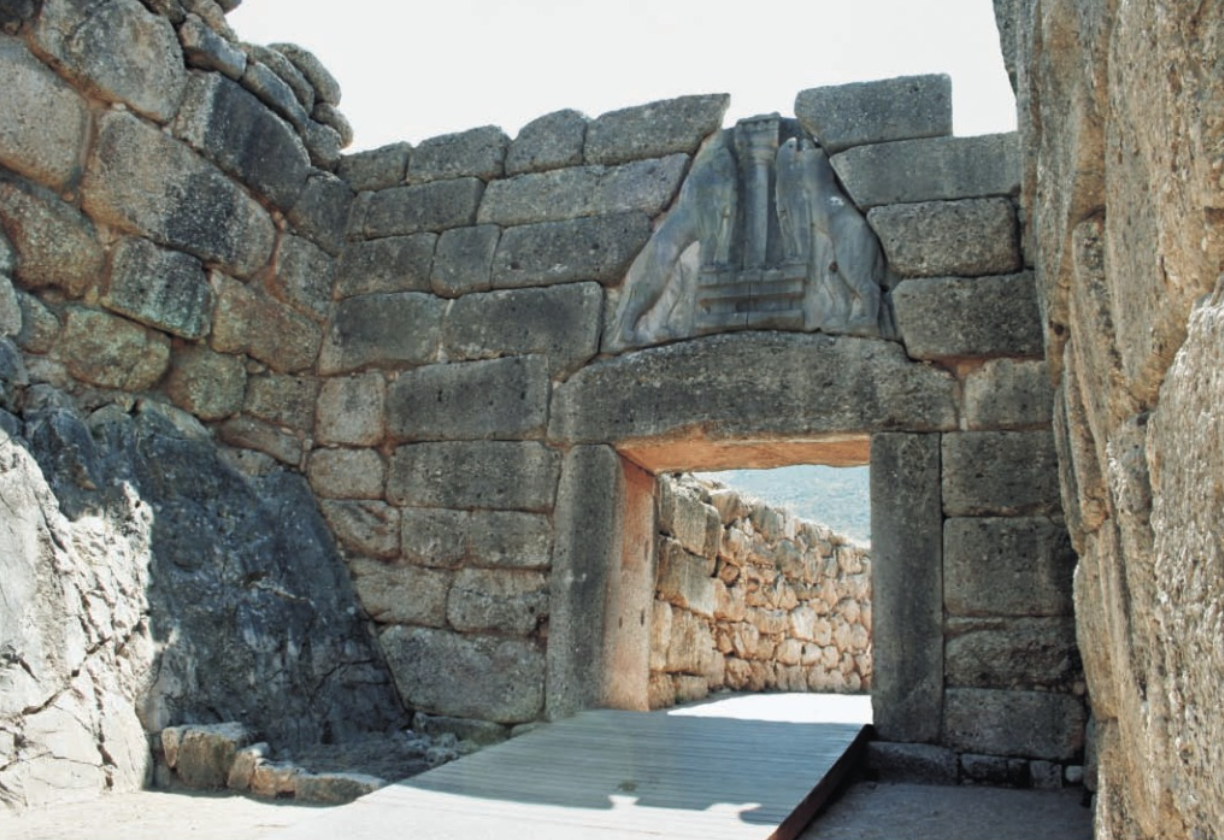

Mycenae Walls and Lion Gate. 1250 BCE
Relieving triangle
Feldman’s International Style
Arises out of transnational elites groups that creates its own culture from local cultures

Mycenae, Treasury of Atreus (Tholos tomb)
Influenced by Minoan masonry and eastern sculpture techniques
Distinction from Minoan: hillside built over it for increased stability
Key features in Iron Age Greece
development of the Polis (city)
Organization/standardization of Greek religion
Connection with the past
Return of writing
colonization
Iron age burial practices
cremation, grave markers

