1.2 Etruscan + Rome
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Augustus
First emperor of Rome
portrait sculpture
this sculpture is a non-idealized version of people
relief sculpture
known for its narrative value ; appeared on altars, arches and tombs
sarcrophagus
Roman marble or limestome coffin with elaborate carving
bust
a sculpture depicting a head, neck, and upper chest of a figure
Roman fresco technique
fresco technique involving painting directly on a plaster wall
buon fresco (true fresco)
the paints are applied to wet plaster and thus become part of the wall's surface
mosaic
Patterns or pictures made by embedding small pieces (tesserae) of stone or glass in cement on surfaces such as walls and floors; also, the technique of making such works.
tesserae
the small piece of stone, glass, or other object that is pieced together with many others to create a mosaic
Pax Romana
A period of peace and prosperity throughout the Roman Empire, lasting from 27 B.C. to A.D. 180.
equestrian
type of sculpture of Romans
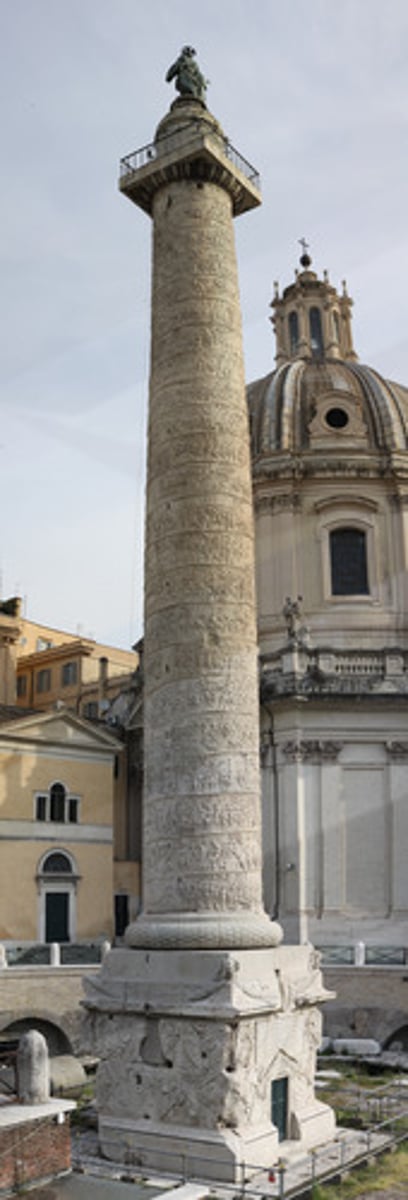
column of victory
a monument in the form of a column, erected in memory of a victorious battle, war, or revolution ; the column typically stands on a base and is crowned with a victory symbol, such as a statue

opus caementicium
Roman concrete
components of opus caementicium
lime mortar, sand, water, and stones
