Biology Chapter 3 Molecules of Life
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Biological/Organic Molecules
Large molecules that are essential for life.
Macromolecules
Molecules that are large in size and are made up by combining smaller units together.
Molecule
A substance that is made up of two or more atoms bound together.
Carbohydrates
Large molecules that contain the elements carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. The primary fuel for our bodies.
Monosaccharides
The simplest form of carbohydrates and they are simple sugars.
Glucose
Has 3 fates in your body once you eat and digest: provides immediate energy, can be stored short term as glycogen, or can be stored long term and converted to fat.
Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates that are made up of two or more sugar molecules.
Disaccharides
Contain two different sugar molecules, more complex than a monosaccharide but still not very complex.
Sucrose
A common disaccharide made up of a glucose and a fructose molecule.
Lactose
Another common disaccharide, the sugar found in milk.
Polysaccharides
Contain thousands of sugar molecules that are linked together with a glycosidic bond.
Glycosidic Bond
A special type of covalent bond that forms between sugar molecules.
Starch
Found in plants and is used as fuel storage for plants.
Cellulose
The structural component of plants (fiber, we can't digest it).
Glycogen
Found in the liver and muscle of humans.
Short Term Energy
Eating simple carbohydrates will provide you a short burst of energy but it wears off quickly.
Long Term Energy
A diet of complex carbs provides a sustained release of energy for a longer period of time.
Lipids
Come in several forms and include triglycerides, sterols, and phospholipids.
Triglycerides
Dietary fats that serve different functions in the body and are composed of a head region and a tail region that are linked together.

Sterols
A group of lipids that help with regulating growth and development with a basic structure of 4 carbon rings.

Phospholipids
The main component of our cell membranes and the cell membranes of all living organisms that have similar structure as triglycerides.

Glycerol Molecule
A small molecule that is made up of 3 carbons bound to 3 oxygen and 5 hydrogen.
Fatty Acids
The tail region of triglycerides that are hydrophobic and are made up of 3 tails linked to the glycerol head.
Functions of Triglycerides
store lots of energy for long term storage, insulation for organisms, cushioning between organs and tissues and bones and skin.
Types of Triglycerides
Naturally occur in two different forms: fats and oils.
Fats
Derived primarily from animal sources, solid at room temperature, composed of saturated fatty acids.
Oils
Derived primarily from plant sources, liquid at room temperature, composed of unsaturated fatty acids.
Saturated Fatty Acids
In the fatty acid tails of a fat, each carbon is bound to at least 2 hydrogen atoms, making them straight and solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Fatty acid tails have at least one carbon bound to only one hydrogen, allowing for double bonds that create kinks, making them liquid at room temperature.
Trans-Fats
Human made fats manufactured to increase shelf life and improve texture of foods; linked to increased risk of high cholesterol and heart disease.
Hydrogenated Oil
Created through the hydrogenation process which bombards unsaturated fat with hydrogen atoms, creating trans-fats.
Cholesterol
A type of lipid that is an important component of most cell membranes that helps maintain fluidity during temperature changes; produced by liver cells.
Steroid Hormones
Compounds derived from cholesterol that regulate growth, sexual development, maturation, and sex cell development.
Anabolic Steroids
Often abused by athletes to increase muscle mass.
Fatty Acid Tails
The structural components of triglycerides that determine whether they are saturated or unsaturated and are hydrophobic.
Saturated
Refers to fatty acids where carbon is fully bonded, resulting in straight tails.
Unsaturated
Refers to fatty acids with double bonds, resulting in kinks in the tails.
High Cholesterol
A condition that can be exacerbated by a diet high in trans fats.
Heart Disease
A health condition linked to high levels of cholesterol and trans fats in a person's diet.
Cell Membrane
A double layer of phospholipids, where the tails interact with each other forming the middle area and the heads facing inward and outward toward the fluid.

Side Chains
The ____ ______ in sterols determine the type of sterol based on their modifications off the basic structure of four interlinked rings.
Proteins
The major building blocks of organisms, used as structural components, integral in producing hair, feathers, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, and essential for muscle contraction.
Protein Hemoglobin
Responsible for the transport of oxygen around our bodies.
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins, linked together by peptide bonds to form proteins.
Peptide Bond
A special covalent bond that links amino acids together in a protein.
Polypeptide
Another name for a protein, consisting of many peptide bonds.
Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids that must be obtained from our diet; 10 out of the 20 amino acids are essential.
Complete Proteins
Foods that contain all the essential amino acids.
