Overview of the Nervous System and Its Functions
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Innervate
To supply nerves to a body part.
Neurons
Basic building blocks of the nervous system.
Dendrite
Conducts messages towards the cell body.
Axon
Conducts messages away from the cell body.
Synapse
Gap where neurotransmitters transmit signals.
Myelin Sheath
Insulates nerve fibers to speed up impulses.
Node of Ranvier
Gaps in myelin sheath for faster transmission.
Cell Body
Contains nucleus; maintains neuron functions.
Motor Neuron
Connects to muscles or glands; signals movement.
Sensory Neuron
Transmits signals from sensory receptors to CNS.
Interneuron
Connects neurons within the CNS; processes information.
Synaptic Transmission
Chemical transmission of impulses across a synapse.
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messengers transmitting signals between neurons.
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter involved in muscle activation.
Noradrenalin
Neurotransmitter affecting arousal and alertness.
Serotonin
Regulates mood and emotional states.
Dopamine
Influences pleasure, motivation, and reward.
Enzymatic Breakdown
Process of degrading neurotransmitters in synapse.
Acetylcholinesterase
Enzyme breaking down acetylcholine in synapse.
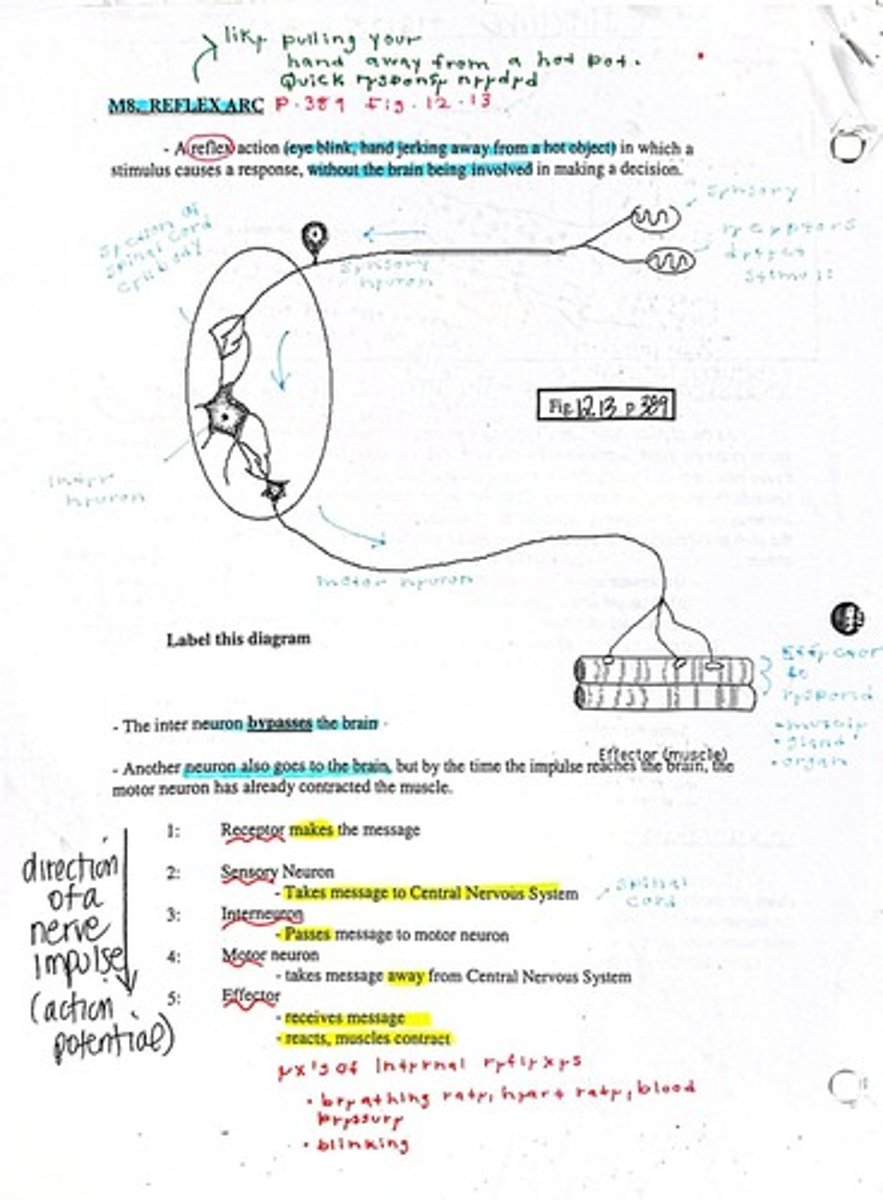
Reflex Arc
Pathway for reflex actions involving sensory and motor neurons.
Action Potential
Electrical impulse traveling along a neuron.
Synaptic Cleft
Space between pre and post-synaptic neurons.
Presynaptic Membrane
Membrane of neuron releasing neurotransmitters.
Postsynaptic Membrane
Membrane of neuron receiving neurotransmitters.
Reflex Action
Automatic response to stimulus, bypassing brain.
Effector
Muscle or gland that responds to a stimulus.
Depolarization
Change in membrane potential, sodium influx.