Voussoirs
wedge shaped blocks holding the curve of the arch
key stone
a central stone at the summit of an arch, locking the whole together.
centering
method to create arches with wedge-shaped stones
triumphal arch
In Roman architecture, a freestanding arch commemorating an important event, such as a military victory or the opening of a new road.
Trajan's Column
a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars.
Arch
from wedge-shaped stones formed by the use of centering
vault
a curved ceiling made of arches
barrel vault
a vault forming a half cylinder
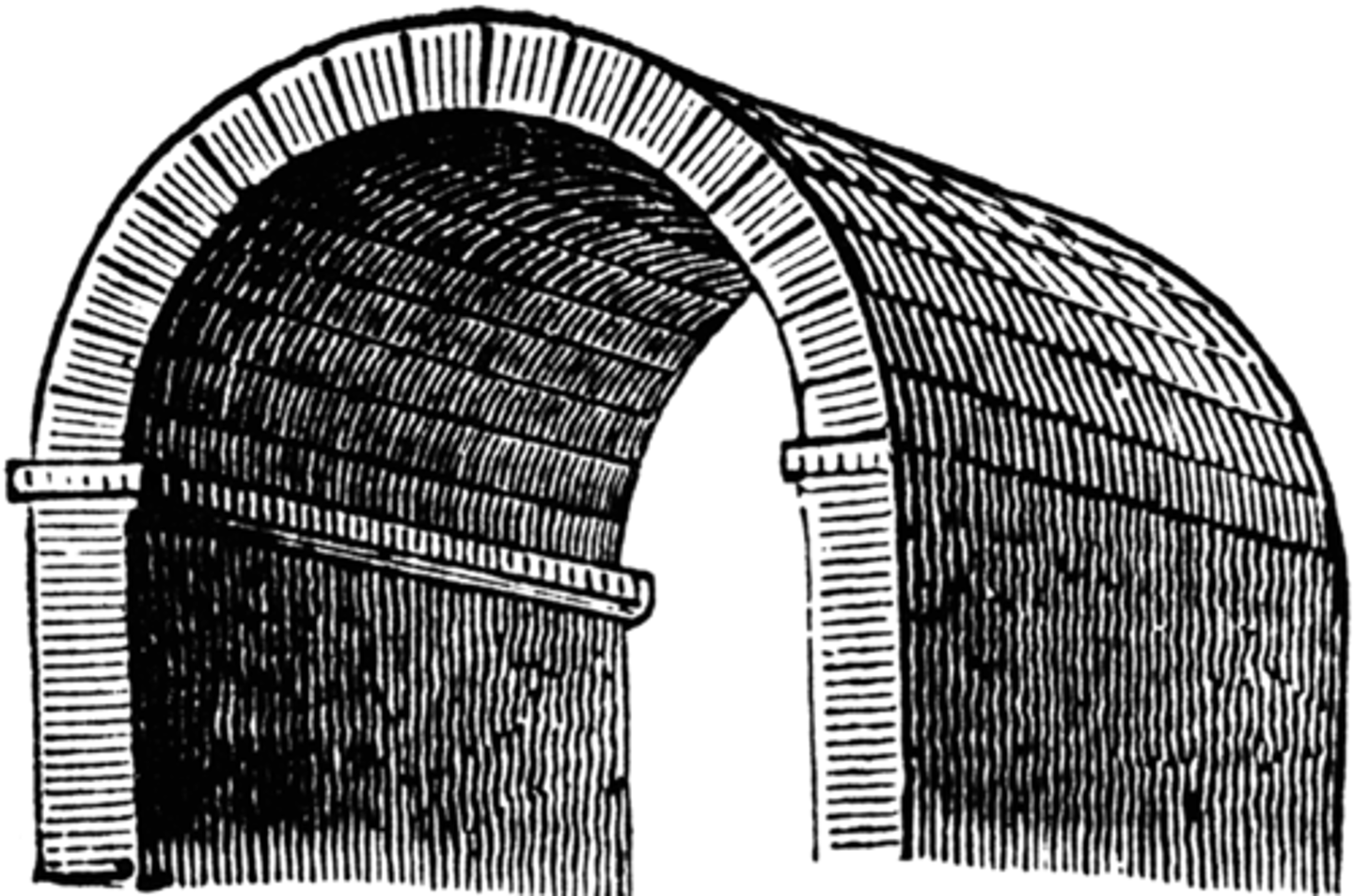
groin vault
formed at the point at which 2 barrel vaults intersect at right angles
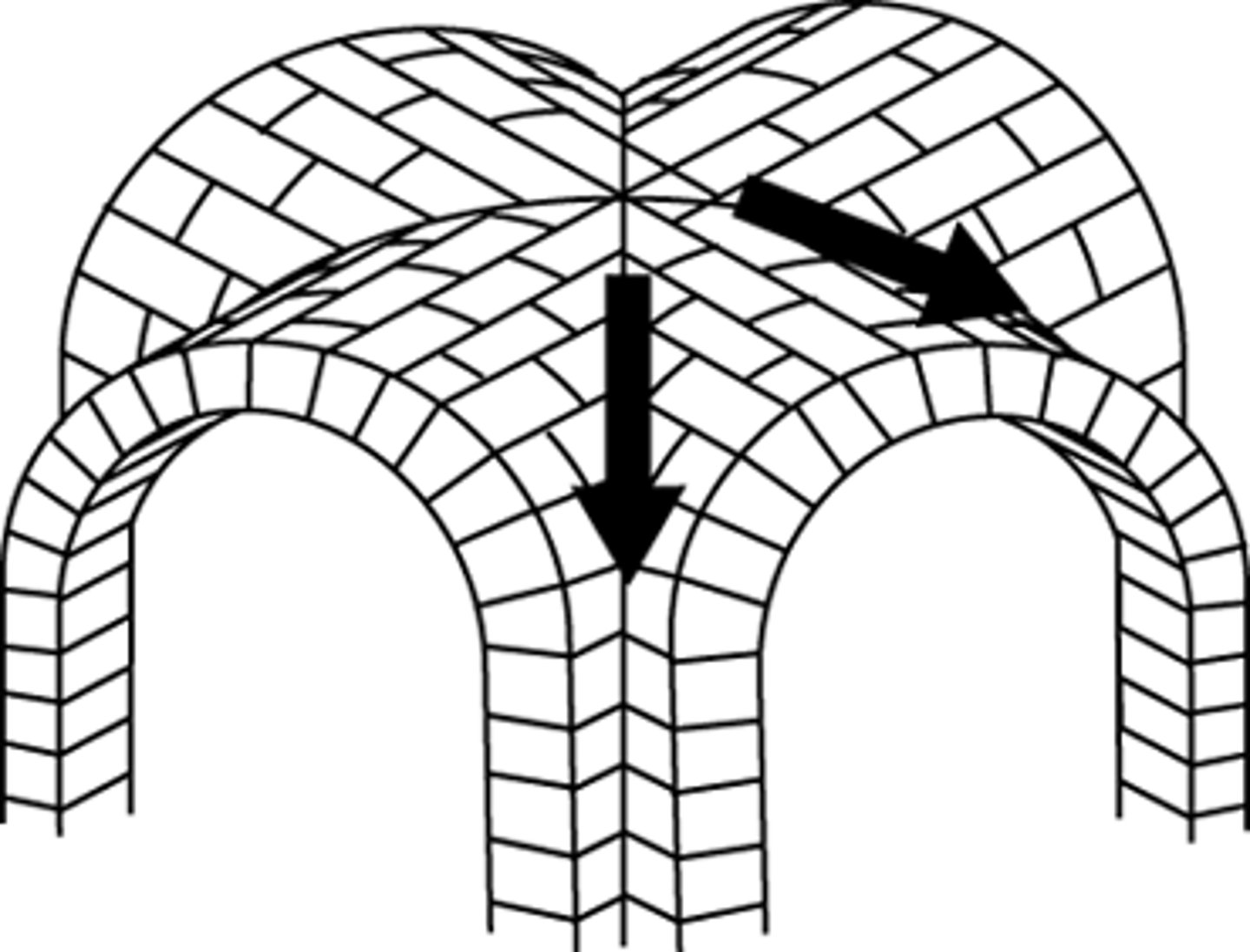
rib vault
A vault in which diagonal arches form rib-like patterns. These arches partially support a roof, in some cases forming a weblike design
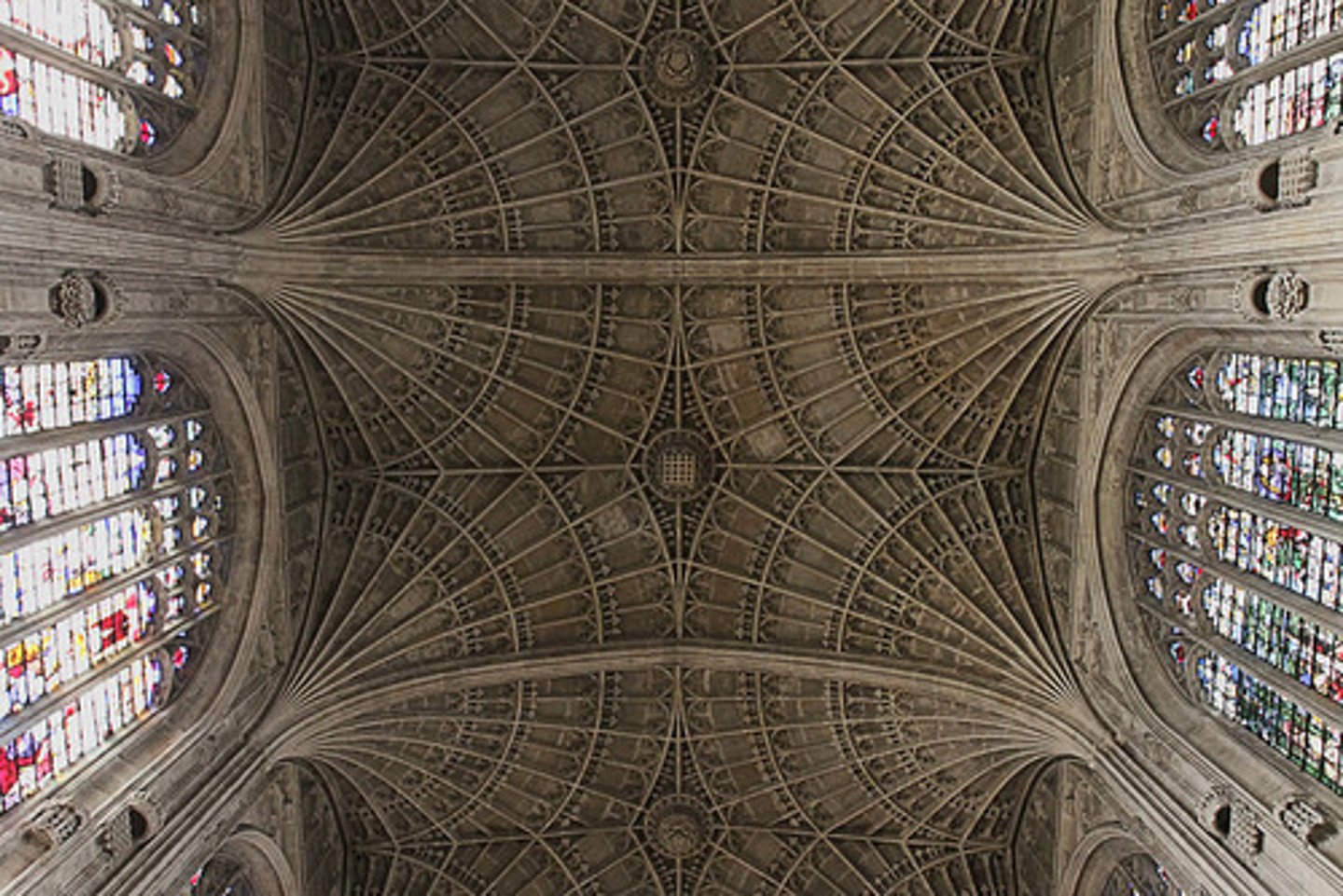
fan vault
a form of vault used in the perpendicular Gothic style, in which the ribs are all of the same curve and spaced equidistantly, in a way that resembles a fan or the spokes of an inverted umbrella.

dome
a rounded vault forming the roof of a building or structure, typically with a circular base.
Oculus
a round opening at the center of a dome
portico
a structure consisting of a roof supported by columns at regular intervals, typically attached as a porch to a building.