Primary Structure
The initial structural form of a protein, comprised of amino acids in a linking chain.
Secondary Structure
Occurs when parts of the amino acids in a protein chain interact, causing the protein to fold into zig-zag or spiral shapes.
Tertiary Structure
The three-dimensional shape of a protein formed by further folding due to interactions of the side chains of the amino acids.
Quaternary Structure
The result of the interaction between different protein chains or multiple polypeptides, forming a functional protein.
Hemoglobin (as a quaternary structure)
An example of a quaternary structure protein that has 4 subunits (4 different protein chains) bound together.
Protein Structure Influences Function
Proteins can appear in 4 different structural forms, only two of which comprise a functional protein.
Environmental Sensitivity of Proteins
Proteins are highly sensitive to environmental conditions, with different proteins having different optimal operating environments.
Hydrophobic
Referring to the property of being water-repelling; characteristic of the fatty acid tails in phospholipids.
Hydrophilic
Referring to the property of being water-attracting; characteristic of the glycerol head in phospholipids.
Immune System Role of Proteins
Proteins protect our bodies from foreign invaders and play a large part in our immune system.
Clotting Proteins
Specialized proteins that help clot our blood when we get injured.
Transport Function of Proteins
Proteins help transport essential elements in our bodies and cells.
Optimal Operating Environments
Different proteins have different optimal operating environments.
Enzyme Proteins
Proteins in your stomach help break down food.
pH Sensitivity of Proteins
Proteins are sensitive to changes in pH and temperature.
Denaturation
When a protein's structure is being altered and the folding that created the functional 3D shape is changed to make the protein dysfunctional.
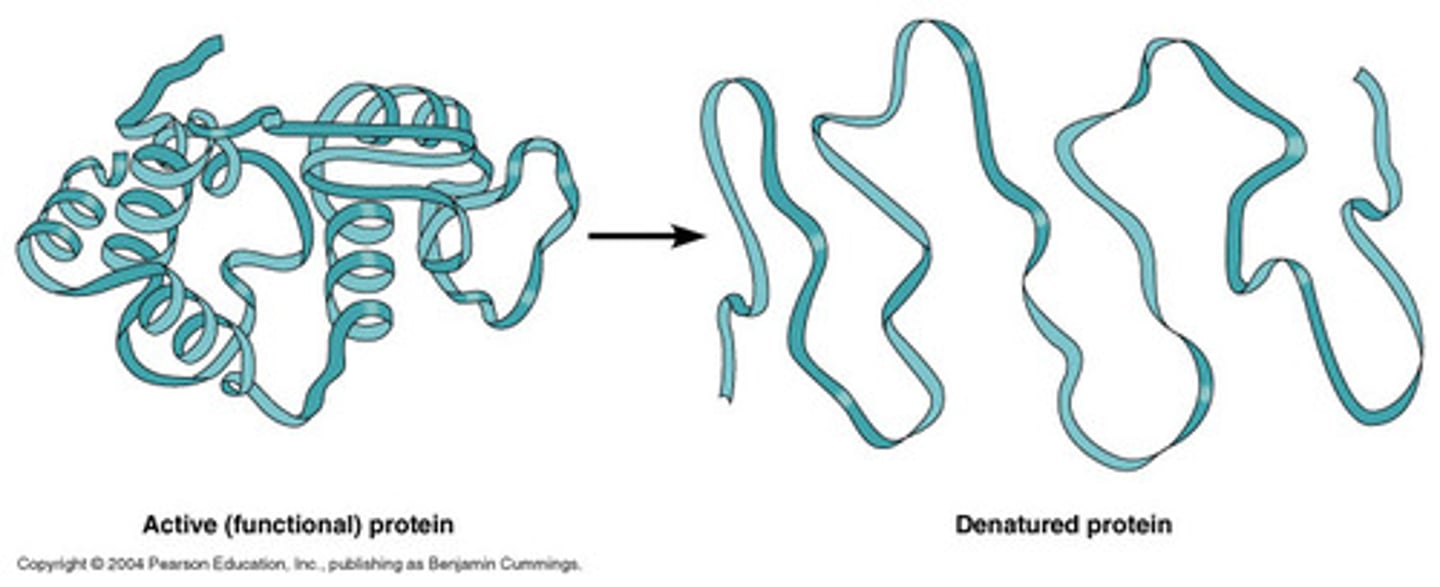
Enzymes
Proteins that help speed up biological, chemical reactions and act as a catalyst to speed up the reaction rates.