The Nestor Cup
first clear Greek writing
Found in Magna Graecia (Italy)
shows writing as a technology
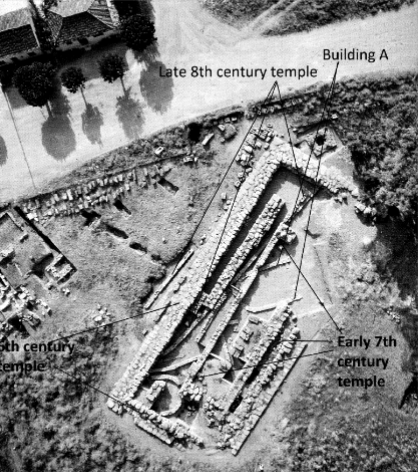

Apollo Daphnephoros at Eretria
One of the earliest sanctuaries
Standardization of Greek Deities
Hero cults
Some Bronze Age ruins were still visible, this caused ritual veneration of these earlier remains and the creation of myths.

Hirschfeld krater
Example of narrative art that tells a story
Geometric period (1100-700 BCE)
Period of major conceptual and technological innovations. Beginnings of states and identities. Death is a key part of society
Colonization in the Greek Iron Age
Areas like Sicily, Magna Graecia, Ionia
New cities could have parent-child relationship with the founding city
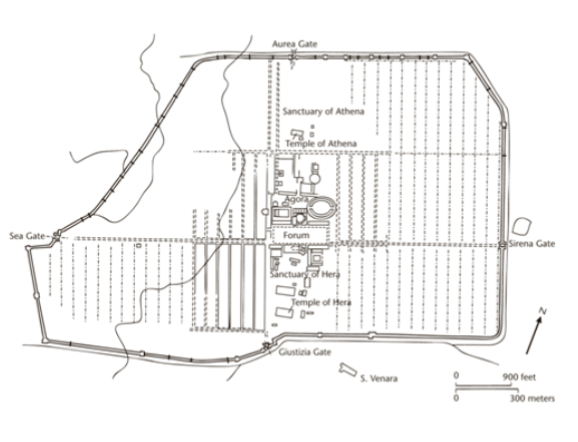
Paestum / Poseidonia
Founded in 600 PC
Major shipping center
Bouleuterion
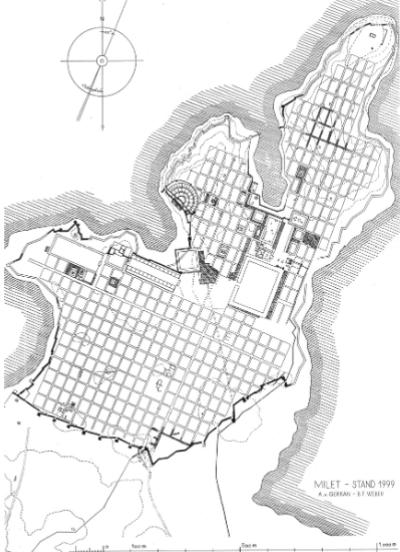
Plan of Miletus
Preserves a Hippodamean plan (grid plan)
Panhellenism
Idea that Greek language, religion, and culture unify people across Polis. Develops as early as the 8th century. Shared sanctuaries
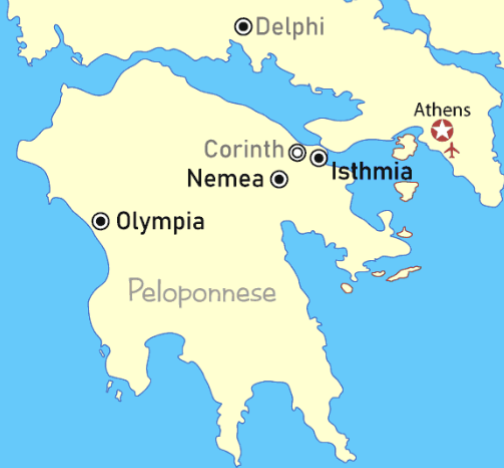
Panhellenic sanctuary locations
Olympia, Delphi, Nemea, Isthmia
Daedalic style
Earliest examples of Greek free-standing sculpture
Triangular shape of hair, narrow face with sharp features, flat volumes of body and clothing
Terracotta statuette from Syracuse
Wild Goat Style
cycladic
bands of wild animals with filling ornaments
Iconography
a set of defined types and scenes used to depict particular characters and stories
Standardization