Vitruvius
Established certain rules for standardizing Greek orders for architecture; De Architectura
1/4
According to vitruvius, the entablature shall be _____ of the column
1/6
According to vitruvius, the top of a shaft shall be _____ smaller than its base
Roman Orders
Tuscan and Composite
Tuscan Order
a simplified doric order with ionic measurements. an order of ancient architecture featuring slender, smooth columns that sit on simple bases; no carvings on the frieze or in the capitals

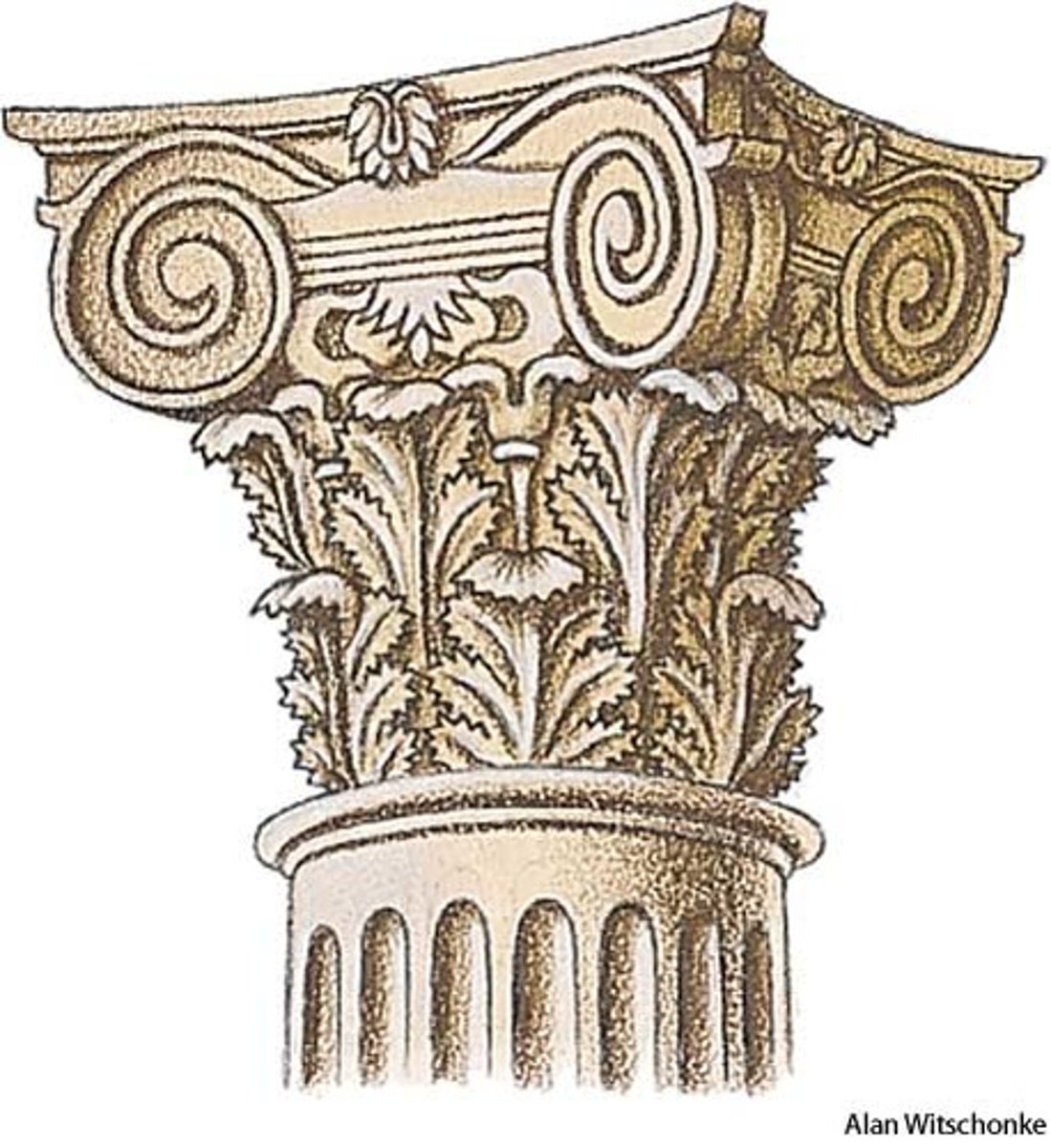
Composite Order
a Roman order that combines the Corinthian acanthus leaves with the spiral scrolls of the Ionic order. was the most commonly used style in Rome.

Roman Corinthian
was the most commonly used style in Rome. The capital is slightly smaller and the acanthus leaves are also different
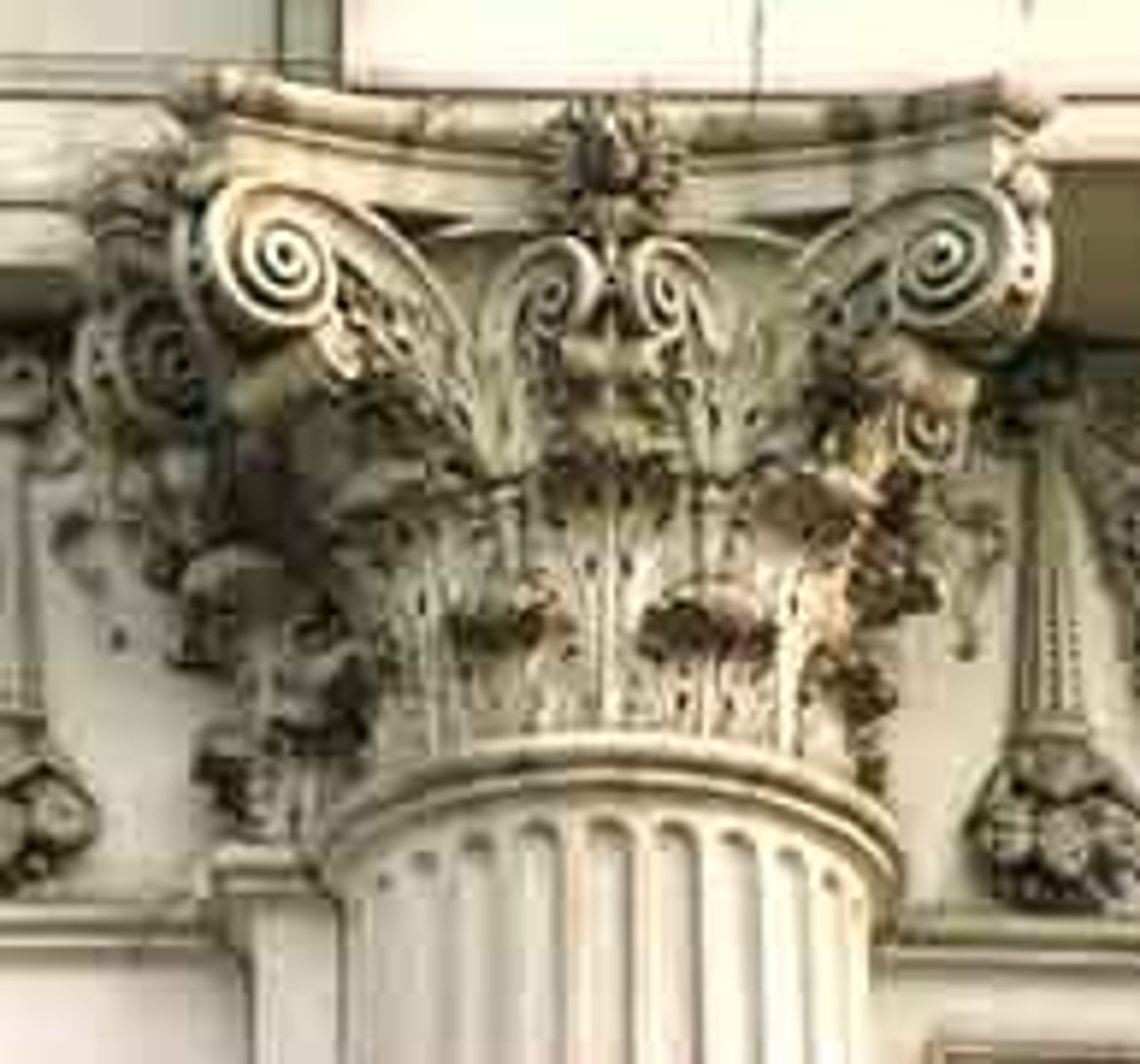

Roman Ionic
The volute capitals were smaller and the ornaments around the next were omitted. The volutes were something repeated on all four sides.