Activation Energy
The energy needed for the chemical reaction to occur without an enzyme.
Lock and Key Configuration
Enzymes have a ____ ___ ___ _____________ in which each enzyme is specific for certain chemicals.
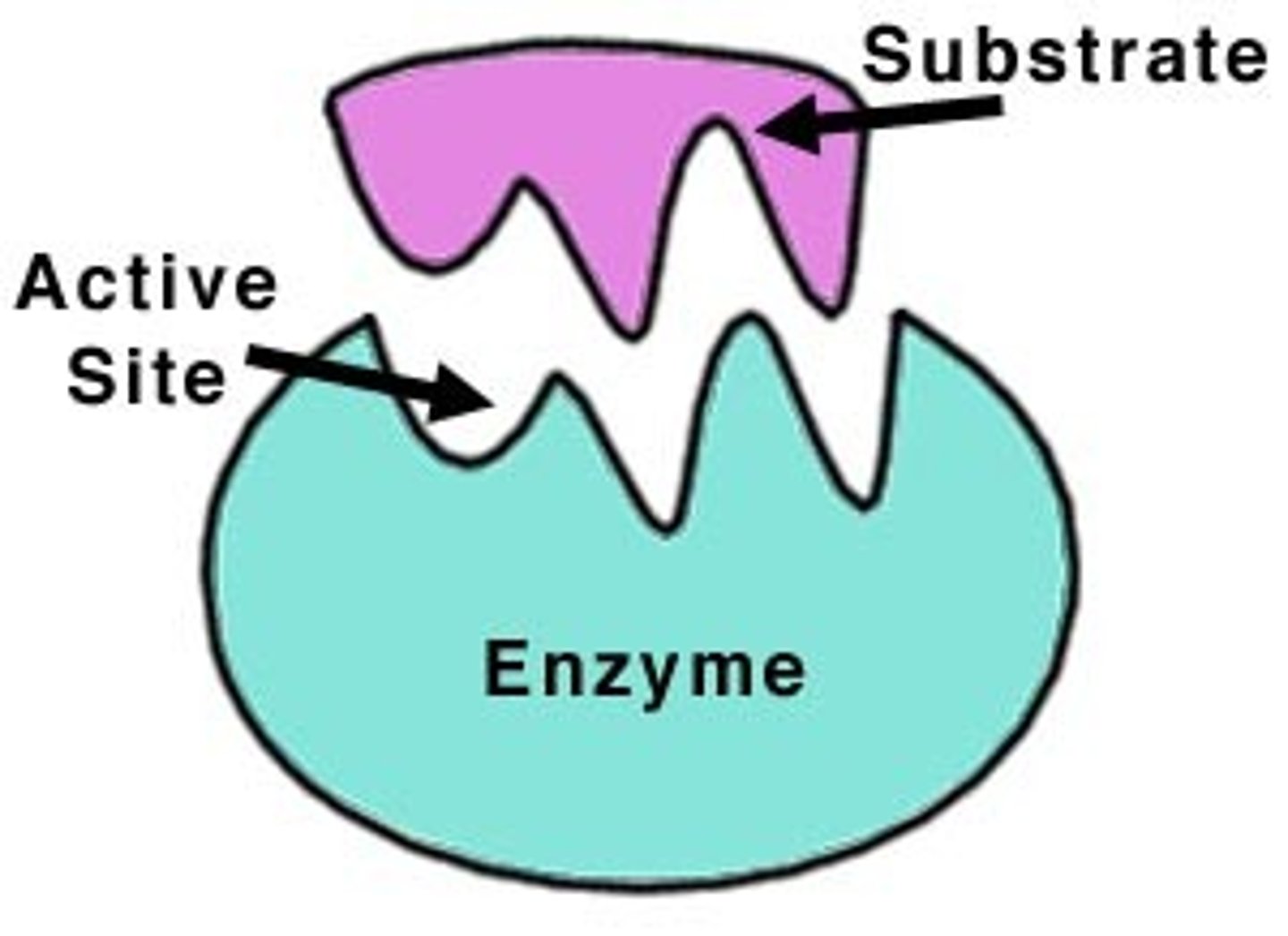
Active Site
The area where the chemical with the correct shape fits into the enzyme.
Substrate
The chemical that fits into the enzyme and is the subject of the reaction.