Temple of Hera at Olympia
Peristyle (columns all around)
Shrine
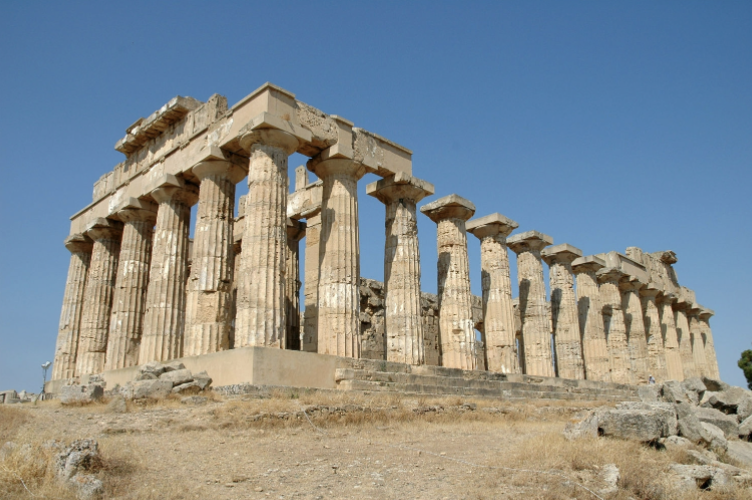

Temple E at Selinum, Sicily
Hera or Aphrodite
Peripteral, hexastyle
Amphiprostyle
porches on both sides

Early Black figure pottery
This one depicts Herakles and Geryon

Attic Kouros from 590 BCE
Example of Archaic Kouroi
Idealized young man without much variation
Nudity
Archaic smile
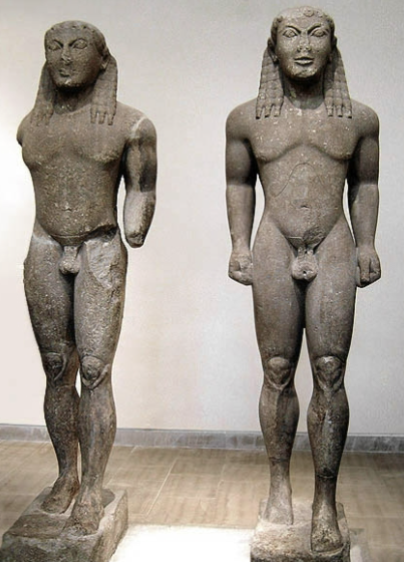

Kleobis and Biton Kouroi
Argive treasury at Delphi by Polymedes of Argos 580BCE
Shows regional variation
Heroic nudity, but wearing boots
depiction of mythological characters (regional identity)

Anavysos Kouros (540-515 BCE)
Grave marker
development towards more naturalistic style
Korai
Depictions of young women
Richness of drapery and hair
Votives or grave markers
Kerameikos cemetery
used from Bronze Age, rise of elite family burials
Olympia
dedicated to Zeus
know important city states
severe style
transition from the Archaic period to the Classical period. More realistic and natural
Centaurmachy
mythical battle between centaurs and Lapiths