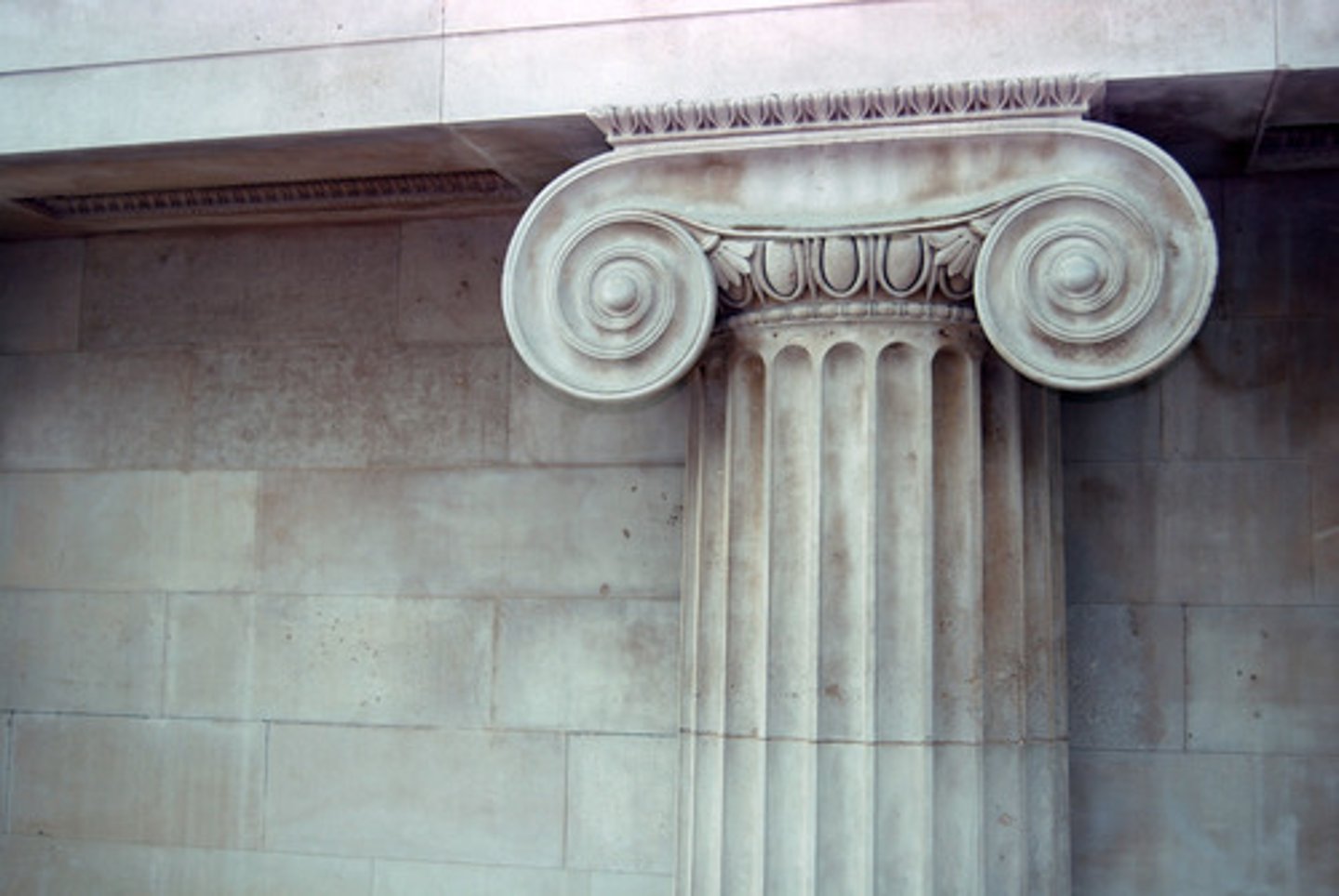

plinth
an architectural support or base (as for a column or statue)
Pedestal
A high base onto which a column would stand. Usually 1.3 or 1.4 the height of the column, it is treated with a cornice top and a projecting plinth at the bottom.
Pilasters
a rectangular column, especially one projecting from a wall. meant as decoration to create vertical subdivisions to a wall
Forum
monumental center of religious, political, and social life of Ancient Rome. Rome's public meeting place. Counterpart of the agora and is composed of temples, triumphal arches, pillars of victories, Roman basilicas and shops
Pantheon
Built by Marcus Agrippa, finished by Emperor Hadrian. A temple to Roman deities. Bears a perfect dome in the world, the largest reinforced concrete dome in the world
Marcus Agrippa and Emperor Hadrian
Built the Roman Pantheon
equal
the diameter of the Pantheon's floor plan is ______ to the height of the dome
engaged column
a half-round column attached to a wall
coffers
A recessed decorative panel that is used to reduce the weight of and to decorate ceilings or vaults.
oculus
the round central opening of a dome
Church of St. Mary of the Martyrs
new name of the Roman pantheon
Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine
largest building in the Roman Forum
Scaena Frons
In Roman theatre, the ornate three-dimensional facade of the stage house.
Acanthus Leaves
The leaves at the top of corinthian columns.
Flavian Amphitheater
Colosseum for roman games. A combination of roman arch and vault construction
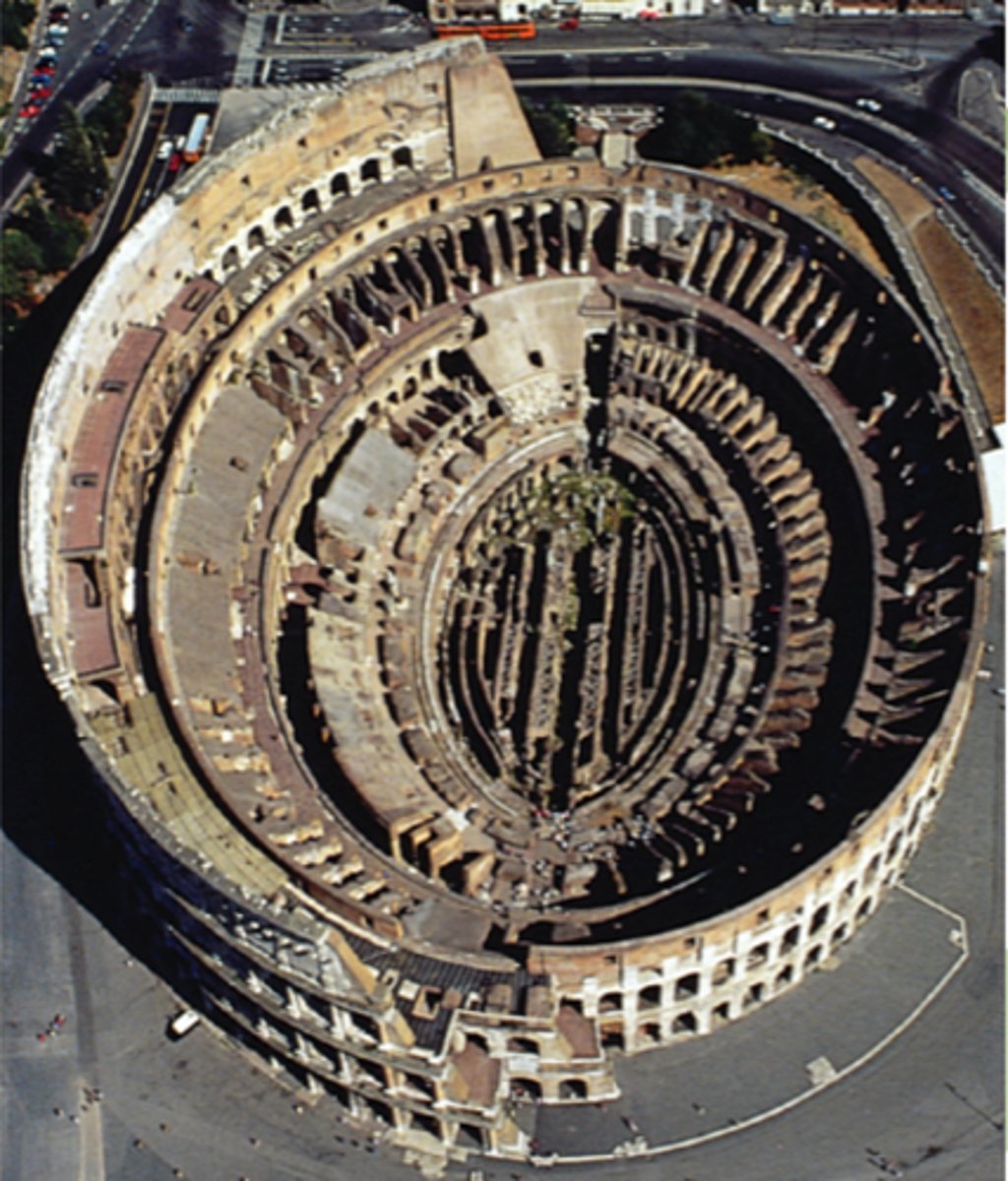

48M
height of Flavian Ampitheater exterior walls
Velarium
In a Roman amphitheater, the cloth awning that could be rolled down from the top to shield spectators from sun or rain.
Ara Pacis
Commissioned by Augustus for peace. One of the greatest marble monuments.