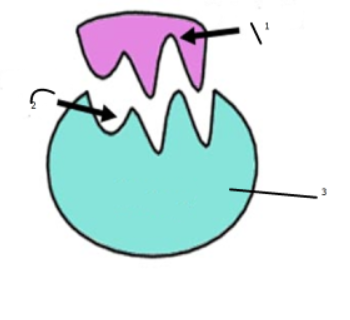
Enzymatic Reaction Products
The result of the enzymatic reaction produces two products.
Reusability of Enzymes
Once the reaction is finished, the enzyme is ready to perform another reaction.
Nucleic Acids
Macromolecules whose function is to store information that is passed around the body about making the body and the regulation of cellular activity.
Nucleotides
The building blocks of nucleic acids composed of a sugar molecule (5 carbon sugar), phosphate group (slight negative charge), and a nitrogenous base (bases used depend on the nucleic acid in question).
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
A type of nucleic acid that stores genetic information.

Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
A type of nucleic acid that helps decipher the info stored in DNA.
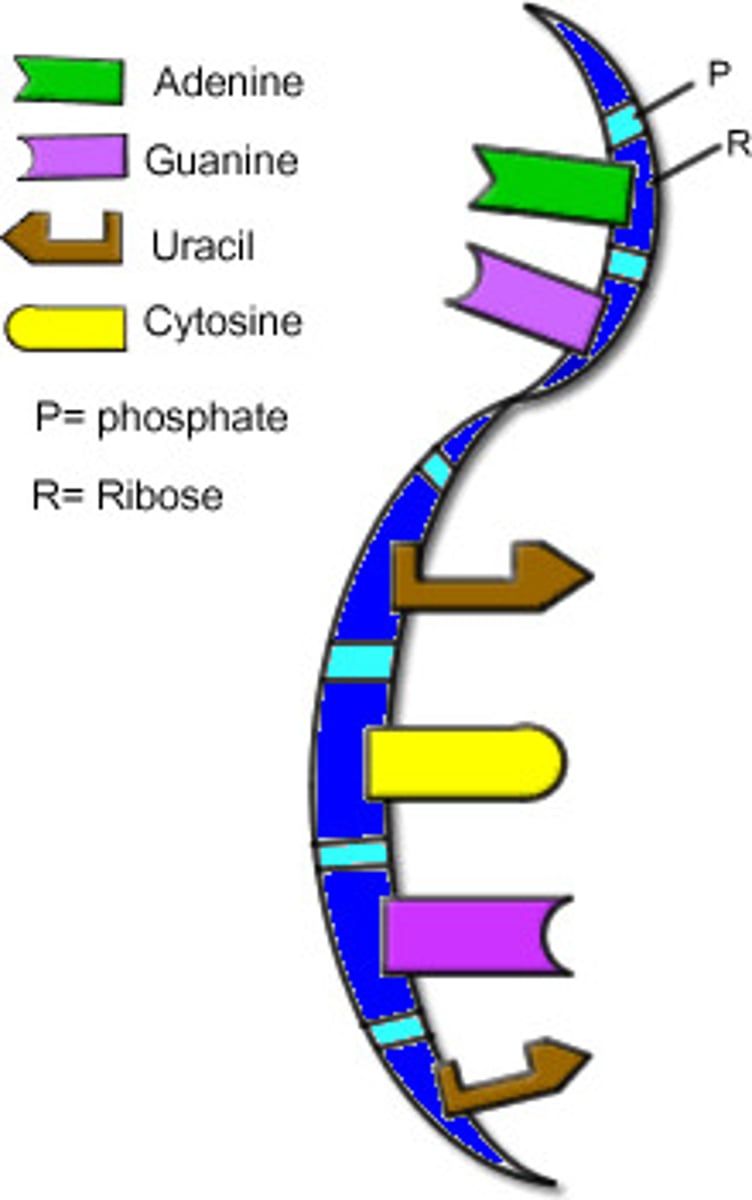
Structure of DNA
DNA is double stranded and spirals on itself to form a helical structure.
Function of DNA
The storage of genetic information necessary to direct the production of proteins.
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T) and their sequence determines the message and info being stored.
RNA Structure
Single stranded, made up of a Ribose sugar, and has a Uracil nitrogenous base
Role of RNA
RNA acts as the middleman molecule that takes instructions for protein production from DNA.
Phosphate Sugar Backbone
Forms the outside structure of the helical structure of DNA.
Fidelity of Information
The stored info in nucleic acids is available to be passed on to other cells and offspring where the fidelity of the info is maintained.
Characteristics of Lipids
Nonpolar, have a lot more energy than a carbohydrate, hydrophobic.