Threshold Potential
Minimum stimulus required to trigger action potential.
Saltatory Conduction
Impulse jumps between nodes of Ranvier.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord, information processing center.
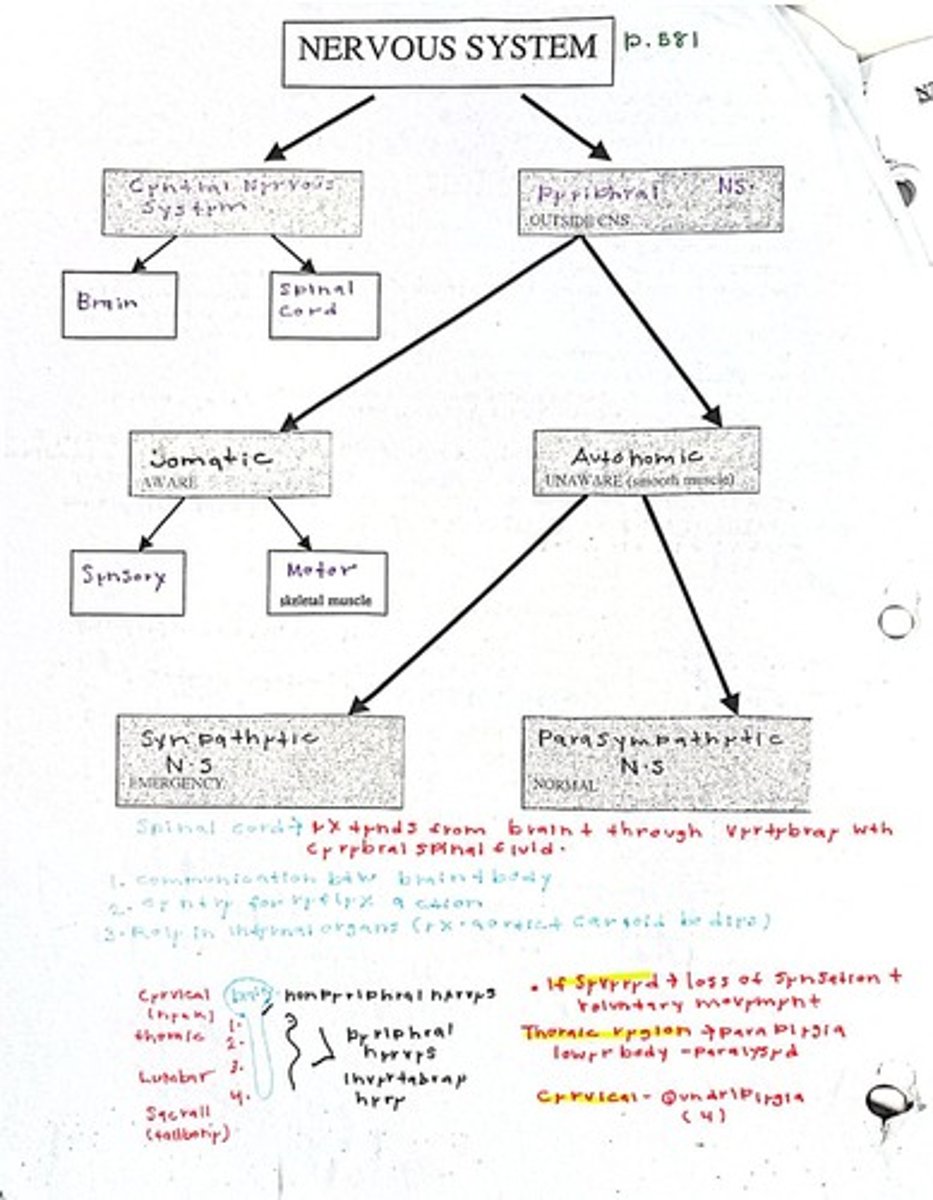
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Nerves outside CNS, connects to limbs and organs.
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary movements and external senses.
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary body functions automatically.
Sympathetic System
Prepares body for 'fight or flight' response.
Parasympathetic System
Restores body to calm state, conserves energy.
Ion Channels
Proteins that allow ions to cross membranes.
Voltage-Gated Channels
Open in response to membrane potential changes.
CNS Protection
Encased in bone and meninges for safety.
Cardiac Activity Regulation
Controlled by autonomic nervous system involuntarily.
Myelinated Axons
Axons covered with myelin for faster conduction.
Impulse Speed
Myelinated axons conduct impulses up to 200 m/s.
Receptor
Detects stimulus and initiates response.
Preganglionic Neuron
Longer than postganglionic in parasympathetic system.
Postganglionic Neuron
Shorter than preganglionic in parasympathetic system.
Central Nervous System
Includes brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves outside the central nervous system.
Adrenal Gland
Produces hormones for stress response.
Adrenalin
Hormone that triggers fight or flight response.
Medulla Oblongata
Controls unconscious bodily functions.
Cerebrum
Responsible for consciousness and information processing.

Thalamus
Sorting center for sensory impulses to cerebrum.
Cerebellum
Coordinates balance and muscle movements.