Roman Temple
Roman structure on top of a podium. Has a deep portico and utilizes peripteral or engaged columns
Domus
Roman house of the middle class, a structure designed for either a nuclear or extended family located in a city or town
fauces
a narrow doorway in a domus
atrium
a large centralized reception hall in a domus
cubicula
a number of small rooms in a domus
tablinum
office of the head of household in a domus
pars urbana
public part of the house
pars rustica
private part of the house
triclinium or oecus
dining rooms in a domus
hortus
small garden in a domus
Insulae
Roman blocks of flats up to 5 storeys high used as a shop and apartment
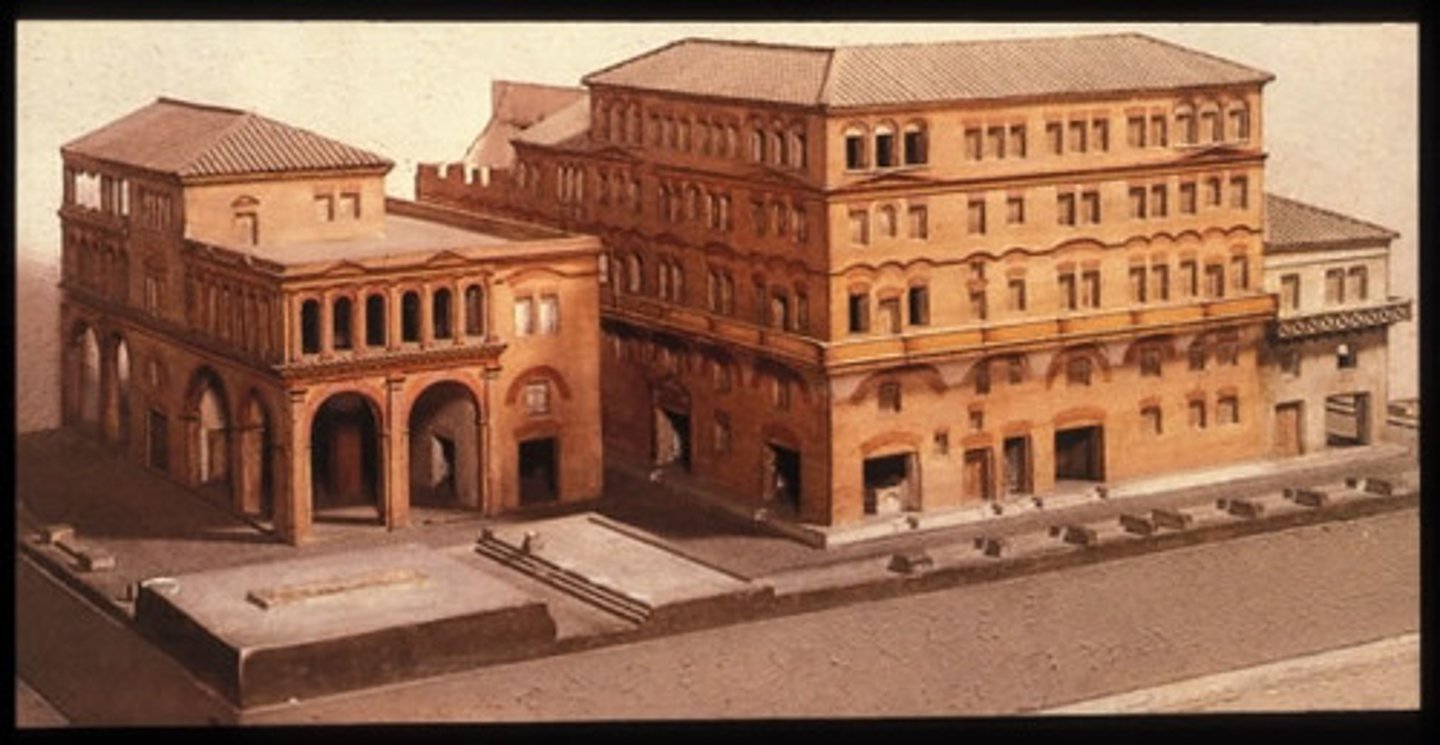

Villa
Houses the upper-class Romans; Roman country homes
Roman Theatre
More impressive skene than the Greek. It was built on level ground. Has a semi-circular orchestra
Roman Amphitheater
A roman structure Smaller than a coliseum; an oval or circular building with rising tiers of seats around.
Roman Coliseum
Roman architecture that is twice the size of an amphiteater; holds sporting events of gladiators
Aqueducts Large
Roman reservoirs for lead pipes to transport water to towns
Thermae or balnae
Palatial public baths of imperial Rome that portrays the customs of the pleasure-loving populace
caldarium
The hot-bath section of a Roman bathing establishment.
tepidarium
warm-bath section of a Roman bathing establishment
Frigidarium
The cold-bath section of a Roman bathing establishment
Lanconicum
Part of a Thermae; dry sweating room
Unctuaria
The room for oils and unguents in the thermae.
Apodyteria
The dressing room of the Thermae.
Circus
an arena in ancient Rome known as the Hippodrome; a long hairpin race course for chariot races
Circus Maximus
largest hippodrome in Rome
Roman Basilica
Houses the Roman law court; eventually became a hall of justice and commercial exchange
Roman tombs
Roman pyramidial shaped; monumental and had sculpture memorials
Roman atrium
A roman courtyard
Murrhine
Fragile opalescent glassware made by the romans and used for ornamental and useful purposes; imbedded with semiprecious stones

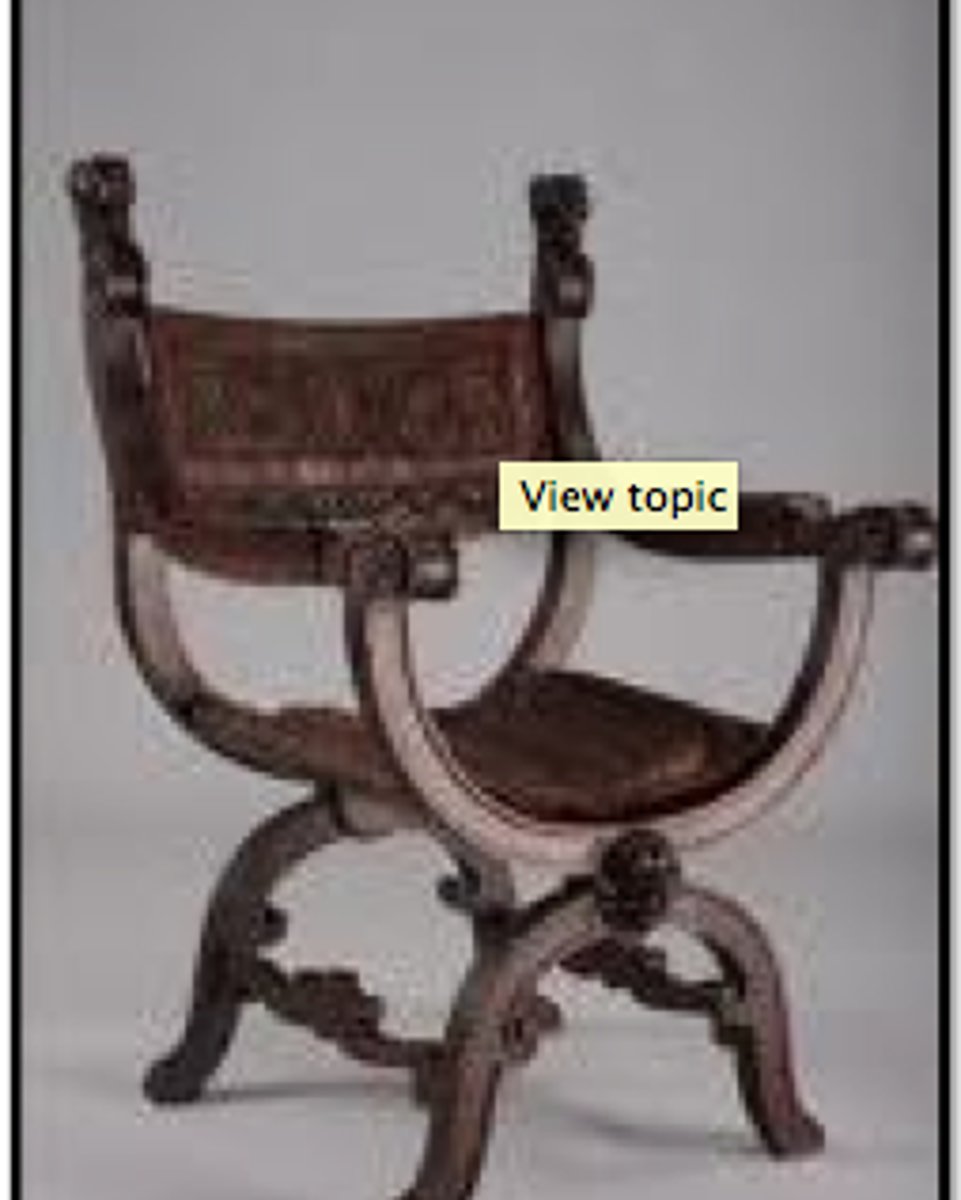
curule chair
A style of chair reserved in ancient Rome for the use of the highest government dignitaries and usually made like a campstool with curved legs.