West pediment of Temple of
Olympian Zeus
Temple of Olympian Zeus
472-456BC by Libon
Big ass statue of Zeus in it
Severe style metopes
Siphnian Treasury
530-525 BC
Early example of Ionic
Key features of Ionic
continuous narrative for frieze, bases for columns
caryatids
columns but instead of being boring they’re women
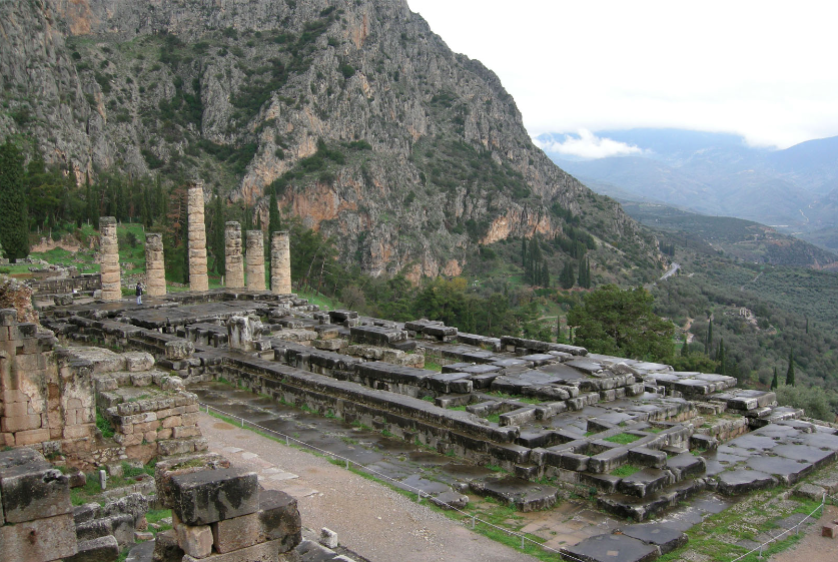

Temple of Apollo in Delphi
Recessed area under temple
Pediments

Riace Bronzes
460 BCE
Red figure pottery
allows for finer detail, more exploration of narrative structure
OK slides done review parthenon stuff tho
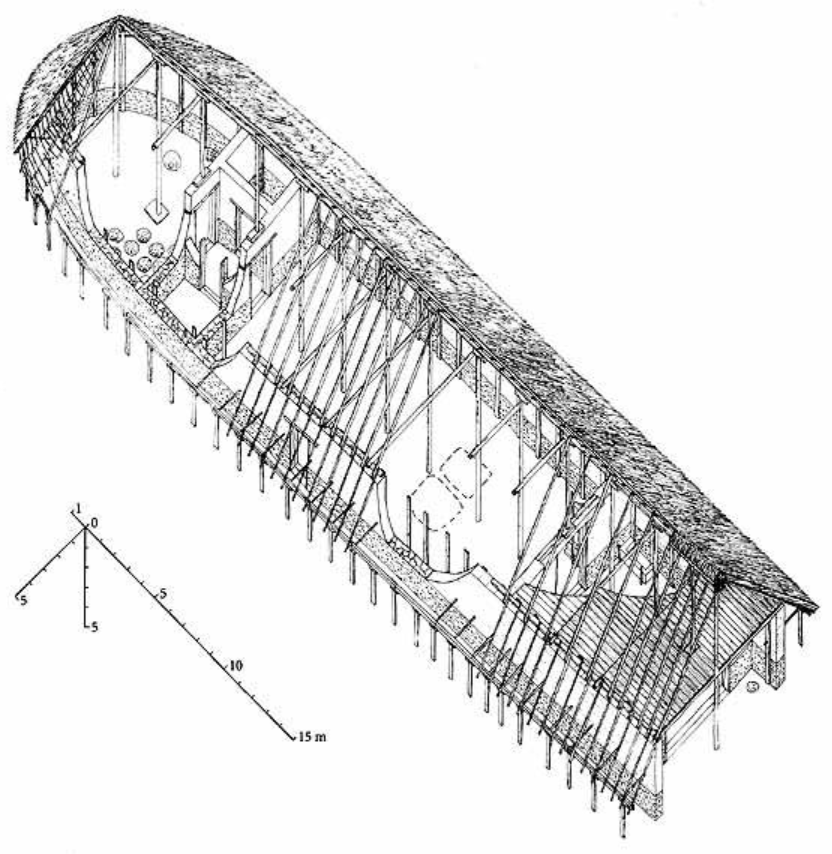
Lefkandi
Iron Age, had important burials with imported items