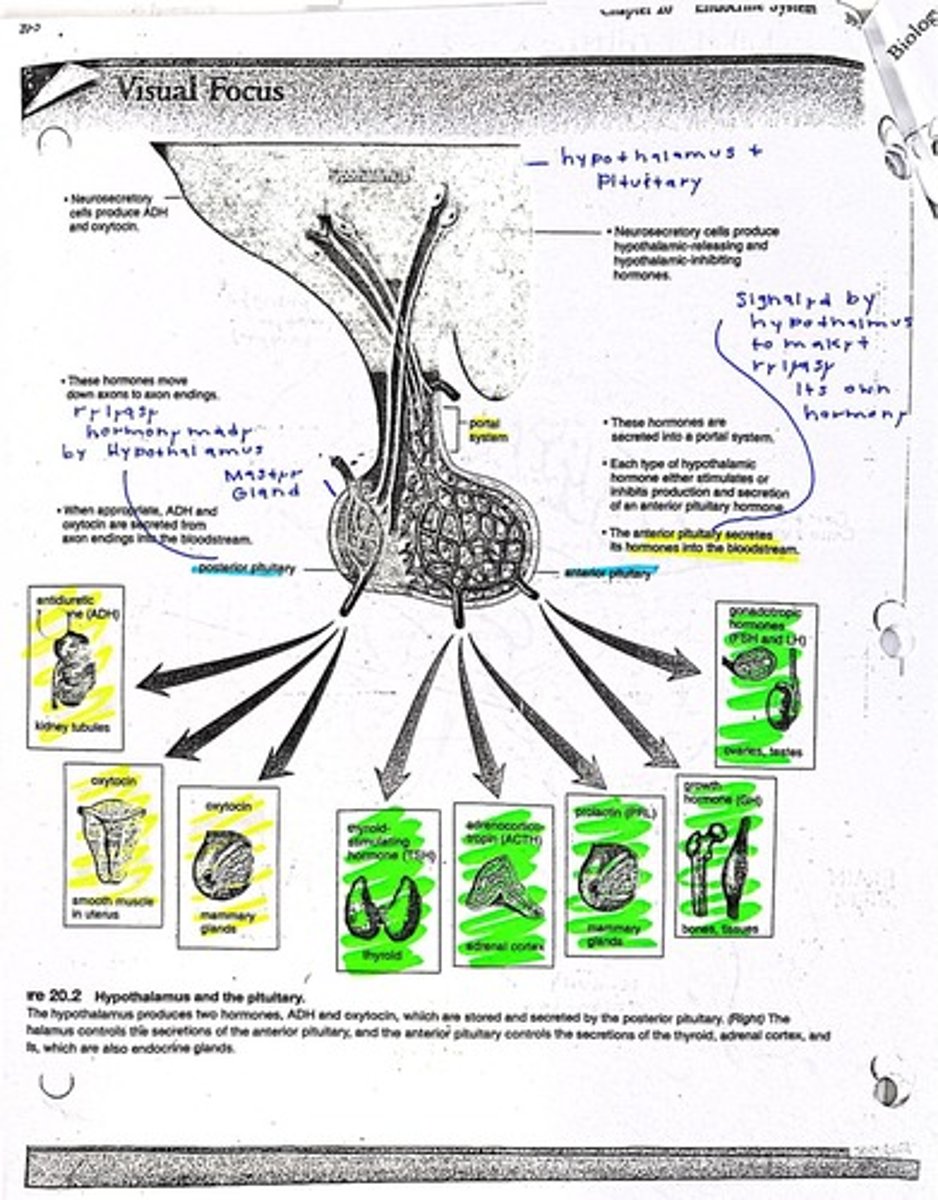
Hypothalamus
Regulates homeostasis and links nervous systems.
Corpus Callosum
Connects left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Pituitary Gland
Master gland controlling endocrine functions.

Sympathetic Impulses
Increase heart rate and blood flow.
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal body conditions.
Proprioception
Awareness of body position in space.
Cortex
Outer layer of the cerebrum.
Sensory Impulses
Messages sent to the brain for processing.
Posterior Pituitary
Stores hormones made in the hypothalamus for release.
Anterior Pituitary
Produces hormones stimulated by hypothalamic releasing factors.
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone)
Regulates water reabsorption in kidneys.
Oxytocin
Stimulates uterine contractions and milk production.
Growth Hormone (GH)
Stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulates milk production in mammary glands.
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
Stimulates growth of ovarian follicles and sperm production.
LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
Triggers ovulation and testosterone production.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Stimulates adrenal cortex to produce cortisol.
Negative Feedback System
Regulates hormone levels by inhibiting further secretion.
Neurosecretory Cells
Produce hormones like ADH and oxytocin in hypothalamus.
Portal System
Blood vessel system connecting hypothalamus and anterior pituitary.
Releasing Factors
Hormones from hypothalamus that stimulate anterior pituitary.
Inhibiting Factors
Hormones that suppress anterior pituitary hormone release.
Nerve Impulse
Signal transmitted along a neuron via action potentials.
Resting Potential
Stable membrane potential of a neuron at rest.
Refractory Period
Time after action potential when neuron cannot fire.