Pozzolana
natural cement. The Romans made this cement with ash that was blown out of the volcano Vesuvius. it is waterproof and hardens even when it is wet; the hydraulic cement used by the Romans
Cubicula
mortuary chapels; a number of small rooms surrounded the atrium and peristyle where the family ate and slept in Anicent rome
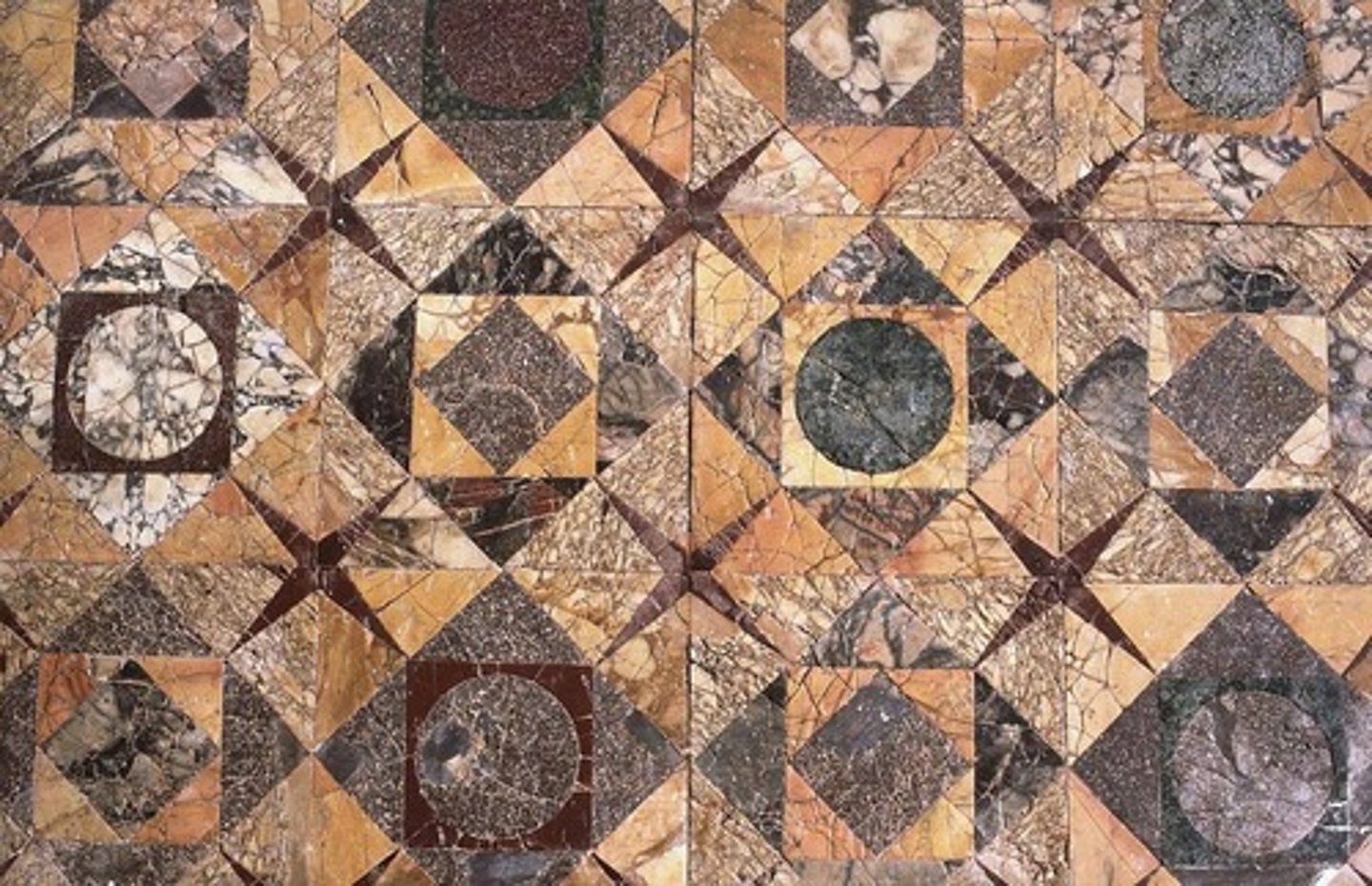
opus sectile
A type of marble mosaic pattern; "cut work"; produced geometrical patterns

megalographia
a Greek term of art for any representation, especially pictures, statues, that is life size
Dosseret
A thickened abacus or supplementary capital set above a column capital to receive the thrust of an arch.
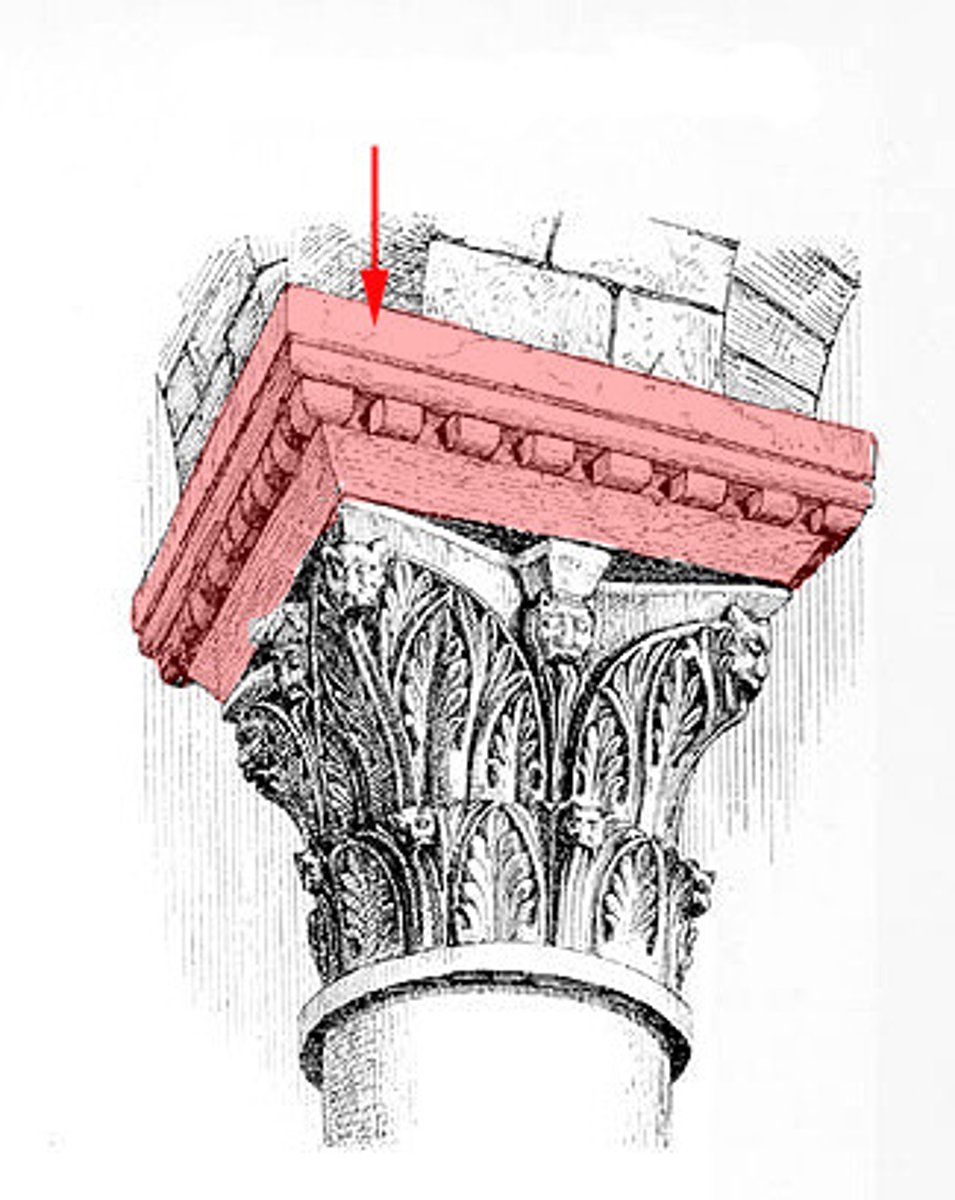
Tablinum
Roman office of the head of the house
cubiculum
Roman bedroom
Exedra
Roman kitchen
triclinium
Roman dining room
impluvium
a rectangular basin in a Roman house that is placed in the open-air atrium in order to collect rainwater

compluvium
a square opening in the roof of the ancient Roman atrium toward which the roof sloped and through which the rain fell into the impluvium

curule
First chair with cushion; x-shaped chair originally a folding stool.
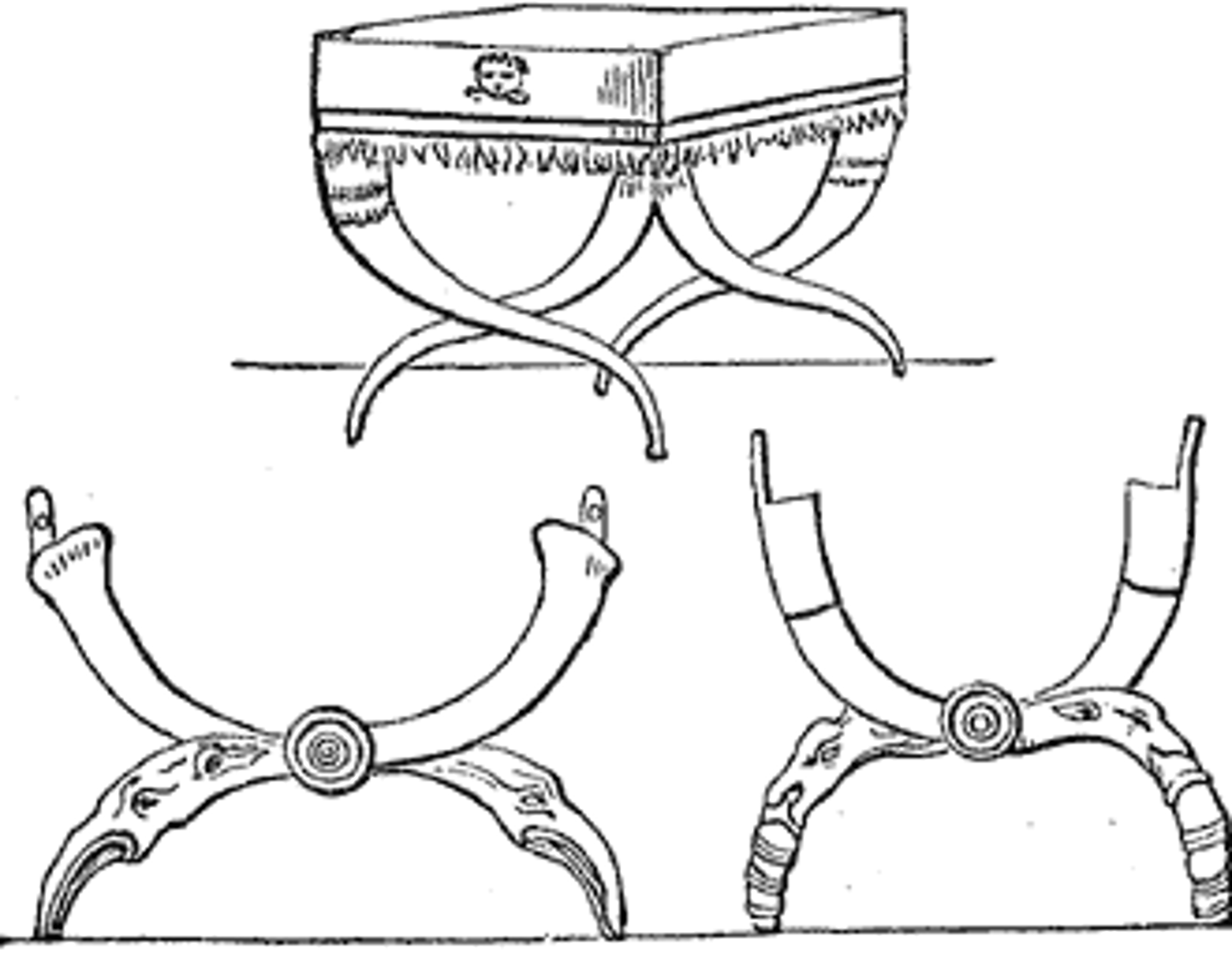
bisellium
Roman double chair or settee
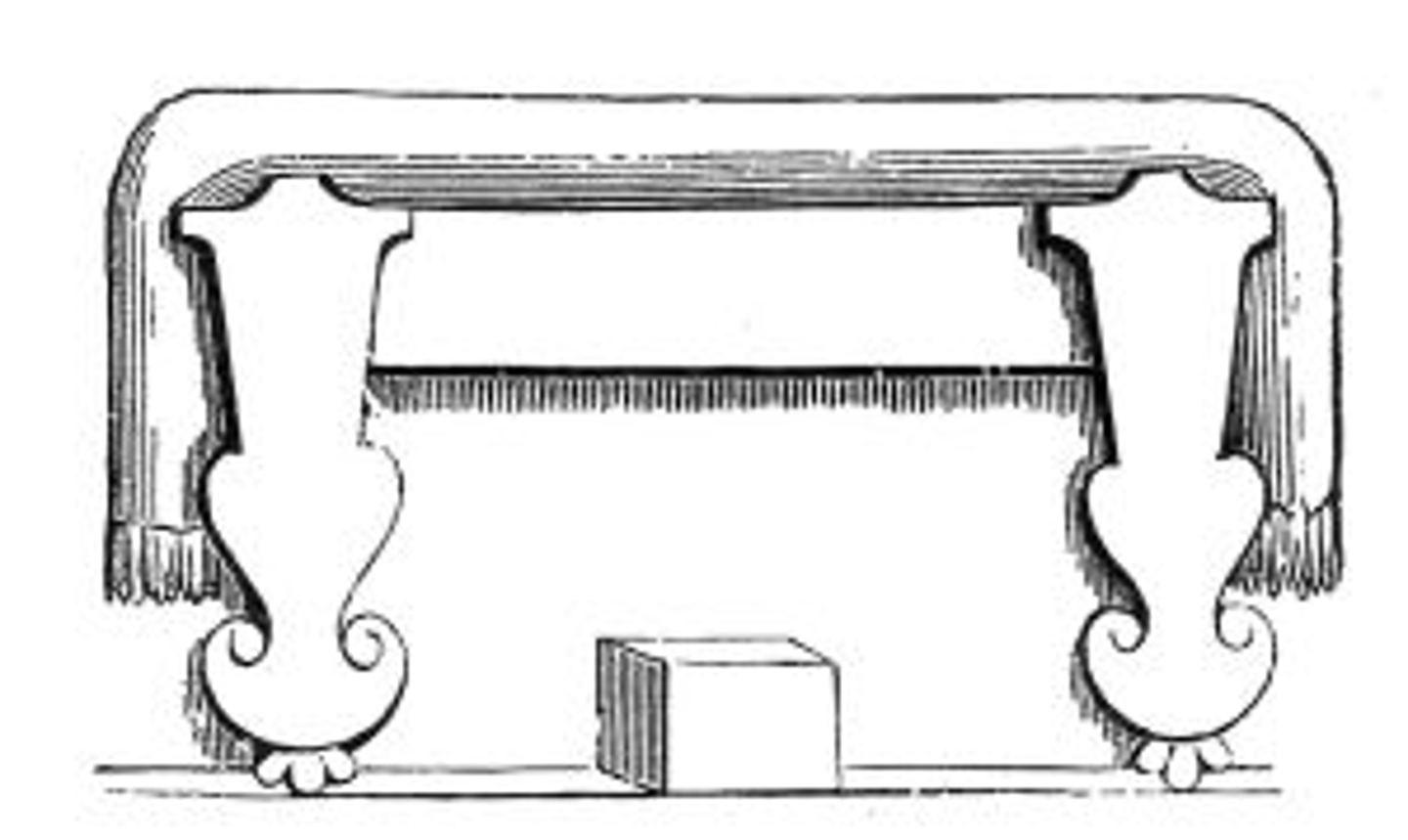
solium
Roman throne chair for men with animal feet for head of the family
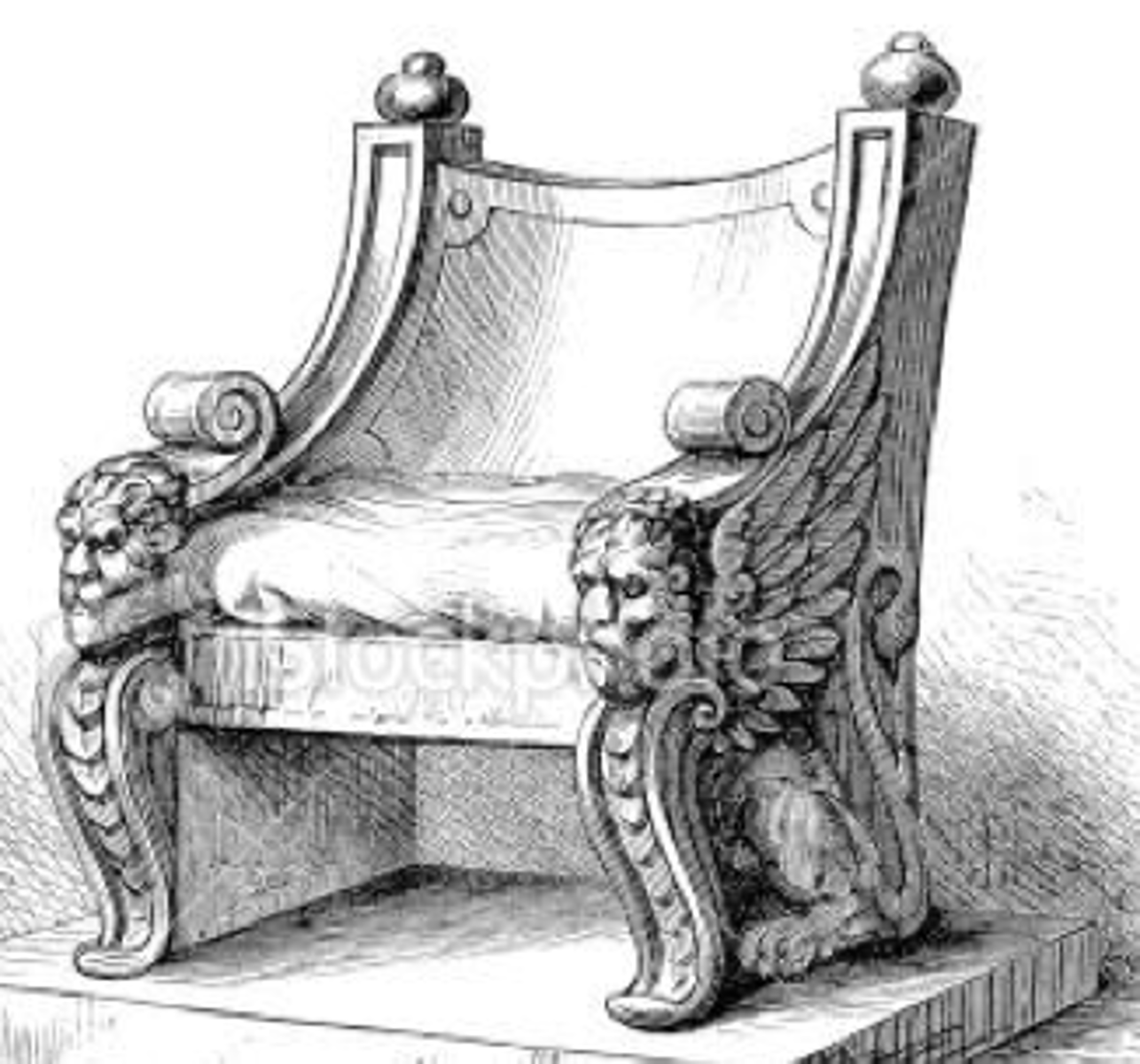
subselium
Roman bench
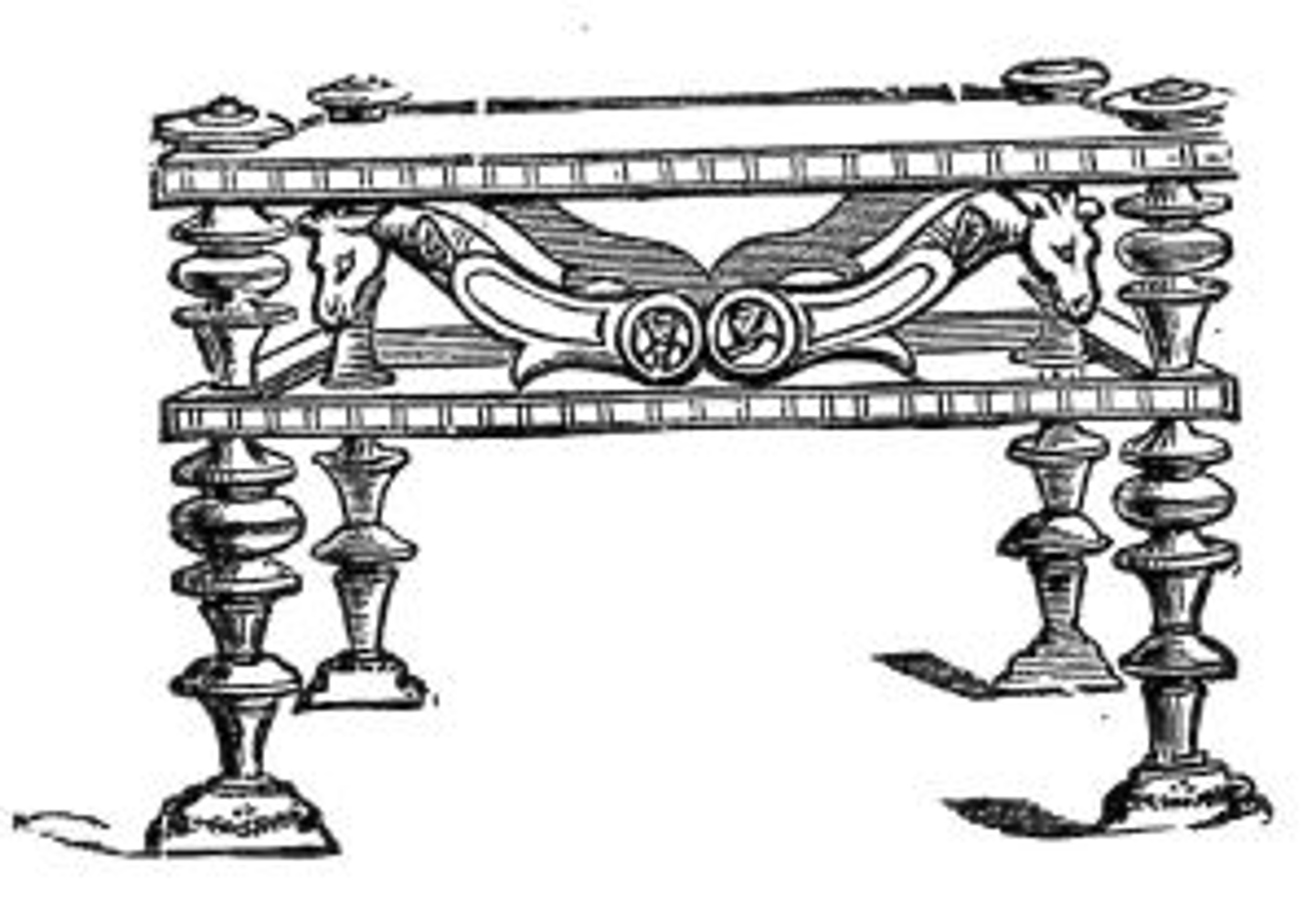
Cathedra
Roman's Klismos chair
